Svarbu
Vertimas yra bendruomenės pastangos, prie kurių jūs galite prisijungti. Šis puslapis šiuo metu išverstas 48.89%.
24.1. Introducing GNSS/GPS Data
24.1.1. What is GPS?
GPS, the Global Positioning System, is a satellite-based system that allows anyone with a GPS receiver to find their exact position anywhere in the world. GPS is used as an aid in navigation, for example in airplanes, in boats and by hikers. The GPS receiver uses the signals from the satellites to calculate its latitude, longitude and (sometimes) elevation. Most receivers also have the capability to store:
locations (known as waypoints)
sequences of locations that make up a planned route
and a track log of the receiver’s movement over time.
Waypoints, routes and tracks are the three basic feature types in GPS data. QGIS displays waypoints in point layers, while routes and tracks are displayed in linestring layers.
Pastaba
QGIS supports also GNSS receivers. But we keep using the term GPS in this documentation.
24.1.2. Transferring or loading GPS data
24.1.2.1. Loading a GPX file
There are dozens of different file formats for storing GPS data. The format that QGIS uses is called GPX (GPS eXchange format), which is a standard interchange format that can contain any number of waypoints, routes and tracks in the same file.
To load a GPX file:
Open the GPS tab in the Data Source Manager dialog, i.e.:
Use the … Browse button next to the GPX dataset option to select the GPX file
Use the check boxes to select the Feature types you want to load from the file. Each feature type (Waypoints, Tracks or Routes) will be loaded in a separate layer.
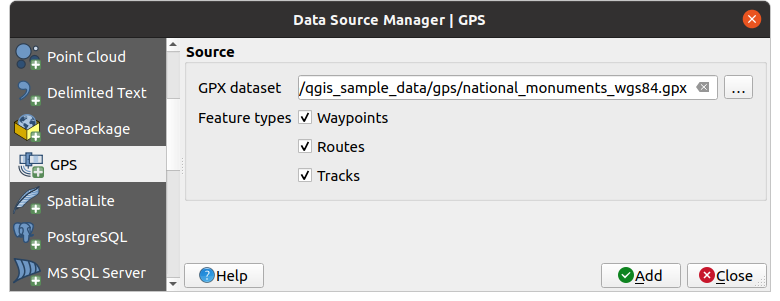
Fig. 24.1 Loading GPS Data dialog
24.1.2.2. Loading to or from a device
There are lots of different types of GPS devices and formats. Since QGIS uses GPX files, you need a way to convert other GPS file formats to GPX. QGIS can do that using the free program GPSBabel. GPSBabel can help you convert waypoints, tracks, and routes between popular GPS receivers such as Garmin or Magellan and mapping programs like Google Earth or Basecamp. Literally hundreds of GPS receivers and programs are supported. It can also transfer GPS data between your computer and a GPS device.
Under 
![]()
![]() ,
QGIS allows you to define your own device type and set parameters of conversion
that could later be used by the Processing GPS algorithms.
,
QGIS allows you to define your own device type and set parameters of conversion
that could later be used by the Processing GPS algorithms.
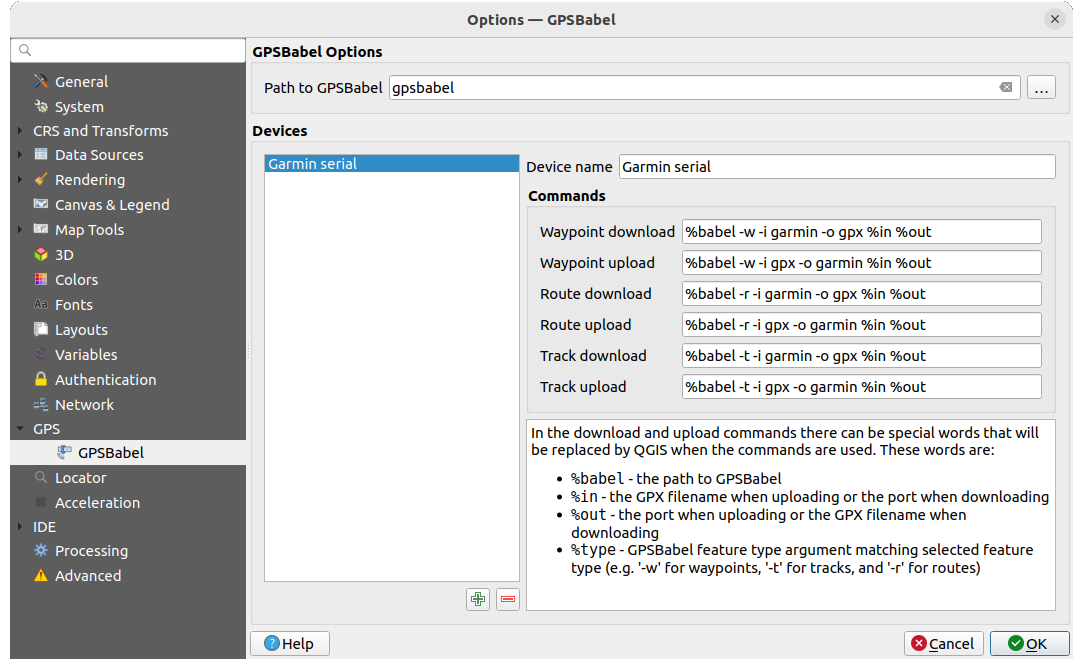
Fig. 24.2 GPS Babel nustatymai
Iš pradžių turite nurodyti kelią iki GPSBabel programos.
Tada galite pridėti jūsų įrenginį. Galite atnaujinti įrenginių sąrašą, naudodami mygtukus symbologyAdd| Pridėti naują įrenginį ar
 Išimti įrenginį.
Išimti įrenginį.Kiekvienam įrenginiui:
nurodote Įrenginio pavadinimą
sukonfigūruojate skirtingas komandas, kurias QGIS naudos bendravimui su įrenginiu, tokias kaip:
Atsisiųsti taškus iš įrengnio
Įkelti taškus į įrenginį
Atsisiųsti maršrutą iš įrenginio
Įkelti maršrutą į įrenginį
Atsisiųsti pėdsaką iš įrenginio
Įkelti pėdsaką į įrenginį
Nors komandos paprastai yra GPSBabel komandos, jūs taipogi galite naudoti bet kokią komandinės eilutės programą, kuri sukuria GPX failą. QGIS pakeis raktažodžius
%type,%inir%outkomandos vykdymo metu.As an example, if you create a device type with the download command
gpsbabel %type -i garmin -o gpx %in %outand then use it to download waypoints from port/dev/ttyS0to the fileoutput.gpx, QGIS will replace the keywords and run the commandgpsbabel -w -i garmin -o gpx /dev/ttyS0 output.gpx.Visas komandinės eilutės parinktis, kurių gali prireikti jūsų atvejui, rasite GPSBabel vadove.
Sukūrus naują įrenginio tipą jis atsiras įrenginių sąrašuose GPS atsiuntimo ir nusiuntimo algoritmuose.
Pastaba
GPS units allow you to store data in different coordinate systems. When downloading a GPX file (from your GPS unit or a web site) and then loading it in QGIS, be sure that the data stored in the GPX file uses WGS 84 (latitude/longitude). QGIS expects this, and it is the official GPX specification. See GPX 1.1 Schema Documentation.

