25.1.20. 벡터 선택
25.1.20.1. 속성으로 추출하기
입력 레이어에서 벡터 레이어 2개를 생성합니다. 첫 번째 레이어는 일치하는 피처만 담고, 두 번째 레이어는 일치하지 않는 피처를 모두 담을 것입니다.
산출 레이어에 피처를 추가하는 기준은 입력 레이어의 속성값을 바탕으로 합니다.
더 보기
파라미터
라벨 |
명칭 |
유형 |
설명 |
|---|---|---|---|
Input layer |
|
[vector: any] |
피처를 추출할 레이어 |
Selection attribute |
|
[tablefield: any] |
레이어의 필터링 필드 |
Operator |
|
[enumeration] 기본값: 0 |
다음과 같은 많은 연산자를 사용할 수 있습니다:
|
Value 부가적 |
|
[string] |
평가할 값 |
Extracted (attribute) |
|
[same as input] 기본값: |
일치하는 피처를 저장할 산출 벡터 레이어를 지정합니다. 다음 가운데 하나로 저장할 수 있습니다:
이 파라미터에서 파일 인코딩도 변경할 수 있습니다. |
Extracted (non-matching) |
|
[same as input] 기본값: |
일치하지 않는 피처를 저장할 산출 벡터 레이어를 지정합니다. 다음 가운데 하나로 저장할 수 있습니다:
이 파라미터에서 파일 인코딩도 변경할 수 있습니다. |
산출물
라벨 |
명칭 |
유형 |
설명 |
|---|---|---|---|
Extracted (attribute) |
|
[same as input] |
입력 레이어에서 일치하는 피처를 담은 벡터 레이어 |
Extracted (non-matching) |
|
[same as input] |
입력 레이어에서 일치하지 않는 피처를 담은 벡터 레이어 |
파이썬 코드
알고리즘 ID: qgis:extractbyattribute
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
공간 처리 툴박스에 있는 알고리즘 위에 마우스를 가져가면 알고리즘 ID 를 표시합니다. 파라미터 목록(dictionary) 은 파라미터 명칭 및 값을 제공합니다. 파이썬 콘솔에서 공간 처리 알고리즘을 어떻게 실행하는지 자세히 알고 싶다면 콘솔에서 공간 처리 알고리즘 사용 을 참조하세요.
25.1.20.2. 표현식으로 추출하기
입력 레이어에서 벡터 레이어 2개를 생성합니다. 첫 번째 레이어는 일치하는 피처만 담고, 두 번째 레이어는 일치하지 않는 피처를 모두 담을 것입니다.
산출 레이어에 피처를 추가하는 기준은 QGIS 표현식을 바탕으로 합니다. 표현식에 대해 더 자세히 알고 싶다면 표현식 을 참조하세요.
더 보기
파라미터
라벨 |
명칭 |
유형 |
설명 |
|---|---|---|---|
Input layer |
|
[vector: any] |
입력 벡터 레이어 |
Expression |
|
[expression] |
벡터 레이어를 필터링할 표현식 |
Matching features |
|
[same as input] 기본값: |
일치하는 피처를 저장할 산출 벡터 레이어를 지정합니다. 다음 가운데 하나로 저장할 수 있습니다:
이 파라미터에서 파일 인코딩도 변경할 수 있습니다. |
Non-matching |
|
[same as input] 기본값: |
일치하지 않는 피처를 저장할 산출 벡터 레이어를 지정합니다. 다음 가운데 하나로 저장할 수 있습니다:
이 파라미터에서 파일 인코딩도 변경할 수 있습니다. |
산출물
라벨 |
명칭 |
유형 |
설명 |
|---|---|---|---|
Matching features |
|
[same as input] |
입력 레이어에서 일치하는 피처를 담은 벡터 레이어 |
Non-matching |
|
[same as input] |
입력 레이어에서 일치하지 않는 피처를 담은 벡터 레이어 |
파이썬 코드
알고리즘 ID: qgis:extractbyexpression
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
공간 처리 툴박스에 있는 알고리즘 위에 마우스를 가져가면 알고리즘 ID 를 표시합니다. 파라미터 목록(dictionary) 은 파라미터 명칭 및 값을 제공합니다. 파이썬 콘솔에서 공간 처리 알고리즘을 어떻게 실행하는지 자세히 알고 싶다면 콘솔에서 공간 처리 알고리즘 사용 을 참조하세요.
25.1.20.3. 위치로 추출하기
입력 레이어에서 일치하는 피처만 담고 있는 새 벡터 레이어를 생성합니다.
산출 레이어에 피처를 추가하는 기준은 입력 레이어의 각 피처와 추가 레이어의 피처들 사이의 공간 관계를 바탕으로 합니다.
Exploring spatial relations
Geometric predicates are boolean functions used to determine the spatial relation a feature has with another by comparing whether and how their geometries share a portion of space.
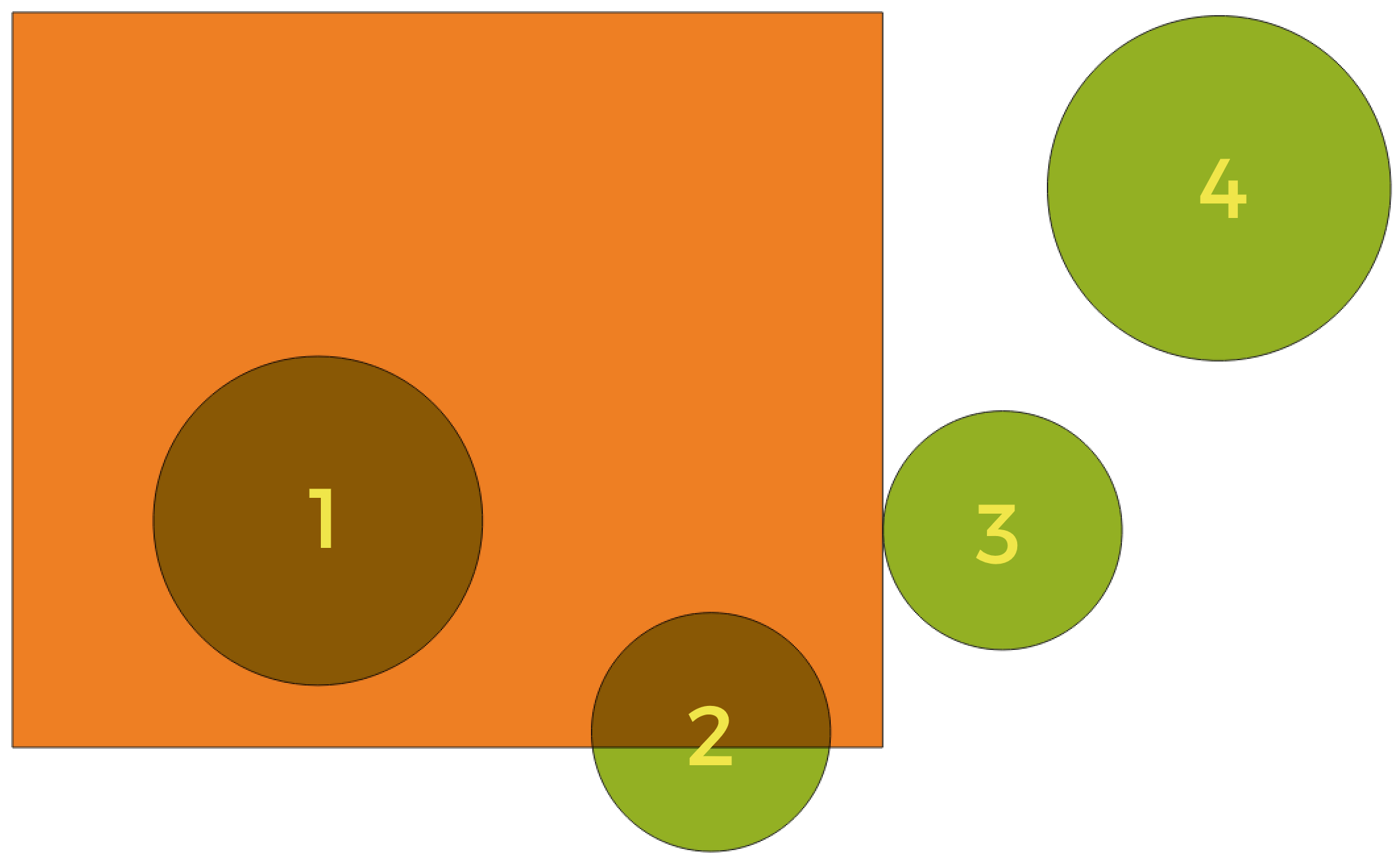
그림 25.111 Looking for spatial relations between layers
Using the figure above, we are looking for the green circles by spatially comparing them to the orange rectangle feature. Available geometric predicates are:
- Intersect
Tests whether a geometry intersects another. Returns 1 (true) if the geometries spatially intersect (share any portion of space - overlap or touch) and 0 if they don’t. In the picture above, this will return circles 1, 2 and 3.
- Contain
Returns 1 (true) if and only if no points of b lie in the exterior of a, and at least one point of the interior of b lies in the interior of a. In the picture, no circle is returned, but the rectangle would be if you would look for it the other way around, as it contains circle 1 completely. This is the opposite of are within.
- Disjoint
Returns 1 (true) if the geometries do not share any portion of space (no overlap, not touching). Only circle 4 is returned.
- Equal
Returns 1 (true) if and only if geometries are exactly the same. No circles will be returned.
- Touch
Tests whether a geometry touches another. Returns 1 (true) if the geometries have at least one point in common, but their interiors do not intersect. Only circle 3 is returned.
- Overlap
Tests whether a geometry overlaps another. Returns 1 (true) if the geometries share space, are of the same dimension, but are not completely contained by each other. Only circle 2 is returned.
- Are within
Tests whether a geometry is within another. Returns 1 (true) if geometry a is completely inside geometry b. Only circle 1 is returned.
- Cross
Returns 1 (true) if the supplied geometries have some, but not all, interior points in common and the actual crossing is of a lower dimension than the highest supplied geometry. For example, a line crossing a polygon will cross as a line (true). Two lines crossing will cross as a point (true). Two polygons cross as a polygon (false). In the picture, no circles will be returned.
파라미터
라벨 |
명칭 |
유형 |
설명 |
|---|---|---|---|
Extract features from |
|
[vector: any] |
입력 벡터 레이어 |
Where the features (geometric predicate) |
|
[enumeration] [list] 기본값: [0] |
선택을 위한 공간 조건을 지정합니다. 다음 가운데 하나 이상을 지정할 수 있습니다:
조건을 하나 이상 선택한 경우, 적어도 하나는 (OR 연산자) 추출할 피처를 만족시켜야 합니다. |
By comparing to the features from |
|
[vector: any] |
교차 벡터 레이어 |
Extracted (location) |
|
[same as input] 기본값: |
비교 레이어의 하나 이상의 피처와 선택한 공간 관계(들)을 가지는 피처를 저장할 산출 벡터 레이어를 지정합니다. 다음 가운데 하나로 저장할 수 있습니다:
이 파라미터에서 파일 인코딩도 변경할 수 있습니다. |
산출물
라벨 |
명칭 |
유형 |
설명 |
|---|---|---|---|
Extracted (location) |
|
[same as input] |
비교 레이어의 하나 이상의 피처와 선택한 공간 관계(들)을 가지는 입력 레이어의 피처를 저장한 산출 벡터 레이어 |
파이썬 코드
알고리즘 ID: qgis:extractbylocation
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
공간 처리 툴박스에 있는 알고리즘 위에 마우스를 가져가면 알고리즘 ID 를 표시합니다. 파라미터 목록(dictionary) 은 파라미터 명칭 및 값을 제공합니다. 파이썬 콘솔에서 공간 처리 알고리즘을 어떻게 실행하는지 자세히 알고 싶다면 콘솔에서 공간 처리 알고리즘 사용 을 참조하세요.
25.1.20.4. Extract within distance
NEW in 3.22
Creates a new vector layer that only contains matching features from an input layer. Features are copied wherever they are within the specified maximum distance from the features in an additional reference layer.
파라미터
라벨 |
명칭 |
유형 |
설명 |
|---|---|---|---|
Extract features from |
|
[vector: any] |
Input vector layer to copy features from |
By comparing to the features from |
|
[vector: any] |
Vector layer whose features closeness is used |
Where the features are within |
|
[number] Default: 100 |
The maximum distance around reference features to select input features within |
Modify current selection by |
|
[enumeration] 기본값: 0 |
알고리즘의 선택 작업을 어떻게 관리해야 할지 지정합니다. 다음 가운데 하나를 선택할 수 있습니다:
|
Extracted (location) |
|
[same as input] 기본값: |
Specify the output vector layer for the features that are within the set distance from reference features. One of:
이 파라미터에서 파일 인코딩도 변경할 수 있습니다. |
산출물
라벨 |
명칭 |
유형 |
설명 |
|---|---|---|---|
Extracted (location) |
|
[same as input] |
Vector layer with features from the input layer matching the condition of distance from reference features |
파이썬 코드
Algorithm ID: native:extractwithindistance
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
공간 처리 툴박스에 있는 알고리즘 위에 마우스를 가져가면 알고리즘 ID 를 표시합니다. 파라미터 목록(dictionary) 은 파라미터 명칭 및 값을 제공합니다. 파이썬 콘솔에서 공간 처리 알고리즘을 어떻게 실행하는지 자세히 알고 싶다면 콘솔에서 공간 처리 알고리즘 사용 을 참조하세요.
25.1.20.5. 랜덤하게 추출하기
벡터 레이어를 받아 입력 레이어에 있는 피처의 하위 집합만을 담고 있는 새 벡터 레이어를 생성합니다.
하위 집합은 피처 ID를 사용해서 랜덤하게 정의됩니다. 백분율 또는 개수 값을 사용해서 하위 집합에 들어갈 피처의 총 개수를 정의합니다.
더 보기
파라미터
라벨 |
명칭 |
유형 |
설명 |
|---|---|---|---|
Input layer |
|
[vector: any] |
피처를 선택할 소스 벡터 레이어 |
Method |
|
[enumeration] 기본값: 0 |
랜덤 선택 메소드를 설정합니다. 다음 가운데 하나를 선택할 수 있습니다:
|
Number/percentage of selected features |
|
[number] 기본값: 10 |
선택할 피처들의 개수 또는 백분율 |
Extracted (random) |
|
[vector: any] 기본값: |
랜덤하게 선택한 피처를 저장할 산출 벡터 레이어를 지정합니다. 다음 가운데 하나로 저장할 수 있습니다:
이 파라미터에서 파일 인코딩도 변경할 수 있습니다. |
산출물
라벨 |
명칭 |
유형 |
설명 |
|---|---|---|---|
Extracted (random) |
|
[same as input] |
입력 레이어에서 랜덤하게 선택한 피처를 담고 있는 벡터 레이어 |
파이썬 코드
알고리즘 ID: qgis:randomextract
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
공간 처리 툴박스에 있는 알고리즘 위에 마우스를 가져가면 알고리즘 ID 를 표시합니다. 파라미터 목록(dictionary) 은 파라미터 명칭 및 값을 제공합니다. 파이썬 콘솔에서 공간 처리 알고리즘을 어떻게 실행하는지 자세히 알고 싶다면 콘솔에서 공간 처리 알고리즘 사용 을 참조하세요.
25.1.20.6. 하위 집합 내에서 랜덤하게 추출하기
벡터 레이어를 받아 입력 레이어에 있는 피처의 하위 집합만을 담고 있는 새 벡터 레이어를 생성합니다.
하위 집합은 피처 ID를 사용해서 랜덤하게 정의됩니다. 백분율 또는 개수 값을 사용해서 하위 집합에 들어갈 피처의 총 개수를 정의합니다. 백분율/개수 값은 전체 레이어가 아니라 각 범주에 적용됩니다. 범주는 지정한 속성에 따라 정의됩니다.
더 보기
파라미터
라벨 |
명칭 |
유형 |
설명 |
|---|---|---|---|
Input layer |
|
[vector: any] |
피처를 선택할 벡터 레이어 |
ID field |
|
[tablefield: any] |
피처를 선택할 소스 벡터 레이어의 범주 |
Method |
|
[enumeration] 기본값: 0 |
랜덤 선택 메소드를 설정합니다. 다음 가운데 하나를 선택할 수 있습니다:
|
Number/percentage of selected features |
|
[number] 기본값: 10 |
선택할 피처들의 개수 또는 백분율 |
Extracted (random stratified) |
|
[same as input] 기본값: |
랜덤하게 선택한 피처를 저장할 산출 벡터 레이어를 지정합니다. 다음 가운데 하나로 저장할 수 있습니다:
이 파라미터에서 파일 인코딩도 변경할 수 있습니다. |
산출물
라벨 |
명칭 |
유형 |
설명 |
|---|---|---|---|
Extracted (random stratified) |
|
[same as input] |
입력 레이어에서 랜덤하게 선택한 피처를 담고 있는 벡터 레이어 |
파이썬 코드
알고리즘 ID: qgis:randomextractwithinsubsets
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
공간 처리 툴박스에 있는 알고리즘 위에 마우스를 가져가면 알고리즘 ID 를 표시합니다. 파라미터 목록(dictionary) 은 파라미터 명칭 및 값을 제공합니다. 파이썬 콘솔에서 공간 처리 알고리즘을 어떻게 실행하는지 자세히 알고 싶다면 콘솔에서 공간 처리 알고리즘 사용 을 참조하세요.
25.1.20.7. 랜덤하게 선택하기
벡터 레이어를 받아 입력 레이어에 있는 피처의 하위 집합을 선택합니다. 이 알고리즘은 새 레이어를 생성하지 않습니다.
하위 집합은 피처 ID를 사용해서 랜덤하게 정의됩니다. 백분율 또는 개수 값을 사용해서 하위 집합에 들어갈 피처의 총 개수를 정의합니다.
기본 메뉴:
더 보기
파라미터
라벨 |
명칭 |
유형 |
설명 |
|---|---|---|---|
Input layer |
|
[vector: any] |
피처를 선택할 벡터 레이어 |
Method |
|
[enumeration] 기본값: 0 |
랜덤 선택 메소드를 설정합니다. 다음 가운데 하나를 선택할 수 있습니다:
|
Number/percentage of selected features |
|
[number] 기본값: 10 |
선택할 피처들의 개수 또는 백분율 |
산출물
라벨 |
명칭 |
유형 |
설명 |
|---|---|---|---|
Input layer |
|
[same as input] |
선택한 피처를 가진 입력 레이어 |
파이썬 코드
알고리즘 ID: qgis:randomselection
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
공간 처리 툴박스에 있는 알고리즘 위에 마우스를 가져가면 알고리즘 ID 를 표시합니다. 파라미터 목록(dictionary) 은 파라미터 명칭 및 값을 제공합니다. 파이썬 콘솔에서 공간 처리 알고리즘을 어떻게 실행하는지 자세히 알고 싶다면 콘솔에서 공간 처리 알고리즘 사용 을 참조하세요.
25.1.20.8. 하위 집합 내에서 랜덤하게 선택하기
벡터 레이어를 받아 입력 레이어에 있는 피처의 하위 집합을 선택합니다. 이 알고리즘은 새 레이어를 생성하지 않습니다.
하위 집합은 피처 ID를 사용해서 랜덤하게 정의됩니다. 백분율 또는 개수 값을 사용해서 하위 집합에 들어갈 피처의 총 개수를 정의합니다.
백분율/개수 값은 전체 레이어가 아니라 각 범주에 적용됩니다.
범주는 지정한 속성에 따라 정의됩니다. 알고리즘을 위한 입력 파라미터로 속성을 지정합니다.
어떤 새 산출물도 생성하지 않습니다.
기본 메뉴:
더 보기
파라미터
라벨 |
명칭 |
유형 |
설명 |
|---|---|---|---|
Input layer |
|
[vector: any] |
피처를 선택할 벡터 레이어 |
ID field |
|
[tablefield: any] |
피처를 선택할 입력 레이어의 범주 |
Method |
|
[enumeration] 기본값: 0 |
랜덤 선택 메소드를 설정합니다. 다음 가운데 하나를 선택할 수 있습니다:
|
Number/percentage of selected features |
|
[number] 기본값: 10 |
선택할 피처들의 개수 또는 백분율 |
산출물
라벨 |
명칭 |
유형 |
설명 |
|---|---|---|---|
Input layer |
|
[same as input] |
선택한 피처를 가진 입력 레이어 |
파이썬 코드
알고리즘 ID: qgis:randomselectionwithinsubsets
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
공간 처리 툴박스에 있는 알고리즘 위에 마우스를 가져가면 알고리즘 ID 를 표시합니다. 파라미터 목록(dictionary) 은 파라미터 명칭 및 값을 제공합니다. 파이썬 콘솔에서 공간 처리 알고리즘을 어떻게 실행하는지 자세히 알고 싶다면 콘솔에서 공간 처리 알고리즘 사용 을 참조하세요.
25.1.20.9. 속성으로 선택하기
벡터 레이어에서 선택 집합을 생성합니다.
피처를 선택하는 기준은 입력 레이어의 속성값을 바탕으로 합니다.
더 보기
파라미터
라벨 |
명칭 |
유형 |
설명 |
|---|---|---|---|
Input layer |
|
[vector: any] |
피처를 선택할 벡터 레이어 |
Selection attribute |
|
[tablefield: any] |
레이어의 필터링 필드 |
Operator |
|
[enumeration] 기본값: 0 |
다음과 같은 많은 연산자를 사용할 수 있습니다:
|
Value 부가적 |
|
[string] |
평가할 값 |
Modify current selection by |
|
[enumeration] 기본값: 0 |
알고리즘의 선택 작업을 어떻게 관리해야 할지 지정합니다. 다음 가운데 하나를 선택할 수 있습니다:
|
산출물
라벨 |
명칭 |
유형 |
설명 |
|---|---|---|---|
Input layer |
|
[same as input] |
선택한 피처를 가진 입력 레이어 |
파이썬 코드
알고리즘 ID: qgis:selectbyattribute
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
공간 처리 툴박스에 있는 알고리즘 위에 마우스를 가져가면 알고리즘 ID 를 표시합니다. 파라미터 목록(dictionary) 은 파라미터 명칭 및 값을 제공합니다. 파이썬 콘솔에서 공간 처리 알고리즘을 어떻게 실행하는지 자세히 알고 싶다면 콘솔에서 공간 처리 알고리즘 사용 을 참조하세요.
25.1.20.10. 표현식으로 선택하기
벡터 레이어에서 선택 집합을 생성합니다.
피처를 선택하는 기준은 QGIS 표현식을 바탕으로 합니다. 표현식에 대해 더 자세히 알고 싶다면 표현식 을 참조하세요.
더 보기
파라미터
라벨 |
명칭 |
유형 |
설명 |
|---|---|---|---|
Input layer |
|
[vector: any] |
입력 벡터 레이어 |
Expression |
|
[expression] |
입력 레이어를 필터링할 표현식 |
Modify current selection by |
|
[enumeration] 기본값: 0 |
알고리즘의 선택 작업을 어떻게 관리해야 할지 지정합니다. 다음 가운데 하나를 선택할 수 있습니다:
|
산출물
라벨 |
명칭 |
유형 |
설명 |
|---|---|---|---|
Input layer |
|
[same as input] |
선택한 피처를 가진 입력 레이어 |
파이썬 코드
알고리즘 ID: qgis:selectbyexpression
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
공간 처리 툴박스에 있는 알고리즘 위에 마우스를 가져가면 알고리즘 ID 를 표시합니다. 파라미터 목록(dictionary) 은 파라미터 명칭 및 값을 제공합니다. 파이썬 콘솔에서 공간 처리 알고리즘을 어떻게 실행하는지 자세히 알고 싶다면 콘솔에서 공간 처리 알고리즘 사용 을 참조하세요.
25.1.20.11. 위치로 선택하기
벡터 레이어에서 선택 집합을 생성합니다.
피처를 선택하는 기준은 입력 레이어의 각 피처와 추가 레이어의 피처들 사이의 공간 관계를 바탕으로 합니다.
기본 메뉴:
Exploring spatial relations
Geometric predicates are boolean functions used to determine the spatial relation a feature has with another by comparing whether and how their geometries share a portion of space.

그림 25.112 Looking for spatial relations between layers
Using the figure above, we are looking for the green circles by spatially comparing them to the orange rectangle feature. Available geometric predicates are:
- Intersect
Tests whether a geometry intersects another. Returns 1 (true) if the geometries spatially intersect (share any portion of space - overlap or touch) and 0 if they don’t. In the picture above, this will return circles 1, 2 and 3.
- Contain
Returns 1 (true) if and only if no points of b lie in the exterior of a, and at least one point of the interior of b lies in the interior of a. In the picture, no circle is returned, but the rectangle would be if you would look for it the other way around, as it contains circle 1 completely. This is the opposite of are within.
- Disjoint
Returns 1 (true) if the geometries do not share any portion of space (no overlap, not touching). Only circle 4 is returned.
- Equal
Returns 1 (true) if and only if geometries are exactly the same. No circles will be returned.
- Touch
Tests whether a geometry touches another. Returns 1 (true) if the geometries have at least one point in common, but their interiors do not intersect. Only circle 3 is returned.
- Overlap
Tests whether a geometry overlaps another. Returns 1 (true) if the geometries share space, are of the same dimension, but are not completely contained by each other. Only circle 2 is returned.
- Are within
Tests whether a geometry is within another. Returns 1 (true) if geometry a is completely inside geometry b. Only circle 1 is returned.
- Cross
Returns 1 (true) if the supplied geometries have some, but not all, interior points in common and the actual crossing is of a lower dimension than the highest supplied geometry. For example, a line crossing a polygon will cross as a line (true). Two lines crossing will cross as a point (true). Two polygons cross as a polygon (false). In the picture, no circles will be returned.
파라미터
라벨 |
명칭 |
유형 |
설명 |
|---|---|---|---|
Select features from |
|
[vector: any] |
입력 벡터 레이어 |
Where the features (geometric predicate) |
|
[enumeration] [list] 기본값: [0] |
선택을 위한 공간 조건을 지정합니다. 다음 가운데 하나 이상을 지정할 수 있습니다:
조건을 하나 이상 선택한 경우, 적어도 하나는 (OR 연산자) 추출할 피처를 만족시켜야 합니다. |
By comparing to the features from |
|
[vector: any] |
교차 벡터 레이어 |
Modify current selection by |
|
[enumeration] 기본값: 0 |
알고리즘의 선택 작업을 어떻게 관리해야 할지 지정합니다. 다음 가운데 하나를 선택할 수 있습니다:
|
산출물
라벨 |
명칭 |
유형 |
설명 |
|---|---|---|---|
Input layer |
|
[same as input] |
선택한 피처를 가진 입력 레이어 |
파이썬 코드
알고리즘 ID: qgis:selectbylocation
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
공간 처리 툴박스에 있는 알고리즘 위에 마우스를 가져가면 알고리즘 ID 를 표시합니다. 파라미터 목록(dictionary) 은 파라미터 명칭 및 값을 제공합니다. 파이썬 콘솔에서 공간 처리 알고리즘을 어떻게 실행하는지 자세히 알고 싶다면 콘솔에서 공간 처리 알고리즘 사용 을 참조하세요.
25.1.20.12. Select within distance
NEW in 3.22
creates a selection in a vector layer. Features are selected wherever they are within the specified maximum distance from the features in an additional reference layer.
파라미터
라벨 |
명칭 |
유형 |
설명 |
|---|---|---|---|
Select features from |
|
[vector: any] |
Input vector layer to select features from |
By comparing to the features from |
|
[vector: any] |
Vector layer whose features closeness is used |
Where the features are within |
|
[number] Default: 100 |
The maximum distance around reference features to select input features |
Modify current selection by |
|
[enumeration] 기본값: 0 |
알고리즘의 선택 작업을 어떻게 관리해야 할지 지정합니다. 다음 가운데 하나를 선택할 수 있습니다:
|
산출물
라벨 |
명칭 |
유형 |
설명 |
|---|---|---|---|
Input layer |
|
[same as input] |
선택한 피처를 가진 입력 레이어 |
파이썬 코드
Algorithm ID: native:selectwithindistance
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
공간 처리 툴박스에 있는 알고리즘 위에 마우스를 가져가면 알고리즘 ID 를 표시합니다. 파라미터 목록(dictionary) 은 파라미터 명칭 및 값을 제공합니다. 파이썬 콘솔에서 공간 처리 알고리즘을 어떻게 실행하는지 자세히 알고 싶다면 콘솔에서 공간 처리 알고리즘 사용 을 참조하세요.