25.1.20. Vector selection
25.1.20.1. Extract by attribute
Creates two vector layers from an input layer: one will contain only matching features while the second will contain all the non-matching features.
The criteria for adding features to the resulting layer is based on the values of an attribute from the input layer.
Siehe auch
Parameter
Label |
Name |
Type |
Beschreibung |
|---|---|---|---|
Input layer |
|
[vector: any] |
Layer to extract features from. |
Selection attribute |
|
[tablefield: any] |
Filtering field of the layer |
Operator |
|
[enumeration] Default: 0 |
Many different operators are available:
|
Value Optional |
|
[string] |
Value to be evaluated |
Extracted (attribute) |
|
[same as input] Default: |
Specify the output vector layer for matching features. One of:
The file encoding can also be changed here. |
Extracted (non-matching) |
|
[same as input] Default: |
Specify the output vector layer for non-matching features. One of:
The file encoding can also be changed here. |
Ausgaben
Label |
Name |
Type |
Beschreibung |
|---|---|---|---|
Extracted (attribute) |
|
[same as input] |
Vector layer with matching features from the input layer |
Extracted (non-matching) |
|
[same as input] |
Vector layer with non-matching features from the input layer |
Python code
Algorithm ID: qgis:extractbyattribute
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
The algorithm id is displayed when you hover over the algorithm in the Processing Toolbox. The parameter dictionary provides the parameter NAMEs and values. See Verarbeitung Algorithmen von der Konsole aus verwenden for details on how to run processing algorithms from the Python console.
25.1.20.2. Extract by expression
Creates two vector layers from an input layer: one will contain only matching features while the second will contain all the non-matching features.
The criteria for adding features to the resulting layer is based on a QGIS expression. For more information about expressions see the Ausdrücke.
Siehe auch
Parameter
Label |
Name |
Type |
Beschreibung |
|---|---|---|---|
Input layer |
|
[vector: any] |
Input vector layer |
Expression |
|
[expression] |
Expression to filter the vector layer |
Matching features |
|
[same as input] Default: |
Specify the output vector layer for matching features. One of:
The file encoding can also be changed here. |
Non-matching |
|
[same as input] Default: |
Specify the output vector layer for non-matching features. One of:
The file encoding can also be changed here. |
Ausgaben
Label |
Name |
Type |
Beschreibung |
|---|---|---|---|
Matching features |
|
[same as input] |
Vector layer with matching features from the input layer |
Non-matching |
|
[same as input] |
Vector layer with non-matching features from the input layer |
Python code
Algorithm ID: qgis:extractbyexpression
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
The algorithm id is displayed when you hover over the algorithm in the Processing Toolbox. The parameter dictionary provides the parameter NAMEs and values. See Verarbeitung Algorithmen von der Konsole aus verwenden for details on how to run processing algorithms from the Python console.
25.1.20.3. Extract by location
Creates a new vector layer that only contains matching features from an input layer.
The criteria for adding features to the resulting layer is based on the spatial relationship between each feature and the features in an additional layer.
Siehe auch
Exploring spatial relations
Geometrische Prädikate sind boolesche Funktionen, die verwendet werden, um die räumliche Beziehung eines Features zu einem anderen zu bestimmen, indem verglichen wird, ob und wie ihre Geometrien einen Teil des Raums teilen.
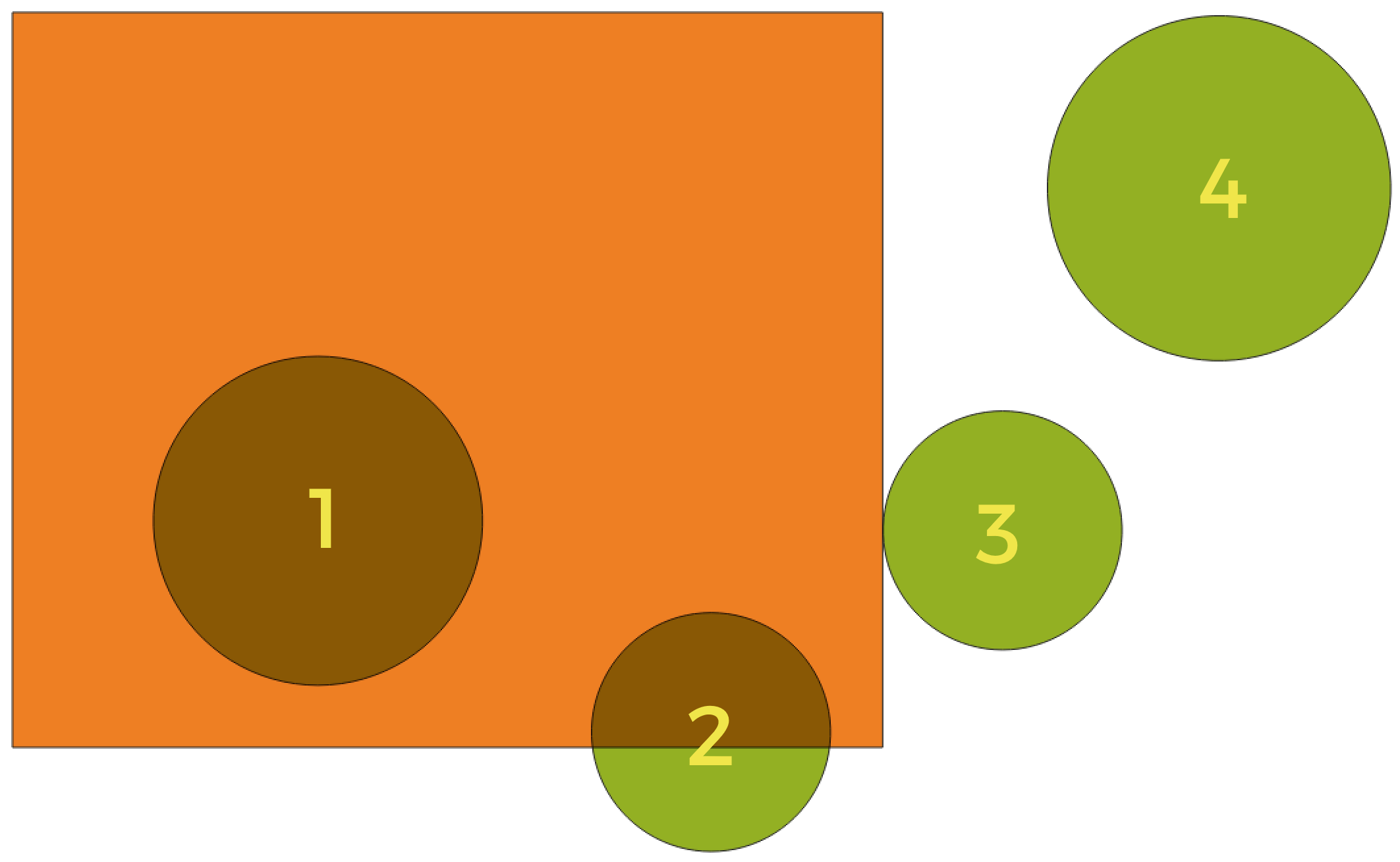
Abb. 25.111 Suche nach räumlichen Beziehungen zwischen Layern
Unter Verwendung der obigen Abbildung suchen wir nach den grünen Kreisen, indem wir sie räumlich mit dem orangefarbenen Rechteck-Feature vergleichen. Verfügbare geometrische Prädikate sind:
- Schneidet
Testet, ob eine Geometrie eine andere schneidet. Gibt 1 (wahr) zurück, wenn sich die Geometrien räumlich überschneiden (einen Teil des Raums teilen – überlappen oder berühren) und 0, wenn dies nicht der Fall ist. Im obigen Bild werden die Kreise 1, 2 und 3 zurückgegeben.
- Enthält
Gibt 1 (wahr) zurück, wenn und nur wenn keine Punkte von b außerhalb von a liegen und mindestens ein Punkt des Inneren von b innerhalb von a liegt. Im Bild wird kein Kreis zurückgegeben, sondern das Rechteck wäre es, wenn man es umgekehrt suchen würde, da es den Kreis 1 komplett enthält. Das ist das Gegenteil von sind innerhalb.
- Getrennt
Gibt 1 (wahr) zurück, wenn die Geometrien keinen Teil des Raums teilen (keine Überlappung, keine Berührung). Nur Kreis 4 wird zurückgegeben.
- Gleich
Gibt 1 (wahr) zurück, wenn und nur wenn die Geometrien genau gleich sind. Es werden keine Kreise zurückgegeben.
- Berührt
Testet, ob eine Geometrie eine andere berührt. Gibt 1 (wahr) zurück, wenn die Geometrien mindestens einen Punkt gemeinsam haben, aber ihre Innenräume sich nicht schneiden. Nur Kreis 3 wird zurückgegeben.
- Überlappt
Testet, ob eine Geometrie eine andere überlappt. Gibt 1 (wahr) zurück, wenn die Geometrien sich den Raum teilen, dieselbe Dimension haben, aber nicht vollständig ineinander liegen. Nur Kreis 2 wird zurückgegeben.
- Sind innerhalb
Testet, ob sich eine Geometrie in einer anderen befindet. Gibt 1 (wahr) zurück, wenn sich Geometrie a vollständig innerhalb von Geometrie b befindet. Nur Kreis 1 wird zurückgegeben.
- Kreuzen
Gibt 1 (wahr) zurück, wenn die bereitgestellten Geometrien einige, aber nicht alle inneren Punkte gemeinsam haben und die tatsächliche Kreuzung eine geringere Dimension als die höchste bereitgestellte Geometrie hat. Beispielsweise wird eine Linie, die ein Polygon kreuzt, als Linie gekreuzt (wahr). Zwei Linien, die sich kreuzen, kreuzen sich als Punkt (wahr). Zwei Polygone kreuzen sich als Polygon (falsch). Im Bild werden keine Kreise zurückgegeben.
Parameter
Label |
Name |
Type |
Beschreibung |
|---|---|---|---|
Extract features from |
|
[vector: any] |
Input vector layer |
Where the features (geometric predicate) |
|
[enumeration] [list] Default: [0] |
Spatial condition for the selection. One or more of:
If more than one condition is chosen, at least one of them (OR operation) has to be met for a feature to be extracted. |
By comparing to the features from |
|
[vector: any] |
Intersection vector layer |
Extracted (location) |
|
[same as input] Default: |
Specify the output vector layer for the features that have the chosen spatial relationship(s) with one or more features in the comparison layer. One of:
The file encoding can also be changed here. |
Ausgaben
Label |
Name |
Type |
Beschreibung |
|---|---|---|---|
Extracted (location) |
|
[same as input] |
Vector layer with features from the input layer that have the chosen spatial relationship(s) with one or more features in the comparison layer. |
Python code
Algorithm ID: qgis:extractbylocation
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
The algorithm id is displayed when you hover over the algorithm in the Processing Toolbox. The parameter dictionary provides the parameter NAMEs and values. See Verarbeitung Algorithmen von der Konsole aus verwenden for details on how to run processing algorithms from the Python console.
25.1.20.4. Extract within distance
NEW in 3.22
Creates a new vector layer that only contains matching features from an input layer. Features are copied wherever they are within the specified maximum distance from the features in an additional reference layer.
Siehe auch
Parameter
Label |
Name |
Type |
Beschreibung |
|---|---|---|---|
Extract features from |
|
[vector: any] |
Input vector layer to copy features from |
By comparing to the features from |
|
[vector: any] |
Vector layer whose features closeness is used |
Where the features are within |
|
[number] Default: 100 |
The maximum distance around reference features to select input features within |
Modify current selection by |
|
[enumeration] Default: 0 |
How the selection of the algorithm should be managed. One of:
|
Extracted (location) |
|
[same as input] Default: |
Specify the output vector layer for the features that are within the set distance from reference features. One of:
The file encoding can also be changed here. |
Ausgaben
Label |
Name |
Type |
Beschreibung |
|---|---|---|---|
Extracted (location) |
|
[same as input] |
Vector layer with features from the input layer matching the condition of distance from reference features |
Python code
Algorithm ID: native:extractwithindistance
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
The algorithm id is displayed when you hover over the algorithm in the Processing Toolbox. The parameter dictionary provides the parameter NAMEs and values. See Verarbeitung Algorithmen von der Konsole aus verwenden for details on how to run processing algorithms from the Python console.
25.1.20.5. Random extract
Takes a vector layer and generates a new one that contains only a subset of the features in the input layer.
The subset is defined randomly, based on feature IDs, using a percentage or count value to define the total number of features in the subset.
Siehe auch
Parameter
Label |
Name |
Type |
Beschreibung |
|---|---|---|---|
Input layer |
|
[vector: any] |
Source vector layer to select the features from |
Method |
|
[enumeration] Default: 0 |
Random selection methods. One of:
|
Number/percentage of selected features |
|
[number] Default: 10 |
Number or percentage of features to select |
Extracted (random) |
|
[vector: any] Default: |
Specify the output vector layer for the randomly selected features. One of:
The file encoding can also be changed here. |
Ausgaben
Label |
Name |
Type |
Beschreibung |
|---|---|---|---|
Extracted (random) |
|
[same as input] |
Vector layer containing randomly selected features from the input layer |
Python code
Algorithm ID: qgis:randomextract
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
The algorithm id is displayed when you hover over the algorithm in the Processing Toolbox. The parameter dictionary provides the parameter NAMEs and values. See Verarbeitung Algorithmen von der Konsole aus verwenden for details on how to run processing algorithms from the Python console.
25.1.20.6. Random extract within subsets
Takes a vector layer and generates a new one that contains only a subset of the features in the input layer.
The subset is defined randomly, based on feature IDs, using a percentage or count value to define the total number of features in the subset. The percentage/count value is not applied to the whole layer, but instead to each category. Categories are defined according to a given attribute.
Siehe auch
Parameter
Label |
Name |
Type |
Beschreibung |
|---|---|---|---|
Input layer |
|
[vector: any] |
Vector layer to select the features from |
ID field |
|
[tablefield: any] |
Category of the source vector layer to select the features from |
Method |
|
[enumeration] Default: 0 |
Random selection method. One of:
|
Number/percentage of selected features |
|
[number] Default: 10 |
Number or percentage of features to select |
Extracted (random stratified) |
|
[same as input] Default: |
Specify the output vector layer for the randomly selected features. One of:
The file encoding can also be changed here. |
Ausgaben
Label |
Name |
Type |
Beschreibung |
|---|---|---|---|
Extracted (random stratified) |
|
[same as input] |
Vector layer containing randomly selected features from the input layer |
Python code
Algorithm ID: qgis:randomextractwithinsubsets
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
The algorithm id is displayed when you hover over the algorithm in the Processing Toolbox. The parameter dictionary provides the parameter NAMEs and values. See Verarbeitung Algorithmen von der Konsole aus verwenden for details on how to run processing algorithms from the Python console.
25.1.20.7. Random selection
Takes a vector layer and selects a subset of its features. No new layer is generated by this algorithm.
The subset is defined randomly, based on feature IDs, using a percentage or count value to define the total number of features in the subset.
Default menu:
Siehe auch
Parameter
Label |
Name |
Type |
Beschreibung |
|---|---|---|---|
Input layer |
|
[vector: any] |
Vector layer for the selection |
Method |
|
[enumeration] Default: 0 |
Random selection method. One of:
|
Number/percentage of selected features |
|
[number] Default: 10 |
Number or percentage of features to select |
Ausgaben
Label |
Name |
Type |
Beschreibung |
|---|---|---|---|
Input layer |
|
[same as input] |
The input layer with features selected |
Python code
Algorithm ID: qgis:randomselection
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
The algorithm id is displayed when you hover over the algorithm in the Processing Toolbox. The parameter dictionary provides the parameter NAMEs and values. See Verarbeitung Algorithmen von der Konsole aus verwenden for details on how to run processing algorithms from the Python console.
25.1.20.8. Random selection within subsets
Takes a vector layer and selects a subset of its features. No new layer is generated by this algorithm.
The subset is defined randomly, based on feature IDs, using a percentage or count value to define the total number of features in the subset.
The percentage/count value is not applied to the whole layer, but instead to each category.
Categories are defined according to a given attribute, which is also specified as an input parameter for the algorithm.
No new outputs are created.
Default menu:
Siehe auch
Parameter
Label |
Name |
Type |
Beschreibung |
|---|---|---|---|
Input layer |
|
[vector: any] |
Vector layer to select features in |
ID field |
|
[tablefield: any] |
Category of the input layer to select the features from |
Method |
|
[enumeration] Default: 0 |
Random selection method. One of:
|
Number/percentage of selected features |
|
[number] Default: 10 |
Number or percentage of features to select |
Ausgaben
Label |
Name |
Type |
Beschreibung |
|---|---|---|---|
Input layer |
|
[same as input] |
The input layer with features selected |
Python code
Algorithm ID: qgis:randomselectionwithinsubsets
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
The algorithm id is displayed when you hover over the algorithm in the Processing Toolbox. The parameter dictionary provides the parameter NAMEs and values. See Verarbeitung Algorithmen von der Konsole aus verwenden for details on how to run processing algorithms from the Python console.
25.1.20.9. Select by attribute
Erstellt eine Auswahl in einem Vektorlayer.
The criteria for selecting features is based on the values of an attribute from the input layer.
Siehe auch
Parameter
Label |
Name |
Type |
Beschreibung |
|---|---|---|---|
Input layer |
|
[vector: any] |
Vector layer to select features in |
Selection attribute |
|
[tablefield: any] |
Filtering field of the layer |
Operator |
|
[enumeration] Default: 0 |
Many different operators are available:
|
Value Optional |
|
[string] |
Value to be evaluated |
Modify current selection by |
|
[enumeration] Default: 0 |
How the selection of the algorithm should be managed. One of:
|
Ausgaben
Label |
Name |
Type |
Beschreibung |
|---|---|---|---|
Input layer |
|
[same as input] |
The input layer with features selected |
Python code
Algorithm ID: qgis:selectbyattribute
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
The algorithm id is displayed when you hover over the algorithm in the Processing Toolbox. The parameter dictionary provides the parameter NAMEs and values. See Verarbeitung Algorithmen von der Konsole aus verwenden for details on how to run processing algorithms from the Python console.
25.1.20.10. Select by expression
Erstellt eine Auswahl in einem Vektorlayer.
The criteria for selecting features is based on a QGIS expression. For more information about expressions see the Ausdrücke.
Siehe auch
Parameter
Label |
Name |
Type |
Beschreibung |
|---|---|---|---|
Input layer |
|
[vector: any] |
Input vector layer |
Expression |
|
[expression] |
Expression to filter the input layer |
Modify current selection by |
|
[enumeration] Default: 0 |
How the selection of the algorithm should be managed. One of:
|
Ausgaben
Label |
Name |
Type |
Beschreibung |
|---|---|---|---|
Input layer |
|
[same as input] |
The input layer with features selected |
Python code
Algorithm ID: qgis:selectbyexpression
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
The algorithm id is displayed when you hover over the algorithm in the Processing Toolbox. The parameter dictionary provides the parameter NAMEs and values. See Verarbeitung Algorithmen von der Konsole aus verwenden for details on how to run processing algorithms from the Python console.
25.1.20.11. Auswahl nach der Lage
Erstellt eine Auswahl in einem Vektorlayer.
Die Kriterien für die Auswahl von Features basieren auf der räumlichen Beziehung zwischen jedem Feature und den Features in eines zusätzlichen Layers.
Default menu:
Siehe auch
Exploring spatial relations
Geometrische Prädikate sind boolesche Funktionen, die verwendet werden, um die räumliche Beziehung eines Features zu einem anderen zu bestimmen, indem verglichen wird, ob und wie ihre Geometrien einen Teil des Raums teilen.

Abb. 25.112 Suche nach räumlichen Beziehungen zwischen Layern
Unter Verwendung der obigen Abbildung suchen wir nach den grünen Kreisen, indem wir sie räumlich mit dem orangefarbenen Rechteck-Feature vergleichen. Verfügbare geometrische Prädikate sind:
- Schneidet
Testet, ob eine Geometrie eine andere schneidet. Gibt 1 (wahr) zurück, wenn sich die Geometrien räumlich überschneiden (einen Teil des Raums teilen – überlappen oder berühren) und 0, wenn dies nicht der Fall ist. Im obigen Bild werden die Kreise 1, 2 und 3 zurückgegeben.
- Enthält
Gibt 1 (wahr) zurück, wenn und nur wenn keine Punkte von b außerhalb von a liegen und mindestens ein Punkt des Inneren von b innerhalb von a liegt. Im Bild wird kein Kreis zurückgegeben, sondern das Rechteck wäre es, wenn man es umgekehrt suchen würde, da es den Kreis 1 komplett enthält. Das ist das Gegenteil von sind innerhalb.
- Getrennt
Gibt 1 (wahr) zurück, wenn die Geometrien keinen Teil des Raums teilen (keine Überlappung, keine Berührung). Nur Kreis 4 wird zurückgegeben.
- Gleich
Gibt 1 (wahr) zurück, wenn und nur wenn die Geometrien genau gleich sind. Es werden keine Kreise zurückgegeben.
- Berührt
Testet, ob eine Geometrie eine andere berührt. Gibt 1 (wahr) zurück, wenn die Geometrien mindestens einen Punkt gemeinsam haben, aber ihre Innenräume sich nicht schneiden. Nur Kreis 3 wird zurückgegeben.
- Überlappt
Testet, ob eine Geometrie eine andere überlappt. Gibt 1 (wahr) zurück, wenn die Geometrien sich den Raum teilen, dieselbe Dimension haben, aber nicht vollständig ineinander liegen. Nur Kreis 2 wird zurückgegeben.
- Sind innerhalb
Testet, ob sich eine Geometrie in einer anderen befindet. Gibt 1 (wahr) zurück, wenn sich Geometrie a vollständig innerhalb von Geometrie b befindet. Nur Kreis 1 wird zurückgegeben.
- Kreuzen
Gibt 1 (wahr) zurück, wenn die bereitgestellten Geometrien einige, aber nicht alle inneren Punkte gemeinsam haben und die tatsächliche Kreuzung eine geringere Dimension als die höchste bereitgestellte Geometrie hat. Beispielsweise wird eine Linie, die ein Polygon kreuzt, als Linie gekreuzt (wahr). Zwei Linien, die sich kreuzen, kreuzen sich als Punkt (wahr). Zwei Polygone kreuzen sich als Polygon (falsch). Im Bild werden keine Kreise zurückgegeben.
Parameter
Label |
Name |
Type |
Beschreibung |
|---|---|---|---|
Select features from |
|
[vector: any] |
Input vector layer |
Where the features (geometric predicate) |
|
[enumeration] [list] Default: [0] |
Spatial condition for the selection. One or more of:
If more than one condition is chosen, at least one of them (OR operation) has to be met for a feature to be extracted. |
By comparing to the features from |
|
[vector: any] |
Intersection vector layer |
Modify current selection by |
|
[enumeration] Default: 0 |
How the selection of the algorithm should be managed. One of:
|
Ausgaben
Label |
Name |
Type |
Beschreibung |
|---|---|---|---|
Input layer |
|
[same as input] |
The input layer with features selected |
Python code
Algorithm ID: qgis:selectbylocation
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
The algorithm id is displayed when you hover over the algorithm in the Processing Toolbox. The parameter dictionary provides the parameter NAMEs and values. See Verarbeitung Algorithmen von der Konsole aus verwenden for details on how to run processing algorithms from the Python console.
25.1.20.12. Select within distance
NEW in 3.22
creates a selection in a vector layer. Features are selected wherever they are within the specified maximum distance from the features in an additional reference layer.
Siehe auch
Parameter
Label |
Name |
Type |
Beschreibung |
|---|---|---|---|
Select features from |
|
[vector: any] |
Input vector layer to select features from |
By comparing to the features from |
|
[vector: any] |
Vector layer whose features closeness is used |
Where the features are within |
|
[number] Default: 100 |
The maximum distance around reference features to select input features |
Modify current selection by |
|
[enumeration] Default: 0 |
How the selection of the algorithm should be managed. One of:
|
Ausgaben
Label |
Name |
Type |
Beschreibung |
|---|---|---|---|
Input layer |
|
[same as input] |
The input layer with features selected |
Python code
Algorithm ID: native:selectwithindistance
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
The algorithm id is displayed when you hover over the algorithm in the Processing Toolbox. The parameter dictionary provides the parameter NAMEs and values. See Verarbeitung Algorithmen von der Konsole aus verwenden for details on how to run processing algorithms from the Python console.