Importante
A tradução é um esforço comunitário você pode contribuir. Esta página está atualmente traduzida em 57.78%.
24.1. Introducing GNSS/GPS Data
24.1.1. O que é GPS?
GPS, the Global Positioning System, is a satellite-based system that allows anyone with a GPS receiver to find their exact position anywhere in the world. GPS is used as an aid in navigation, for example in airplanes, in boats and by hikers. The GPS receiver uses the signals from the satellites to calculate its latitude, longitude and (sometimes) elevation. Most receivers also have the capability to store:
locations (known as waypoints)
sequences of locations that make up a planned route
and a track log of the receiver’s movement over time.
Waypoints, routes and tracks are the three basic feature types in GPS data. QGIS displays waypoints in point layers, while routes and tracks are displayed in linestring layers.
Nota
O QGIS também suporta receptores GNSS. Mas continuamos usando o termo GPS nesta documentação.
24.1.2. Transferring or loading GPS data
24.1.2.1. Loading a GPX file
Existem dezenas de formatos de arquivo diferentes para armazenar dados GPS. O formato que o QGIS usa é chamado GPX (formato GPS eXchange), que é um formato padrão de intercâmbio que pode conter qualquer número de pontos de passagem, rotas e trilhas no mesmo arquivo.
To load a GPX file:
Open the GPS tab in the Data Source Manager dialog, i.e.:
Use the … Browse button next to the GPX dataset option to select the GPX file
Use the check boxes to select the Feature types you want to load from the file. Each feature type (Waypoints, Tracks or Routes) will be loaded in a separate layer.
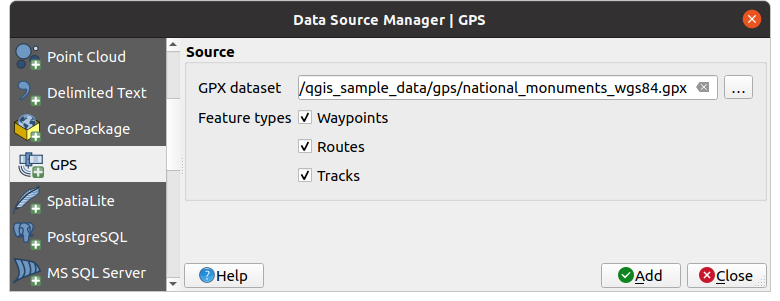
Fig. 24.1 Carregando a janela de dados do GPS
24.1.2.2. Loading to or from a device
There are lots of different types of GPS devices and formats. Since QGIS uses GPX files, you need a way to convert other GPS file formats to GPX. QGIS can do that using the free program GPSBabel. GPSBabel can help you convert waypoints, tracks, and routes between popular GPS receivers such as Garmin or Magellan and mapping programs like Google Earth or Basecamp. Literally hundreds of GPS receivers and programs are supported. It can also transfer GPS data between your computer and a GPS device.
Under 
![]()
![]() ,
QGIS allows you to define your own device type and set parameters of conversion
that could later be used by the Processing GPS algorithms.
,
QGIS allows you to define your own device type and set parameters of conversion
that could later be used by the Processing GPS algorithms.
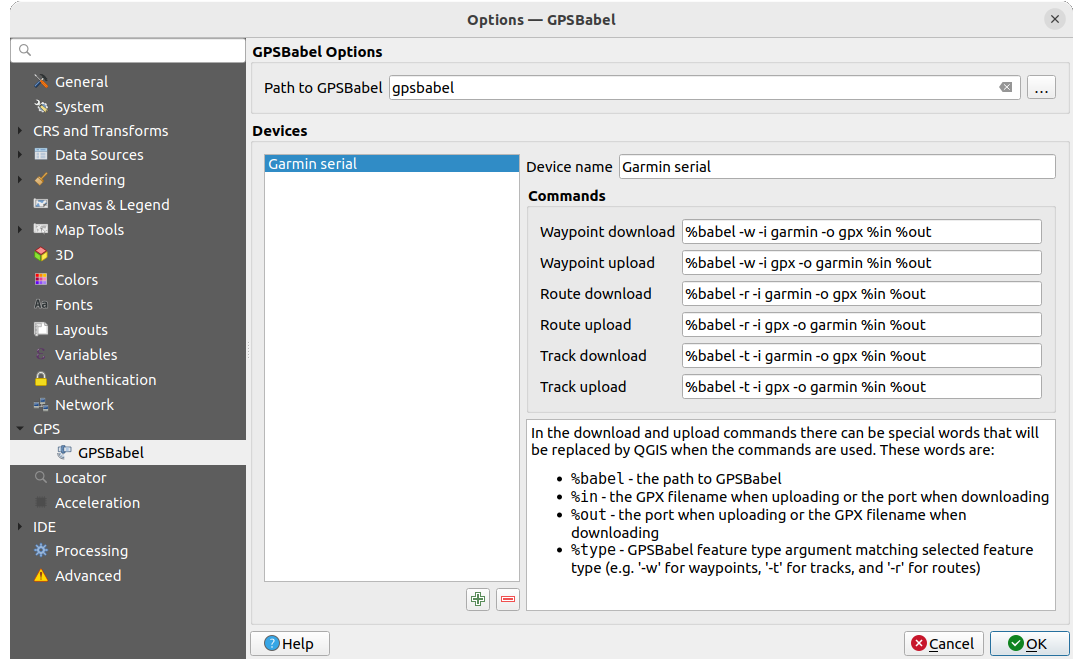
Fig. 24.2 Configurações do GPS Babel
Primeiro você tem que definir os binários Path to GPSBabel.
Então você pode querer adicionar seu dispositivo. Você pode atualizar a lista de dispositivos usando o botão
 Adicionar novo dispositivo ou
Adicionar novo dispositivo ou  Remover dispositivo.
Remover dispositivo.Para cada aparelho:
Você fornece um Nome do dispositivo
Você configura diferentes Comandos que o QGIS usará ao interagir com ele, como:
Baixar Waypoint do dispositivo.
Upload de waypoint para o dispositivo
Download de rota do dispositivo
Encaminhar upload para o dispositivo
Faixa de download do dispositivo
Track upload para o dispositivo
Embora os comandos sejam geralmente comandos GPSBabel, você também pode usar qualquer outro programa de linha de comando que possa criar um arquivo GPX.O QGIS substituirá as palavras-chave``%type``,
%in, e%outquando rodar o comando.As an example, if you create a device type with the download command
gpsbabel %type -i garmin -o gpx %in %outand then use it to download waypoints from port/dev/ttyS0to the fileoutput.gpx, QGIS will replace the keywords and run the commandgpsbabel -w -i garmin -o gpx /dev/ttyS0 output.gpx.Leia o manual do GPSBabel para as opções de linha de comando que podem ser específicas para o seu caso de uso.
Uma vez que você criou um novo tipo de dispositivo, ele aparecerá nas listas de dispositivos para os algoritmos de download e upload do GPS.
Nota
GPS units allow you to store data in different coordinate systems. When downloading a GPX file (from your GPS unit or a web site) and then loading it in QGIS, be sure that the data stored in the GPX file uses WGS 84 (latitude/longitude). QGIS expects this, and it is the official GPX specification. See GPX 1.1 Schema Documentation.

