24.1.9. Modeler tools
Warning
These tools are only available in the model designer. They are not available in the Processing Toolbox.
24.1.9.1. Calculate expression
It calculates the result of a QGIS expression and eliminates the need to use the same expression multiple times throughout a model when the same result is required more than once. Additionally, it enables use cases that would otherwise not be possible. For instance, you can generate a timestamp value once and use it multiple times within the model, if the timestamp were recalculated every time, the values would vary during the model’s runtime.
Parameters
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Input |
|
[expression] |
Expression to calculate |
Outputs
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Value |
|
[Result Value] |
Calculated result value, the data type of the output will vary based on the specific expression used in the algorithm. |
Python code
Algorithm ID: native:calculateexpression
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
The algorithm id is displayed when you hover over the algorithm in the Processing Toolbox. The parameter dictionary provides the parameter NAMEs and values. See Using processing algorithms from the console for details on how to run processing algorithms from the Python console.
24.1.9.2. Conditional branch
Adds a conditional branch into a model, allowing parts of the model to be executed based on the result of an expression evaluation. Mostly by using tool dependencies to control the flow of a model.
Parameters
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Field |
|
[string] |
Name of the condition |
Field |
|
[expression] |
Expression to evaluate |
Outputs
None.
Python code
Algorithm ID: native:condition
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
The algorithm id is displayed when you hover over the algorithm in the Processing Toolbox. The parameter dictionary provides the parameter NAMEs and values. See Using processing algorithms from the console for details on how to run processing algorithms from the Python console.
24.1.9.3. Create directory
Creates a new directory on a file system. Directories will be created recursively, creating all required parent directories in order to construct the full specified directory path. No errors will be raised if the directory already exists.
Parameters
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Directory path |
|
[string] |
Folder path to create |
Outputs
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Output |
|
[folder] |
Created folder |
Python code
Algorithm ID: native:createdirectory
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
The algorithm id is displayed when you hover over the algorithm in the Processing Toolbox. The parameter dictionary provides the parameter NAMEs and values. See Using processing algorithms from the console for details on how to run processing algorithms from the Python console.
24.1.9.4. Feature filter
Filters features from the input layer and redirects
them to one or several outputs.
If you do not know about any attribute names that are common to all
possible input layers, filtering is only possible on the feature
geometry and general record mechanisms, such as $id and uuid.
Parameters
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Input layer |
|
[vector: any] |
The input layer. |
Outputs and filters (one or more) |
|
[same as input] |
The output layers with filters (as many as there are filters). |
Outputs
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Output (one or more) |
|
[same as input] |
The output layers with filtered features (as many as there are filters). |
Python code
Algorithm ID: native:filter
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
The algorithm id is displayed when you hover over the algorithm in the Processing Toolbox. The parameter dictionary provides the parameter NAMEs and values. See Using processing algorithms from the console for details on how to run processing algorithms from the Python console.
24.1.9.5. Filter layers by type
Filters layers by their type. Incoming layers will be directed to different outputs based on whether they are a vector or raster layer.
Parameters
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Input layer |
|
[layer] |
Generic Map Layer |
Outputs
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Vector features Optional |
|
[vector] |
A Vector Layer of the input, if compatible |
Raster layer Optional |
|
[raster] |
A Raster Layer of the input, if compatible |
Python code
Algorithm ID: native:filterlayersbytype
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
The algorithm id is displayed when you hover over the algorithm in the Processing Toolbox. The parameter dictionary provides the parameter NAMEs and values. See Using processing algorithms from the console for details on how to run processing algorithms from the Python console.
24.1.9.6. Load layer into project
Loads a layer to the current project.
Parameters
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Layer |
|
[layer] |
Layer to load in the legend |
Loaded layer name |
|
[string] |
Name of the loaded layer |
Outputs
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Layer |
|
[same as input] |
The (renamed) loaded layer |
Python code
Algorithm ID: native:loadlayer
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
The algorithm id is displayed when you hover over the algorithm in the Processing Toolbox. The parameter dictionary provides the parameter NAMEs and values. See Using processing algorithms from the console for details on how to run processing algorithms from the Python console.
24.1.9.7. Raise exception
Raises an exception and cancels a model’s execution. The exception message can be customized, and optionally an expression based condition can be specified. If an expression condition is used, then the exception will only be raised if the expression result is true. A false result indicates that no exception will be raised, and the model execution can continue uninterrupted.
Parameters
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Message |
|
[string] |
Message to display |
Condition Optional |
|
[expression] |
Expression to evaluate if true |
Outputs
A message in the log panel.
Python code
Algorithm ID: native:raiseexception
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
The algorithm id is displayed when you hover over the algorithm in the Processing Toolbox. The parameter dictionary provides the parameter NAMEs and values. See Using processing algorithms from the console for details on how to run processing algorithms from the Python console.
24.1.9.8. Raise message
Raises an information message in the log. The message can be customized, and optionally an expression based condition can be specified. If an expression condition is used, then the message will only be logged if the expression result is true. A false result indicates that no message will be logged.
Parameters
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Information message |
|
[string] |
Message to display |
Condition Optional |
|
[expression] |
Expression to evaluate if true |
Outputs
A message in the log panel.
Python code
Algorithm ID: native:raisemessage
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
The algorithm id is displayed when you hover over the algorithm in the Processing Toolbox. The parameter dictionary provides the parameter NAMEs and values. See Using processing algorithms from the console for details on how to run processing algorithms from the Python console.
24.1.9.9. Raise warning
Raises a warning message in the log. The warning message can be customized, and optionally an expression based condition can be specified. If an expression condition is used, then the warning will only be logged if the expression result is true. A false result indicates that no warning will be logged.
Parameters
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Message |
|
[string] |
Message to display |
Condition Optional |
|
[expression] |
Expression to evaluate if true |
Outputs
A message in the log panel.
Python code
Algorithm ID: native:raisewarning
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
The algorithm id is displayed when you hover over the algorithm in the Processing Toolbox. The parameter dictionary provides the parameter NAMEs and values. See Using processing algorithms from the console for details on how to run processing algorithms from the Python console.
24.1.9.10. Rename layer
Renames a layer.
Parameters
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Layer |
|
[layer] |
Layer to rename |
New name |
|
[string] |
The new name of the layer |
Outputs
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Layer |
|
[same as input] |
The (renamed) output layer |
Python code
Algorithm ID: native:renamelayer
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
The algorithm id is displayed when you hover over the algorithm in the Processing Toolbox. The parameter dictionary provides the parameter NAMEs and values. See Using processing algorithms from the console for details on how to run processing algorithms from the Python console.
24.1.9.11. Save log to file
Saves the model’s execution log to a file. Optionally, the log can be saved in a HTML formatted version.
Parameters
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Use HTML |
|
[Boolean] Default: False |
Use HTML formatting |
Outputs
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
File |
|
[string] |
Destination of the log |
Python code
Algorithm ID: native:savelog
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
The algorithm id is displayed when you hover over the algorithm in the Processing Toolbox. The parameter dictionary provides the parameter NAMEs and values. See Using processing algorithms from the console for details on how to run processing algorithms from the Python console.
24.1.9.12. Set project variable
Sets an expression variable for the current project.
Parameters
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Variable name |
|
[string] |
Name of the variable |
Variable value |
|
[string] |
Value to be stored |
Outputs
None.
Python code
Algorithm ID: native:setprojectvariable
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
The algorithm id is displayed when you hover over the algorithm in the Processing Toolbox. The parameter dictionary provides the parameter NAMEs and values. See Using processing algorithms from the console for details on how to run processing algorithms from the Python console.
24.1.9.13. String concatenation
Concatenates two strings into a single one in the Processing Modeler.
Parameters
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Input 1 |
|
[string] |
First string |
Input 2 |
|
[string] |
Second string |
Outputs
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Concatenation |
|
[string] |
The concatenated string |
Python code
Algorithm ID: native:stringconcatenation
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
The algorithm id is displayed when you hover over the algorithm in the Processing Toolbox. The parameter dictionary provides the parameter NAMEs and values. See Using processing algorithms from the console for details on how to run processing algorithms from the Python console.
24.1.9.14. Variable distance buffer
Warning
This algorithm is deprecated and can be removed anytime. Prefer using Buffer algorithm instead.
Computes a buffer area for all the features in an input layer.
The size of the buffer for a given feature is defined by an attribute, so it allows different features to have different buffer sizes.
See also
Parameters
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Input layer |
|
[vector: any] |
Input vector layer |
Distance field |
|
[tablefield: numeric] |
Attribute for the distance radius of the buffer |
Segments |
|
[numeric: integer] Default: 5 |
Controls the number of line segments to use to approximate a quarter circle when creating rounded offsets. |
Dissolve result |
|
[boolean] Default: False |
Choose to dissolve the final buffer, resulting in a single feature covering all input features. 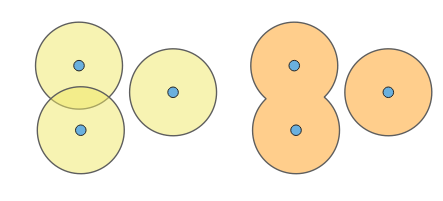
Fig. 24.8 Normal and dissolved buffer |
End cap style |
|
[enumeration] Default: Round |
Controls how line endings are handled in the buffer. 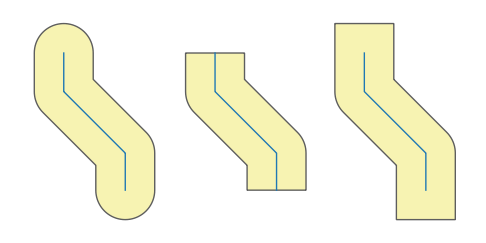
Fig. 24.9 Round, flat and square cap styles |
Join style |
|
[enumeration] Default: Round |
Specifies whether round, miter or beveled joins should be used when offsetting corners in a line. |
Miter limit |
|
[numeric: double] Default: 2.0 |
Only applicable for mitered join styles, and controls the maximum distance from the offset curve to use when creating a mitered join. |
Outputs
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Buffer |
|
[vector: polygon] |
Buffer polygon vector layer. |
Python code
Algorithm ID: qgis:variabledistancebuffer
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
The algorithm id is displayed when you hover over the algorithm in the Processing Toolbox. The parameter dictionary provides the parameter NAMEs and values. See Using processing algorithms from the console for details on how to run processing algorithms from the Python console.