24.1.6. Fix Geometry
24.1.6.1. Add missing vertices along borders
Adds the missing vertices along polygons borders, based on an error layer from the Missing vertices along borders algorithm.
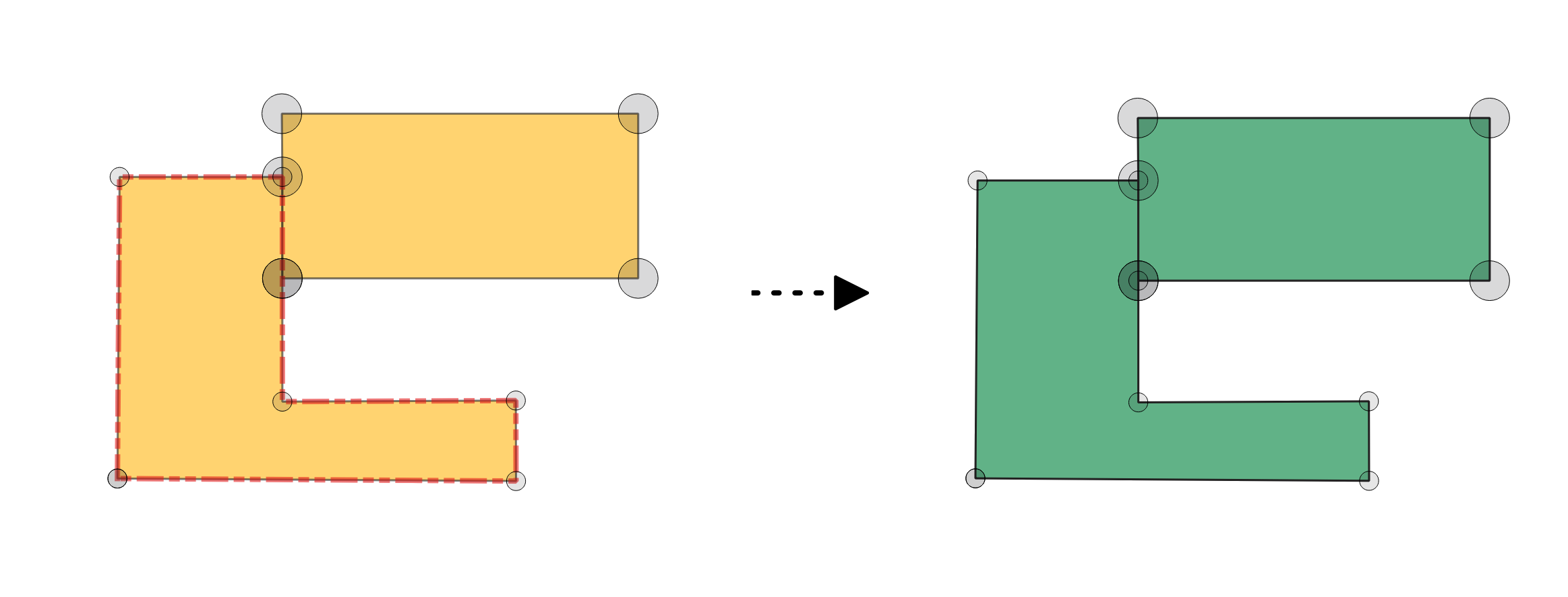
Fig. 24.16 Fixing missing vertices along polygon borders.
Parameters
Basic parameters
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Input layer |
|
[vector: polygon] |
Layer with the geometries to fix, same as input in the check algorithm. |
Error layer |
|
[vector: point] |
Point layer with the errors location, generated by the check algorithm. |
Field of original feature unique identifier |
|
[tablefield: any] |
Field storing unique values for feature identification in input layer, as set in the check algorithm. |
Field of part index |
|
[tablefield: integer] Default: |
Field storing the erroneous feature’s geometry part number. |
Field of ring index |
|
[tablefield: integer] Default: |
Field storing the erroneous feature’s geometry ring number. |
Field of vertex index |
|
[tablefield: integer] Default: |
Field storing the erroneous feature’s geometry vertex number. |
Border vertices fixed layer |
|
[vector: polygon] Default: |
Specification of the output layer containing fixed features. One of:
The file encoding can also be changed here. |
Report layer from fixing border vertices |
|
[vector: point] Default: |
Specification of the output layer containing the fixes location. One of:
The file encoding can also be changed here. |
Advanced parameters
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Tolerance |
|
[numeric: integer] Default: 8 |
Numerical precision of geometric operations, given as an integer n, meaning that two vertices less than 10-n apart (in map units) are considered to be merged. |
Outputs
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Report layer from fixing border vertices |
|
[vector: point] |
Output point layer representing the error locations and fix applied. The output layer contains the following fields:
|
Border vertices fixed layer |
|
[vector: polygon] |
Output layer with the geometry fix applied to the input features. The layer contains the same fields as in the input layer. |
Python code
Algorithm ID: native:fixgeometrymissingvertex
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
The algorithm id is displayed when you hover over the algorithm in the Processing Toolbox. The parameter dictionary provides the parameter NAMEs and values. See Using processing algorithms from the console for details on how to run processing algorithms from the Python console.
24.1.6.2. Convert to strictly multipart
Converts multipart geometries that consists of only one geometry into singlepart geometries, based on an error layer from the Strictly multipart algorithm. Layer geometry type will not be changed and will remain multipart.
See also
Parameters
Basic parameters
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Input layer |
|
[vector: line, polygon] |
Layer with the geometries to fix, same as input in the check algorithm. |
Error layer |
|
[vector: point] |
Point layer with the errors location, generated by the check algorithm. |
Field of original feature unique identifier |
|
[tablefield: any] |
Field storing unique values for feature identification in input layer, as set in the check algorithm. |
Strictly-multipart layer |
|
[vector: same as input] Default: |
Specification of the output layer containing fixed features. One of:
The file encoding can also be changed here. |
Report layer from fixing multipart |
|
[vector: point] Default: |
Specification of the output layer containing the centroids of the fixed geometries. One of:
The file encoding can also be changed here. |
Advanced parameters
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Tolerance |
|
[numeric: integer] Default: 8 |
Numerical precision of geometric operations, given as an integer n, meaning that two vertices less than 10-n apart (in map units) are considered to be merged. |
Outputs
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Report layer from fixing multipart |
|
[vector: point] |
Output point layer representing the error locations and fix applied. The output layer contains the following fields:
|
Strictly-multipart layer |
|
[vector: same as input] |
Output layer with the geometry fix applied to the input features. The layer contains the same fields as in the input layer. |
Python code
Algorithm ID: native:fixgeometrymultipart
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
The algorithm id is displayed when you hover over the algorithm in the Processing Toolbox. The parameter dictionary provides the parameter NAMEs and values. See Using processing algorithms from the console for details on how to run processing algorithms from the Python console.
24.1.6.3. Delete duplicated vertices
Deletes duplicated vertices from the input geometries, based on errors reported by the Duplicated vertices algorithm.
See also
Parameters
Basic parameters
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Input layer |
|
[vector: line, polygon] |
Layer with the geometries to fix, same as input in the check algorithm. |
Error layer |
|
[vector: point] |
Point layer with the errors location, generated by the check algorithm. |
Field of original feature unique identifier |
|
[tablefield: any] |
Field storing unique values for feature identification in input layer, as set in the check algorithm. |
Field of part index |
|
[tablefield: integer] Default: |
Field storing the erroneous feature’s geometry part number. |
Field of ring index |
|
[tablefield: integer] Default: |
Field storing the erroneous feature’s geometry ring number. |
Field of vertex index |
|
[tablefield: integer] Default: |
Field storing the erroneous feature’s geometry vertex number. |
Fixed duplicate vertices layer |
|
[vector: same as input] Default: |
Specification of the output layer containing fixed features. One of:
The file encoding can also be changed here. |
Report layer from fixing duplicate vertices |
|
[vector: point] Default: |
Specification of the output layer containing the fixes location. One of:
The file encoding can also be changed here. |
Advanced parameters
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Tolerance |
|
[numeric: integer] Default: 8 |
Numerical precision of geometric operations, given as an integer n, meaning that two vertices less than 10-n apart (in map units) are considered to be merged. |
Outputs
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Report layer from fixing duplicate vertices |
|
[vector: point] |
Output point layer representing the error locations and fix applied. The output layer contains the following fields:
|
Fixed duplicate vertices layer |
|
[vector: same as input] |
Output layer with the geometry fix applied to the input features. The layer contains the same fields as in the input layer. |
Python code
Algorithm ID: native:fixgeometryduplicatenodes
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
The algorithm id is displayed when you hover over the algorithm in the Processing Toolbox. The parameter dictionary provides the parameter NAMEs and values. See Using processing algorithms from the console for details on how to run processing algorithms from the Python console.
24.1.6.4. Delete features
Deletes error features based on an error layer from some check geometry algorithms, such as:
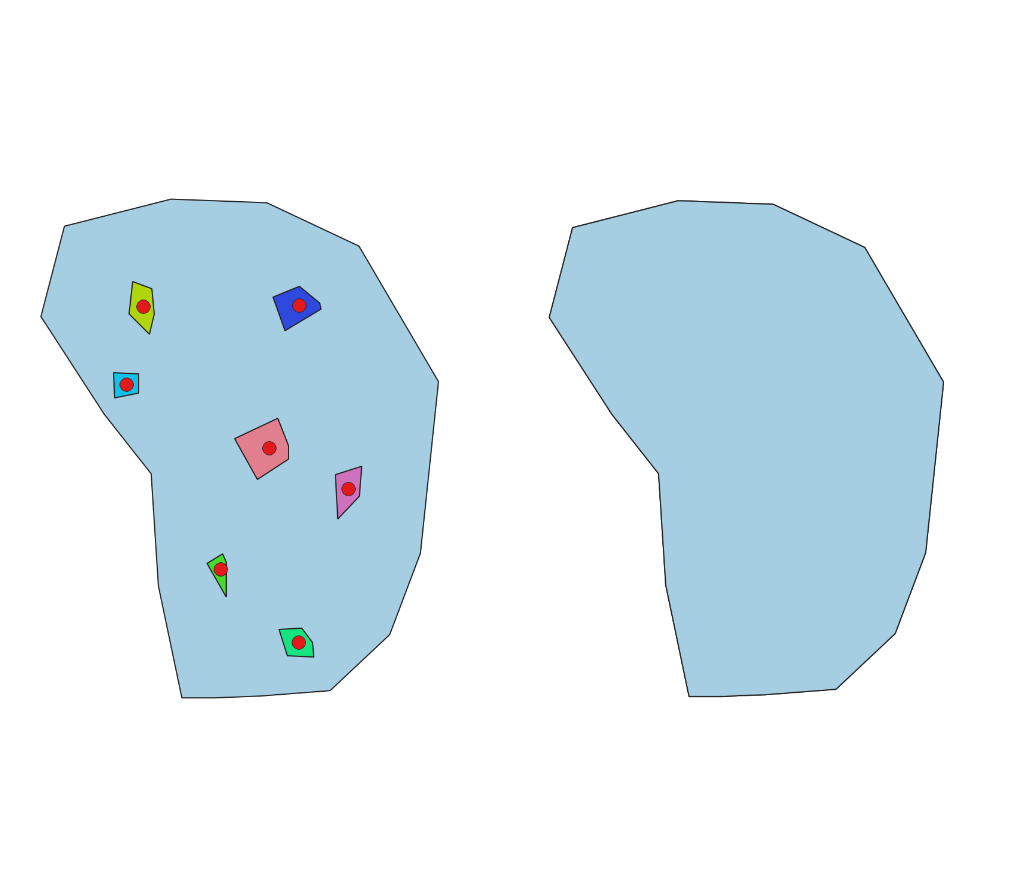
Fig. 24.17 Fixing errors from the “Features inside polygon” algorithm check.
See also
Parameters
Basic parameters
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Input layer |
|
[vector: geometry] |
Layer with the geometries to fix, same as input in the check algorithm. |
Error layer |
|
[vector: point] |
Point layer with the errors location, generated by the check algorithm. |
Field of original feature unique identifier |
|
[tablefield: any] |
Field storing unique values for feature identification in input layer, as set in the check algorithm. |
Cleaned layer |
|
[vector: same as input] Default: |
Specification of the output layer containing fixed features. One of:
The file encoding can also be changed here. |
Report layer from deleting features |
|
[vector: point] Default: |
Specification of the output layer containing the fixes location. One of:
The file encoding can also be changed here. |
Outputs
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Report layer from deleting features |
|
[vector: point] |
Output point layer representing the error locations and fix applied. The output layer contains the following fields:
|
Cleaned layer |
|
[vector: same as input] |
Output layer with features removed based on detected errors. The layer contains the same fields as in the input layer. |
Python code
Algorithm ID: native:fixgeometrydeletefeatures
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
The algorithm id is displayed when you hover over the algorithm in the Processing Toolbox. The parameter dictionary provides the parameter NAMEs and values. See Using processing algorithms from the console for details on how to run processing algorithms from the Python console.
24.1.6.5. Delete overlaps
Deletes overlapping areas based on an error layer from the Overlaps algorithm.
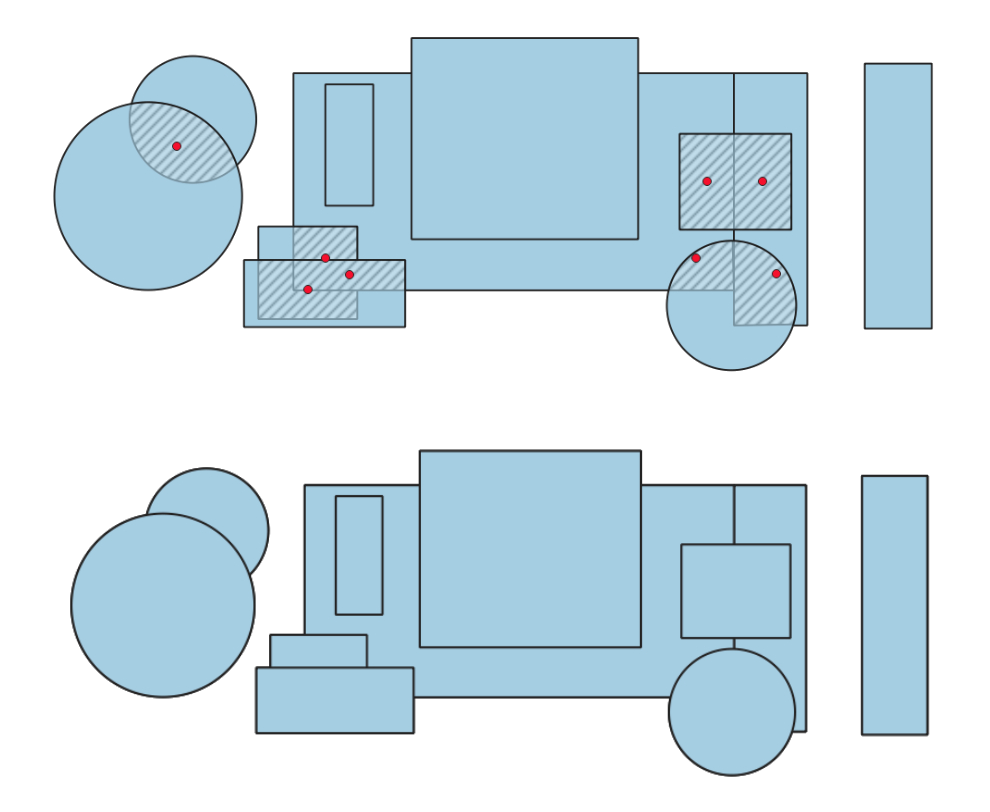
Fig. 24.18 Deleting overlapping areas.
Parameters
Basic parameters
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Input layer |
|
[vector: polygon] |
Layer with the geometries to fix, same as input in the check algorithm. |
Error layer |
|
[vector: point] |
Point layer with the errors location, generated by the check algorithm. |
Field of original feature unique identifier |
|
[tablefield: any] |
Field storing unique values for feature identification in input layer, as set in the check algorithm. |
Field of overlap feature unique identifier |
|
[tablefield: any] |
Field storing unique values for the overlapping feature identification in input layer, as set in the check algorithm. |
Field of error value |
|
[tablefield: any] |
Field storing the error value for each feature, as set in the check algorithm. |
No-overlap layer |
|
[vector: polygon] Default: |
Specification of the output layer containing fixed features. One of:
The file encoding can also be changed here. |
Report layer from fixing overlaps |
|
[vector: point] Default: |
Specification of the output layer containing the fixes location. One of:
The file encoding can also be changed here. |
Advanced parameters
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Tolerance |
|
[numeric: integer] Default: 8 |
Numerical precision of geometric operations, given as an integer n, meaning that two vertices less than 10-n apart (in map units) are considered to be merged. |
Outputs
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Report layer from fixing overlaps |
|
[vector: point] |
Output point layer representing the error locations and fix applied. The output layer contains the following fields:
|
No-overlap layer |
|
[vector: polygon] |
Output layer with input features edited. Overlapping areas reported as errors are removed. The layer contains the same fields as in the input layer. |
Python code
Algorithm ID: native:fixgeometryoverlap
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
The algorithm id is displayed when you hover over the algorithm in the Processing Toolbox. The parameter dictionary provides the parameter NAMEs and values. See Using processing algorithms from the console for details on how to run processing algorithms from the Python console.
24.1.6.6. Delete small angles
Deletes vertices based on an error layer from the Small angles algorithm. When deletion of a vertex results in a duplicate vertex (when a spike vertex is deleted), the duplicate vertex is deleted to keep a single vertex and preserve topology.
Attention
This algorithm removes the vertex at the reported small angles, generating new segments that may form a new small angle.
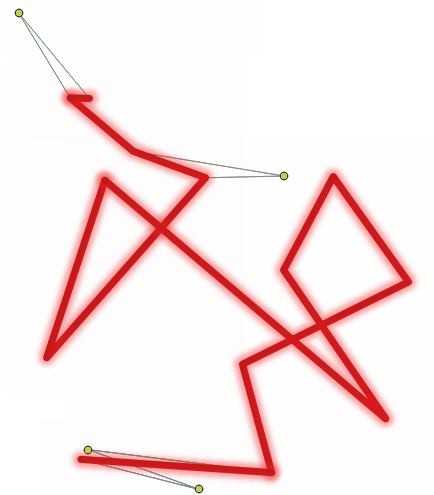
Fig. 24.19 Fixing reported errors on a line feature for angles lower than 15°.
Parameters
Basic parameters
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Input layer |
|
[vector: line, polygon] |
Layer with the geometries to fix, same as input in the check algorithm |
Error layer |
|
[vector: point] |
Point layer with the errors location, generated by the check algorithm |
Field of original feature unique identifier |
|
[tablefield: any] |
Field storing unique values for feature identification in input layer, as set in the check algorithm |
Field of part index |
|
[tablefield: integer] Default: |
Field storing the erroneous feature’s geometry part number. |
Field of ring index |
|
[tablefield: integer] Default: |
Field storing the erroneous feature’s geometry ring number. |
Field of vertex index |
|
[tablefield: integer] Default: |
Field storing the erroneous feature’s geometry vertex number. |
Small angle fixed layer |
|
[vector: same as input] Default: |
Specification of the output layer containing fixed features. One of:
The file encoding can also be changed here. |
Report layer from fixing small angles |
|
[vector: point] Default: |
Specification of the output layer containing the fixes location. One of:
The file encoding can also be changed here. |
Advanced parameters
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Tolerance |
|
[numeric: integer] Default: 8 |
Numerical precision of geometric operations, given as an integer n, meaning that two vertices less than 10-n apart (in map units) are considered to be merged. |
Outputs
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Report layer from fixing small angles |
|
[vector: point] |
Output point layer representing the error locations and fix applied. The output layer contains the following fields:
|
Small angle fixed layer |
|
[same as input] |
Output layer with the geometry fix applied to the input features The layer contains the same fields as in the input layer. |
Python code
Algorithm ID: native:fixgeometryangle
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
The algorithm id is displayed when you hover over the algorithm in the Processing Toolbox. The parameter dictionary provides the parameter NAMEs and values. See Using processing algorithms from the console for details on how to run processing algorithms from the Python console.
24.1.6.7. Fill gaps
Fills the gaps based on a gap and neighbors layer from the Small gaps algorithm. Three different fixing methods are available.
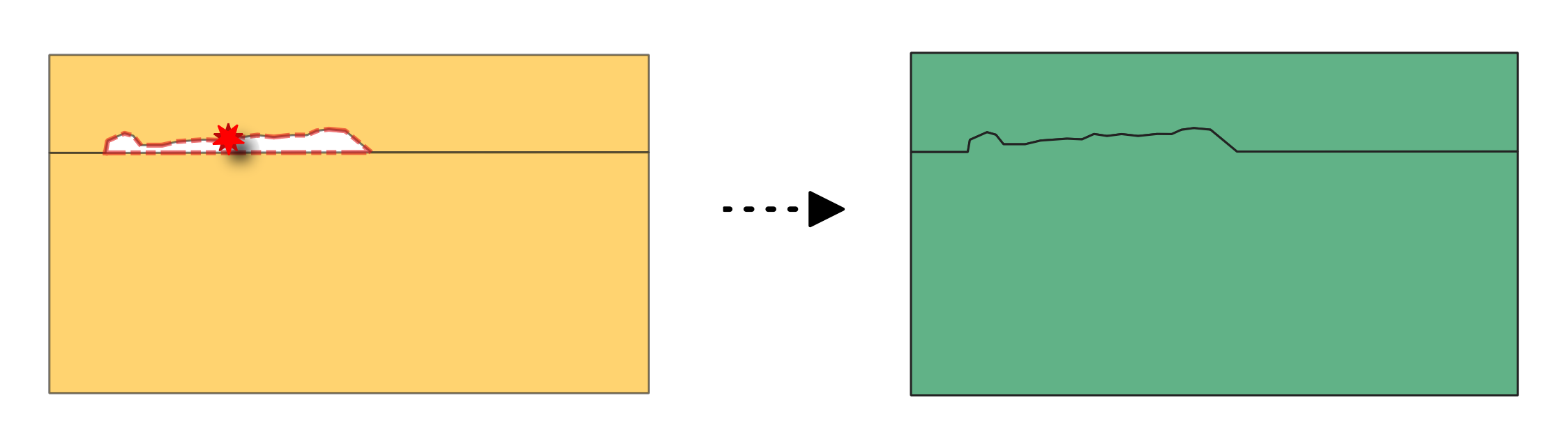
Fig. 24.20 Fixing gap between polygon features using the Add to largest neighbouring area method.
Parameters
Basic parameters
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Input layer |
|
[vector: polygon] |
Layer with the geometries to fix, same as input in the check algorithm. |
Neighbors layer |
|
[vector: table] |
Relational table with the unique ID of the gap and its neighbors in input layer, generated by the check algorithm. |
Gaps layer |
|
[vector: polygon] |
Polygon layer with the gaps geometries, generated by the check algorithm. |
Method |
|
[enumeration] Default: 0 |
Method to apply to the gap fixing. Possible values are:
|
Field of original feature unique identifier |
|
[tablefield: any] Default: gc_errorid |
Field storing unique values for feature identification in input layer, as set in the check algorithm. |
Field of error id |
|
[tablefield: any] |
Field storing the error ID for each gap, as output by the check algorithm. |
Gaps-filled layer |
|
[vector: polygon] Default: |
Specification of the output layer containing fixed features. One of:
The file encoding can also be changed here. |
Report layer from fixing gaps |
|
[vector: point] Default: |
Specification of the output layer containing the fixes location. One of:
The file encoding can also be changed here. |
Advanced parameters
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Tolerance |
|
[numeric: integer] Default: 8 |
Numerical precision of geometric operations, given as an integer n, meaning that two vertices less than 10-n apart (in map units) are considered to be merged. |
Outputs
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Report layer from fixing gaps |
|
[vector: point] |
Output point layer representing the error locations and fix applied. The output layer contains the following fields:
|
Gaps-filled layer |
|
[vector: polygon] |
Output layer of polygons without gaps. The layer contains the same fields as in the input layer. |
Python code
Algorithm ID: native:fixgeometrygap
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
The algorithm id is displayed when you hover over the algorithm in the Processing Toolbox. The parameter dictionary provides the parameter NAMEs and values. See Using processing algorithms from the console for details on how to run processing algorithms from the Python console.
24.1.6.8. Fill holes
Deletes holes in polygon geometries based on an error layer from the Holes algorithm.
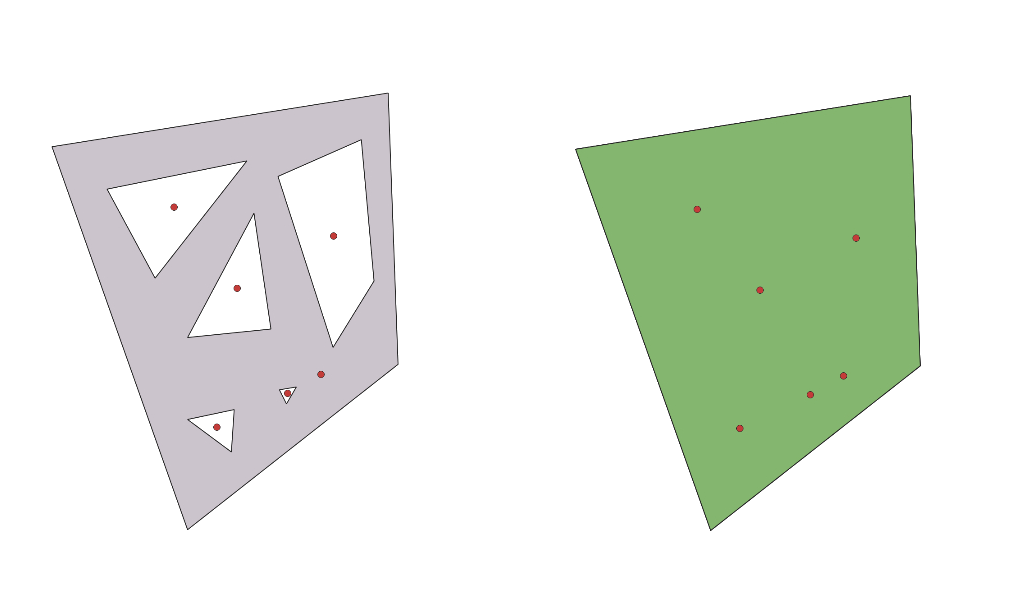
Fig. 24.21 Deleting holes in a polygon feature.
See also
Parameters
Basic parameters
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Input layer |
|
[vector: line, polygon] |
Layer with the geometries to fix, same as input in the check algorithm |
Error layer |
|
[vector: point] |
Point layer with the errors location, generated by the check algorithm |
Field of original feature unique identifier |
|
[tablefield: any] |
Field storing unique values for feature identification in input layer, as set in the check algorithm |
Field of part index |
|
[tablefield: integer]
Default: |
Field storing the erroneous feature’s geometry part number. |
Field of ring index |
|
[tablefield: integer] Default: |
Field storing the erroneous feature’s geometry ring number. |
Field of vertex index |
|
[tablefield: integer] Default: |
Field storing the erroneous feature’s geometry vertex number. |
Holes-filled layer |
|
[vector: polygon] Default: |
Specification of the output layer containing fixed features. One of:
The file encoding can also be changed here. |
Report layer from fixing holes |
|
[vector: point] Default: |
Specification of the output layer containing the fixes location. One of:
The file encoding can also be changed here. |
Advanced parameters
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Tolerance |
|
[numeric: integer] Default: 8 |
Numerical precision of geometric operations, given as an integer n, meaning that two vertices less than 10-n apart (in map units) are considered to be merged. |
Outputs
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Report layer from fixing holes |
|
[vector: point] |
Output point layer representing the error locations and fix applied. The output layer contains the following fields:
|
Holes-filled layer |
|
[vector: polygon] |
Output layer of polygons without holes. The layer contains the same fields as in the input layer. |
Python code
Algorithm ID: native:fixgeometryhole
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
The algorithm id is displayed when you hover over the algorithm in the Processing Toolbox. The parameter dictionary provides the parameter NAMEs and values. See Using processing algorithms from the console for details on how to run processing algorithms from the Python console.
24.1.6.9. Fix small polygons
Merges neighboring polygons according to the chosen method, based on an error layer from the Small polygons or Sliver polygons algorithm.
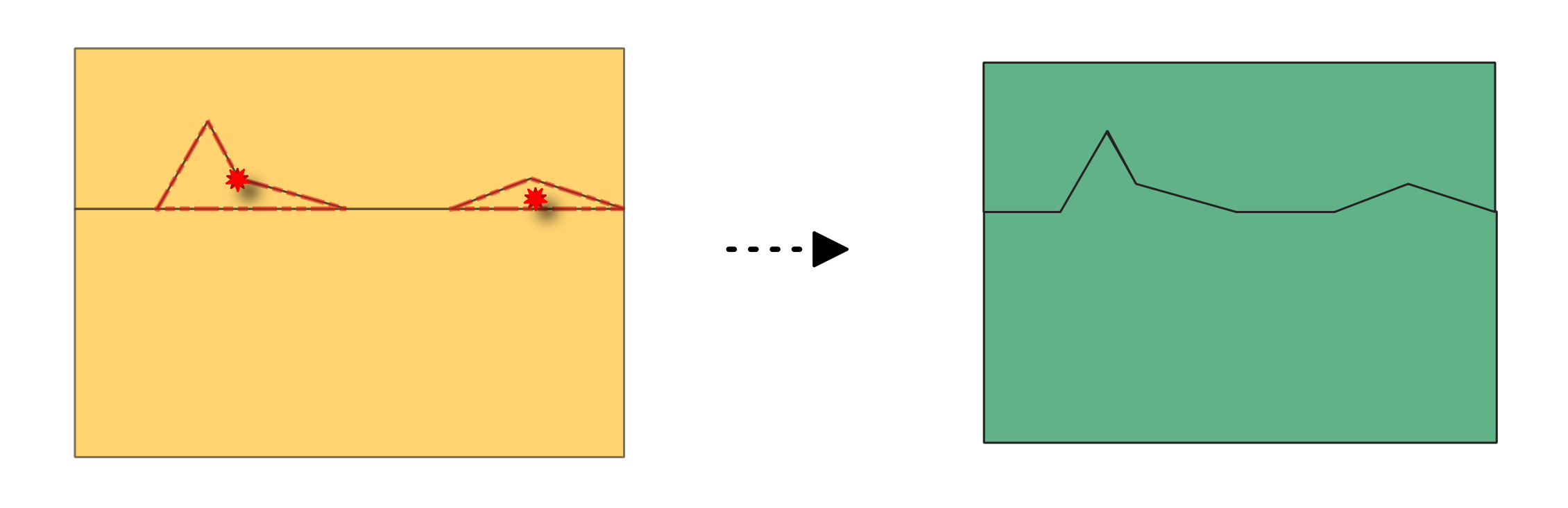
Fig. 24.22 Before and after fixing small polygons (method: merge with neighboring polygon with largest area).
See also
Parameters
Basic parameters
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Input layer |
|
[vector: polygon] |
Layer with the geometries to fix, same as input in the check algorithm. |
Error layer |
|
[vector: point] |
Point layer with the errors location, generated by the check algorithm. |
Method |
|
[enumeration] Default: 0 |
Method to apply to the small polygon geometries:
|
Field to consider when merging polygons with the identical attribute method Optional |
|
[tablefield: any] |
Field in the input layer to consider when merging polygons with the identical attribute method. |
Field of original feature unique identifier |
|
[tablefield: any] |
Field storing unique values for feature identification in input layer, as set in the check algorithm. |
Field of part index |
|
[tablefield: integer]
Default: |
Field storing the erroneous feature’s geometry part number. |
Field of ring index |
|
[tablefield: integer] Default: |
Field storing the erroneous feature’s geometry ring number. |
Field of vertex index |
|
[tablefield: integer] Default: |
Field storing the erroneous feature’s geometry vertex number. |
Small polygons merged layer |
|
[vector: polygon] Default: |
Specification of the output layer containing fixed features. One of:
The file encoding can also be changed here. |
Report layer from merging small polygons |
|
[vector: point] Default: |
Specification of the output layer containing the fixes location. One of:
The file encoding can also be changed here. |
Advanced parameters
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Tolerance |
|
[numeric: integer] Default: 8 |
Numerical precision of geometric operations, given as an integer n, meaning that two vertices less than 10-n apart (in map units) are considered to be merged. |
Outputs
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Report layer from merging small polygons |
|
[vector: point] |
Output point layer representing the error locations and fix applied. The output layer contains the following fields:
|
Small polygons merged layer |
|
[vector: polygon] |
Output layer of polygons with small polygons merged according to the chosen method. The layer contains the same fields as in the input layer. |
Python code
Algorithm ID: native:fixgeometryarea
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
The algorithm id is displayed when you hover over the algorithm in the Processing Toolbox. The parameter dictionary provides the parameter NAMEs and values. See Using processing algorithms from the console for details on how to run processing algorithms from the Python console.
24.1.6.10. Split self-intersecting geometries
Splits self-intersecting geometries based on an error layer from the Self-intersections algorithm.
Note
This algorithm detects invalid polygon geometries (self-intersections).
To ensure these invalid features are not filtered out before processing, open
 Advanced options next to the Input layer and set
Invalid feature filtering to
Advanced options next to the Input layer and set
Invalid feature filtering to Do not Filter (Better Performance).
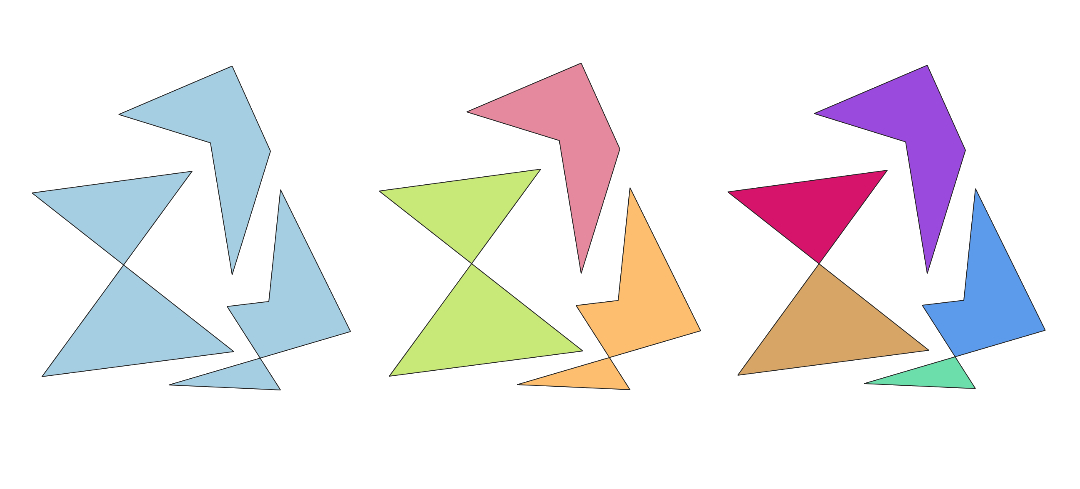
Fig. 24.23 Fixing self-intersection using various methods: as multi-part (middle), and multiple single-part geometries (right).
Parameters
Basic parameters
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Input layer |
|
[vector: line, polygon] |
Layer with the geometries to fix, same as input in the check algorithm |
Error layer |
|
[vector: point] |
Point layer with the errors location, generated by the check algorithm |
Method |
|
[enumeration] |
Method to apply to the self-intersecting geometries:
|
Field of original feature unique identifier |
|
[tablefield: any] |
Field storing unique values for feature identification in input layer, as set in the check algorithm |
Field of part index |
|
[tablefield: integer] Default: |
Field storing the erroneous feature’s geometry part number. |
Field of ring index |
|
[tablefield: integer] Default: |
Field storing the erroneous feature’s geometry ring number. |
Field of vertex index |
|
[tablefield: integer] Default: |
Field storing the erroneous feature’s geometry vertex number. |
Field of segment 1 |
|
[tablefield: integer] Default: |
Field storing the number of the first segment involved in the erroneous intersection. |
Field of segment 2 |
|
[tablefield: integer] Default: |
Field storing the number of the second segment involved in the erroneous intersection. |
Self-intersections fixed layer |
|
[vector: same as input] Default: |
Specification of the output layer containing fixed features. One of:
The file encoding can also be changed here. |
Report layer from fixing self-intersections |
|
[vector: point] Default: |
Specification of the output layer containing the fixes location. One of:
The file encoding can also be changed here. |
Advanced parameters
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Tolerance |
|
[numeric: integer] Default: 8 |
Numerical precision of geometric operations, given as an integer n, meaning that two vertices less than 10-n apart (in map units) are considered to be merged. |
Outputs
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Report layer from fixing self-intersections |
|
[vector: point] |
Output point layer representing the error locations and fix applied. The output layer contains the following fields:
|
Self-intersections fixed layer |
|
[vector: same as input] |
Output layer with the geometry fix applied to the input features. The layer contains the same fields as in the input layer. |
Python code
Algorithm ID: native:fixgeometryselfintersection
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
The algorithm id is displayed when you hover over the algorithm in the Processing Toolbox. The parameter dictionary provides the parameter NAMEs and values. See Using processing algorithms from the console for details on how to run processing algorithms from the Python console.