7. Interface do QGIS
A interface gráfica do usuário do QGIS (GUI) é mostrada na figura abaixo (os números de 1 a 5 em círculos amarelos indicam elementos importantes da GUI do QGIS e são discutidos abaixo).
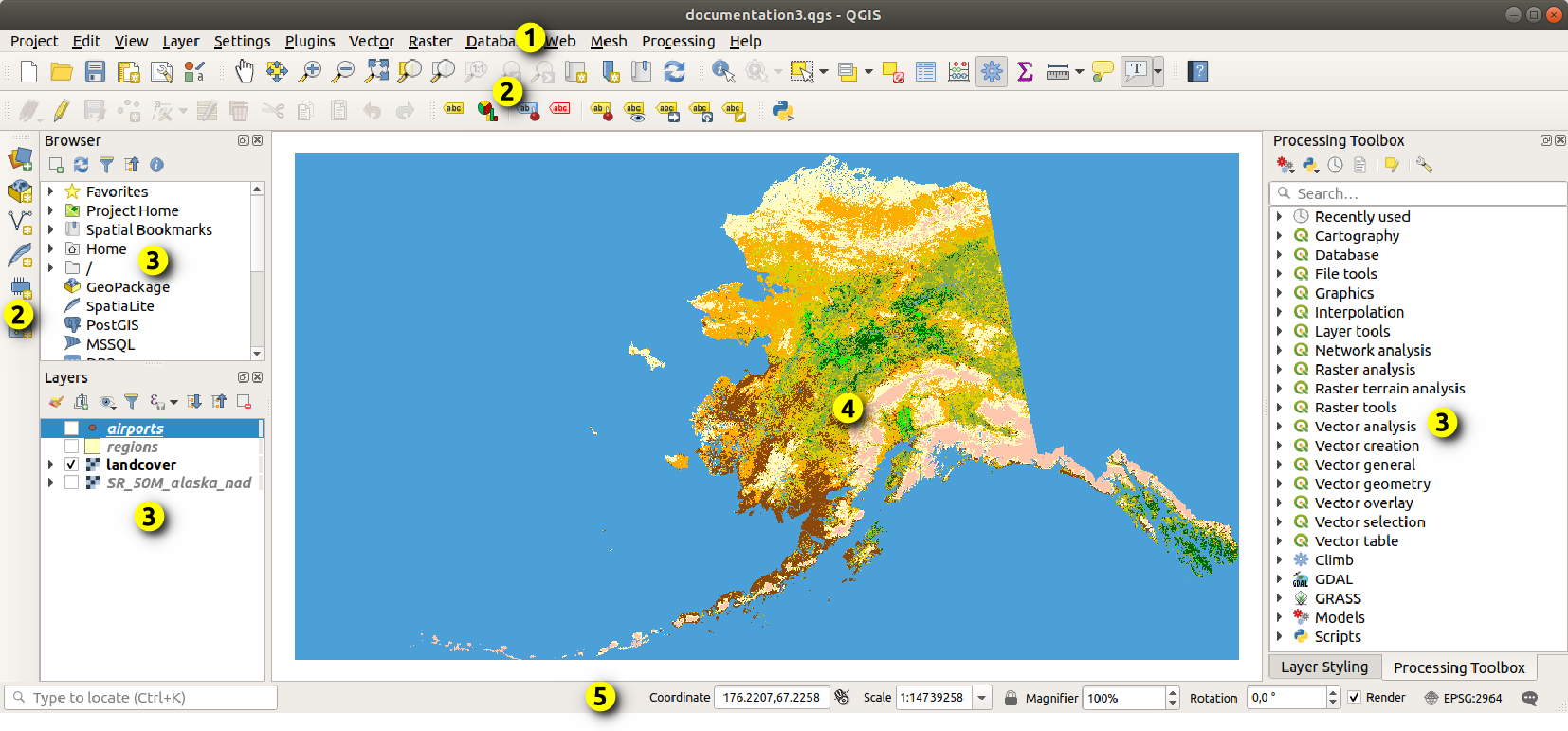
Fig. 7.1 GUI QGIS com dados de amostra do Alasca
Nota
Suas decorações de janela (barra de título, etc) podem parecer diferentes dependendo do seu sistema operacional e gerenciador de janelas.
A principal GUI QGIS (Fig. 7.1) consiste em cinco componentes / tipos de componentes:
Role para baixo para informações mais detalhadas destes.
7.2. Painéis e Barras de Ferramentas
From the menu (or  ),
you can switch QGIS widgets ()
and toolbars () on and off.
To (de)activate any of them, right-click the menu bar or toolbar and
choose the item you want.
Panels and toolbars can be moved and placed wherever you like within
the QGIS interface.
The list can also be extended with the activation of Core or
external plugins.
),
you can switch QGIS widgets ()
and toolbars () on and off.
To (de)activate any of them, right-click the menu bar or toolbar and
choose the item you want.
Panels and toolbars can be moved and placed wherever you like within
the QGIS interface.
The list can also be extended with the activation of Core or
external plugins.
7.2.1. Barra de ferramentas
The toolbars provide access to most of the functions in the menus, plus additional tools for interacting with the map. Each toolbar item has pop-up help available. Hover your mouse over the item and a short description of the tool’s purpose will be displayed.
As barras de ferramentas disponíveis são:
Toolbar name |
Referência principal para ferramentas |
|---|---|
Advanced Digitizing |
|
Annotations |
|
Atributos |
|
Data Source Manager |
|
Banco de Dados |
|
Digitalização |
|
GRASS |
|
Ajuda |
|
Rótulo |
|
Gerenciar camadas |
|
Navegação de mapa |
|
Mesh Digitizing |
|
Complementos |
|
Projeto |
Trabalhando com Arquivos de Projetos, Preparando os mapas, Biblioteca de estilo |
Processing Algorithms |
|
Raster |
|
Seleção |
|
Shape digitizing |
|
Snapping |
|
Vetor |
|
Web |
Nota
Third-party plugins can extend the default toolbar with their own tools or provide their own toolbar.
Dica
Restaurar barra de ferramentas
Se você ocultou acidentalmente uma barra de ferramentas, é possível recuperá-la usando: (ou  ). Se, por algum motivo, uma barra de ferramentas (ou qualquer outro widget) desaparecer totalmente da interface, você encontrará dicas para recuperá-la em restoring initial GUI.
). Se, por algum motivo, uma barra de ferramentas (ou qualquer outro widget) desaparecer totalmente da interface, você encontrará dicas para recuperá-la em restoring initial GUI.
7.2.2. Painéis
O QGIS fornece muitos painéis. Painéis são widgets especiais com os quais você pode interagir (selecionar opções, marcar caixas, preencher valores…) para executar tarefas mais complexas.
Abaixo está uma lista dos painéis padrão fornecidos pelo QGIS:
Panel name |
Atalho |
Referência |
|---|---|---|
Advanced Digitizing |
Ctrl+4 |
|
Browser |
Ctrl+2 |
|
Browser (2) |
||
Debugging/Development Tools |
F12 |
|
Elevation Profile |
||
Geometry Validation |
||
GPS Information |
Ctrl+0 |
|
GRASS Tools |
||
Layer Order |
Ctrl+9 |
|
Layer Styling |
Ctrl+3 |
|
Layers |
Ctrl+1 |
|
Log Messages |
||
Overview |
Ctrl+8 |
|
Processing Toolbox |
||
Results Viewer |
||
Snapping and Digitizing Options |
||
Spatial Bookmark Manager |
Ctrl+7 |
|
Statistics |
Ctrl+6 |
|
Temporal Controller |
||
Tile Scale |
||
Undo/Redo |
Ctrl+5 |
|
Vertex Editor |
7.3. Barra de Status
A barra de status fornece informações gerais sobre a visualização do mapa e ações processadas ou disponíveis, e oferece ferramentas para gerenciar a visualização do mapa.
7.3.1. Barra de localização
No lado esquerdo da barra de status, a barra de localização, um elemento de pesquisa rápida, ajuda você a encontrar e executar qualquer recurso ou opção no QGIS:
Clique no elemento de texto para ativar a barra de pesquisa do localizador ou pressione Ctrl+K.
Type a text associated with the item you are looking for (name, tag, keyword, …). By default, results are returned for the enabled locator filters, but you can limit the search to a certain scope by prefixing your text with the locator filters prefix, ie. typing
l cadwill return only the layers whose name containscad.O filtro também pode ser selecionado com um clique duplo no menu que aparece ao acessar o elemento localizador.
Clicar em um resultado para executar a ação correspondente, dependendo do tipo de item.
Dica
Limit the lookup to particular field(s) of the active layer
By default, a search with the “active layer features” filter (f) runs
through the whole attribute table of the layer. You can limit the search to
a particular field using the @ prefix. E.g., f @name sal or
@name sal returns only the features whose “name” attribute contains ‘sal’.
Text autocompletion is active when writing and the suggestion can be applied
using Tab key.
A more advanced control on the queried fields is possible from the layer Fields tab. Read Propriedades dos campos for details.
Searching is handled using threads, so that results always become available as quickly as possible, even if slow search filters are installed. They also appear as soon as they are encountered by a filter, which means that e.g. a file search filter will show results one by one as the file tree is scanned. This ensures that the UI is always responsive, even if a very slow search filter is present (e.g. one which uses an online service).
Nota
The Nominatim locator tool may behave differently (no autocompletion search, delay of fetching results, …) with respect to the OpenStreetMap Nominatim usage policy.
7.3.2. Reportando ações
Na área ao lado da barra de localização, um resumo das ações que você executou será mostrado quando necessário (como selecionar feições em uma camada, remover camada, distância e direção da panorâmica) ou uma longa descrição da ferramenta sobre a que você está passando (não disponível para todas as ferramentas).
No caso de operações demoradas, como coleta de estatísticas em camadas matricial, execução de algoritmos de processamento ou renderização de várias camadas na visualização do mapa, uma barra de progresso é exibida na barra de status.
7.3.3. Control the map canvas
A opção ![]() Coordenada mostra a posição atual do mouse, seguindo-o enquanto se move pela visualização do mapa. Você pode definir as unidades (e precisão) na guia . Clique no pequeno botão à esquerda da caixa de texto para alternar entre a opção Coordenada e a opção
Coordenada mostra a posição atual do mouse, seguindo-o enquanto se move pela visualização do mapa. Você pode definir as unidades (e precisão) na guia . Clique no pequeno botão à esquerda da caixa de texto para alternar entre a opção Coordenada e a opção  Extensão que mostra as coordenadas dos cantos inferior-esquerdo e superior direito da visualização do mapa em unidades de mapa.
Extensão que mostra as coordenadas dos cantos inferior-esquerdo e superior direito da visualização do mapa em unidades de mapa.
Next to the coordinate display you will find the Scale display. It shows the scale of the map view. There is a scale selector, which allows you to choose between predefined and custom scales.
On the right side of the scale display, press the  button
to lock the scale to use the magnifier to zoom in or out.
The magnifier allows you to zoom in to a map without altering the map
scale, making it easier to tweak the positions of labels and symbols
accurately.
The magnification level is expressed as a percentage.
If the Magnifier has a level of 100%, then the current map
is not magnified, i.e. is rendered at accurate scale relative to the monitor’s resolution (DPI).
A default magnification value can be defined within
,
which is very useful for high-resolution screens to enlarge small
symbols. In addition, a setting in
controls whether QGIS respects each monitor’s physical DPI or uses the overall system logical DPI.
button
to lock the scale to use the magnifier to zoom in or out.
The magnifier allows you to zoom in to a map without altering the map
scale, making it easier to tweak the positions of labels and symbols
accurately.
The magnification level is expressed as a percentage.
If the Magnifier has a level of 100%, then the current map
is not magnified, i.e. is rendered at accurate scale relative to the monitor’s resolution (DPI).
A default magnification value can be defined within
,
which is very useful for high-resolution screens to enlarge small
symbols. In addition, a setting in
controls whether QGIS respects each monitor’s physical DPI or uses the overall system logical DPI.
À direita da ferramenta de ampliação, você pode definir uma rotação atual no sentido horário para a visualização do mapa em graus.
On the right side of the status bar, the  Render
checkbox can be used to temporarily suspend the map view rendering
(see section Controlling map rendering).
Render
checkbox can be used to temporarily suspend the map view rendering
(see section Controlling map rendering).
To the right of the  Render function, you find the
Render function, you find the
![]() EPSG:code button showing the current project CRS.
Clicking on this opens the Project Properties dialog and lets you
reproject the map view or adjust any other project property.
EPSG:code button showing the current project CRS.
Clicking on this opens the Project Properties dialog and lets you
reproject the map view or adjust any other project property.
Dica
Calculando a escala correta do seu Mapa da tela/visualização
When you start QGIS, the default CRS is WGS 84 (EPSG 4326) and
units are degrees. This means that QGIS will interpret any
coordinate in your layer as specified in degrees.
To get correct scale values, you can either manually change this
setting in the General tab under
(e.g. to meters), or you
can use the ![]() EPSG:code icon seen above.
In the latter case, the units are set to what the project projection
specifies (e.g.,
EPSG:code icon seen above.
In the latter case, the units are set to what the project projection
specifies (e.g., +units=us-ft).
Note that CRS choice on startup can be set in .
7.3.4. Mensagens
The  Messages button next to it opens the
Log Messages Panel which has information on underlying
processes (QGIS startup, plugins loading, processing tools…)
Messages button next to it opens the
Log Messages Panel which has information on underlying
processes (QGIS startup, plugins loading, processing tools…)