Svarbu
Vertimas yra bendruomenės pastangos, prie kurių jūs galite prisijungti. Šis puslapis šiuo metu išverstas 78.47%.
24.1.21. Vektorių kūrimas
24.1.21.1. Paslinktų (lygiagrečių) linijų masyvas
Sukuria sluoksnyje linijinių geoobjektų kopijas, kuriant kelias paslinktas kiekvieno geoobjekto versijas. Kiekviena nauja versija papildomai paslenkama nurodytą atstumą.
Teigiamas atstumas paslinks linijas į kairę, o neigiami atstumai - į dešinę.
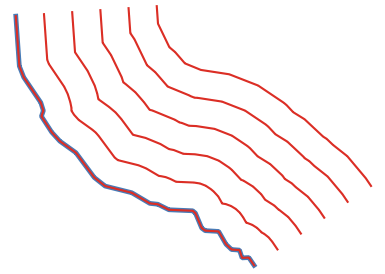
Fig. 24.45 Mėlynas - pradinis sluoksnis, raudonas - paslinktasis
 Leidžia linijų geoobjektus keisti vietoje
Leidžia linijų geoobjektus keisti vietoje
Įspėjimas
Šis algoritmas išmeta esamus pirminius raktus ar FID reikšmes ir perkuria jas išvesties sluoksniuose.
Taip pat žiūrėkite
Parametrai
Baziniai parametrai
Užrašas |
Pavadinimas |
Tipas |
Aprašymas |
|---|---|---|---|
Įvesties sluoksnis |
|
[vektorius: linija] |
Įvesties linijų vektorinis sluoksnis, kurį reikia naudoti poslinkiams. |
Kuriamų geoobjektų skaičius |
|
Numatytas: 10 |
Kiekvienam geoobjektui kuriamų paslinktų kopijų skaičius |
Poslinkio žingsnio atstumas |
|
Numatytas: 1.0 |
Atstumas tarp dviejų viena po kitos einančių paslinktų kopijų |
Paslinktos linijos |
|
[vektorius: linija] Numatytas: |
Nurodykite išvesties linijų sluoksnį su paslinktais geoobjektais. Vienas iš:
Čia taipogi galima pakeisti failo koduotę. |
Išmanesni parametrai
Užrašas |
Pavadinimas |
Tipas |
Aprašymas |
|---|---|---|---|
Segmentai |
|
[skaičius: slankaus kablelio] Numatyta: 8 |
Linijos segmentų skaičius, kurį naudoti aproksimuojant apskritimo ketvirtį kuriant apvalius poslinkius |
Jungimo stilius |
|
[sąrašas] Numatytas: 0 |
Nurodykite, kokie turi būti naudojami jungimai paslenkant linijų kampus: apvalūs, nukirsti ar nuožulnūs. Vienas iš:

Fig. 24.46 Apvalūs, mitros ir kampo jungimo stiliai |
Mitros riba |
|
[skaičius: slankaus kablelio] Numatyta: 2.0 |
Nustato maksimalų atstumą nuo paslenkamos geometrijos kuriant mitros jungtį. Nurodomas kaip poslinkio atstumo koeficientas (taikoma tik mitros jungimo stiliui). Minimalus: 1.0 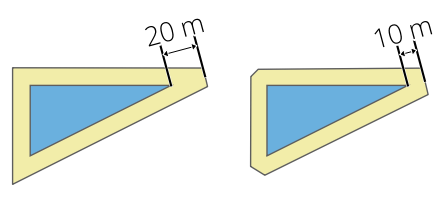
Fig. 24.47 10m buferis su 2 riba ir 10m buferis su 1 riba |
Išvestys
Užrašas |
Pavadinimas |
Tipas |
Aprašymas |
|---|---|---|---|
Paslinktos linijos |
|
[vektorius: linija] |
Išvesties linijų sluoksnis su pradiniais ir paslinktais geoobjektais. Atributai bus kopijuojami į atitinkamas išvestis. Bus pridėti šie, su įvesties parametrais susiję atributai: |
Pythono kodas
Algoritmo ID: native:arrayoffsetlines
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
algoritmo id rodomas, kai užvedate pelę virš algoritmo apdorojimo įrankinėje. parametrų žodynas teikia parametrų pavadinimus ir reikšmes. Daugiau informacijos apie tai, kaip vykdyti apdorojimo algoritmus Pythono konsolėje rasite skyriuje Using processing algorithms from the console.
24.1.21.2. Pakeistų geoobjektų masyvas
Sukuria sluoksnyje kelias pakeistas geoobjektų kopijas. Kiekviena kopija inkrementiškai pastumta nurodytu atstumu X, Y ir/ar Z ašyse.
Geometrijoje esančias M reikšmes taipogi galima keisti.
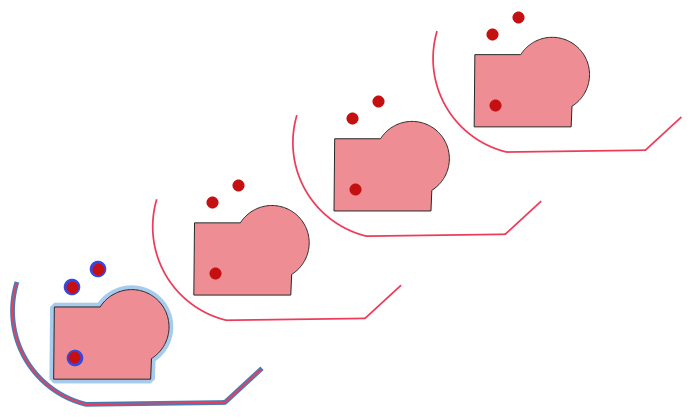
Fig. 24.48 Įvesties sluoksnis mėlynas, išvesties sluoksnis su pakeistais geoobjektais - raudonas
 Leidžia taškų, linijų ir poligonų geoobjektus keisti vietoje
Leidžia taškų, linijų ir poligonų geoobjektus keisti vietoje
Įspėjimas
Šis algoritmas išmeta esamus pirminius raktus ar FID reikšmes ir perkuria jas išvesties sluoksniuose.
Taip pat žiūrėkite
Parametrai
Užrašas |
Pavadinimas |
Tipas |
Aprašymas |
|---|---|---|---|
Įvesties sluoksnis |
|
[vektorius: geometrija] |
Keičiamas įvesties sluoksnis |
Kuriamų geoobjektų skaičius |
|
Numatytas: 10 |
Kiekvieno geoobjekto kuriamų kopijų skaičius |
Žingsnio atstumas (x-ašis) |
|
Numatytas: 0.0 |
X ašyje taikomas poslinkis |
Žingsnio atstumas (y-ašis) |
|
Numatytas: 0.0 |
Y ašyje taikomas poslinkis |
Žingsnio atstumas (z-ašis) |
|
Numatytas: 0.0 |
Z ašyje taikomas poslinkis |
Žingsnio atstumas (m reikšmės) |
|
Numatytas: 0.0 |
M taikomas poslinkis |
Pakeista |
|
[toks pat, kaip įvestis] Numatytas: |
Išvesties linijų sluoksnis su pakeistomis (pastumtomis) geoobjektų kopijomis. Originalūs geoobjektai irgi nukopijuojami. Vienas iš:
Čia taipogi galima pakeisti failo koduotę. |
Išvestys
Užrašas |
Pavadinimas |
Tipas |
Aprašymas |
|---|---|---|---|
Pakeista |
|
[toks pat, kaip įvestis] |
Išvesties vektorinis sluoksnis su pakeistomis (paslinktomis) geoobjektų kopijomis. Pradiniai geoobjektai irgi nukopijuojami. |
Pythono kodas
Algoritmo ID: native:arraytranslatedfeatures
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
algoritmo id rodomas, kai užvedate pelę virš algoritmo apdorojimo įrankinėje. parametrų žodynas teikia parametrų pavadinimus ir reikšmes. Daugiau informacijos apie tai, kaip vykdyti apdorojimo algoritmus Pythono konsolėje rasite skyriuje Using processing algorithms from the console.
24.1.21.3. Kurti tinklelį
Sukuria vektorinį sluoksnį su tinkleliu, dengiančiu nurodytą apimtį. Tinklelio celės gali būti įvairių formų:
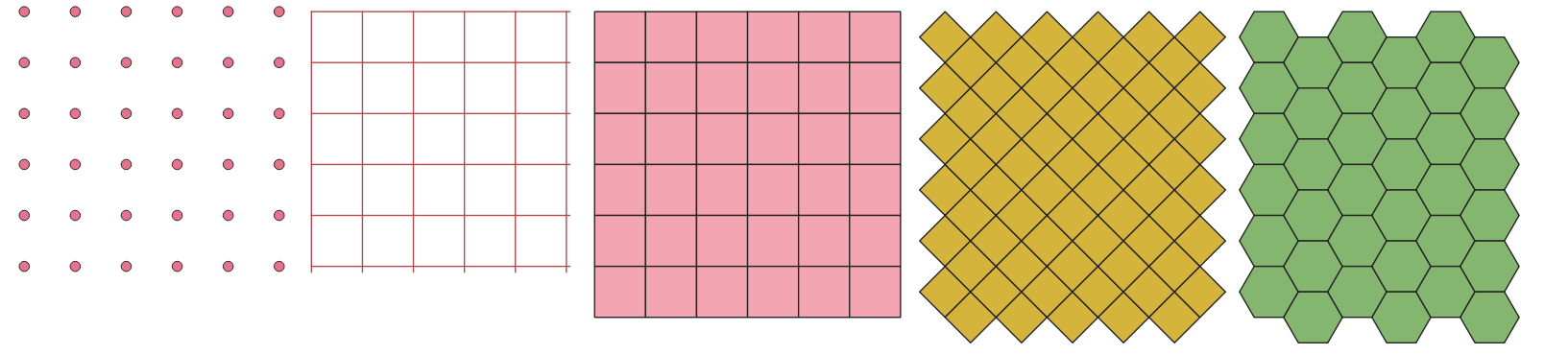
Fig. 24.49 Skirtingos tinklelio celių formos, taikomos tai pačiai apimčiai, be persidengimų
Kiekvieno tinklelio elemento dydis ir/ar vieta nurodoma naudojant horizontalų ir vertikalų atstumą. Reikia nurodyti išvesties sluoksnio CRS. Tinklelio apimties ir tarpų reikšmės turi būti išreikštos CRS koordinatėmis ir vienetais.
Numatytas meniu:
Parametrai
Užrašas |
Pavadinimas |
Tipas |
Aprašymas |
|---|---|---|---|
Tinklelio tipas |
|
[sąrašas] Numatytas: 0 |
Tinklelio forma. Vienas iš:
|
Tinklelio apimtis |
|
[apimtis] |
Tinklelio apimtis Galimi metodai yra:
|
Horizontalus dydis |
|
[skaičius: slankaus kablelio] Numatytas: 1.0 |
Tinklelio celės dydis X-ašyje |
Vertikalus dydis |
|
[skaičius: slankaus kablelio] Numatytas: 1.0 |
Tinklelio celės dydis Y-ašyje |
Horizontalus persidengimas |
|
[skaičius: slankaus kablelio] Numatytas: 0.0 |
Persidengimo tarp dviejų greta esančių tinklelio celių dydis X ašyje. |
Vertikalus persidengimas |
|
[skaičius: slankaus kablelio] Numatytas: 0.0 |
Persidengimo tarp dviejų greta esančių tinklelio celių dydis Y ašyje. |
Tinklelio CRS |
|
[crs] Numatyta: Projekto CRS |
Tinkleliui taikoma koordinačių atskaitos sistema |
Tinklelis |
|
[vektorius: geometrija] Numatytas: |
Gautas vektorinis tinklelio sluoksnis. Vienas iš:
Čia taipogi galima pakeisti failo koduotę. |
Išvestys
Užrašas |
Pavadinimas |
Tipas |
Aprašymas |
|---|---|---|---|
Tinklelis |
|
[vektorius: geometrija] |
Gautas vektorinis tinklelio sluoksnis. Išvesties geometrijų tipas (taškas, linija ar poligonas) priklauso nuo Tinklelio tipo. Geoobjektai kuriami nuo viršaus žemyn ir iš kairės į dešinę. Atributų lentelė užpildoma:
|
Pythono kodas
Algoritmo ID: native:creategrid
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
algoritmo id rodomas, kai užvedate pelę virš algoritmo apdorojimo įrankinėje. parametrų žodynas teikia parametrų pavadinimus ir reikšmes. Daugiau informacijos apie tai, kaip vykdyti apdorojimo algoritmus Pythono konsolėje rasite skyriuje Using processing algorithms from the console.
24.1.21.4. Kurti taškų sluoksnį iš lentelės
Kuria taškų sluoksnį iš lentelės su stulpeliais, turinčiais koordinačių laukus.
Be X ir Y koordinačių jūs dar galite nurodyti Z ir M laukus.
Įspėjimas
Šis algoritmas išmeta esamus pirminius raktus ar FID reikšmes ir perkuria jas išvesties sluoksniuose.
Parametrai
Užrašas |
Pavadinimas |
Tipas |
Aprašymas |
|---|---|---|---|
Įvesties sluoksnis |
|
[vector: any] |
Įvesties vektorinis sluoksnis arba lentelė. |
X laukas |
|
[tablefield: any] |
Laukas su X koordinate. |
Y laukas |
|
[tablefield: any] |
Laukas su Y koordinate. |
Z laukas Pasirinktinis |
|
[tablefield: any] |
Laukas su Z koordinate. |
M laukas Pasirinktinis |
|
[tablefield: any] |
Laukas su M koordinate. |
Paskirties CRS |
|
[crs] Numatytoji: |
Sluoksniui naudotina koordinačių atskaitos sistema. Daroma prielaida, kad pateiktos koordinatės suderinamos. |
Taškai iš lentelės |
|
[vektorius: taškas] Numatytas: |
Nurodykite gaunamą taškų sluoksnį. Vienas iš:
Čia taipogi galima pakeisti failo koduotę. |
Išvestys
Užrašas |
Pavadinimas |
Tipas |
Aprašymas |
|---|---|---|---|
Taškai iš lentelės |
|
[vektorius: taškas] |
Gaunamas taškų sluoksnis |
Pythono kodas
Algoritmo ID: native:createpointslayerfromtable
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
algoritmo id rodomas, kai užvedate pelę virš algoritmo apdorojimo įrankinėje. parametrų žodynas teikia parametrų pavadinimus ir reikšmes. Daugiau informacijos apie tai, kaip vykdyti apdorojimo algoritmus Pythono konsolėje rasite skyriuje Using processing algorithms from the console.
24.1.21.5. Kurti taškus (pikselių centroidus) palei liniją
Kuria vektorinį taškų sluoksnį iš įvesties rastro ir linijų sluoksnio.
Taškai atitinka pikselių centroidus, kurie susikerta su linijų sluoksniu.
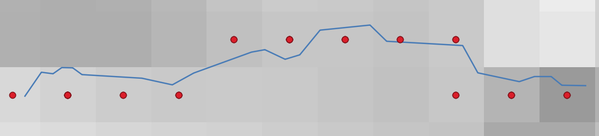
Fig. 24.50 Pikselių centroidų taškai
Parametrai
Užrašas |
Pavadinimas |
Tipas |
Aprašymas |
|---|---|---|---|
Rastro sluoksnis |
|
[rastras] |
Įvesties rastro sluoksnis |
Vektorinis sluoksnis |
|
[vektorius: linija] |
Įvesties vektorinis linijų sluoksnis |
Taškai palei liniją |
|
[vektorius: taškas] Numatytas: |
Gaunamas taškų sluoksnis su pikselių centroidais. Vienas iš:
Čia taipogi galima pakeisti failo koduotę. |
Išvestys
Užrašas |
Pavadinimas |
Tipas |
Aprašymas |
|---|---|---|---|
Taškai palei liniją |
|
[vektorius: taškas] |
Gaunamas taškų sluoksnis su pikselių centroidais |
Pythono kodas
Algoritmo ID: qgis:generatepointspixelcentroidsalongline
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
algoritmo id rodomas, kai užvedate pelę virš algoritmo apdorojimo įrankinėje. parametrų žodynas teikia parametrų pavadinimus ir reikšmes. Daugiau informacijos apie tai, kaip vykdyti apdorojimo algoritmus Pythono konsolėje rasite skyriuje Using processing algorithms from the console.
24.1.21.6. Generate points (pixel centroids) inside polygon
Generates a point vector layer from an input raster and polygon layer.
The points correspond to the pixel centroids that intersect the polygon layer.
Įspėjimas
Šis algoritmas išmeta esamus pirminius raktus ar FID reikšmes ir perkuria jas išvesties sluoksniuose.
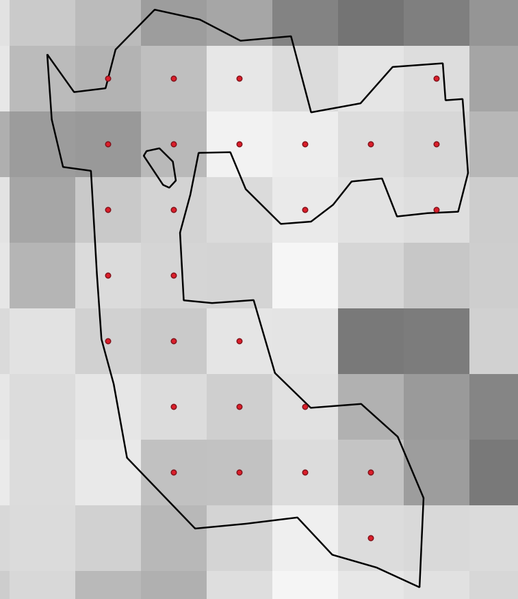
Fig. 24.51 Pikselių centroidų taškai
Parametrai
Užrašas |
Pavadinimas |
Tipas |
Aprašymas |
|---|---|---|---|
Rastro sluoksnis |
|
[rastras] |
Įvesties rastro sluoksnis |
Vektorinis sluoksnis |
|
[vektorius: poligonas] |
Įvesties poligonų vektorinis sluoksnis |
Points inside polygons |
|
[vektorius: taškas] Numatytas: |
Resulting point layer of pixel centroids. One of:
Čia taipogi galima pakeisti failo koduotę. |
Išvestys
Užrašas |
Pavadinimas |
Tipas |
Aprašymas |
|---|---|---|---|
Points inside polygons |
|
[vektorius: taškas] |
Resulting point layer of pixel centroids |
Pythono kodas
Algorithm ID: native:generatepointspixelcentroidsinsidepolygons
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
algoritmo id rodomas, kai užvedate pelę virš algoritmo apdorojimo įrankinėje. parametrų žodynas teikia parametrų pavadinimus ir reikšmes. Daugiau informacijos apie tai, kaip vykdyti apdorojimo algoritmus Pythono konsolėje rasite skyriuje Using processing algorithms from the console.
24.1.21.7. Import geotagged photos
Creates a point layer corresponding to the geotagged locations from JPEG or HEIC/HEIF images from a source folder.
The point layer will contain a single PointZ feature per input file from which the geotags could be read. Any altitude information from the geotags will be used to set the point’s Z value.
Besides longitude and latitude also altitude, direction and timestamp information, if present in the photo, will be added to the point as attributes.
Parametrai
Užrašas |
Pavadinimas |
Tipas |
Aprašymas |
|---|---|---|---|
Input folder |
|
[aplankas] |
Path to the source folder containing the geotagged photos |
Scan recursively |
|
[boolean] Numatytas: ne |
If checked, the folder and its subfolders will be scanned |
Photos Pasirinktinis |
|
[vektorius: taškas] Numatytas: |
Specify the point vector layer for the geotagged photos. One of:
Čia taipogi galima pakeisti failo koduotę. |
Invalid photos table Pasirinktinis |
|
[vektorius: lentelė] Numatytas: |
Specify the table of unreadable or non-geotagged photos. One of:
Čia taipogi galima pakeisti failo koduotę. |
Išvestys
Užrašas |
Pavadinimas |
Tipas |
Aprašymas |
|---|---|---|---|
Photos |
|
[vektorius: taškas] |
Point vector layer with geotagged photos. The form of the layer is automatically filled with paths and photo previews settings. |
Invalid photos table Pasirinktinis |
|
[vektorius: lentelė] |
Table of unreadable or non-geotagged photos can also be created. |
Pythono kodas
Algorithm ID: native:importphotos
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
algoritmo id rodomas, kai užvedate pelę virš algoritmo apdorojimo įrankinėje. parametrų žodynas teikia parametrų pavadinimus ir reikšmes. Daugiau informacijos apie tai, kaip vykdyti apdorojimo algoritmus Pythono konsolėje rasite skyriuje Using processing algorithms from the console.
24.1.21.8. Points to path
Converts a point layer to a line layer, by joining points in an order defined by an expression or a field in the input point layer.
Points can be grouped by a field or an expression to distinguish line features.
In addition to the line vector layer, a text file is output that describes the resulting line as a start point and a sequence of bearings / directions (relative to azimuth) and distances.
Pastaba
Šis algoritmas naudoja elipse paremtus skaičiavimus ir atsižvelgia į dabartinius elipsoido nustatymus.
Parametrai
Užrašas |
Pavadinimas |
Tipas |
Aprašymas |
|---|---|---|---|
Input point layer |
|
[vektorius: taškas] |
Input point vector layer |
Create closed paths |
|
[boolean] Numatytas: ne |
If checked, the first and last points of the line will be connected and close the generated path |
Order expression Pasirinktinis |
|
[išraiška] |
Field or expression providing the order to connect the points in the path.
If not set, the feature ID ( |
Sort text containing numbers naturally |
|
[boolean] Numatytas: ne |
If checked, naturally sorts the features based on the provided expression (i.e., ‚a9‘ < ‚a10‘). |
Path group expression Pasirinktinis |
|
[išraiška] |
Point features of the same value in the field or expression will be grouped in the same line. If not set, a single path is drawn with all the input points. |
Paths |
|
[vektorius: linija] Numatytas: |
Specify the line vector layer of the path. One of:
Čia taipogi galima pakeisti failo koduotę. |
Directory for text output Pasirinktinis |
|
[aplankas] Numatytas: |
Specify the directory that will contain the description files of points and paths. One of:
|
Išvestys
Užrašas |
Pavadinimas |
Tipas |
Aprašymas |
|---|---|---|---|
Paths |
|
[vektorius: linija] |
Line vector layer of the path |
Directory for text output |
|
[aplankas] |
Directory containing description files of points and paths |
Pythono kodas
Algorithm ID: native:pointstopath
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
algoritmo id rodomas, kai užvedate pelę virš algoritmo apdorojimo įrankinėje. parametrų žodynas teikia parametrų pavadinimus ir reikšmes. Daugiau informacijos apie tai, kaip vykdyti apdorojimo algoritmus Pythono konsolėje rasite skyriuje Using processing algorithms from the console.
24.1.21.9. Random points along line
Creates a new point layer, with points placed on the lines of another layer.
For each line in the input layer, a given number of points is added to the resulting layer. The procedure for adding a point is to:
randomly select a line feature from the input layer
if the feature is multi-part, randomly select a part of it
randomly select a segment of that line
randomly select a position on that segment.
The procedure means that curved parts of the lines (with relatively short segments) will get more points than straight parts (with relatively long segments), as demonstrated in the illustration below, where the output of the Random points along lines algorithm can be compared with the output of the Random points on lines algorithm (that produces points with an, on average, even distribution along the lines).
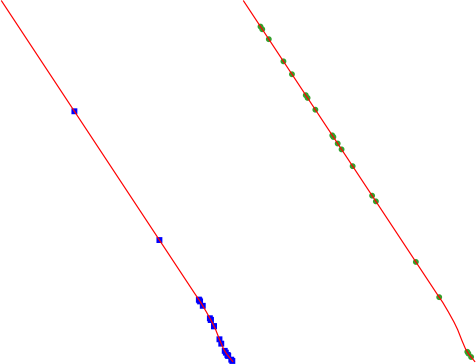
Fig. 24.52 Example algorithm output. Left: Random points along line, right: Random points on lines
A minimum distance can be specified, to avoid points being too close to each other.
Įspėjimas
Šis algoritmas išmeta esamus pirminius raktus ar FID reikšmes ir perkuria jas išvesties sluoksniuose.
Taip pat žiūrėkite
Parametrai
Užrašas |
Pavadinimas |
Tipas |
Aprašymas |
|---|---|---|---|
Input point layer |
|
[vektorius: linija] |
Įvesties vektorinis linijų sluoksnis |
Number of points |
|
[skaičius: sveikas skaičius] Numatytas: 1 |
Number of points to create |
Minimum distance between points |
|
[skaičius: slankaus kablelio] Numatytas: 0.0 |
The minimum distance between points |
Random points |
|
[vektorius: taškas] Numatytas: |
The output random points. One of:
Čia taipogi galima pakeisti failo koduotę. |
Išvestys
Užrašas |
Pavadinimas |
Tipas |
Aprašymas |
|---|---|---|---|
Random points |
|
[vektorius: taškas] |
The output random points layer. |
Pythono kodas
Algorithm ID: qgis:qgisrandompointsalongline
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
algoritmo id rodomas, kai užvedate pelę virš algoritmo apdorojimo įrankinėje. parametrų žodynas teikia parametrų pavadinimus ir reikšmes. Daugiau informacijos apie tai, kaip vykdyti apdorojimo algoritmus Pythono konsolėje rasite skyriuje Using processing algorithms from the console.
24.1.21.10. Random points in extent
Creates a new point layer with a given number of random points, all of them within a given extent.
A distance factor can be specified, to avoid points being too close to each other. If the minimum distance between points makes it impossible to create new points, either distance can be decreased or the maximum number of attempts may be increased.
Numatytas meniu:
Parametrai
Baziniai parametrai
Užrašas |
Pavadinimas |
Tipas |
Aprašymas |
|---|---|---|---|
Input extent |
|
[apimtis] |
Map extent for the random points Galimi metodai yra:
|
Number of points |
|
[skaičius: sveikas skaičius] Numatytas: 1 |
Number of point to create |
Minimum distance between points |
|
[skaičius: slankaus kablelio] Numatytas: 0.0 |
The minimum distance between points |
Paskirties CRS |
|
[crs] Numatyta: Projekto CRS |
CRS of the random points layer |
Random points |
|
[vektorius: taškas] Numatytas: |
The output random points. One of:
Čia taipogi galima pakeisti failo koduotę. |
Išmanesni parametrai
Užrašas |
Pavadinimas |
Tipas |
Aprašymas |
|---|---|---|---|
Maximum number of search attempts given the minimum distance |
|
[skaičius: sveikas skaičius] Default: 200 |
Maximum number of attempts to place the points |
Išvestys
Užrašas |
Pavadinimas |
Tipas |
Aprašymas |
|---|---|---|---|
Random points |
|
[vektorius: taškas] |
The output random points layer. |
Pythono kodas
Algorithm ID: native:randompointsinextent
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
algoritmo id rodomas, kai užvedate pelę virš algoritmo apdorojimo įrankinėje. parametrų žodynas teikia parametrų pavadinimus ir reikšmes. Daugiau informacijos apie tai, kaip vykdyti apdorojimo algoritmus Pythono konsolėje rasite skyriuje Using processing algorithms from the console.
24.1.21.11. Random points in layer bounds
Creates a new point layer with a given number of random points, all of them within the extent of a given layer.
A minimum distance can be specified, to avoid points being too close to each other.
Numatytas meniu:
Įspėjimas
Šis algoritmas išmeta esamus pirminius raktus ar FID reikšmes ir perkuria jas išvesties sluoksniuose.
Parametrai
Užrašas |
Pavadinimas |
Tipas |
Aprašymas |
|---|---|---|---|
Įvesties sluoksnis |
|
[vektorius: poligonas] |
Input polygon layer defining the area |
Number of points |
|
[skaičius: sveikas skaičius] Numatytas: 1 |
Number of points to create |
Minimum distance between points |
|
[skaičius: slankaus kablelio] Numatytas: 0.0 |
The minimum distance between points |
Random points |
|
[vektorius: taškas] Numatytas: |
The output random points. One of:
Čia taipogi galima pakeisti failo koduotę. |
Išvestys
Užrašas |
Pavadinimas |
Tipas |
Aprašymas |
|---|---|---|---|
Random points |
|
[vektorius: taškas] |
The output random points layer. |
Pythono kodas
Algorithm ID: qgis:randompointsinlayerbounds
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
algoritmo id rodomas, kai užvedate pelę virš algoritmo apdorojimo įrankinėje. parametrų žodynas teikia parametrų pavadinimus ir reikšmes. Daugiau informacijos apie tai, kaip vykdyti apdorojimo algoritmus Pythono konsolėje rasite skyriuje Using processing algorithms from the console.
24.1.21.12. Random points in polygons
Creates a point layer with points placed inside the polygons of another layer.
For each feature (polygon / multi-polygon) geometry in the input layer, the given number of points is added to the result layer.
Per feature and global minimum distances can be specified in order to avoid points being too close in the output point layer. If a minimum distance is specified, it may not be possible to generate the specified number of points for each feature. The total number of generated points and missed points are available as output from the algorithm.
The illustration below shows the effect of per feature and global minimum distances and zero/non-zero minimum distances (generated with the same seed, so at least the first point generated will be the same).
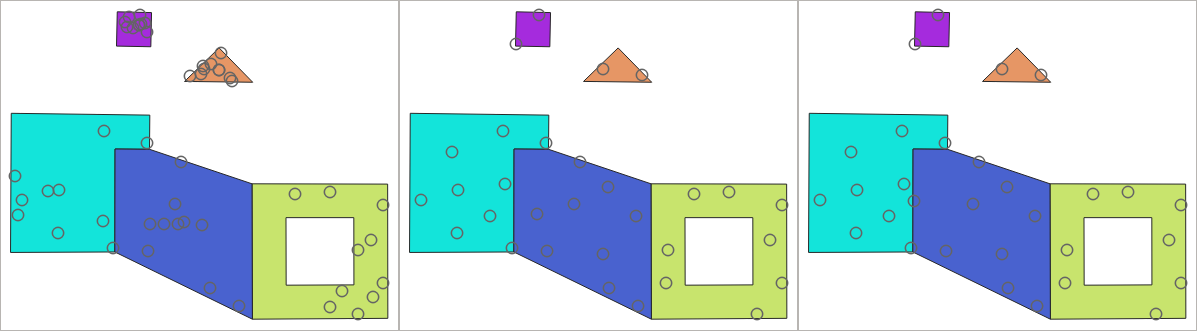
Fig. 24.53 Ten points per polygon feature, left: min. distances = 0, middle: min.distances = 1, right: min. distance = 1, global min. distance = 0
The maximum number of tries per point can be specified. This is only relevant for non-zero minimum distance.
A seed for the random number generator can be provided, making it possible to get identical random number sequences for different runs of the algorithm.
The attributes of the polygon feature on which a point was generated can be included (Include polygon attributes).
If you want approximately the same point density for all the features, you can data-define the number of points using the area of the polygon feature geometry.
Taip pat žiūrėkite
Parametrai
Baziniai parametrai
Užrašas |
Pavadinimas |
Tipas |
Aprašymas |
|---|---|---|---|
Input polygon layer |
|
[vektorius: linija] |
Įvesties poligonų vektorinis sluoksnis |
Number of points for each feature |
|
Numatytas: 1 |
Number of points to create |
Minimum distance between points Pasirinktinis |
|
Numatytas: 0.0 |
The minimum distance between points within one polygon feature |
Random points in polygons |
|
[vektorius: taškas] Numatytas: |
The output random points. One of:
Čia taipogi galima pakeisti failo koduotę. |
Išmanesni parametrai
Užrašas |
Pavadinimas |
Tipas |
Aprašymas |
|---|---|---|---|
Global minimum distance between points Pasirinktinis |
|
Numatytas: 0.0 |
The global minimum distance between points. Should be smaller than the Minimum distance between points (per feature) for that parameter to have an effect. |
Maximum number of search attempts (for Min. dist. > 0) Pasirinktinis |
|
Numatytas: 10 |
The maximum number of tries per point. Only relevant if the minimum distance between points is set (and greater than 0). |
Random seed Pasirinktinis |
|
[skaičius: sveikas skaičius] Numatytas: jokio |
The seed to use for the random number generator. |
Include polygon attributes |
|
[boolean] Numatytas: Taip |
If set, a point will get the attributes from the line on which it is placed. |
Išvestys
Užrašas |
Pavadinimas |
Tipas |
Aprašymas |
|---|---|---|---|
Random points in polygons |
|
[vektorius: taškas] |
The output random points layer. |
Number of features with empty or no geometry |
|
[skaičius: sveikas skaičius] |
|
Total number of points generated |
|
[skaičius: sveikas skaičius] |
|
Number of missed points |
|
[skaičius: sveikas skaičius] |
The number of points that could not be generated due to the minimum distance constraint. |
Number of features with missed points |
|
[skaičius: sveikas skaičius] |
Not including features with empty or no geometry |
Pythono kodas
Algorithm ID: native:randompointsinpolygons
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
algoritmo id rodomas, kai užvedate pelę virš algoritmo apdorojimo įrankinėje. parametrų žodynas teikia parametrų pavadinimus ir reikšmes. Daugiau informacijos apie tai, kaip vykdyti apdorojimo algoritmus Pythono konsolėje rasite skyriuje Using processing algorithms from the console.
24.1.21.13. Random points inside polygons
Creates a new point layer with a given number of random points inside each polygon of the input polygon layer.
Two sampling strategies are available:
Points count: number of points for each feature
Points density: density of points for each feature
A minimum distance can be specified, to avoid points being too close to each other.
Numatytas meniu:
Įspėjimas
Šis algoritmas išmeta esamus pirminius raktus ar FID reikšmes ir perkuria jas išvesties sluoksniuose.
Taip pat žiūrėkite
Parametrai
Užrašas |
Pavadinimas |
Tipas |
Aprašymas |
|---|---|---|---|
Įvesties sluoksnis |
|
[vektorius: poligonas] |
Įvesties poligonų vektorinis sluoksnis |
Sampling strategy |
|
[sąrašas] Numatytas: 0 |
Sampling strategy to use. One of:
|
Point count or density |
|
Numatytas: 1.0 |
The number or density of points, depending on the chosen Sampling strategy. |
Minimum distance between points |
|
[skaičius: slankaus kablelio] Numatytas: 0.0 |
The minimum distance between points |
Random points |
|
[vektorius: taškas] Numatytas: |
The output random points. One of:
Čia taipogi galima pakeisti failo koduotę. |
Išvestys
Užrašas |
Pavadinimas |
Tipas |
Aprašymas |
|---|---|---|---|
Random points |
|
[vektorius: taškas] |
The output random points layer. |
Pythono kodas
Algorithm ID: qgis:randompointsinsidepolygons
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
algoritmo id rodomas, kai užvedate pelę virš algoritmo apdorojimo įrankinėje. parametrų žodynas teikia parametrų pavadinimus ir reikšmes. Daugiau informacijos apie tai, kaip vykdyti apdorojimo algoritmus Pythono konsolėje rasite skyriuje Using processing algorithms from the console.
24.1.21.14. Random points on lines
Creates a point layer with points placed on the lines of another layer.
For each feature (line / multi-line) geometry in the input layer, the given number of points is added to the result layer.
Per feature and global minimum distances can be specified in order to avoid points being too close in the output point layer. If a minimum distance is specified, it may not be possible to generate the specified number of points for each feature. The total number of generated points and missed points are available as output from the algorithm.
The illustration below shows the effect of per feature and global minimum distances and zero/non-zero minimum distances (generated with the same seed, so at least the first point generated will be the same).
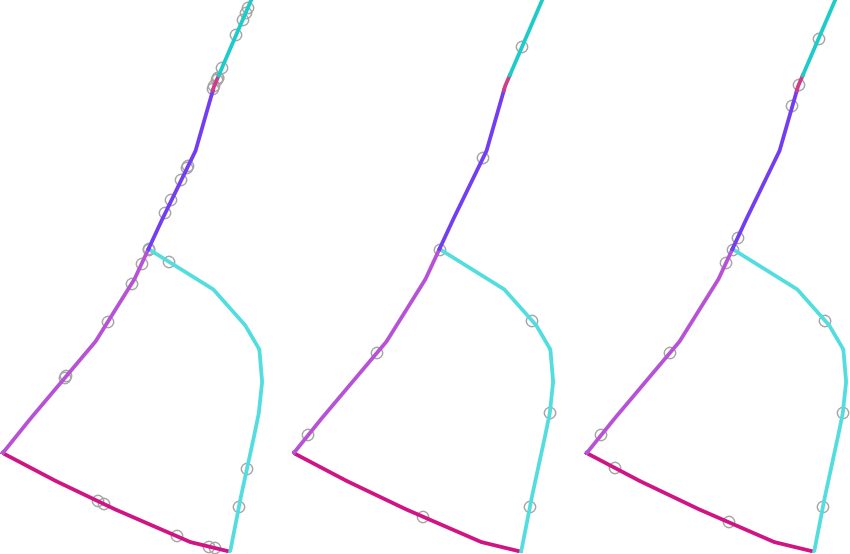
Fig. 24.54 Five points per line feature, left: min. distances = 0, middle: min.distances != 0, right: min. distance != 0, global min. distance = 0
The maximum number of tries per point can be specified. This is only relevant for non-zero minimum distance.
A seed for the random number generator can be provided, making it possible to get identical random number sequences for different runs of the algorithm.
The attributes of the line feature on which a point was generated can be included (Include line attributes).
If you want approximately the same point density for all the line features, you can data-define the number of points using the length of the line feature geometry.
Taip pat žiūrėkite
Parametrai
Baziniai parametrai
Užrašas |
Pavadinimas |
Tipas |
Aprašymas |
|---|---|---|---|
Įvesties linijų sluoksnis |
|
[vektorius: linija] |
Įvesties vektorinis linijų sluoksnis |
Number of points for each feature |
|
Numatytas: 1 |
Number of points to create |
Minimum distance between points (per feature) Pasirinktinis |
|
Numatytas: 0.0 |
The minimum distance between points within one line feature |
Random points on lines |
|
[vektorius: taškas] Numatytas: |
The output random points. One of:
Čia taipogi galima pakeisti failo koduotę. |
Išmanesni parametrai
Užrašas |
Pavadinimas |
Tipas |
Aprašymas |
|---|---|---|---|
Global minimum distance between points Pasirinktinis |
|
Numatytas: 0.0 |
The global minimum distance between points. Should be smaller than the Minimum distance between points (per feature) for that parameter to have an effect. |
Maximum number of search attempts (for Min. dist. > 0) Pasirinktinis |
|
Numatytas: 10 |
The maximum number of tries per point. Only relevant if the minimum distance between points is set (and greater than 0). |
Random seed Pasirinktinis |
|
[skaičius: sveikas skaičius] Numatytas: jokio |
The seed to use for the random number generator. |
Include line attributes |
|
[boolean] Numatytas: Taip |
If set, a point will get the attributes from the line on which it is placed. |
Išvestys
Užrašas |
Pavadinimas |
Tipas |
Aprašymas |
|---|---|---|---|
Random points on lines |
|
[vektorius: taškas] |
The output random points layer. |
Number of features with empty or no geometry |
|
[skaičius: sveikas skaičius] |
|
Number of features with missed points |
|
[skaičius: sveikas skaičius] |
Not including features with empty or no geometry |
Total number of points generated |
|
[skaičius: sveikas skaičius] |
|
Number of missed points |
|
[skaičius: sveikas skaičius] |
The number of points that could not be generated due to the minimum distance constraint. |
Pythono kodas
Algorithm ID: native:randompointsonlines
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
algoritmo id rodomas, kai užvedate pelę virš algoritmo apdorojimo įrankinėje. parametrų žodynas teikia parametrų pavadinimus ir reikšmes. Daugiau informacijos apie tai, kaip vykdyti apdorojimo algoritmus Pythono konsolėje rasite skyriuje Using processing algorithms from the console.
24.1.21.15. Raster pixels to points
Creates a vector layer of points corresponding to each pixel in a raster layer.
Converts a raster layer to a vector layer, by creating point features for each individual pixel’s center in the raster layer. Any NoData pixels are skipped in the output.
Parametrai
Užrašas |
Pavadinimas |
Tipas |
Aprašymas |
|---|---|---|---|
Rastro sluoksnis |
|
[rastras] |
Įvesties rastro sluoksnis |
Juostos numeris |
|
[rastro juosta] |
Raster band to extract data from |
Lauko pavadinimas |
|
[tekstas] Default: ‚VALUE‘ |
Name of the field to store the raster band value |
Vector points |
|
[vektorius: taškas] Numatytas: |
Specify the resulting point layer of pixels centroids. One of:
Čia taipogi galima pakeisti failo koduotę. |
Išvestys
Užrašas |
Pavadinimas |
Tipas |
Aprašymas |
|---|---|---|---|
Vector points |
|
[vektorius: taškas] |
Resulting point layer with pixels centroids |
Pythono kodas
Algorithm ID: native:pixelstopoints
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
algoritmo id rodomas, kai užvedate pelę virš algoritmo apdorojimo įrankinėje. parametrų žodynas teikia parametrų pavadinimus ir reikšmes. Daugiau informacijos apie tai, kaip vykdyti apdorojimo algoritmus Pythono konsolėje rasite skyriuje Using processing algorithms from the console.
24.1.21.16. Raster pixels to polygons
Creates a vector layer of polygons corresponding to each pixel in a raster layer.
Converts a raster layer to a vector layer, by creating polygon features for each individual pixel’s extent in the raster layer. Any NoData pixels are skipped in the output.
Parametrai
Užrašas |
Pavadinimas |
Tipas |
Aprašymas |
|---|---|---|---|
Rastro sluoksnis |
|
[rastras] |
Įvesties rastro sluoksnis |
Juostos numeris |
|
[rastro juosta] |
Raster band to extract data from |
Lauko pavadinimas |
|
[tekstas] Default: ‚VALUE‘ |
Name of the field to store the raster band value |
Vector polygons |
|
[vektorius: poligonas] Numatytas: |
Specify the resulting polygon layer of pixel extents. One of:
Čia taipogi galima pakeisti failo koduotę. |
Išvestys
Užrašas |
Pavadinimas |
Tipas |
Aprašymas |
|---|---|---|---|
Vector polygons |
|
[vektorius: poligonas] |
Resulting polygon layer of pixel extents |
Pythono kodas
Algorithm ID: native:pixelstopolygons
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
algoritmo id rodomas, kai užvedate pelę virš algoritmo apdorojimo įrankinėje. parametrų žodynas teikia parametrų pavadinimus ir reikšmes. Daugiau informacijos apie tai, kaip vykdyti apdorojimo algoritmus Pythono konsolėje rasite skyriuje Using processing algorithms from the console.
24.1.21.17. Regular points
Creates a new point layer with its points placed in a regular grid within a given extent.
The grid is specified either by the spacing between the points (same spacing for all dimensions) or by the number of points to generate. In the latter case, the spacing will be determined from the extent. In order to generate a full rectangular grid, at least the number of points specified by the user is generated for the latter case.
Random offsets to the point spacing can be applied, resulting in a non-regular point pattern.
Numatytas meniu:
Parametrai
Užrašas |
Pavadinimas |
Tipas |
Aprašymas |
|---|---|---|---|
Input extent (xmin, xmax, ymin, ymax) |
|
[apimtis] |
Map extent for the random points Galimi metodai yra:
|
Point spacing/count |
|
[skaičius: sveikas skaičius] Numatytas: 100 |
Spacing between the points, or the number of points, depending
on whether |
Initial inset from corner (LH side) |
|
[skaičius: slankaus kablelio] Numatytas: 0.0 |
Offsets the points relative to the upper left corner. The value is used for both the X and Y axis. |
Apply random offset to point spacing |
|
[boolean] Numatytas: ne |
If checked the points will have a random spacing |
Use point spacing |
|
[boolean] Numatytas: Taip |
If unchecked the point spacing is not taken into account |
Output layer CRS |
|
[crs] Numatyta: Projekto CRS |
CRS of the random points layer |
Regular points |
|
[vektorius: taškas] Numatytas: |
Specify the output regular point layer. One of:
Čia taipogi galima pakeisti failo koduotę. |
Išvestys
Užrašas |
Pavadinimas |
Tipas |
Aprašymas |
|---|---|---|---|
Regular points |
|
[vektorius: taškas] |
The output regular point layer. |
Pythono kodas
Algorithm ID: qgis:regularpoints
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
algoritmo id rodomas, kai užvedate pelę virš algoritmo apdorojimo įrankinėje. parametrų žodynas teikia parametrų pavadinimus ir reikšmes. Daugiau informacijos apie tai, kaip vykdyti apdorojimo algoritmus Pythono konsolėje rasite skyriuje Using processing algorithms from the console.