24.1.3. Check Geometry
24.1.3.1. Dangle-end lines
Detects dangle-end lines in line geometries and reports them as errors. A dangle-end line is a line feature that terminates at a vertex connected to only one segment, resulting in an endpoint without a proper connection.
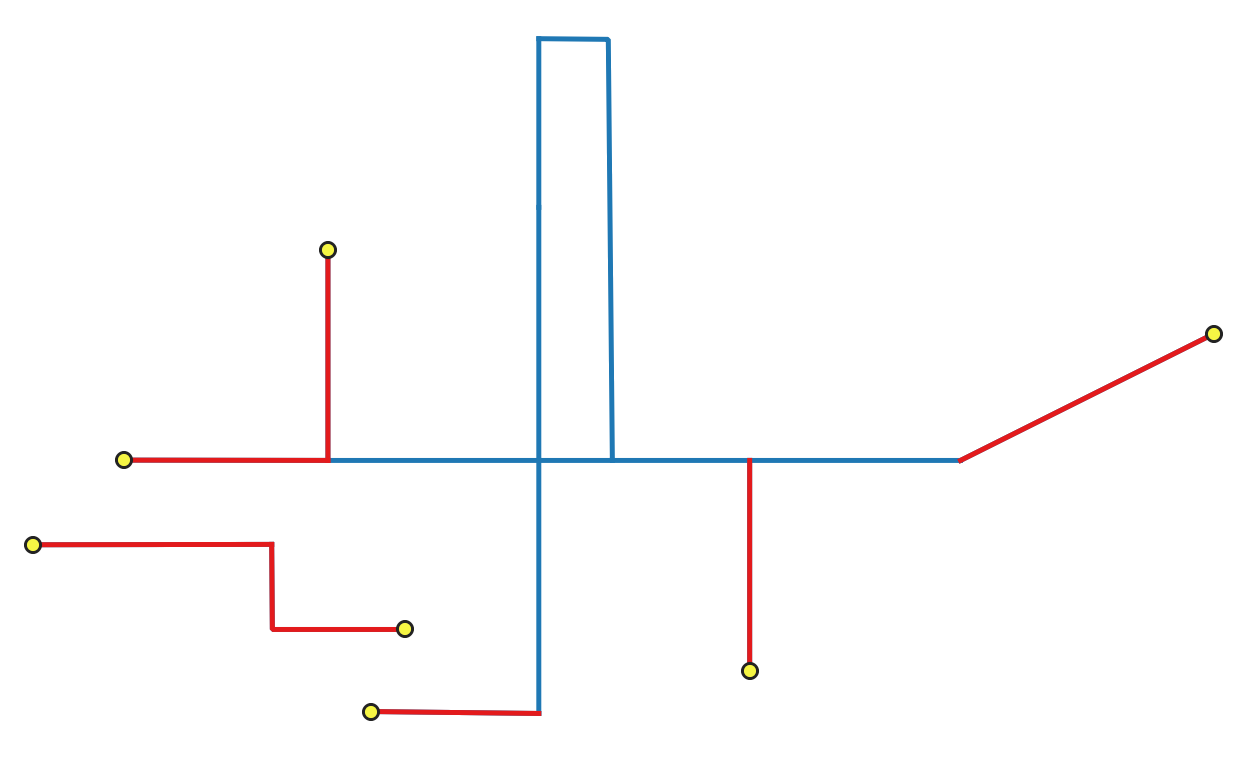
Fig. 24.2 Identifying dangle-end features (in red) and vertices (yellow).
Parameters
Basic parameters
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Input layer |
|
[vector: line] |
Layer with the geometries to check. |
Unique feature identifier |
|
[tablefield: any] |
Field storing unique values for feature identification. |
Dangle-end errors |
|
[vector: point] Default: |
Specification of the output layer containing the errors location. One of:
The file encoding can also be changed here. |
Dangle-end features Optional |
|
[vector: line] Default: |
Line layer containing the identified dangle-end line features. One of:
The file encoding can also be changed here. |
Advanced parameters
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Tolerance |
|
[numeric: integer] Default: 8 |
Numerical precision of geometric operations, given as an integer n, meaning that two vertices less than 10-n apart (in map units) are considered to be merged. |
Outputs
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Dangle-end errors |
|
[vector: point] |
Output point layer representing the error locations and information. The output layer contains the following fields:
|
Dangle-end features |
|
[vector: line] |
Output line layer containing the input dangle-end features.
If no dangle-end features are found, the output layer will be empty.
Available fields are the same as in the |
Python code
Algorithm ID: native:checkgeometrydangle
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
The algorithm id is displayed when you hover over the algorithm in the Processing Toolbox. The parameter dictionary provides the parameter NAMEs and values. See Using processing algorithms from the console for details on how to run processing algorithms from the Python console.
24.1.3.2. Degenerate polygons
Checks the polygons with less than 3 points, which are degenerate polygons. Degenerate polygons are errors.
Note
This algorithm detects invalid polygon geometries (degenerate polygons).
To ensure these invalid features are not filtered out before processing, open
 Advanced options next to the Input layer and set
Invalid feature filtering to
Advanced options next to the Input layer and set
Invalid feature filtering to Do not Filter (Better Performance).
Parameters
Basic parameters
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Input layer |
|
[vector: polygon] |
Layer with the geometries to check. |
Unique feature identifier |
|
[tablefield: any] |
Field storing unique values for feature identification. |
Degenerate polygons errors |
|
[vector: point] Default: |
Specification of the output layer containing the centroid of the degenerate polygons. One of:
The file encoding can also be changed here. |
Degenerate polygons features Optional |
|
[vector: polygon] Default: |
Specification of the output layer containing the degenerate polygons. One of:
The file encoding can also be changed here. |
Advanced parameters
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Tolerance |
|
[numeric: integer] Default: 8 |
Numerical precision of geometric operations, given as an integer n, meaning that two vertices less than 10-n apart (in map units) are considered to be merged. |
Outputs
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Degenerate polygons errors |
|
[vector: point] |
Output point layer representing the error locations and information. The output layer contains the following fields:
|
Degenerate polygons features |
|
[vector: polygon] |
Output polygon layer with features containing the degenerate polygons.
If no degenerate polygon features are found, the output layer will be empty.
Available fields are the same as in the |
Python code
Algorithm ID: native:checkgeometrydegeneratepolygon
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
The algorithm id is displayed when you hover over the algorithm in the Processing Toolbox. The parameter dictionary provides the parameter NAMEs and values. See Using processing algorithms from the console for details on how to run processing algorithms from the Python console.
24.1.3.3. Duplicated geometries
Checks for duplicated geometries in a vector layer, and reports them as errors.
Parameters
Basic parameters
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Input layer |
|
[vector: geometry] |
Layer with the geometries to check |
Unique feature identifier |
|
[tablefield: any] |
Field storing unique values for feature identification |
Duplicate geometries errors |
|
[vector: point] Default: |
Specification of the output layer containing the errors location. One of:
The file encoding can also be changed here. |
Duplicate geometries Optional |
|
[vector: same as input] Default: |
Specification of the output layer containing the geometries that were found to be duplicated. One of:
The file encoding can also be changed here. |
Advanced parameters
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Tolerance |
|
[numeric: integer] Default: 8 |
Numerical precision of geometric operations, given as an integer n, meaning that two vertices less than 10-n apart (in map units) are considered to be merged. |
Outputs
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Duplicate geometries errors |
|
[vector: point] |
Output point layer representing the error locations and information. The output layer contains the following fields:
|
Duplicate geometries |
|
[vector: same as input] |
Output layer containing the geometries that were found to be duplicated.
Available fields are the same as in the |
Python code
Algorithm ID: native:checkgeometryduplicate
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
The algorithm id is displayed when you hover over the algorithm in the Processing Toolbox. The parameter dictionary provides the parameter NAMEs and values. See Using processing algorithms from the console for details on how to run processing algorithms from the Python console.
24.1.3.4. Duplicated vertices
Checks for duplicated vertices in line or polygon geometries, and reports them as errors.
Parameters
Basic parameters
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Input layer |
|
[vector: line, polygon] |
Layer with the geometries to check |
Unique feature identifier |
|
[tablefield: any] |
Field storing unique values for feature identification |
Duplicated vertices errors |
|
[vector: point] Default: |
Specification of the output layer containing the errors location. One of:
The file encoding can also be changed here. |
Duplicated vertices features Optional |
|
[vector: same as input] Default: |
Specification of the output layer containing the features with duplicated vertices. One of:
|
Advanced parameters
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Tolerance |
|
[numeric: integer] Default: 8 |
Numerical precision of geometric operations, given as an integer n, meaning that two vertices less than 10-n apart (in map units) are considered to be merged. |
Outputs
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Duplicated vertices errors |
|
[vector: point] |
Output point layer representing the error locations and information. The output layer contains the following fields:
|
Duplicated vertices features |
|
[vector: same as input] |
Output layer containing the features with duplicated vertices.
Available fields are the same as in the |
Python code
Algorithm ID: native:checkgeometryduplicatenodes
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
The algorithm id is displayed when you hover over the algorithm in the Processing Toolbox. The parameter dictionary provides the parameter NAMEs and values. See Using processing algorithms from the console for details on how to run processing algorithms from the Python console.
24.1.3.5. Features inside polygon
Checks the input geometries contained in the polygons from the polygon layers list. A polygon layer can be checked against itself. Any contained features are reported as errors.
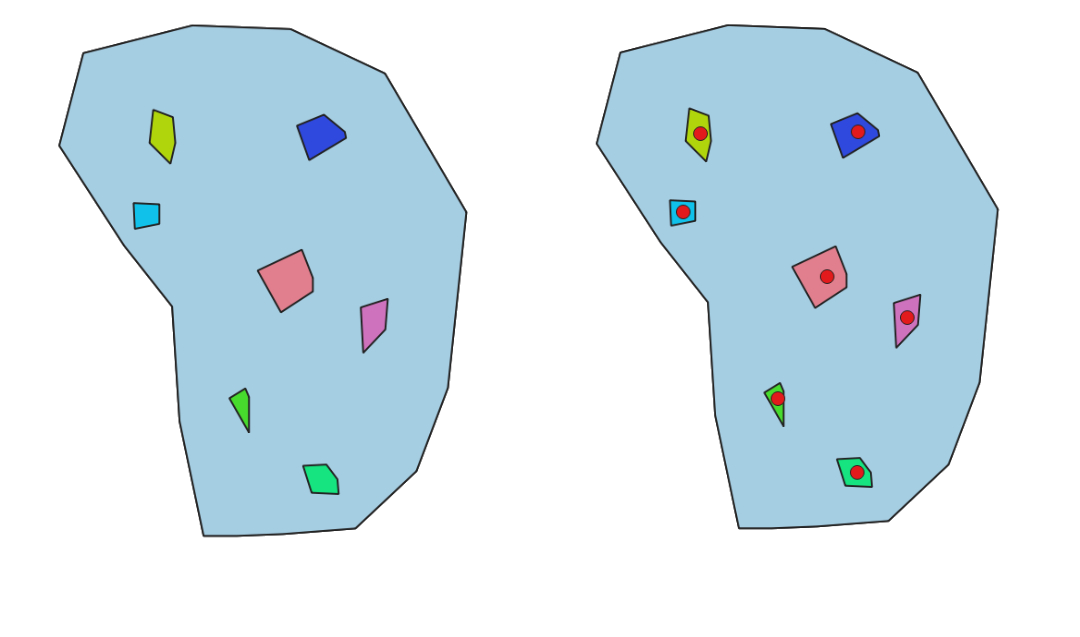
Fig. 24.3 Reporting errors on features inside a polygon.
See also
Parameters
Basic parameters
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Input layer |
|
[vector: geometry] |
Layer with the geometries to check. |
Unique feature identifier |
|
[tablefield: any] |
Field storing unique values for feature identification. |
Polygon layers |
|
[vector: polygon][list] |
List of polygon layers to check against. |
Errors from contained features |
|
[vector: point] Default: |
Point layer representing the contained features. One of:
The file encoding can also be changed here. |
Contained features Optional |
|
[vector: same as input] Default: |
Specification of the output layer containing features within the checked polygons. One of:
The file encoding can also be changed here. |
Advanced parameters
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Tolerance |
|
[numeric: integer] Default: 8 |
Numerical precision of geometric operations, given as an integer n, meaning that two vertices less than 10-n apart (in map units) are considered to be merged. |
Outputs
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Errors from contained features |
|
[vector: point] |
Output point layer representing the error locations and information. The output layer contains the following fields:
|
Contained features |
|
[vector: same as input] |
Output layer containing features within the checked polygons.
Available fields are the same as in the |
Python code
Algorithm ID: native:checkgeometrycontained
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
The algorithm id is displayed when you hover over the algorithm in the Processing Toolbox. The parameter dictionary provides the parameter NAMEs and values. See Using processing algorithms from the console for details on how to run processing algorithms from the Python console.
24.1.3.6. Holes
Detects holes in polygon geometries and reports them as errors.

Fig. 24.4 Reporting errors for holes on a polygon feature.
See also
Parameters
Basic parameters
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Input layer |
|
[vector: polygon] |
Layer with the geometries to check |
Unique feature identifier |
|
[tablefield: any] |
Field storing unique values for feature identification |
Holes errors |
|
[vector: point] Default: |
Specification of the output layer containing the errors location. One of:
The file encoding can also be changed here. |
Polygons with holes Optional |
|
[vector: polygon] Default: |
Polygon layer with the features containing holes. One of:
The file encoding can also be changed here. |
Advanced parameters
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Tolerance |
|
[numeric: integer] Default: 8 |
Numerical precision of geometric operations, given as an integer n, meaning that two vertices less than 10-n apart (in map units) are considered to be merged. |
Outputs
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Holes errors |
|
[vector: point] |
Output point layer representing the error locations and information. The output layer contains the following fields:
|
Polygon with holes |
|
[vector: polygon] |
Output polygon layer with features containing holes.
If no holes are found, the output layer will be empty.
Available fields are the same as in the |
Python code
Algorithm ID: native:checkgeometryhole
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
The algorithm id is displayed when you hover over the algorithm in the Processing Toolbox. The parameter dictionary provides the parameter NAMEs and values. See Using processing algorithms from the console for details on how to run processing algorithms from the Python console.
24.1.3.7. Lines intersecting each other
Checks intersections between line geometries within a layer. Intersections between two different lines are errors.
See also
Parameters
Basic parameters
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Input layer |
|
[vector: line] |
Layer with the geometries to check. |
Unique feature identifier |
|
[tablefield: any] |
Field storing unique values for feature identification. |
Intersection errors |
|
[vector: point] Default: |
Specification of the output layer containing the intersections location. One of:
The file encoding can also be changed here. |
Intersecting feature Optional |
|
[vector: line] Default: |
Specification of the output layer for features intersecting each other. One of:
The file encoding can also be changed here. |
Advanced parameters
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Tolerance |
|
[numeric: integer] Default: 8 |
Numerical precision of geometric operations, given as an integer n, meaning that two vertices less than 10-n apart (in map units) are considered to be merged. |
Outputs
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Intersection errors |
|
[vector: point] |
Output point layer representing the error locations and information. The output layer contains the following fields:
|
Intersecting feature |
|
[vector: line] |
Output layer containing, for each identified intersection, the feature (with same |
Python code
Algorithm ID: native:checkgeometrylineintersection
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
The algorithm id is displayed when you hover over the algorithm in the Processing Toolbox. The parameter dictionary provides the parameter NAMEs and values. See Using processing algorithms from the console for details on how to run processing algorithms from the Python console.
24.1.3.8. Lines intersecting other layer
Checks if the input line layer features intersect with the check layer features. An input feature that intersects with a check layer feature is an error.
See also
Parameters
Basic parameters
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Input layer |
|
[vector: line] |
Layer with the geometries to check. |
Unique feature identifier |
|
[tablefield: any] |
Field storing unique values for feature identification. |
Check layer |
|
[vector: line, polygon] |
Layer with the geometries to check against. |
Line intersecting other layer errors |
|
[vector: point] Default: |
Specification of the output point layer containing the locations of intersection errors. One of:
The file encoding can also be changed here. |
Line intersecting other layer features Optional |
|
[line] Default: |
Line layer with the input features that intersect features in the check layer. One of:
The file encoding can also be changed here. |
Advanced parameters
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Tolerance |
|
[numeric: integer] Default: 8 |
Numerical precision of geometric operations, given as an integer n, meaning that two vertices less than 10-n apart (in map units) are considered to be merged. |
Outputs
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Line intersecting other layer errors |
|
[vector: point] |
Output point layer representing the error location and information. The output layer contains the following fields:
|
Line intersecting other layer features |
|
[vector: line] |
Output layer containing, for each identified intersection, the input feature it belongs to.
If no intersections are found, the output layer will be empty.
Available fields are the same as in the |
Python code
Algorithm ID: native:checkgeometrylinelayerintersection
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
The algorithm id is displayed when you hover over the algorithm in the Processing Toolbox. The parameter dictionary provides the parameter NAMEs and values. See Using processing algorithms from the console for details on how to run processing algorithms from the Python console.
24.1.3.9. Missing vertices along borders
Checks for missing vertices along polygon borders. To be topologically correct, a vertex at the junction of two polygons must be present on both polygons. Missing vertices are errors.
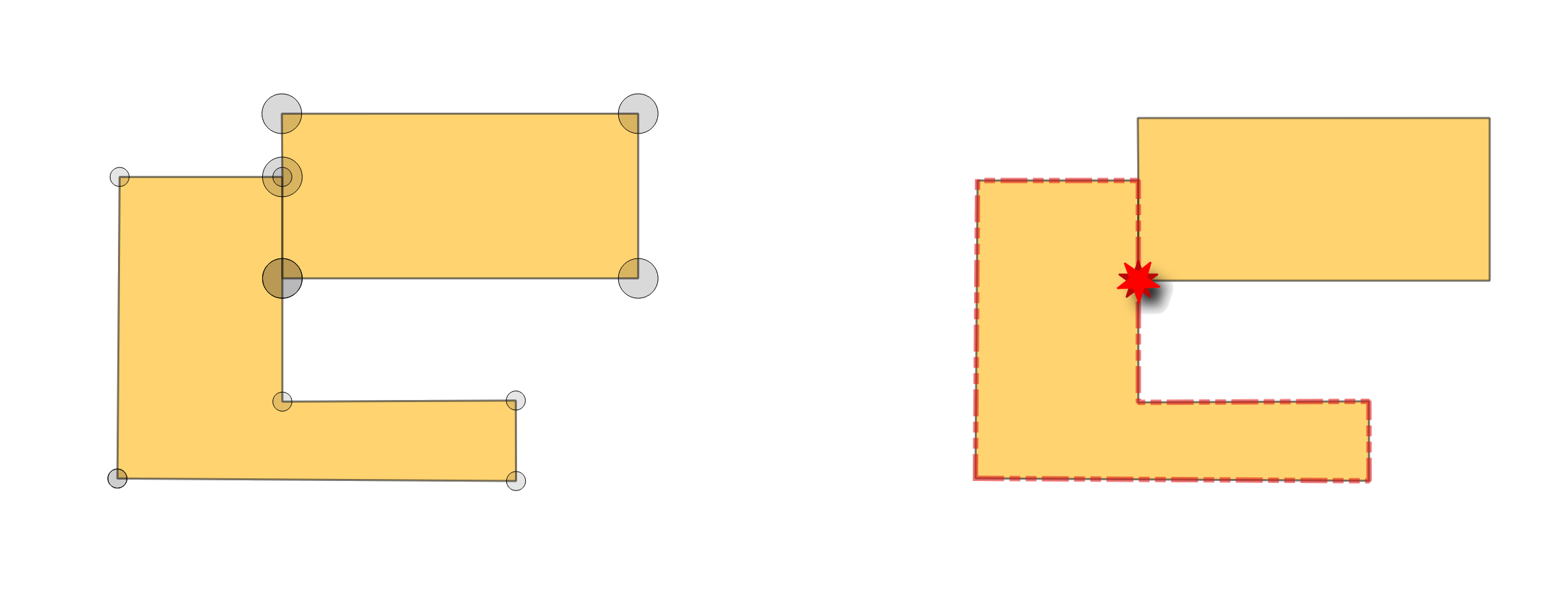
Fig. 24.5 Reporting errors for missing vertices on polygon features.
See also
Parameters
Basic parameters
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Input layer |
|
[vector: polygon] |
Layer with the geometries to check. |
Unique feature identifier |
|
[tablefield: any] |
Field storing unique values for feature identification. |
Missing vertices errors |
|
[vector: point] Default: |
Specification of the output layer containing the errors location. One of:
The file encoding can also be changed here. |
Missing vertices features Optional |
|
[vector: polygon] Default: |
Polygon layer with the features whose vertices are missing. One of:
The file encoding can also be changed here. |
Advanced parameters
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Tolerance |
|
[numeric: integer] Default: 8 |
Numerical precision of geometric operations, given as an integer n, meaning that two vertices less than 10-n apart (in map units) are considered to be merged. |
Outputs
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Missing vertices errors |
|
[vector: point] |
Output point layer representing the error locations and information. The output layer contains the following fields:
|
Missing vertices features |
|
[vector: polygon] |
Output polygon layer with features whose vertices are missing.
There will be as many (duplicate) features as there are missing vertices in each geometry.
If no vertices are missing, the output layer will be empty.
Available fields are the same as in the |
Python code
Algorithm ID: native:checkgeometrymissingvertex
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
The algorithm id is displayed when you hover over the algorithm in the Processing Toolbox. The parameter dictionary provides the parameter NAMEs and values. See Using processing algorithms from the console for details on how to run processing algorithms from the Python console.
24.1.3.10. Overlaps
Calculates overlapping areas in polygon geometries, and reports areas smaller than a given minimum as errors.
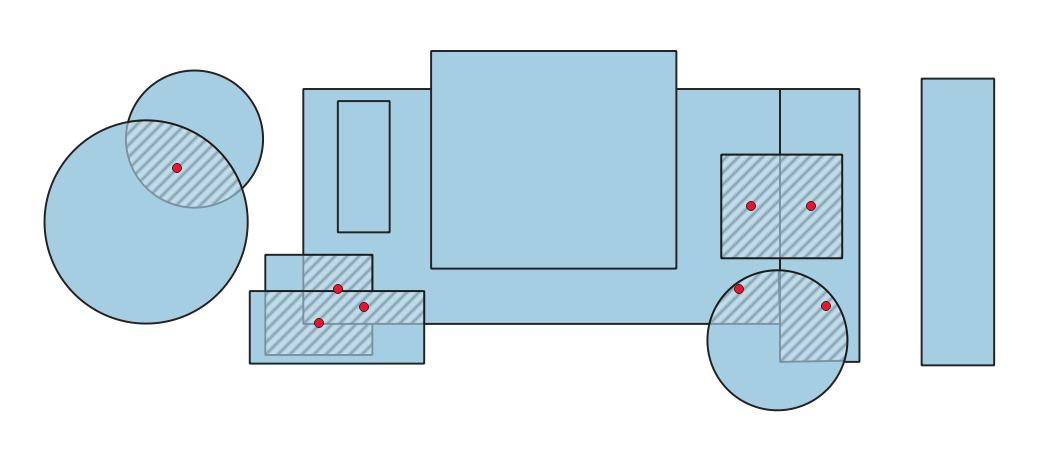
Fig. 24.6 Hashed polygons indicate overlapping areas smaller than the specified minimum.
See also
Parameters
Basic parameters
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Input layer |
|
[vector: polygon] |
Layer with the geometries to check. |
Unique feature identifier |
|
[tablefield: any] |
Field storing unique values for feature identification. |
Minimum overlap area |
|
[numeric: double] |
Minimum area of the overlap to be reported as an error. If set to 0, all overlaps are reported. |
Overlap errors |
|
[vector: point] Default: |
Specification of the output layer containing centroid points of the overlapping areas. One of:
The file encoding can also be changed here. |
Overlap features Optional |
|
[vector: polygon] Default: |
Specification of the output layer for features containing overlaps. One of:
The file encoding can also be changed here. |
Advanced parameters
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Tolerance |
|
[numeric: integer] Default: 8 |
Numerical precision of geometric operations, given as an integer n, meaning that two vertices less than 10-n apart (in map units) are considered to be merged. |
Outputs
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Overlap errors |
|
[vector: point] |
Output point layer representing the error locations and information. The output layer contains the following fields:
|
Overlap features |
|
[vector: polygon] |
Output layer containing the overlapping areas.
Available fields are the same as in the |
Python code
Algorithm ID: native:checkgeometryoverlap
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
The algorithm id is displayed when you hover over the algorithm in the Processing Toolbox. The parameter dictionary provides the parameter NAMEs and values. See Using processing algorithms from the console for details on how to run processing algorithms from the Python console.
24.1.3.11. Points outside lines
Checks if the points in the input layer are covered by a line in the selected line layers. A point not covered by a line is an error.
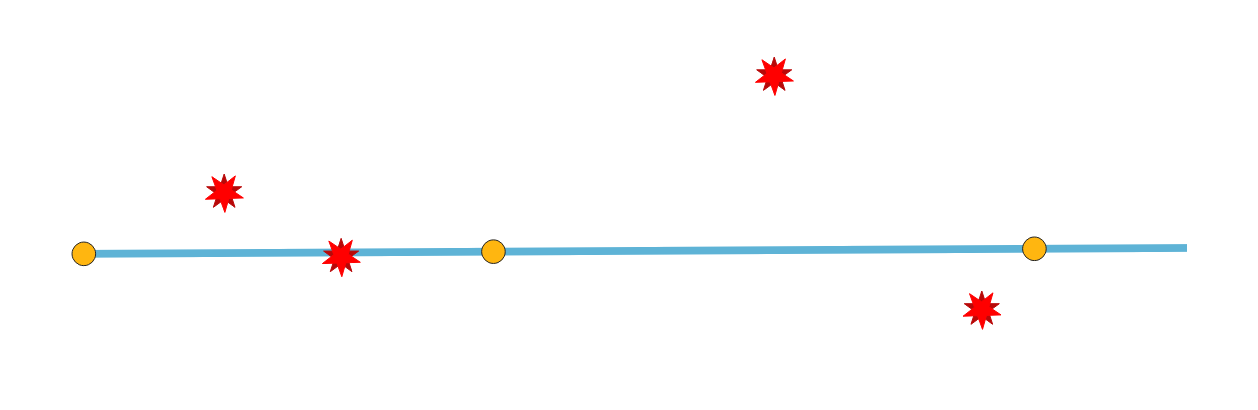
Fig. 24.7 Reporting errors on points not covered by a line.
Parameters
Basic parameters
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Input layer |
|
[vector: point] |
Layer with the geometries to check. |
Unique feature identifier |
|
[tablefield: any] |
Field storing unique values for feature identification. |
Line layers |
|
[vector: line][list] |
Layer(s) with the lines to check against. |
Points not covered by a line |
|
[vector: point] Default: |
Specification of the output layer containing points not covered by a line. One of:
The file encoding can also be changed here. |
Advanced parameters
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Tolerance |
|
[numeric: integer] Default: 8 |
Numerical precision of geometric operations, given as an integer n, meaning that two vertices less than 10-n apart (in map units) are considered to be merged. |
Outputs
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Points not covered by a line |
|
[vector: point] |
Output point layer representing the error locations and information. The output layer contains the following fields:
|
Python code
Algorithm ID: native:checkgeometrypointcoveredbyline
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
The algorithm id is displayed when you hover over the algorithm in the Processing Toolbox. The parameter dictionary provides the parameter NAMEs and values. See Using processing algorithms from the console for details on how to run processing algorithms from the Python console.
24.1.3.12. Points outside polygons
Checks if points from the input layer are in polygons from the selected polygon layers. Points that are not fully inside polygons are errors.
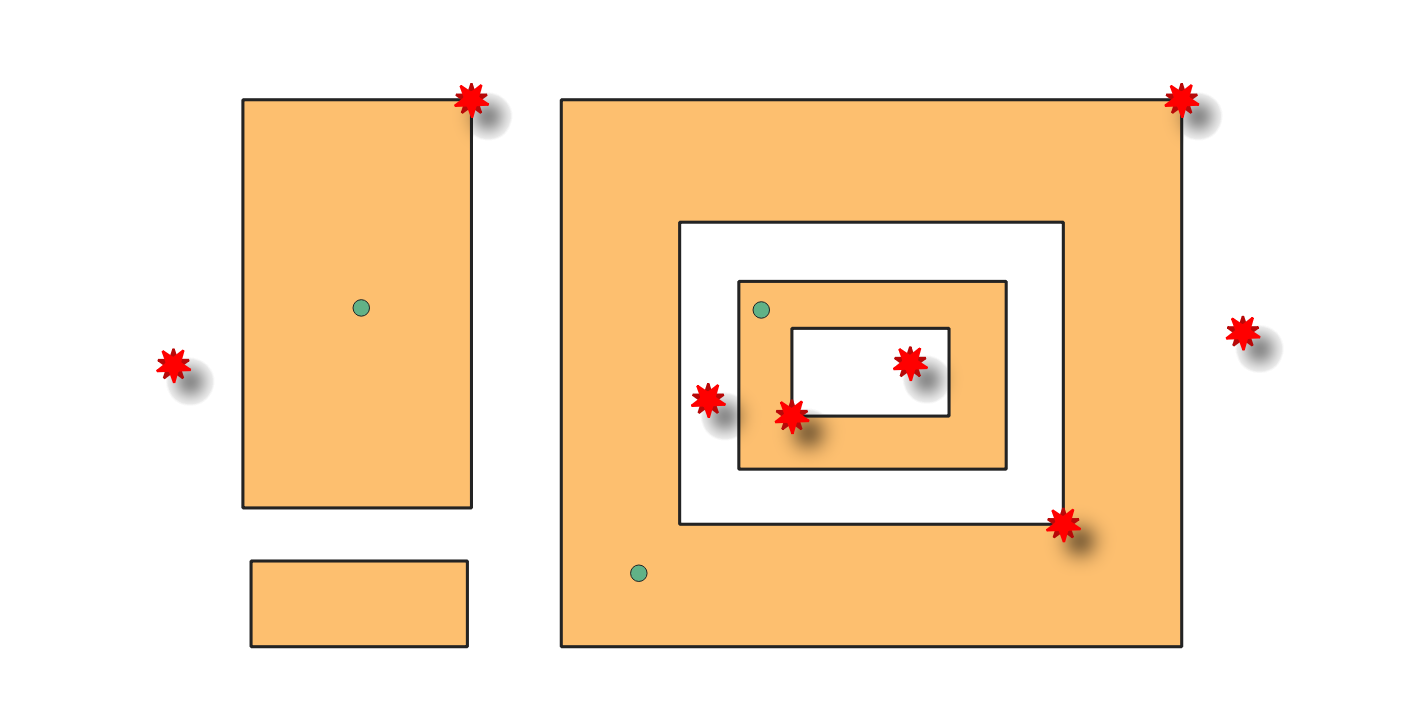
Fig. 24.8 Reporting errors on points outside polygons.
Parameters
Basic parameters
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Input layer |
|
[vector: point] |
Layer with the geometries to check. |
Unique feature identifier |
|
[tablefield: any] |
Field storing unique values for feature identification. |
Polygon layers |
|
[vector: polygon][list] |
Layer(s) with the polygons to check against. |
Points outside polygons errors |
|
[vector: point] Default: |
Specification of the output layer containing points outside the polygons. One of:
The file encoding can also be changed here. |
Advanced parameters
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Tolerance |
|
[numeric: integer] Default: 8 |
Numerical precision of geometric operations, given as an integer n, meaning that two vertices less than 10-n apart (in map units) are considered to be merged. |
Outputs
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Points outside polygons errors |
|
[vector: point] |
Output point layer representing the error locations and information. The output layer contains the following fields:
|
Python code
Algorithm ID: native:checkgeometrypointinpolygon
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
The algorithm id is displayed when you hover over the algorithm in the Processing Toolbox. The parameter dictionary provides the parameter NAMEs and values. See Using processing algorithms from the console for details on how to run processing algorithms from the Python console.
24.1.3.13. Self-contacts
Checks if the geometry has self contact points (in line or polygon), i.e., a vertex that touches more than two segments of the same ring. Self contacts are errors.
Note
This algorithm detects invalid polygon geometries (self-contacts).
To ensure these invalid features are not filtered out before processing, open
 Advanced options next to the Input layer and set
Invalid feature filtering to
Advanced options next to the Input layer and set
Invalid feature filtering to Do not Filter (Better Performance).
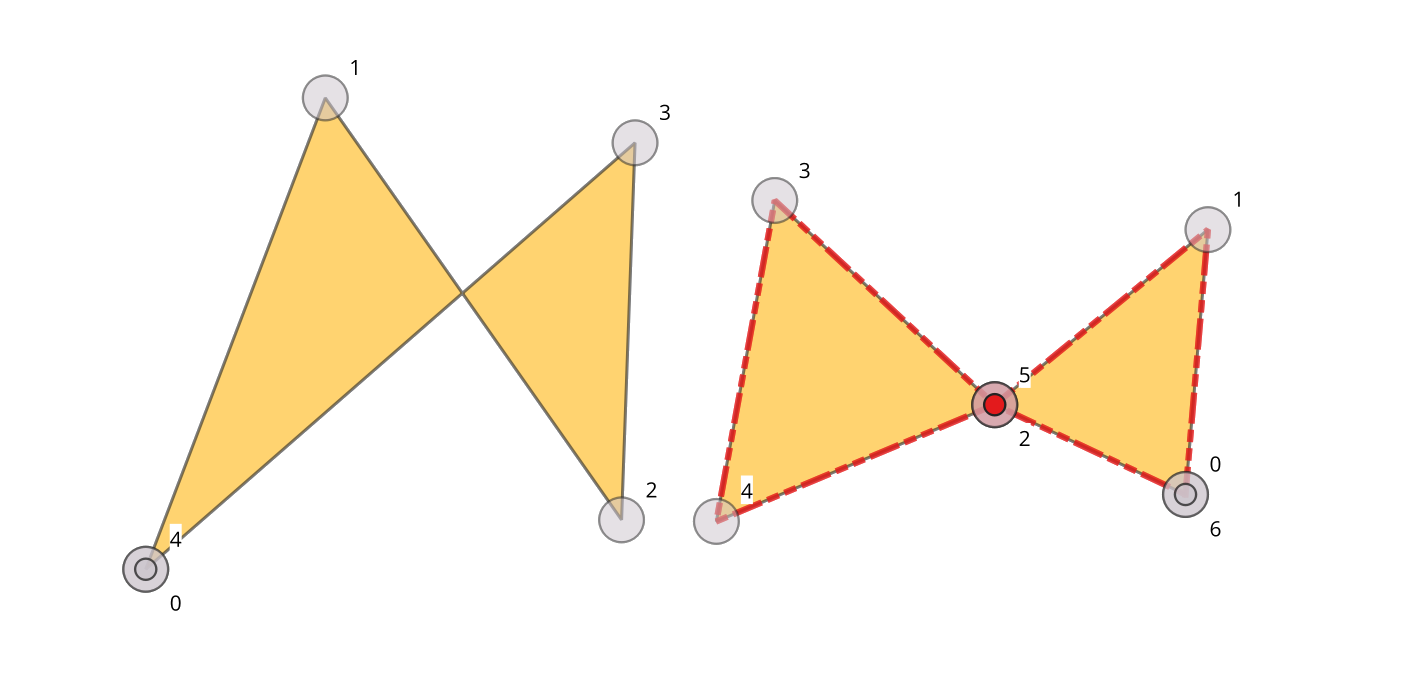
Fig. 24.9 Self-intersection vs self-contact.
See also
Parameters
Basic parameters
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Input layer |
|
[vector: line, polygon] |
Layer with the geometries to check. |
Unique feature identifier |
|
[tablefield: any] |
Field storing unique values for feature identification. |
Self contact error points |
|
[vector: point] Default: |
Specification of the output layer containing the errors location. One of:
The file encoding can also be changed here. |
Self contact features Optional |
|
[same as input] Default: |
Line or polygon layer containing self-contact features. One of:
The file encoding can also be changed here. |
Advanced parameters
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Tolerance |
|
[numeric: integer] Default: 8 |
Numerical precision of geometric operations, given as an integer n, meaning that two vertices less than 10-n apart (in map units) are considered to be merged. |
Outputs
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Self contact error points |
|
[vector: point] |
Output point layer representing the error locations and information. The output layer contains the following fields:
|
Self contact features |
|
[vector: same as input] |
Output polygon or line layer with features containing the self-contact features.
If no self-contact features are found, the output layer will be empty.
Available fields are the same as in the |
Python code
Algorithm ID: native:checkgeometryselfcontact
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
The algorithm id is displayed when you hover over the algorithm in the Processing Toolbox. The parameter dictionary provides the parameter NAMEs and values. See Using processing algorithms from the console for details on how to run processing algorithms from the Python console.
24.1.3.14. Self-intersections
Detects self-intersections in line or polygon geometries, and reports them as errors. Self-intersections occur when the segments of a geometry cross over each other without having a common vertex.
Note
This algorithm detects invalid polygon geometries (self-intersections).
To ensure these invalid features are not filtered out before processing, open
 Advanced options next to the Input layer and set
Invalid feature filtering to
Advanced options next to the Input layer and set
Invalid feature filtering to Do not Filter (Better Performance).
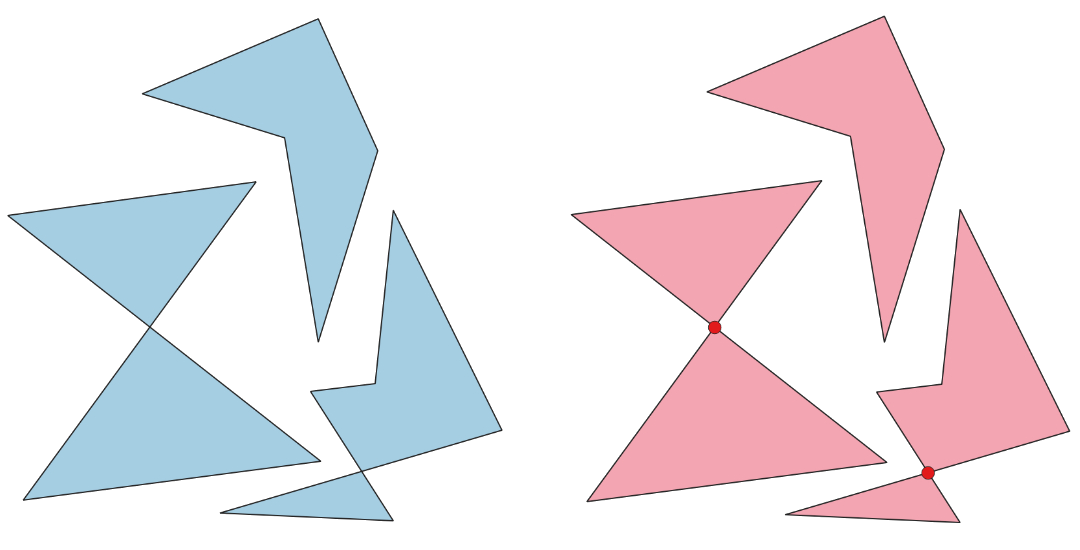
Fig. 24.10 Self-intersection vs self-contact.
Parameters
Basic parameters
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Input layer |
|
[vector: line, polygon] |
Layer with the geometries to check |
Unique feature identifier |
|
[tablefield: any] |
Field storing unique values for feature identification |
Self-intersecting errors |
|
[vector: point] Default: |
Specification of the output layer containing the errors location. One of:
The file encoding can also be changed here. |
Self-intersecting features Optional |
|
[same as input] Default: |
Line or polygon layer containing self-intersected features. One of:
The file encoding can also be changed here. |
Advanced parameters
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Tolerance |
|
[numeric: integer] Default: 8 |
Numerical precision of geometric operations, given as an integer n, meaning that two vertices less than 10-n apart (in map units) are considered to be merged. |
Outputs
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Self-intersecting errors |
|
[vector: point] |
Output point layer representing the error locations and information. The output layer contains the following fields:
|
Self-intersecting features |
|
[vector: line, polygon] |
Output polygon or line layer with features containing the self-intersecting features.
If no self-intersecting features are found, the output layer will be empty.
Available fields are the same as in the |
Python code
Algorithm ID: native:checkgeometryselfintersection
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
The algorithm id is displayed when you hover over the algorithm in the Processing Toolbox. The parameter dictionary provides the parameter NAMEs and values. See Using processing algorithms from the console for details on how to run processing algorithms from the Python console.
24.1.3.15. Sliver polygons
Detects sliver polygons in a polygon layer, i.e., polygons with a thinness greater than a specified value.
The thinness is the ratio between the area of the minimum square containing the polygon and the area of the polygon itself (a square has a thinness value of 1). The thinness value is between 1 and +infinity. A maximum area can be set for limiting the checks to polygons of a lower area. Polygons having a thinness higher than the maximum thinness are errors. To fix sliver polygons, use the Fix small polygons algorithm.
Note
This algorithm detects invalid polygon geometries (sliver polygons).
To ensure these invalid features are not filtered out before processing, open
 Advanced options next to the Input layer and set
Invalid feature filtering to
Advanced options next to the Input layer and set
Invalid feature filtering to Do not Filter (Better Performance).
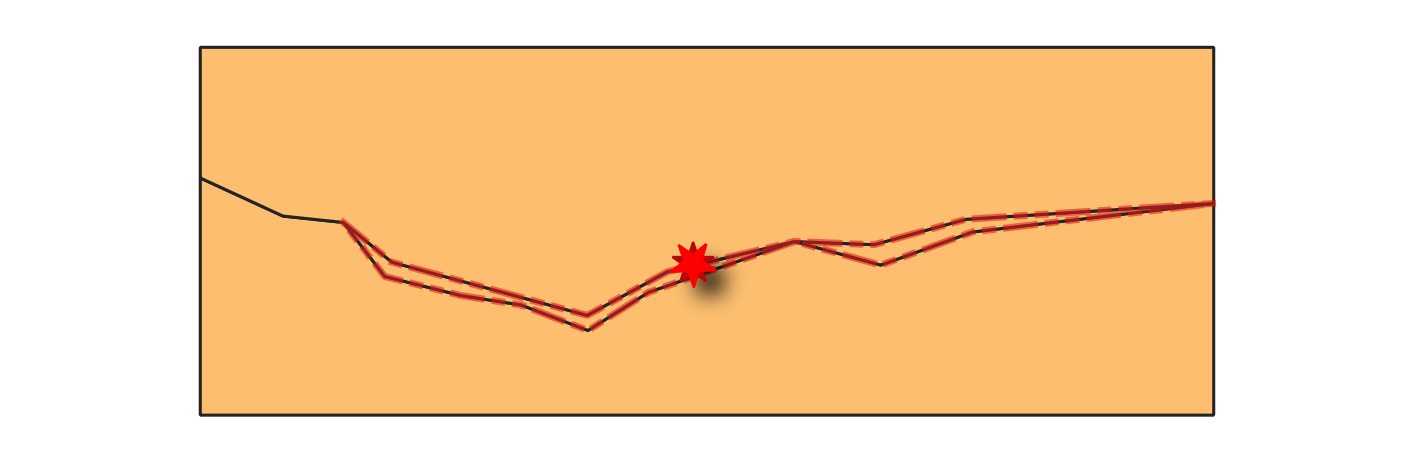
Fig. 24.11 Reporting errors on features with sliver polygons.
See also
Parameters
Basic parameters
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Input layer |
|
[vector: polygon] |
Layer with the geometries to check. |
Unique feature identifier |
|
[tablefield: any] |
Field storing unique values for feature identification. |
Maximum thinness |
|
[numeric: double] Default: 20.0 |
Maximum thinness value of a polygon to be considered valid. Any polygon with a thinness value above this threshold is reported as error. |
Maximum area (map units squared) |
|
[numeric: double] Default: 0.0 |
Maximum area of a polygon to be checked (in map units). Any polygon with an area above this threshold is skipped. A value of 0 means all polygons are checked. |
Sliver polygon errors |
|
[vector: point] Default: |
Specification of the output layer containing the centroid points of sliver polygon features. One of:
The file encoding can also be changed here. |
Sliver polygon features Optional |
|
[vector: polygon] Default: |
Polygon layer containing sliver polygon features. One of:
The file encoding can also be changed here. |
Advanced parameters
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Tolerance |
|
[numeric: integer] Default: 8 |
Numerical precision of geometric operations, given as an integer n, meaning that two vertices less than 10-n apart (in map units) are considered to be merged. |
Outputs
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Sliver polygon errors |
|
[vector: point] |
Output point layer representing the error locations and information. The output layer contains the following fields:
|
Sliver polygon features |
|
[vector: polygon] |
Output layer with features containing the sliver polygons.
If no sliver polygon features are found, the output layer will be empty.
Available fields are the same as in the |
Python code
Algorithm ID: native:checkgeometrysliverpolygon
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
The algorithm id is displayed when you hover over the algorithm in the Processing Toolbox. The parameter dictionary provides the parameter NAMEs and values. See Using processing algorithms from the console for details on how to run processing algorithms from the Python console.
24.1.3.16. Small angles
Compares the angles within line or polygon geometries to a specified threshold, and reports as error any angle below that value.
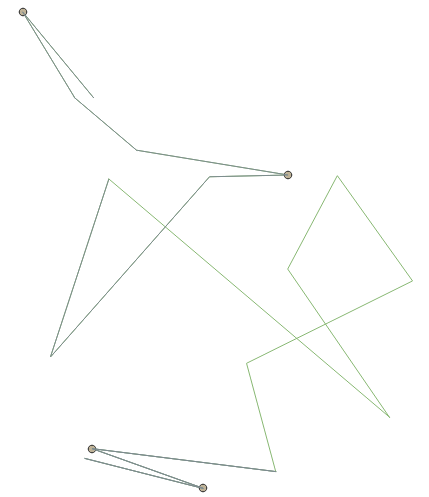
Fig. 24.12 Reporting errors on a line feature for angles lower than 15°.
See also
Parameters
Basic parameters
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Input layer |
|
[vector: line, polygon] |
Layer with the geometries to check. |
Unique feature identifier |
|
[tablefield: any] |
Field storing unique values for feature identification. |
Minimum angle |
|
[numeric: double] |
Allowed minimum angle between adjacent segments in a feature’s geometry. Any angle below this threshold is reported as error. |
Small angle errors |
|
[vector: point] Default: |
Specification of the output layer containing the errors location. One of:
The file encoding can also be changed here. |
Advanced parameters
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Tolerance |
|
[numeric: integer] Default: 8 |
Numerical precision of geometric operations, given as an integer n, meaning that two vertices less than 10-n apart (in map units) are considered to be merged. |
Outputs
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Small angle errors |
|
[vector: point] |
Output point layer representing the error locations and information. The output layer contains the following fields:
|
Python code
Algorithm ID: native:checkgeometryangle
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
The algorithm id is displayed when you hover over the algorithm in the Processing Toolbox. The parameter dictionary provides the parameter NAMEs and values. See Using processing algorithms from the console for details on how to run processing algorithms from the Python console.
24.1.3.17. Small polygons
Detects polygon features whose area is below a specified value as errors.
Note
This algorithm detects invalid polygon geometries (small polygons).
To ensure these invalid features are not filtered out before processing, open
 Advanced options next to the Input layer and set
Invalid feature filtering to
Advanced options next to the Input layer and set
Invalid feature filtering to Do not Filter (Better Performance).
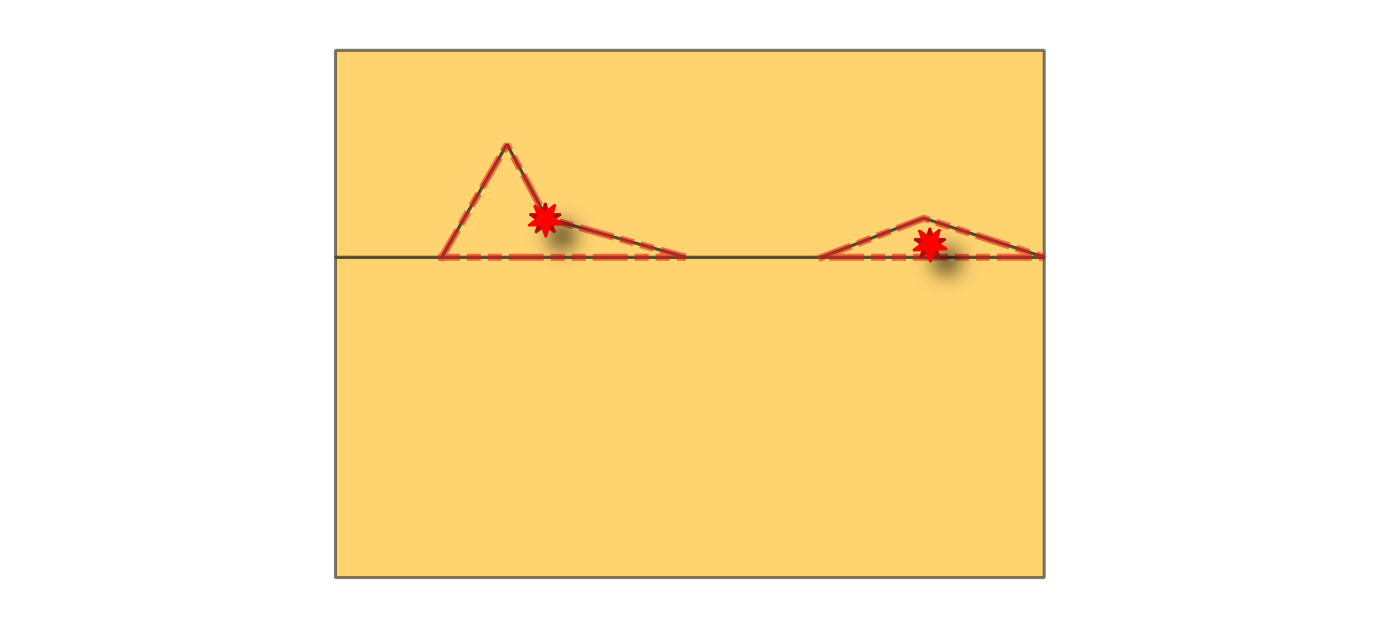
Fig. 24.13 Reporting errors on features with small polygons (below given area threshold).
See also
Parameters
Basic parameters
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Input layer |
|
[vector: polygon] |
Layer with the geometries to check. |
Unique feature identifier |
|
[tablefield: any] |
Field storing unique values for feature identification. |
Area threshold |
|
[numeric: double] Default: 0 |
Minimum area of a polygon to be considered valid, in selected units. Any polygon with an area below this threshold is reported as error. |
Small polygons errors |
|
[vector: point] Default: |
Specification of the output layer containing centroid points of small polygons. One of:
The file encoding can also be changed here. |
Small polygons features Optional |
|
[vector: polygon] Default: |
Specification of the output layer for features containing small polygon features. One of:
The file encoding can also be changed here. |
Advanced parameters
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Tolerance |
|
[numeric: integer] Default: 8 |
Numerical precision of geometric operations, given as an integer n, meaning that two vertices less than 10-n apart (in map units) are considered to be merged. |
Outputs
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Small polygons errors |
|
[vector: point] |
Output point layer representing the error locations and information. The output layer contains the following fields:
|
Small polygons features |
|
[vector: polygon] |
Output polygon layer with features containing the small polygon features.
If no small polygon features are found, the output layer will be empty.
Available fields are the same as in the |
Python code
Algorithm ID: native:checkgeometryarea
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
The algorithm id is displayed when you hover over the algorithm in the Processing Toolbox. The parameter dictionary provides the parameter NAMEs and values. See Using processing algorithms from the console for details on how to run processing algorithms from the Python console.
24.1.3.18. Small gaps
Checks for gaps between polygons in the input layer. Gaps with an area smaller than the gap threshold are reported as errors. If an allowed gaps layer is provided, the algorithm ignores gaps that fall entirely within polygons from this layer. An optional buffer can be applied to the allowed gaps.
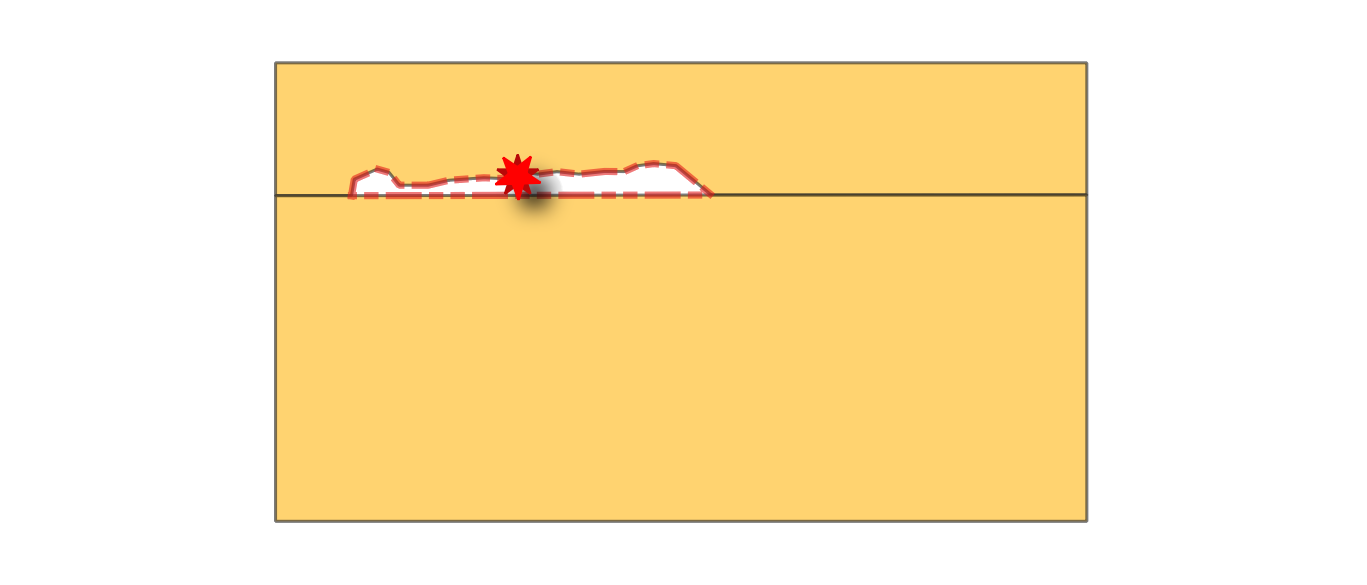
Fig. 24.14 Reporting errors on polygon features for gaps smaller than the specified threshold.
See also
Parameters
Basic parameters
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Input layer |
|
[vector: polygon] |
Layer with the geometries to check. |
Unique feature identifier |
|
[tablefield: any] |
Field storing unique values for feature identification. |
Gap threshold |
|
[numeric: double] Default: 0.0 |
Maximum area of gaps to be reported as errors, in map units. If set to 0, all the gaps are reported. |
Allowed gaps layer Optional |
|
[vector: polygon] |
Optional layer specifying polygons whose areas should be ignored during the gap check. Gaps that fall entirely within these polygons will not be reported as errors. |
Allowed gaps buffer Optional |
|
[numeric: double] Default: 0.0 |
Buffer distance to apply to the allowed gaps layer, in selected units. Gaps located within this buffered area are ignored. Allows adding a spatial tolerance around allowed gaps to avoid reporting near-boundary gaps as errors. |
Neighbors layer |
|
[vector: table] Default: |
Specification of the output table representing the gap ID and the unique ID of its neighbor features. One of:
The file encoding can also be changed here. |
Gap errors Optional |
|
[vector: point] Default: |
Specification of the output layer containing the centroid points of the gaps. One of:
The file encoding can also be changed here. |
Gap features |
|
[vector: polygon] Default: |
Specification of the output layer containing the gap geometries. One of:
The file encoding can also be changed here. |
Advanced parameters
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Tolerance |
|
[numeric: integer] Default: 8 |
Numerical precision of geometric operations, given as an integer n, meaning that two vertices less than 10-n apart (in map units) are considered to be merged. |
Outputs
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Neighbors layer |
|
[vector: table] |
A 1–N relational table, meaning that one gap can be associated with multiple neighboring polygons. The output table contains the following fields:
|
Gap errors |
|
[vector: point] |
Output point layer representing the error locations and information. The output layer contains the following fields:
|
Gap features |
|
[vector: polygon] |
Output layer containing the gap geometries.
Available fields are the same as in the |
Python code
Algorithm ID: native:checkgeometrygap
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
The algorithm id is displayed when you hover over the algorithm in the Processing Toolbox. The parameter dictionary provides the parameter NAMEs and values. See Using processing algorithms from the console for details on how to run processing algorithms from the Python console.
24.1.3.19. Small segments
Calculates length of individual segments in line or polygon geometries, and reports segments shorter than a minimum length as errors.
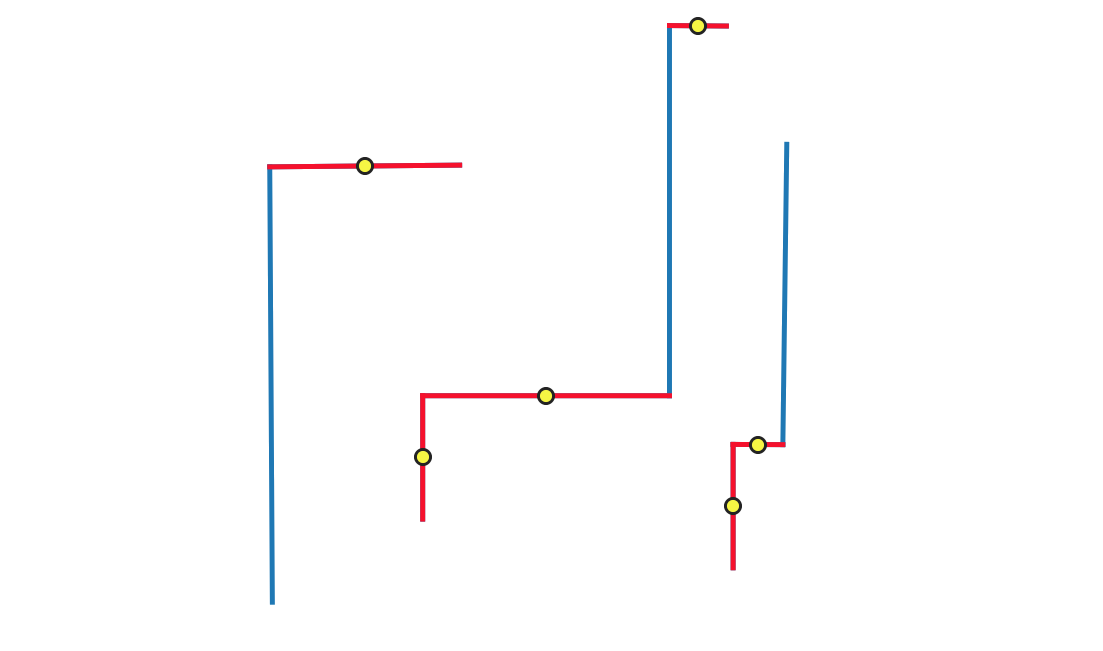
Fig. 24.15 Reporting errors (in red) on single line segments shorter than the given threshold.
See also
Parameters
Basic parameters
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Input layer |
|
[vector: line, polygon] |
Layer with the geometries to check. |
Unique feature identifier |
|
[tablefield: any] |
Field storing unique values for feature identification. |
Minimum segment length |
|
[numeric: double] Default: 0.0 |
Minimum length of segments to be considered valid, in map units. |
Short segments errors |
|
[vector: point] Default: |
Specification of the output layer containing centroid of short segments. One of:
The file encoding can also be changed here. |
Short segments features Optional |
|
[vector: same as input] Default: |
Specification of the output layer for features containing short segments. One of:
The file encoding can also be changed here. |
Advanced parameters
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Tolerance |
|
[numeric: integer] Default: 8 |
Numerical precision of geometric operations, given as an integer n, meaning that two vertices less than 10-n apart (in map units) are considered to be merged. |
Outputs
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Short segments errors |
|
[vector: point] |
Output point layer representing the error locations and information. The output layer contains the following fields:
|
Short segments features |
|
[vector: same as input] |
Output layer containing, for each identified short segment, the feature it belongs to.
Available fields are the same as in the |
Python code
Algorithm ID: native:checkgeometrysegmentlength
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
The algorithm id is displayed when you hover over the algorithm in the Processing Toolbox. The parameter dictionary provides the parameter NAMEs and values. See Using processing algorithms from the console for details on how to run processing algorithms from the Python console.
24.1.3.20. Strictly multipart
Checks if multipart geometries have more than one part. Multipart geometries with only one part are errors.
See also
Parameters
Basic parameters
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Input layer |
|
[vector: geometry] |
Layer with the geometries to check. |
Unique feature identifier |
|
[tablefield: any] |
Field storing unique values for feature identification. |
One-part geometry errors |
|
[vector: point] Default: |
Specification of the output layer containing centroid of the multipart geometries that have only one part. One of:
The file encoding can also be changed here. |
One-part geometry features Optional |
|
[vector: same as input] Default: |
Specification of the output layer for features containing multipart geometries that have only one part. One of:
The file encoding can also be changed here. |
Advanced parameters
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Tolerance |
|
[numeric: integer] Default: 8 |
Numerical precision of geometric operations, given as an integer n, meaning that two vertices less than 10-n apart (in map units) are considered to be merged. |
Outputs
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
One-part geometry errors |
|
[vector: point] |
Output point layer representing the error locations and information. The output layer contains the following fields:
|
One-part geometry features |
|
[vector: same as input] |
Output layer containing features that are multipart but have only one part.
Available fields are the same as in the |
Python code
Algorithm ID: native:checkgeometrymultipart
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
The algorithm id is displayed when you hover over the algorithm in the Processing Toolbox. The parameter dictionary provides the parameter NAMEs and values. See Using processing algorithms from the console for details on how to run processing algorithms from the Python console.