2. Working with Project Files
2.1. Introducing QGIS projects
The state of your QGIS session is called a project.
QGIS works on one project at a time.
A setting can be project-specific or an application-wide default
for new projects (see section Options).
QGIS can save the state of your workspace into a
QGIS project file using the menu options
 or
or
 .
.
Note
If the project has been modified the * symbol will appear in the title bar
and QGIS will, by default, ask you if you would like to save the changes.
This behavior is controlled by the  Prompt to save project and data source changes when required
setting under .
Prompt to save project and data source changes when required
setting under .
You can load existing projects through  ,
or .
,
or .
From the Browser panel you can Open Project, Extract Symbols… – opens the style manager to export symbols to XML, add them to the default style, or export as PNG/SVG. You can also access the File Properties… dialog. The project file can be expanded to see its layers. The context menu of a layer offers the same actions as elsewhere in the browser.
At startup, a list of Project Templates and Recent Projects are displayed, including screenshots, names and file paths (for up to ten projects). The Recent Projects list is handy to access recently used projects. Double-click an entry to open the project or project template. Right-click an entry to Pin to List, Open Directory… or Remove from List. If you see your project on the Recent Projects list but can’t find it in your file manager use the Open Directory… option to help you locate projects that may be missing, moved or renamed. You can also go to Clear List if you want to remove all projects from the Recent Projects list. If you have pinned projects, the Clear List action will be followed by message box asking whether the pinned projects should also be removed. You can also add a layer to create a new project automatically. The lists will then disappear, giving way to the map canvas.
If you want to clear your session and start fresh, go to
 .
This will prompt you to save the existing project if
changes have been made since it was opened or last saved.
.
This will prompt you to save the existing project if
changes have been made since it was opened or last saved.
When you open a fresh project, the title bar will show Untitled Project until you
save it.
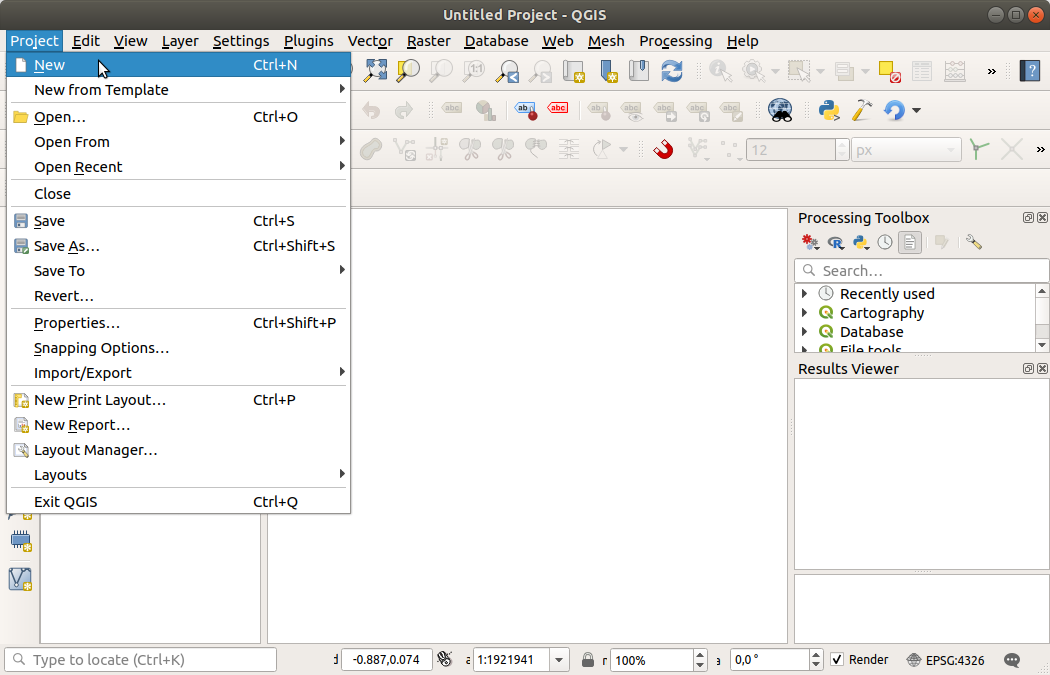
Fig. 2.1 Starting a new project in QGIS
The information saved in a project file includes:
Layers added
Which layers can be queried
Layer properties, including symbolization and styles
Layer notes
2D and 3D map views
Projection for each map view
Last viewed extent for each map
Print layouts
Print layout elements with settings
Print layout atlas settings
Digitizing settings
Table Relations
Project Macros
Project default styles
Plugins settings
QGIS Server settings from the OWS settings tab in the Project properties
Queries stored in the DB Manager
The project file is saved in XML format (see QGS/QGZ - The QGIS Project File Format). This means that it is possible to edit the file outside of QGIS if you know what you are doing. The project file format has been updated several times. Project files from older QGIS versions may not work properly any more.
Note
By default, QGIS will warn you of version differences.
This behavior is controlled in the General tab of
( Warn when opening a project file saved with an older
version of QGIS).
Warn when opening a project file saved with an older
version of QGIS).
Whenever you save a .qgs project file in QGIS, a backup of the
file is created in the same directory as the project file, with the
extension .qgs~.
The extension for QGIS projects is .qgs but when saving from QGIS,
the default is to save using a compressed format with the .qgz
extension.
The .qgs file is embedded in the .qgz file (a zip archive),
together with its associated SQLite database (.qgd) for
auxiliary data.
You can get to these files by unzipping the .qgz file.
Note
The Auxiliary Storage Properties mechanism makes a zipped project particularly useful, since it embeds auxiliary data.
Projects can also be saved/loaded to/from a PostgreSQL, GeoPackage or Oracle database using the following Project menu items:
Both menu items have a sub-menu with a list of extra project storage implementations (PostgreSQL, GeoPackage and Oracle). Clicking the action will open a dialog to pick a GeoPackage connection and project, a PostgreSQL connection, schema and project or Oracle connection, owner and project.
Projects stored in GeoPackage, PostgreSQL or Oracle can also be loaded through the QGIS browser panel, either by double-clicking them or by dragging them to the map canvas.
2.2. Handling broken file paths
When opening a project, QGIS may fail to reach some data sources due to unavailable service/database, or to a renamed or moved file. QGIS then opens the Handle Unavailable Layers dialog, referencing the unfound layers. You can:
Double-click in the Datasource field, adjust the path of each layer and click Apply changes;
Select a row, press Browse to indicate the correct location and click Apply changes;
Press Auto-Find to browse the folders and try to automatically fix all or selected broken path(s). Be aware that the browsing may take some time. Then click Apply changes.
Ignore the message and open your project with the broken path(s) by clicking Keep Unavailable Layers. Your layer is then displayed in the Layers panel, but without any data until you fix the path using the
 Unavailable layer! icon next to it in the
Layers panel, or Repair Data Source… in the
layer contextual menu.
Unavailable layer! icon next to it in the
Layers panel, or Repair Data Source… in the
layer contextual menu.With the Repair Data Source… tool, once a layer path has been fixed, QGIS scans through all other broken paths and tries to auto-fix those that have the same broken file path.
Launching QGIS from command line using the --skipbadlayers option can help you skip the Handle Unavailable Layers dialog at startup.
2.3. Generating output
There are several ways to generate output from your QGIS session. We have already discussed saving as a project file in Introducing QGIS projects. Other ways to produce output files are:
Creating images:
 outputs the map canvas
rendering to an image format (PNG, JPG, TIFF…) at custom scale,
resolution and size. Including georeference information in the
exported image is possible, simply enable
outputs the map canvas
rendering to an image format (PNG, JPG, TIFF…) at custom scale,
resolution and size. Including georeference information in the
exported image is possible, simply enable
 Append georeference information (embedded or via world file).
See Exporting the map view for more details.
Append georeference information (embedded or via world file).
See Exporting the map view for more details.Exporting to PDF files: outputs the map canvas rendering to PDF at custom scale, resolution, and with some advanced settings (simplification, georeferencing, …). See Exporting the map view for more details.
Exporting to DXF files: opens a dialog where you can define the ‘Symbology mode’, the ‘Symbology scale’ and vector layers you want to export to DXF. Through the ‘Symbology mode’, symbols from the original QGIS Symbology can be exported with high fidelity (see section Creating new DXF files).
Designing maps:
 opens a dialog where you can
layout and print the current map canvas (see section
Laying out the maps).
opens a dialog where you can
layout and print the current map canvas (see section
Laying out the maps).
