Importante
La traducción es un esfuerzo comunitario puede unirse. Esta página está actualmente traducida en |progreso de traducción|.
20.1. Introducción a los datos GNSS/GPS
20.1.1. ¿Qué es GPS?
GPS, el Sistema de Posicionamiento Global, es un sistema basado en satélites que permite a cualquier persona con un receptor GPS encontrar su posición exacta en cualquier parte del mundo. El GPS se utiliza como ayuda a la navegación, por ejemplo en aviones, barcos y excursionistas. El receptor GPS utiliza las señales de los satélites para calcular su latitud, longitud y (a veces) elevación. La mayoría de los receptores también tienen capacidad para almacenar:
ubicaciones (conocidas como puntas de vía)
secuencias de lugares que componen una ruta planificada
y una traza del movimiento del receptor a lo largo del tiempo.
Los puntos de vía, las rutas y las trazas son los tres tipos básicos de características de los datos GPS. QGIS muestra los puntos de via en capas de puntos, mientras que las rutas y las trazas se muestran en capas de líneas.
Nota
QGIS también admite receptores GNSS. Pero seguimos usando el término GPS en esta documentación.
20.1.2. Transferencia o carga de datos GPS
20.1.2.1. Cargar un archivo GPX
Hay docenas de formatos de archivo diferentes para almacenar datos GPS. El formato que utiliza QGIS se llama GPX (formato de intercambio de GPS), que es un formato de intercambio estándar que puede contener cualquier número de waypoints, rutas y tracks en el mismo archivo.
Para cargar un archivo GPX:
Abra la pestaña GPS del cuadro de diálogo Gestor de fuentes de datos, es decir:
Utilice el botón … Navegador situado junto a la opción GPX conjunto de datos para seleccionar el archivo GPX
Utilice las casillas de verificación para seleccionar los Tipos de objetos espaciales que desea cargar desde el archivo. Cada tipo de característica (Puntos de vías, Trazas o Rutas) se cargará en una capa separada.
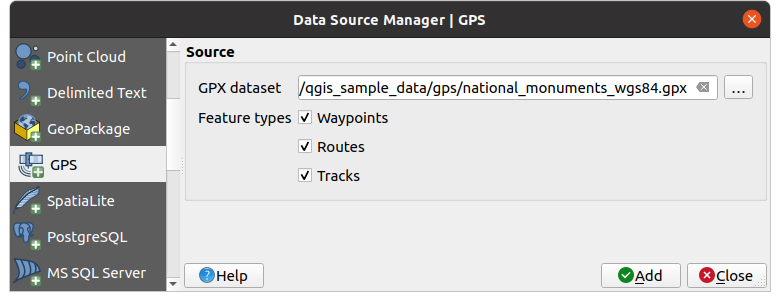
Figura 20.1 Diálogo de carga de datos GPS
20.1.2.2. Carga hacia o desde un dispositivo
Existen muchos tipos diferentes de dispositivos y formatos GPS. Dado que QGIS utiliza archivos GPX, se necesita una forma de convertir otros formatos de archivo GPS a GPX. QGIS puede hacerlo utilizando el programa gratuito GPSBabel. GPSBabel puede ayudarte a convertir waypoints, tracks y rutas entre receptores GPS populares como Garmin o Magellan y programas de mapas como Google Earth o Basecamp. Es compatible con cientos de receptores GPS y programas. También puede transferir datos GPS entre tu ordenador y un dispositivo GPS.
En 
![]()
![]() , QGIS le permite definir su propio tipo de dispositivo y establecer parámetros de conversión que más tarde podrían ser utilizados por el Procesamiento de algoritmos GPS.
, QGIS le permite definir su propio tipo de dispositivo y establecer parámetros de conversión que más tarde podrían ser utilizados por el Procesamiento de algoritmos GPS.
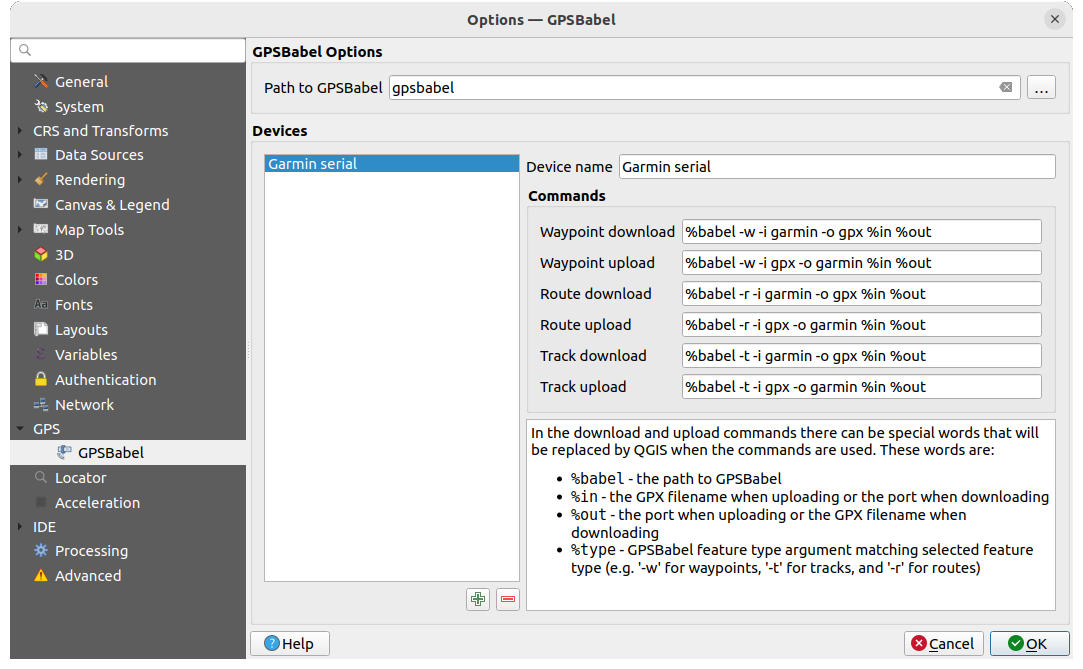
Figura 20.2 Ajustes de GPS Babel
Primero hay que definir la Ruta a los binarios GPSBabel.
A continuación, puede añadir su dispositivo. Puede actualizar la lista de dispositivos con el botón
 Añadir nuevo dispositivo o
Añadir nuevo dispositivo o  Eliminar dispositivo.
Eliminar dispositivo.Para cada dispositivo:
indique una Nombre del dispositivo.
se configuran diferentes Comandos que QGIS utilizará al interactuar con él, tales como:
Descarga de puntos de ruta del dispositivo
Subida de puntos de ruta al dispositivo
Descarga de Ruta del dispositivo
Subida de Ruta al dispositivo
Descarga de Traza desde el dispositivo
Subida de Traza al dispositivo
Aunque los comandos suelen ser los de GPSBabel, también puede utilizar cualquier otro programa de línea de comandos que pueda crear un archivo GPX. QGIS sustituirá las palabras claves
%type,``%in``, y%outcuando ejecuta el comando.Por ejemplo, si crea un tipo de dispositivo con el comando de descarga
gpsbabel %type -i garmin -o gpx %in %outy luego lo usa para descargar puntos de ruta desde el puerto/dev/ttyS0al archivooutput.gpx`, QGIS reemplazará las palabras clave y ejecutará el comandogpsbabel -w -i garmin -o gpx /dev/ttyS0 output.gpx.Lea el manual de GPSBabel para conocer las opciones de línea de comandos que pueden ser específicas para su caso de uso.
Una vez creado un nuevo tipo de dispositivo, aparecerá en las listas de dispositivos para los algoritmos de descarga y carga de GPS.
Nota
Las unidades GPS permiten almacenar datos en diferentes sistemas de coordenadas. Cuando descargue un archivo GPX (de su unidad GPS o de un sitio web) y luego lo cargue en QGIS, asegúrese de que los datos almacenados en el archivo GPX utilizan WGS 84 (latitud/longitud). QGIS lo espera, y es la especificación GPX oficial. Ver GPX 1.1 Schema Documentation.

