24.1.18. Vector selection
24.1.18.1. Extract by attribute
Creates two vector layers from an input layer: one will contain only matching features while the second will contain all the non-matching features.
The criteria for adding features to the resulting layer is based on the values of an attribute from the input layer.
Ver também
Parâmetros
Etiqueta |
Nome |
Tipo |
Descrição |
|---|---|---|---|
Camada de entrada |
|
[vector: any] |
Layer to extract features from. |
Selection attribute |
|
[tablefield: any] |
Filtering field of the layer |
Operator |
|
[enumeration] Padrão: 0 |
Many different operators are available:
|
Value Opcional |
|
[string] |
Value to be evaluated |
Extracted (attribute) |
|
[same as input] Default: |
Specify the output vector layer for matching features. One of:
A codificação do arquivo também pode ser alterada aqui. |
Extracted (non-matching) |
|
[same as input] Default: |
Specify the output vector layer for non-matching features. One of:
|
Saídas
Etiqueta |
Nome |
Tipo |
Descrição |
|---|---|---|---|
Extracted (attribute) |
|
[same as input] |
Vector layer with matching features from the input layer |
Extracted (non-matching) |
|
[same as input] |
Vector layer with non-matching features from the input layer |
Python code
Algorithm ID: qgis:extractbyattribute
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
The algorithm id is displayed when you hover over the algorithm in the Processing Toolbox. The parameter dictionary provides the parameter NAMEs and values. See Usando os algoritmos do processamento a partir do Terminal Python. for details on how to run processing algorithms from the Python console.
24.1.18.2. Extract by expression
Creates two vector layers from an input layer: one will contain only matching features while the second will contain all the non-matching features.
The criteria for adding features to the resulting layer is based on a QGIS expression. For more information about expressions see the Expressões.
Ver também
Parâmetros
Etiqueta |
Nome |
Tipo |
Descrição |
|---|---|---|---|
Camada de entrada |
|
[vector: any] |
Camada vetorial de entrada |
Expressão |
|
[expression] |
Expression to filter the vector layer |
Matching features |
|
[same as input] Default: |
Specify the output vector layer for matching features. One of:
A codificação do arquivo também pode ser alterada aqui. |
Non-matching |
|
[same as input] Default: |
Specify the output vector layer for non-matching features. One of:
|
Saídas
Etiqueta |
Nome |
Tipo |
Descrição |
|---|---|---|---|
Matching features |
|
[same as input] |
Vector layer with matching features from the input layer |
Non-matching |
|
[same as input] |
Vector layer with non-matching features from the input layer |
Python code
Algorithm ID: qgis:extractbyexpression
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
The algorithm id is displayed when you hover over the algorithm in the Processing Toolbox. The parameter dictionary provides the parameter NAMEs and values. See Usando os algoritmos do processamento a partir do Terminal Python. for details on how to run processing algorithms from the Python console.
24.1.18.3. Extract by location
Creates a new vector layer that only contains matching features from an input layer.
The criteria for adding features to the resulting layer is based on the spatial relationship between each feature and the features in an additional layer.
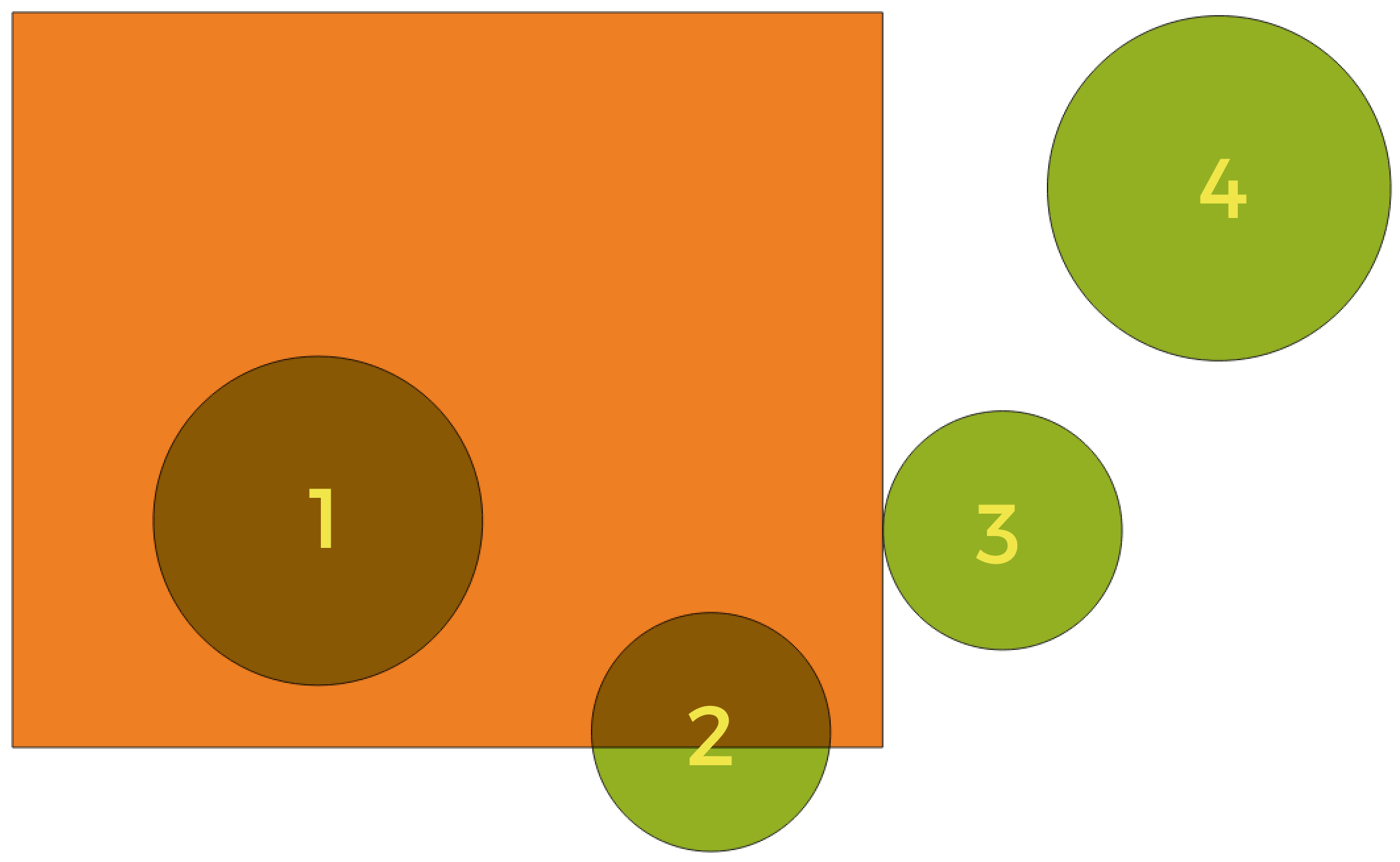
Fig. 24.100 In this example, the dataset from which we want to select (the source vector layer) consists of the green circles, the orange rectangle is the dataset that it is being compared to (the intersection vector layer).
Available geometric predicates are:
- Intersect
Tests whether a geometry intersects another. Returns 1 (true) if the geometries spatially intersect (share any portion of space - overlap or touch) and 0 if they don’t. In the picture above, this will select circles 1, 2 and 3.
- Contain
Retorna 1 (verdadeiro) se e somente se nenhum ponto de b estiver no exterior de a e pelo menos um ponto do interior de b estiver no interior de a. Na imagem, nenhum círculo é selecionado, mas o retângulo seria se você o selecionasse ao contrário, pois ele contém um círculo completamente. Este é o oposto de are within.
- Disjoint
Returns 1 (true) if the geometries do not share any portion of space (no overlap, not touching). Only circle 4 is selected.
- Igual
Retorna 1 (verdadeiro) se e somente se as geometrias forem exatamente iguais. Nenhum círculo será selecionado.
- Touch
Testa se uma geometria toca em outra. Retorna 1 (verdadeiro) se as geometrias tiverem pelo menos um ponto em comum, mas seus interiores não se cruzam. Somente o círculo 3 está selecionado.
- Overlap
Testa se uma geometria sobrepõe outra. Retorna 1 (verdadeiro) se as geometrias compartilharem espaço, têm a mesma dimensão, mas não estão completamente contidas uma na outra. Somente o círculo 2 está selecionado.
- Are within
Tests whether a geometry is within another. Returns 1 (true) if geometry a is completely inside geometry b. Only circle 1 is selected.
- Cross
Retorna 1 (verdadeiro) se as geometrias fornecidas tiverem alguns pontos internos em comum, mas não todos, e o cruzamento real tiver uma dimensão menor que a maior geometria fornecida. Por exemplo, uma linha cruzando um polígono cruzará como uma linha (selecionada). O cruzamento de duas linhas cruzará como um ponto (selecionado). Dois polígonos cruzam como um polígono (não selecionado).
Ver também
Parâmetros
Etiqueta |
Nome |
Tipo |
Descrição |
|---|---|---|---|
Extract features from |
|
[vector: any] |
Camada vetorial de entrada |
Where the features (geometric predicate) |
|
[enumeration] [list] Padrão: [0] |
Spatial condition for the selection. One or more of:
If more than one condition is chosen, at least one of them (OR operation) has to be met for a feature to be extracted. |
By comparing to the features from |
|
[vector: any] |
Intersection vector layer |
Extracted (location) |
|
[same as input] Default: |
Specify the output vector layer for the features that have the chosen spatial relationship(s) with one or more features in the comparison layer. One of:
|
Saídas
Etiqueta |
Nome |
Tipo |
Descrição |
|---|---|---|---|
Extracted (location) |
|
[same as input] |
Vector layer with features from the input layer that have the chosen spatial relationship(s) with one or more features in the comparison layer. |
Python code
Algorithm ID: qgis:extractbylocation
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
The algorithm id is displayed when you hover over the algorithm in the Processing Toolbox. The parameter dictionary provides the parameter NAMEs and values. See Usando os algoritmos do processamento a partir do Terminal Python. for details on how to run processing algorithms from the Python console.
24.1.18.4. Random extract
Takes a vector layer and generates a new one that contains only a subset of the features in the input layer.
The subset is defined randomly, based on feature IDs, using a percentage or count value to define the total number of features in the subset.
Ver também
Parâmetros
Etiqueta |
Nome |
Tipo |
Descrição |
|---|---|---|---|
Camada de entrada |
|
[vector: any] |
Source vector layer to select the features from |
Método |
|
[enumeration] Padrão: 0 |
Random selection methods. One of:
|
Number/percentage of selected features |
|
[number] Padrão: 10 |
Number or percentage of features to select |
Extracted (random) |
|
[vector: any] Default: |
Specify the output vector layer for the randomly selected features. One of:
Vector layer containing randomly selected features |
Saídas
Etiqueta |
Nome |
Tipo |
Descrição |
|---|---|---|---|
Extracted (random) |
|
[same as input] |
Vector layer containing randomly selected features from the input layer |
Python code
Algorithm ID: qgis:randomextract
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
The algorithm id is displayed when you hover over the algorithm in the Processing Toolbox. The parameter dictionary provides the parameter NAMEs and values. See Usando os algoritmos do processamento a partir do Terminal Python. for details on how to run processing algorithms from the Python console.
24.1.18.5. Random extract within subsets
Takes a vector layer and generates a new one that contains only a subset of the features in the input layer.
The subset is defined randomly, based on feature IDs, using a percentage or count value to define the total number of features in the subset. The percentage/count value is not applied to the whole layer, but instead to each category. Categories are defined according to a given attribute.
Ver também
Parâmetros
Etiqueta |
Nome |
Tipo |
Descrição |
|---|---|---|---|
Camada de entrada |
|
[vector: any] |
Vector layer to select the features from |
ID field |
|
[tablefield: any] |
Category of the source vector layer to select the features from |
Método |
|
[enumeration] Padrão: 0 |
Random selection method. One of:
|
Number/percentage of selected features |
|
[number] Padrão: 10 |
Number or percentage of features to select |
Extracted (random stratified) |
|
[same as input] Default: |
Specify the output vector layer for the randomly selected features. One of:
A codificação do arquivo também pode ser alterada aqui. |
Saídas
Etiqueta |
Nome |
Tipo |
Descrição |
|---|---|---|---|
Extracted (random stratified) |
|
[same as input] |
Vector layer containing randomly selected features from the input layer |
Python code
Algorithm ID: qgis:randomextractwithinsubsets
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
The algorithm id is displayed when you hover over the algorithm in the Processing Toolbox. The parameter dictionary provides the parameter NAMEs and values. See Usando os algoritmos do processamento a partir do Terminal Python. for details on how to run processing algorithms from the Python console.
24.1.18.6. Seleção aleatória
Takes a vector layer and selects a subset of its features. No new layer is generated by this algorithm.
The subset is defined randomly, based on feature IDs, using a percentage or count value to define the total number of features in the subset.
Default menu:
Ver também
Parâmetros
Etiqueta |
Nome |
Tipo |
Descrição |
|---|---|---|---|
Camada de entrada |
|
[vector: any] |
Vector layer for the selection |
Método |
|
[enumeration] Padrão: 0 |
Random selection method. One of:
|
Number/percentage of selected features |
|
[number] Padrão: 10 |
Number or percentage of features to select |
Saídas
Etiqueta |
Nome |
Tipo |
Descrição |
|---|---|---|---|
Camada de entrada |
|
[same as input] |
The input layer with features selected |
Python code
Algorithm ID: qgis:randomselection
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
The algorithm id is displayed when you hover over the algorithm in the Processing Toolbox. The parameter dictionary provides the parameter NAMEs and values. See Usando os algoritmos do processamento a partir do Terminal Python. for details on how to run processing algorithms from the Python console.
24.1.18.7. Random selection within subsets
Takes a vector layer and selects a subset of its features. No new layer is generated by this algorithm.
The subset is defined randomly, based on feature IDs, using a percentage or count value to define the total number of features in the subset.
The percentage/count value is not applied to the whole layer, but instead to each category.
Categories are defined according to a given attribute, which is also specified as an input parameter for the algorithm.
No new outputs are created.
Default menu:
Ver também
Parâmetros
Etiqueta |
Nome |
Tipo |
Descrição |
|---|---|---|---|
Camada de entrada |
|
[vector: any] |
Vector layer to select features in |
ID field |
|
[tablefield: any] |
Category of the input layer to select the features from |
Método |
|
[enumeration] Padrão: 0 |
Random selection method. One of:
|
Number/percentage of selected features |
|
[number] Padrão: 10 |
Number or percentage of features to select |
Saídas
Etiqueta |
Nome |
Tipo |
Descrição |
|---|---|---|---|
Camada de entrada |
|
[same as input] |
The input layer with features selected |
Python code
Algorithm ID: qgis:randomselectionwithinsubsets
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
The algorithm id is displayed when you hover over the algorithm in the Processing Toolbox. The parameter dictionary provides the parameter NAMEs and values. See Usando os algoritmos do processamento a partir do Terminal Python. for details on how to run processing algorithms from the Python console.
24.1.18.8. Select by attribute
Creates a selection in a vector layer.
The criteria for selecting features is based on the values of an attribute from the input layer.
Ver também
Parâmetros
Etiqueta |
Nome |
Tipo |
Descrição |
|---|---|---|---|
Camada de entrada |
|
[vector: any] |
Vector layer to select features in |
Selection attribute |
|
[tablefield: any] |
Filtering field of the layer |
Operator |
|
[enumeration] Padrão: 0 |
Many different operators are available:
|
Value Opcional |
|
[string] |
Value to be evaluated |
Modify current selection by |
|
[enumeration] Padrão: 0 |
How the selection of the algorithm should be managed. One of:
|
Saídas
Etiqueta |
Nome |
Tipo |
Descrição |
|---|---|---|---|
Camada de entrada |
|
[same as input] |
The input layer with features selected |
Python code
Algorithm ID: qgis:selectbyattribute
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
The algorithm id is displayed when you hover over the algorithm in the Processing Toolbox. The parameter dictionary provides the parameter NAMEs and values. See Usando os algoritmos do processamento a partir do Terminal Python. for details on how to run processing algorithms from the Python console.
24.1.18.9. Select by expression
Creates a selection in a vector layer.
The criteria for selecting features is based on a QGIS expression. For more information about expressions see the Expressões.
Ver também
Parâmetros
Etiqueta |
Nome |
Tipo |
Descrição |
|---|---|---|---|
Camada de entrada |
|
[vector: any] |
Camada vetorial de entrada |
Expressão |
|
[expression] |
Expression to filter the input layer |
Modify current selection by |
|
[enumeration] Padrão: 0 |
How the selection of the algorithm should be managed. One of:
|
Saídas
Etiqueta |
Nome |
Tipo |
Descrição |
|---|---|---|---|
Camada de entrada |
|
[same as input] |
The input layer with features selected |
Python code
Algorithm ID: qgis:selectbyexpression
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
The algorithm id is displayed when you hover over the algorithm in the Processing Toolbox. The parameter dictionary provides the parameter NAMEs and values. See Usando os algoritmos do processamento a partir do Terminal Python. for details on how to run processing algorithms from the Python console.
24.1.18.10. Selecionar pela localização
Creates a selection in a vector layer.
The criteria for selecting features is based on the spatial relationship between each feature and the features in an additional layer.

Fig. 24.101 In this example, the dataset from which we want to select (the source vector layer) consists of the green circles, the orange rectangle is the dataset that it is being compared to (the intersection vector layer).
Available geometric predicates are:
- Intersect
Tests whether a geometry intersects another. Returns 1 (true) if the geometries spatially intersect (share any portion of space - overlap or touch) and 0 if they don’t. In the picture above, this will select circles 1, 2 and 3.
- Contain
Retorna 1 (verdadeiro) se e somente se nenhum ponto de b estiver no exterior de a e pelo menos um ponto do interior de b estiver no interior de a. Na imagem, nenhum círculo é selecionado, mas o retângulo seria se você o selecionasse ao contrário, pois ele contém um círculo completamente. Este é o oposto de are within.
- Disjoint
Returns 1 (true) if the geometries do not share any portion of space (no overlap, not touching). Only circle 4 is selected.
- Igual
Retorna 1 (verdadeiro) se e somente se as geometrias forem exatamente iguais. Nenhum círculo será selecionado.
- Touch
Testa se uma geometria toca em outra. Retorna 1 (verdadeiro) se as geometrias tiverem pelo menos um ponto em comum, mas seus interiores não se cruzam. Somente o círculo 3 está selecionado.
- Overlap
Testa se uma geometria sobrepõe outra. Retorna 1 (verdadeiro) se as geometrias compartilharem espaço, têm a mesma dimensão, mas não estão completamente contidas uma na outra. Somente o círculo 2 está selecionado.
- Are within
Tests whether a geometry is within another. Returns 1 (true) if geometry a is completely inside geometry b. Only circle 1 is selected.
- Cross
Retorna 1 (verdadeiro) se as geometrias fornecidas tiverem alguns pontos internos em comum, mas não todos, e o cruzamento real tiver uma dimensão menor que a maior geometria fornecida. Por exemplo, uma linha cruzando um polígono cruzará como uma linha (selecionada). O cruzamento de duas linhas cruzará como um ponto (selecionado). Dois polígonos cruzam como um polígono (não selecionado).
Default menu:
Ver também
Parâmetros
Etiqueta |
Nome |
Tipo |
Descrição |
|---|---|---|---|
Select features from |
|
[vector: any] |
Camada vetorial de entrada |
Where the features (geometric predicate) |
|
[enumeration] [list] Padrão: [0] |
Spatial condition for the selection. One or more of:
If more than one condition is chosen, at least one of them (OR operation) has to be met for a feature to be extracted. |
By comparing to the features from |
|
[vector: any] |
Intersection vector layer |
Modify current selection by |
|
[enumeration] Padrão: 0 |
How the selection of the algorithm should be managed. One of:
|
Saídas
Etiqueta |
Nome |
Tipo |
Descrição |
|---|---|---|---|
Camada de entrada |
|
[same as input] |
The input layer with features selected |
Python code
Algorithm ID: qgis:selectbylocation
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
The algorithm id is displayed when you hover over the algorithm in the Processing Toolbox. The parameter dictionary provides the parameter NAMEs and values. See Usando os algoritmos do processamento a partir do Terminal Python. for details on how to run processing algorithms from the Python console.