Wichtig
Übersetzen ist eine Gemeinschaftsleistung Sie können mitmachen. Diese Seite ist aktuell zu 100.00% übersetzt.
27.3. Die Werkzeugkiste
Die Verarbeitungswerkzeuge () ist das Hauptelement der Verarbeitungs-GUI und dasjenige, das Sie bei Ihrer täglichen Arbeit am ehesten verwenden werden. Sie zeigt eine Liste aller verfügbaren Algorithmen, gruppiert in verschiedenen Blöcken, die Anbieter genannt werden, sowie benutzerdefinierte Modelle und Skripte, die Sie hinzufügen können, um die Palette der Werkzeuge zu erweitern. Die Toolbox ist somit der Zugangspunkt, um sie auszuführen, sei es als einzelner Prozess oder als Batch-Prozess, der mehrere Ausführungen desselben Algorithmus auf verschiedenen Eingabesätzen umfasst.
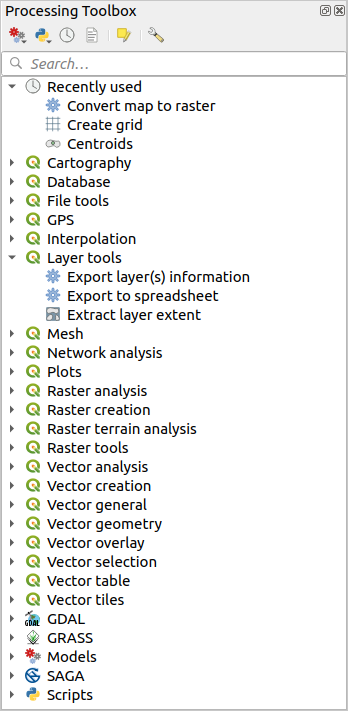
Abb. 27.6 Verarbeitungswerkzeuge
Anbieter können im Dialog Verarbeitungseinstellungen (de)aktiviert werden. Standardmäßig sind nur Provider aktiv, die nicht auf Anwendungen von Drittanbietern angewiesen sind (d.h. solche, die nur QGIS-Elemente zur Ausführung benötigen). Algorithmen, die externe Anwendungen benötigen, müssen möglicherweise zusätzlich konfiguriert werden. Die Konfiguration von Providern wird in einem späteren Kapitel in diesem Handbuch erklärt.
Im oberen Teil des Werkzeugkastens finden Sie eine Reihe von Werkzeugen:
mit
 Modelle arbeiten: Erzeuge neues Modell…, Vorhandenes Modell öffnen… und Modell zur Werkzeugkiste hinzufügen…;
Modelle arbeiten: Erzeuge neues Modell…, Vorhandenes Modell öffnen… und Modell zur Werkzeugkiste hinzufügen…;mit
 Skripte arbeiten: Erzeuge neues Skript…, Neues Skript aus Vorlage erzeugen…, Vorhandenes Skript öffnen… und Skript zur Werkzeugkiste hinzufügen…;
Skripte arbeiten: Erzeuge neues Skript…, Neues Skript aus Vorlage erzeugen…, Vorhandenes Skript öffnen… und Skript zur Werkzeugkiste hinzufügen…;schalten Sie die Werkzeugkiste mit der Schaltfläche
 Objekte insitu ändern auf die gefilterte Ansicht um: Es werden nur die Algorithmen angezeigt, die für die Ausführung auf dem aktiven Layer geeignet sind, ohne dass ein neuer Layer ausgegeben wird;
Objekte insitu ändern auf die gefilterte Ansicht um: Es werden nur die Algorithmen angezeigt, die für die Ausführung auf dem aktiven Layer geeignet sind, ohne dass ein neuer Layer ausgegeben wird;
Unterhalb dieser Symbolleiste befindet sich ein Feld für die Suche, mit dem Sie die benötigten Werkzeuge leicht finden können. Sie können jedes Wort oder jeden Satz in das Textfeld eingeben. Beachten Sie, dass sich die Anzahl der Algorithmen, Modelle oder Skripte in der Toolbox während der Eingabe auf diejenigen reduziert, die den von Ihnen eingegebenen Text in ihrem Namen oder Schlüsselwort enthalten.
Bemerkung
Oben in der Liste der Algorithmen werden die zuletzt verwendeten Tools angezeigt; das ist praktisch, wenn Sie ein Tool erneut ausführen möchten.
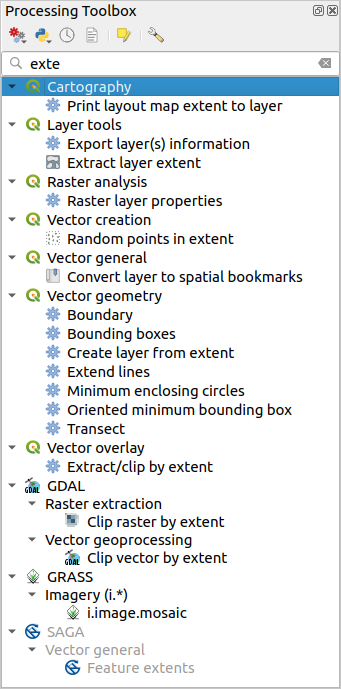
Abb. 27.7 Im Fenster Verarbeitungswerkzeuge werden nur passende Suchergebnisse angezeigt
Um ein Werkzeug auszuführen, doppelklicken Sie einfach auf den Namen des Werkzeugs in der Toolbox.
27.3.1. Der Algorithmus Dialog
Nach einem Doppelklick auf den Namen des Algorithmus, den Sie ausführen möchten, wird ein Dialogfeld ähnlich dem in Abb. 27.8 unten angezeigt (in diesem Fall entspricht das Dialogfeld dem Algorithmus Zentroide).
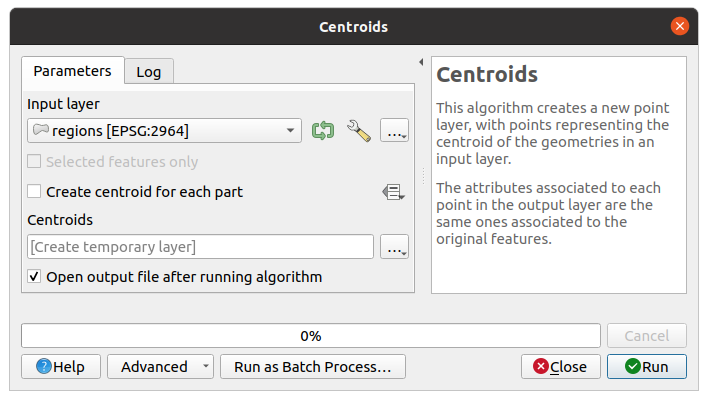
Abb. 27.8 Algorithmus-Dialog - Parameter-Reiter
Der Dialog zeigt auf der linken Seite zwei Reiter (Parameter und Protokoll), auf der rechten Seite die Algorithmusbeschreibung und am unteren Rand eine Reihe von Schaltflächen.
27.3.1.1. Parameter-Typen
Die Registerkarte Parameter dient zum Einstellen der Eingabewerte, die der Algorithmus zur Ausführung benötigt. Sie zeigt eine Liste von Eingabewerten und Konfigurationsparametern, die eingestellt werden müssen. Je nach den Anforderungen des auszuführenden Algorithmus hat sie natürlich einen anderen Inhalt und wird automatisch auf der Grundlage dieser Anforderungen erstellt.
Tipp
Eigene Standardwerte für Algorithmusparameter festlegen
Algorithmus-Dialoge öffnen sich mit einigen Parametern, die mit Werten aus der QGIS-Installation vorbelegt sind. Es ist jedoch möglich, Ihre eigenen Standardwerte für bestimmte Algorithmus-Parameter zu setzen, sodass sie beim Start des Algorithmus verwendet werden.
Obwohl die Anzahl und Art der Parameter von den Eigenschaften des Algorithmus abhängt, ist die Struktur für alle ähnlich. Die Parameter, die Sie in der Tabelle finden, können folgende Typen sein:
Ein Vektorlayer, um aus einer Liste aller in QGIS verfügbaren (aktuell geöffneten) Vektorlayer auszuwählen. Sie können auch ungeladene Layer verwenden: Drücken Sie die Schaltfläche … auf der rechten Seite des Widgets und wählen Sie:
Datei auswählen…: wählt eine Datei auf der Festplatte mit dem Datei-Explorer des Betriebssystems aus
Layer suchen…: öffnet das Browser Bedienfeld, das es erlaubt, die Layer direkt aus Datenbankquellen (PostgreSQL, SQL Server, Oracle, …), Webservices (WFS, AFS, …) oder Dateien auf der Festplatte zu übernehmen.
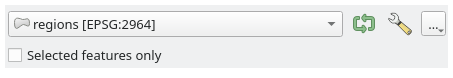
Abb. 27.9 Vektorlayer-Auswahlfeld
Bemerkung
Standardmäßig zeigt das Layer-Widget das KBS des Layers zusammen mit seinem Namen an. Wenn Sie diese zusätzlichen Informationen nicht sehen möchten, können Sie diese Funktion im Dialogfeld Verarbeitungseinstellungen deaktivieren, indem Sie die Option deaktivieren.
Das Vektor-Eingabe-Widget hat außerdem folgende Elemente:
eine Schaltfläche Iteration
 : Wenn diese Schaltfläche aktiviert ist, wird der Algorithmus wiederholt für jedes seiner Objekte ausgeführt, anstatt nur einmal für den gesamten Layer, und erzeugt so viele Ausgaben wie der Algorithmus ausgeführt wird. Auf diese Weise kann der Prozess automatisiert werden, wenn alle Objekte in einem Layer separat verarbeitet werden müssen. Enthält der Algorithmus mehrere Eingabevektoren, über die iteriert werden kann, wird die Iteration nur für den ersten aktivierten Parameter durchgeführt, und zwar in der Reihenfolge, in der die Parameter im Algorithmus angegeben sind.
: Wenn diese Schaltfläche aktiviert ist, wird der Algorithmus wiederholt für jedes seiner Objekte ausgeführt, anstatt nur einmal für den gesamten Layer, und erzeugt so viele Ausgaben wie der Algorithmus ausgeführt wird. Auf diese Weise kann der Prozess automatisiert werden, wenn alle Objekte in einem Layer separat verarbeitet werden müssen. Enthält der Algorithmus mehrere Eingabevektoren, über die iteriert werden kann, wird die Iteration nur für den ersten aktivierten Parameter durchgeführt, und zwar in der Reihenfolge, in der die Parameter im Algorithmus angegeben sind.|Optionen| Fortgeschrittene Optionen, um Einstellungen für diesen spezifischen Parameter vorzunehmen. Diese Einstellungen betreffen:
Filterung ungültiger Objekte: ermöglicht es, die Standardmethode für die Behandlung von Objekten mit ungültigen Geometrien zu überschreiben
guilabel:Zu verarbeitende Objekte beschränken: optionale Begrenzung der Anzahl der verarbeiteten Objekte aus der Quelle
Objektfilter: ermöglicht die Eingabe eines Ausdrucks zur dynamischen Unterteilung des Layers beim Ausführen des Tools, sodass keine separaten Schritte zur Festlegung von Layer-Filtern oder zur Erstellung von Layer-Untergruppen erforderlich sind.
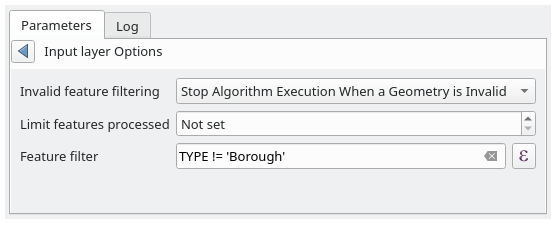
Abb. 27.10 Erweiterte Optionen für das Vektor-Eingabe-Widget
Es ist auch möglich, die Ausführung des Algorithmus auf Nur gewählte Objekte zu beschränken.
Eine Tabelle, um aus einer Liste aller in QGIS verfügbaren auszuwählen. Nicht-räumliche Tabellen werden in QGIS wie Vektor-Layer geladen und verwenden das gleiche Werkzeug.
Ein Rasterlayer, zur Auswahl aus einer Liste aller in QGIS verfügbaren Layer. Der Selektor enthält auch einen … Button auf der rechten Seite, mit dem Sie Dateinamen auswählen können, die Layer repräsentieren, die derzeit nicht in QGIS geladen sind.
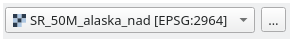
Abb. 27.11 Raster-Eingabe-Widget
Eine Option, um aus einer Auswahlliste von möglichen Optionen auszuwählen.
Ein numerischer Wert, der in ein Eingabefeld eingegeben wird. In einigen Kontexten (wenn der Parameter auf der Ebene des Objekts und nicht des Layers gilt), finden Sie eine Schaltfläche
 Datendefinierte Übersteuerung an seiner Seite, die es Ihnen ermöglicht, den Ausdruckseditor zu öffnen und einen mathematischen Ausdruck einzugeben, um variable Werte für den Parameter zu erzeugen. Einige nützliche Variablen, die sich auf die in QGIS geladenen Daten beziehen, können zu Ihrem Ausdruck hinzugefügt werden, sodass Sie einen von einer dieser Variablen abgeleiteten Wert auswählen können, wie z.B. die Zellengröße eines Layers oder die nördlichste Koordinate eines anderen Layers.
Datendefinierte Übersteuerung an seiner Seite, die es Ihnen ermöglicht, den Ausdruckseditor zu öffnen und einen mathematischen Ausdruck einzugeben, um variable Werte für den Parameter zu erzeugen. Einige nützliche Variablen, die sich auf die in QGIS geladenen Daten beziehen, können zu Ihrem Ausdruck hinzugefügt werden, sodass Sie einen von einer dieser Variablen abgeleiteten Wert auswählen können, wie z.B. die Zellengröße eines Layers oder die nördlichste Koordinate eines anderen Layers.
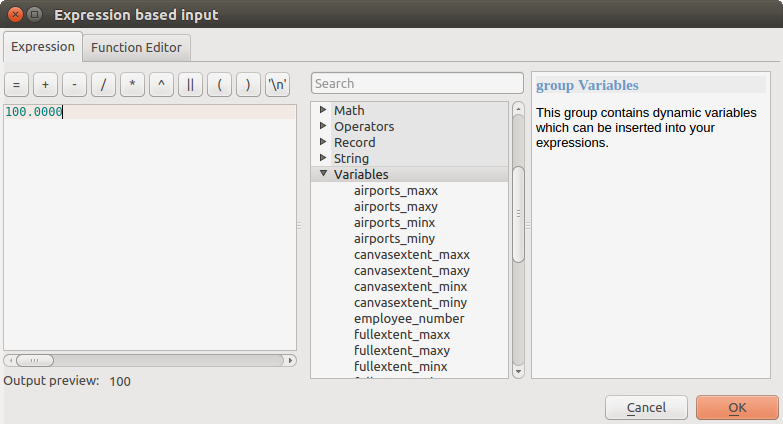
Abb. 27.12 Ausdrucksbasierte Eingabe
Ein Bereich mit Minimal- und Maximalwerten, die in zwei Feldern eingegeben werden.
Eine Textzeichenfolge, die in ein Textfeld eingefügt werden kann.
Ein Feld, um aus der Attributtabelle eines Layer oder einer einzelnen Tabelle zu wählen, die in einem anderen Parameter ausgewählt wurde.
Ein Koordinatenbezugssystem. Sie können es unter den zuletzt verwendeten aus der Dropdown-Liste oder aus dem Dialogfeld KBS-Auswahl auswählen, das erscheint, wenn Sie auf die Schaltfläche auf der rechten Seite klicken.
Ein Ausdehnung, ein Eingabefeld, das ein Rechteck durch seine Eckkoordinaten im Format
xmin, xmax, ymin, ymaxdefiniert. Drücken Sie die Schaltfläche Auf aktuelle Kartenansicht setzen, um die Kartenansicht zu verwenden. Wenn Sie auf den Pfeil auf der rechten Seite des Werteselektors klicken, erscheint ein Pop-up-Menü, das Ihnen folgende Optionen bietet:
Auf aktuelle Kartenansicht setzen, um die Kartenansicht zu verwenden. Wenn Sie auf den Pfeil auf der rechten Seite des Werteselektors klicken, erscheint ein Pop-up-Menü, das Ihnen folgende Optionen bietet:menuselection:Aus Layer berechnen –>: füllt das Textfeld mit den Koordinaten des Begrenzungsrahmens eines Layers, der aus den geladenen Layern ausgewählt werden kann
menuselection:Aus Layoutkarte berechnen –>: füllt das Textfeld mit den Koordinaten eines aus einem Layout im aktuellen Projekt ausgewählten Kartenelements
: füllt das Textfeld mit den Koordinaten eines gespeicherten Lesezeichens
Zeichnen auf der Kartenansicht: Das Parameterfenster wird ausgeblendet, so dass Sie auf die Kartenansicht klicken und ziehen können. Sobald Sie das Ausdehnungsrechteck definiert haben, erscheint das Dialogfeld wieder und enthält die Werte im Textfeld für die Ausdehnung.

Abb. 27.13 Ausdehnung Auswahl
Eine Liste von Elementen (Raster- oder Vektor-Layer, Tabellen, Felder), aus der Sie auswählen können. Klicken Sie auf die Schaltfläche … links neben der Option, um einen Dialog wie den folgenden anzuzeigen. Die Mehrfachauswahl ist erlaubt, und wenn der Dialog geschlossen wird, wird die Anzahl der ausgewählten Elemente im Parametertextfeld-Widget angezeigt.
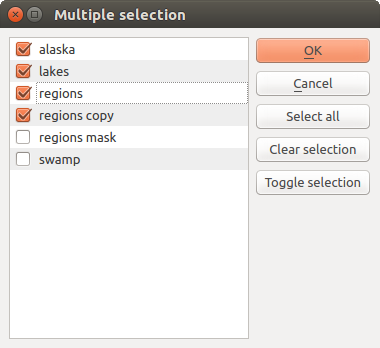
Abb. 27.14 Mehrfachauswahl
Eine kleine Tabelle, die vom Benutzer bearbeitet werden kann. Diese werden u.a. zur Definition von Parametern wie Lookup-Tabellen verwendet.
Klicken Sie auf den Knopf auf der rechten Seite, um die Tabelle zu sehen und zu editieren.
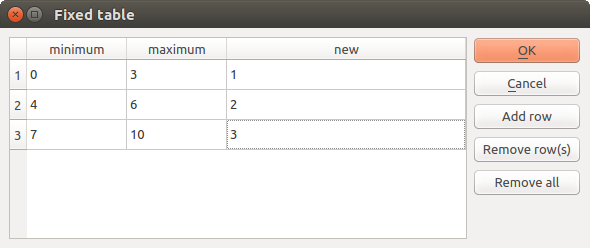
Abb. 27.15 Tabelle
In Abhängigkeit vom Algorithmus kann die Anzahl der Zeilen verändert werden oder auch nicht, indem Sie auf den Knopf rechts neben dem Fenster klicken.
Bemerkung
Einige Algorithmen benötigen viele Parameter, z.B. müssen Sie bei Raster calculator manuell die Zellengröße, den Umfang und das KBS angeben. Sie können die manuelle Auswahl aller Parameter vermeiden, wenn der Algorithmus über den Parameter Referenz Layer verfügt. Mit diesem Parameter können Sie einen Layer auswählen, dessen Eigenschaften (Zellgröße, Ausdehnung, KBS) verwendet werden.
27.3.1.2. Protokollierung der Ausführung
Neben der Registerkarte Parameter gibt es eine weitere Registerkarte namens Protokoll (siehe Abb. 27.16 unten). In diese Registerkarte werden die Informationen geschrieben, die der Algorithmus während seiner Ausführung liefert, sodass Sie die Ausführung verfolgen können und mehr Details über den Algorithmus erfahren, während er läuft. Informationen zur Algorithmusausführung werden auch im Bedienfeld ausgegeben
Beachten Sie, dass nicht alle Algorithmen Informationen in die Registerkarte Protokoll schreiben, und viele von ihnen laufen möglicherweise im Stillen, ohne dass sie eine andere Ausgabe als die endgültigen Dateien erzeugen. In diesem Fall sollten Sie das Bedienfeld Protokoll überprüfen.
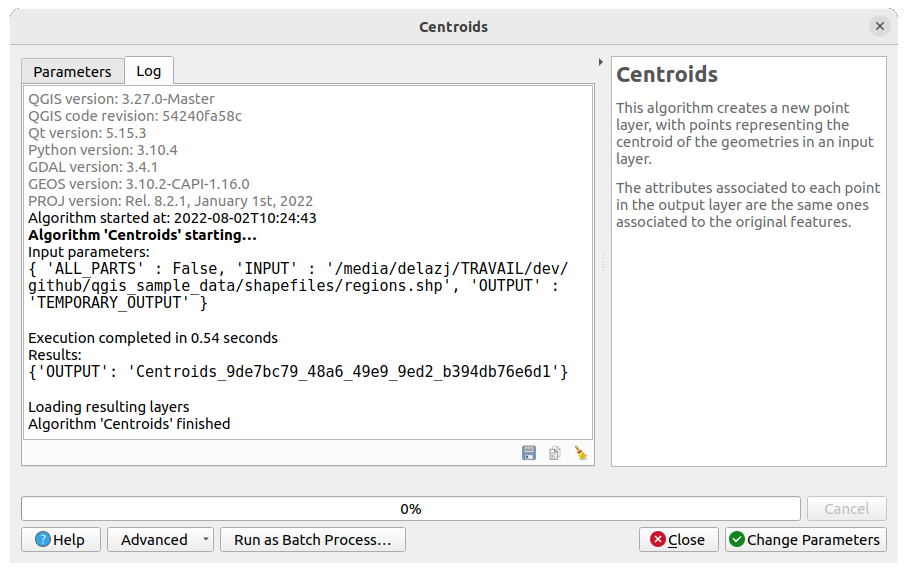
Abb. 27.16 Algorithmus-Dialog - Protokoll-Reiter
Am unteren Rand der Registerkarte Protokoll finden Sie die Schaltflächen  Protokoll in Datei speichern,
Protokoll in Datei speichern,  Protokoll in Zwischenablage kopieren und
Protokoll in Zwischenablage kopieren und ![]() Protokoll löschen. Diese sind besonders praktisch, wenn Sie die Option Dialog nach Ausführung des Algorithmus offen lassen im Allgemein Teil der Verarbeitungsoptionen aktiviert haben.
Protokoll löschen. Diese sind besonders praktisch, wenn Sie die Option Dialog nach Ausführung des Algorithmus offen lassen im Allgemein Teil der Verarbeitungsoptionen aktiviert haben.
27.3.1.3. Andere Werkzeuge
Auf der rechten Seite des Dialogs finden Sie eine kurze Beschreibung des Algorithmus, die Ihnen hilft, seinen Einsatzzweck und seine Grundideen zu verstehen. Wenn eine solche Beschreibung nicht verfügbar ist, wird das Bedienfeld nicht angezeigt.
Für eine detailliertere Hilfedatei, die z. B. eine Beschreibung aller verwendeten Parameter oder Beispiele enthält, finden Sie am unteren Rand des Dialogs eine Schaltfläche Hilfe, die Sie zur Dokumentation der Verarbeitungsalgorithmen oder zur Dokumentation des Anbieters (für einige Drittanbieter) führt.
Das Ausklappmenü unten links auf dem Fenster bietet Funktionen zur Wiederverwendung der im Dialog definierten Konfiguration, ohne den Algorithmus auszuführen:
 Algorithmeneinstellungen…: erlaubt das Überschreiben von Verarbeitungseinstellungen für die aktuelle Algorithmusausführung. Weitere Einzelheiten unter Algorithmus-Einstellungen überschreiben.
Algorithmeneinstellungen…: erlaubt das Überschreiben von Verarbeitungseinstellungen für die aktuelle Algorithmusausführung. Weitere Einzelheiten unter Algorithmus-Einstellungen überschreiben. Als Python-Befehl kopieren: ermöglicht das einfache Kopieren des entsprechenden PyQGIS-Befehls, um das Werkzeug mit den im Dialog definierten Parametern auszuführen
Als Python-Befehl kopieren: ermöglicht das einfache Kopieren des entsprechenden PyQGIS-Befehls, um das Werkzeug mit den im Dialog definierten Parametern auszuführen Als qgis_process-Befehl kopieren: erlaubt die einfache Generierung von qgis_process Kommando, inklusive der Umgebungseinstellungen wie Entfernungseinheiten, Flächeneinheiten, Ellipsoid, und komplexer Parameterwerte wie GeoPackage Ausgaben mit bestimmten Layern
Als qgis_process-Befehl kopieren: erlaubt die einfache Generierung von qgis_process Kommando, inklusive der Umgebungseinstellungen wie Entfernungseinheiten, Flächeneinheiten, Ellipsoid, und komplexer Parameterwerte wie GeoPackage Ausgaben mit bestimmten Layern Als JSON kopieren: alle Einstellungen des Befehls werden in ein
Als JSON kopieren: alle Einstellungen des Befehls werden in ein JSONFormat kopiert, bereit, von qgis_process verwendet zu werden. Dies ist ein bequemer Weg, um das erwartete Format der Befehle zu sehen, sogar für komplexe Parameter (wie TIN Interpolationsparameter). Sie können diese einfach speichern und später wiederherstellen, indem Sie die Werte einfügen.
Die Schaltfläche Als Batch-Prozess starten… löst den Batch-Verarbeitungsmodus aus, der es erlaubt, mehrere Instanzen des Algorithmus mit einer Vielzahl von Parametern zu konfigurieren und auszuführen. Ein Als Einzelprozess starten… hilft Ihnen, aus dem Batch-Modus zurückzuschalten.
Wenn die Ausführung eines Algorithmus beendet ist (entweder erfolgreich oder nicht), wird eine neue Schaltfläche Parameter ändern angezeigt, solange die Registerkarte Protokoll aktiv ist.
27.3.1.4. Algorithmus-Einstellungen überschreiben
Ausgelöst durch das Erweitert-Dropdown-Menü am unteren Rand eines Algorithmus-Dialogs, zeigt die Option Algorithmuseinstellungen… ein Bedienfeld, das dem Benutzer erlaubt, allgemeine Verarbeitungseinstellungen zu kontrollieren, die nur für die Ausführung dieses Algorithmus gelten. Es ist als Ort gedacht, an dem ein Benutzer seine Globalen Verarbeitungseinstellungen ad-hoc überschreiben kann, ohne seine üblichen Standardeinstellungen ändern zu müssen.
Die folgenden Einstellungen können überschrieben werden:
Filterung ungültiger Objekte: Im Gegensatz zu den bestehenden parametrischen Einstellungen gilt die hier festgelegte Behandlungsmethode für alle Eingaben des Algorithmus.
Berechnungseinstellungen, wie z.B. Abstandseinheiten und Flächeneinheiten, die für Entfernungs-/Flächenmessungen verwendet werden
Umgebungseinstellungen, wie Temporärerverzeichnis und Zu verwendende Threadanzahl
27.3.1.5. Anmerkung zum Thema Projektionen
Die Ausführung der Verarbeitungsalgorithmen erfolgt immer im Koordinatenbezugssystem (KBS) des Input-Layers. Aufgrund der on-the-fly Reprojektion von QGIS kann es vorkommen, dass sich zwei Layer scheinbar überlappen und übereinstimmen, was aber nicht der Fall ist, wenn die Originalkoordinaten verwendet werden, ohne sie auf ein gemeinsames Koordinatensystem zu projizieren. Wann immer Sie mehr als einen Layer als Eingabe für einen nativen QGIS Algorithmus verwenden, egal ob Vektor oder Raster, werden die Layer alle neu projiziert, um mit dem Koordinatenreferenzsystem des ersten Eingabe-Layers übereinzustimmen.
Dies gilt jedoch weniger für die meisten Algorithmen anderer Entwickler, die in der Verarbeitungs-Umgebung verfügbar sind. Diese gehen größtenteils davon aus, dass sich alle Layer bereits in einem gemeinsamen Koordinatensystem befinden und zur Analyse bereit sind.
Standardmäßig wird im Parameterdialog eine Beschreibung des KBS jedes Layers zusammen mit seinem Namen angezeigt, was die Auswahl von Layern, die das gleiche KBS haben, für die Verwendung als Eingabe-Layer erleichtert. Wenn Sie diese zusätzlichen Informationen nicht sehen möchten, können Sie diese Funktion im Dialogfeld Verarbeitungseinstellungen deaktivieren, indem Sie die Option Layer-KBS-Definition in Auswahlfeldern anzeigen abwählen.
Wenn Sie versuchen, einen Algorithmus auszuführen, der als Eingabe zwei oder mehr Layer mit nicht übereinstimmenden KBS verwendet, wird ein Warndialog angezeigt. Dies geschieht dank der Option Warnung vor der Ausführung, wenn die KBS der Layer nicht übereinstimmen.
Sie können den Algorithmus immer noch ausführen, seien Sie sich aber dessen bewusst, dass dies in den meisten Fällen zu falschen Ergebnissen führt, so z.B. leere Layer, da sich die Eingabe-Layer nicht überlappen.
Tipp
Verwenden Sie Verarbeitungsalgorithmen um die Projektion anzugleichen
Wenn ein Algorithmus aufgrund von nicht übereinstimmenden KBS nicht erfolgreich auf mehreren Eingabe-Layern ausgeführt werden kann, verwenden Sie den QGIS-internen Algorithmus Reproject layer, um die Layer auf das gleiche KBS zu projizieren, bevor Sie den Algorithmus mit diesen Ausgaben ausführen.
27.3.2. Von Algorithmen erstellte Datenobjekte
Von Algorithmen erstellte Datenobjekte können jeder der folgenden Typen sein:
Rasterlayer
Vektorlayer
Tabelle
HTML-Datei (wird für Text und grafische Ausgabe verwendet)
These are all saved to disk, and the parameters table will contain a text box corresponding to each one of these outputs, where you can type the output channel to use for saving it. An output channel contains the information needed to save the resulting object somewhere. In the most usual case, you will save it to a file, but in the case of vector layers, and when they are generated by native algorithms (algorithms not using external applications) you can also save to a PostGIS, GeoPackage or SpatiaLite database, or a memory layer.Diese werden alle auf der Festplatte gespeichert, und die Parametertabelle enthält für jede dieser Ausgaben ein Textfeld, in das Sie den Ausgabekanal eingeben können, der zum Speichern verwendet werden soll. Ein Ausgabekanal enthält die Informationen, die benötigt werden, um das resultierende Objekt irgendwo zu speichern. Im Normalfall werden Sie es in einer Datei speichern, aber im Falle von Vektorlayern und wenn sie von nativen Algorithmen (Algorithmen, die keine externen Anwendungen verwenden) erzeugt werden, können Sie auch in einer PostGIS-, GeoPackage- oder SpatiaLite-Datenbank oder in einem Memory Layer speichern
Um einen Ausgabekanal auszuwählen, klicken Sie einfach auf den Knopf auf der rechten Seite des Textfelds und Sie werden ein kleines Kontextmenü mit den verfügbaren Optionen sehen.
Im häufigsten Fall werden Sie Speichern in einer Datei auswählen. Wenn Sie diese Option auswählen, werden Sie in einem „Datei-speichern“- Dialog aufgefordert, den gewünschten Dateipfad auszuwählen. Unterstützte Dateierweiterungen werden in der Dateiformatauswahl des Dialogs gezeigt, abhängig von der Art der Ausgabe und des Algorithmus.
Das Format der Ausgabe wird durch die Dateinamenerweiterung definiert. Die unterstützten Formate hängen davon ab, was vom Algorithmus selbst unterstützt wird. Um ein Format auszuwählen, wählen Sie einfach die entsprechende Dateierweiterung aus (oder fügen Sie sie hinzu, wenn Sie stattdessen direkt den Dateipfad eingeben). Wenn die Erweiterung des eingegebenen Dateipfads keinem der unterstützten Formate entspricht, wird eine Standarderweiterung an den Dateipfad angehängt, und das dieser Erweiterung entsprechende Dateiformat wird zum Speichern des Layers oder der Tabelle verwendet. Die Standard-Erweiterungen sind .dbf für Tabellen, .tif für Raster-Layer und .gpkg für Vektor-Layer. Diese können im Einstellungsdialog geändert werden, indem man ein anderes von QGIS unterstütztes Format auswählt.
Wenn Sie keinen Dateinamen in das Ausgabefeld eingeben (oder die entsprechende Option im Kontextmenü wählen), wird das Ergebnis als temporäre Datei im entsprechenden Standard-Dateiformat gespeichert und beim Beenden von QGIS gelöscht (Vorsicht, falls Sie Ihr Projekt speichern und es temporäre Layer enthält).
Sie können einen Standardordner für Ausgabedatenobjekte festlegen. Gehen Sie in den Einstellungsdialog (Sie können ihn über das Menü öffnen), und in der Gruppe Allgemein finden Sie einen Parameter namens Ausgabeordner. Dieser Ausgabeordner wird als Standardpfad verwendet, wenn Sie bei der Ausführung eines Algorithmus nur einen Dateinamen ohne Pfad eingeben (z. B. myfile.shp).
Wenn Sie einen Algorithmus ausführen, der einen Vektorlayer im iterativen Modus verwendet, wird der eingegebene Dateipfad als Basispfad für alle erstellten Dateien, die mithilfe des Basisnamens benannt werden und an die eine Nummer, die den Index der Iteration darstellt, angehängt wird, verwendet. Die Dateierweiterung (und das Format) wird für alle so erstellten Dateien benutzt.
Algorithmen erzeugen neben Raster Layern und Tabellen auch Grafiken und Texte als HTML-Dateien. Diese Ergebnisse werden am Ende der Algorithmusausführung in einem neuen Dialogfeld angezeigt. Dieser Dialog speichert die Ergebnisse aller Algorithmen während der aktuellen Sitzung und kann jederzeit durch Auswahl von aus dem QGIS-Hauptmenü angezeigt werden.
Einige externe Anwendungen können Dateien (ohne besondere Einschränkungen bei der Dateinamen-Erweiterung) als Ausgabe erzeugen, die nicht zu einer der oben genannten Kategorien gehören. Diese Ausgabedateien werden nicht von QGIS verarbeitet (weder geöffnet noch in das aktuelle QGIS-Projekt integriert), da diese meistens nicht von QGIS unterstützt werden. Dies ist beispielsweise der Fall beim LAS-Format für LIDAR-Daten. Die Dateien werden erstellt, aber Sie werden nicht in QGIS angezeigt.
Für alle anderen Arten von Ausgaben finden Sie ein Kontrollkästchen, mit dem Sie festlegen können, ob die Datei in QGIS geladen werden soll oder nicht, wenn sie durch den Algorithmus erzeugt wurde. Standardmäßig werden alle Dateien angezeigt.
Optionale Ausgaben werden nicht unterstützt, alle Ausgaben werden erstellt, aber Sie können über das entsprechende Kontrollkästchen definieren, wenn Sie an einer bestimmten Ausgabe nicht interessiert sind, was es im Wesentlichen zu einer optionalen Ausgabe macht (Der Layer wird zwar erstellt, aber nur temporär im Hintergrund, wenn Sie das Textfeld leer lassen, und wieder gelöscht, sobald Sie QGIS schließen).



