Важно
Перевод - это работа сообщества : ссылка:Вы можете присоединиться. Эта страница в настоящее время переводится |прогресс перевода|.
9.2. Список функций
Ниже перечислены функции, операторы и переменные, доступные в QGIS, сгруппированные по категориям.
9.2.1. Агрегатные функции
Эта группа содержит функции, которые агрегируют значения по слоям и полям.
Показать/скрыть список функций
9.2.1.1. aggregate
Возвращает совокупное значение, рассчитанное с использованием объектов другого слоя.
Синтаксис |
aggregate(layer, aggregate, expression, [filter], [concatenator=““], [order_by]) [] обозначает необязательные аргументы |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.1.2. array_agg
Возвращает массив агрегированных значений из поля или выражения.
Синтаксис |
array_agg(expression, [group_by], [filter], [order_by]) [] обозначает необязательные аргументы |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.1.3. collect
Возвращает многокомпонентную геометрию агрегированных геометрий из выражения
Синтаксис |
collect(expression, [group_by], [filter]) [] обозначает необязательные аргументы |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.1.4. concatenate
Возвращает все агрегированные строки из поля или выражения, соединенные разделителем.
Синтаксис |
concatenate(expression, [group_by], [filter], [concatenator], [order_by]) [] обозначает необязательные аргументы |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.1.5. concatenate_unique
Возвращает все уникальные строки из поля или выражения, соединенные разделителем.
Синтаксис |
concatenate_unique(expression, [group_by], [filter], [concatenator], [order_by]) [] обозначает необязательные аргументы |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.1.6. count
Возвращает количество совпадающих признаков.
Синтаксис |
count(expression, [group_by], [filter]) [] обозначает необязательные аргументы |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.1.7. count_distinct
Возвращает количество уникальных значений.
Синтаксис |
count_distinct(expression, [group_by], [filter]) [] обозначает необязательные аргументы |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.1.8. count_missing
Возвращает количество отсутствующих (NULL) значений.
Синтаксис |
count_missing(expression, [group_by], [filter]) [] обозначает необязательные аргументы |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.1.9. iqr
Возвращает рассчитанный межквартильный размах из поля или выражения.
Синтаксис |
iqr(expression, [group_by], [filter]) [] обозначает необязательные аргументы |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.1.10. majority
Возвращает совокупное большинство значений (наиболее часто встречающееся значение) из поля или выражения.
Синтаксис |
majority(expression, [group_by], [filter]) [] обозначает необязательные аргументы |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.1.11. max_length
Возвращает максимальную длину строк из поля или выражения.
Синтаксис |
max_length(expression, [group_by], [filter]) [] обозначает необязательные аргументы |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.1.12. maximum
Возвращает совокупное максимальное значение из поля или выражения.
Синтаксис |
maximum(expression, [group_by], [filter]) [] обозначает необязательные аргументы |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.1.13. mean
Возвращает совокупное среднее значение из поля или выражения.
Синтаксис |
mean(expression, [group_by], [filter]) [] обозначает необязательные аргументы |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.1.14. median
Возвращает совокупное медианное значение из поля или выражения.
Синтаксис |
median(expression, [group_by], [filter]) [] обозначает необязательные аргументы |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.1.15. min_length
Возвращает минимальную длину строк из поля или выражения.
Синтаксис |
min_length(expression, [group_by], [filter]) [] обозначает необязательные аргументы |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.1.16. minimum
Возвращает совокупное минимальное значение из поля или выражения.
Синтаксис |
minimum(expression, [group_by], [filter]) [] обозначает необязательные аргументы |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.1.17. minority
Возвращает совокупное меньшинство значений (наименее встречающееся значение) из поля или выражения.
Синтаксис |
minority(expression, [group_by], [filter]) [] обозначает необязательные аргументы |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.1.18. q1
Возвращает рассчитанный первый квартиль из поля или выражения.
Синтаксис |
q1(expression, [group_by], [filter]) [] обозначает необязательные аргументы |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.1.19. q3
Возвращает рассчитанный третий квартиль из поля или выражения.
Синтаксис |
q3(expression, [group_by], [filter]) [] обозначает необязательные аргументы |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.1.20. range
Возвращает совокупный диапазон значений (максимум - минимум) из поля или выражения.
Синтаксис |
range(expression, [group_by], [filter]) [] обозначает необязательные аргументы |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.1.21. relation_aggregate
Возвращает совокупное значение, рассчитанное с использованием всех соответствующих дочерних объектов из отношения слоя.
Синтаксис |
relation_aggregate(relation, aggregate, expression, [concatenator=““], [order_by]) [] обозначает необязательные аргументы |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
Дополнительная информация: Setting relations between multiple layers
9.2.1.22. stdev
Возвращает совокупное значение стандартного отклонения из поля или выражения.
Синтаксис |
stdev(expression, [group_by], [filter]) [] обозначает необязательные аргументы |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.1.23. sum
Возвращает совокупное суммарное значение из поля или выражения.
Синтаксис |
sum(expression, [group_by], [filter]) [] обозначает необязательные аргументы |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.2. Функции массива
Эта группа содержит функции для создания и манипулирования массивами (также известными как структуры данных списка). Порядок значений в массиве имеет значение, в отличие от структуры данных :ref:`“map“<maps_functions> `, где порядок пар ключ-значение не имеет значения, а значения идентифицируются по их ключам.
Показать/скрыть список функций
9.2.2.1. array
Возвращает массив, содержащий все значения, переданные в качестве параметра.
Синтаксис |
массив(значение1, значение2, …) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.2.2. array_all
Возвращает TRUE, если массив содержит все значения заданного массива.
Синтаксис |
array_all(array_a, array_b) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.2.3. array_append
Возвращает массив с добавлением заданного значения в конец.
Синтаксис |
array_append(array, value) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.2.4. array_cat
Возвращает массив, содержащий все заданные массивы, соединенные вместе.
Синтаксис |
array_cat(массив1, массив2, …) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.2.5. array_contains
Возвращает TRUE, если массив содержит заданное значение.
Синтаксис |
array_contains(array, value) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.2.6. array_count
Подсчитывает количество вхождений заданного значения в массиве.
Синтаксис |
array_count(array, value) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.2.7. array_distinct
Возвращает массив, содержащий уникальные значения заданного массива.
Синтаксис |
array_distinct(array) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.2.8. array_filter
Возвращает массив, содержащий только те элементы, для которых выражение имеет значение true.
Синтаксис |
array_filter(массив, выражение, [limit=0]) [] обозначает необязательные аргументы |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.2.9. array_find
Возвращает наименьший индекс (0 для первого) значения в массиве. Возвращает -1, если значение не найдено.
Синтаксис |
array_find(array, value) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.2.10. array_first
Возвращает первое значение массива.
Синтаксис |
array_first(array) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.2.11. array_foreach
Возвращает массив с вычисленным значением заданного выражения для каждого элемента.
Синтаксис |
array_foreach(array, expression) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.2.12. array_get
Возвращает N-е значение (0 для первого) или последнее -N-е значение (-1 для последнего) массива.
Синтаксис |
array_get(array, pos) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
Подсказка
Вы также можете использовать оператор :ref:`index ([])<expression_function_Operators_index> ` для получения значения из массива.
9.2.2.13. array_insert
Возвращает массив с добавлением заданного значения в заданной позиции.
Синтаксис |
array_insert(array, pos, value) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.2.14. array_intersect
Возвращает TRUE, если хотя бы один элемент массива array1 присутствует в массиве array2.
Синтаксис |
array_intersect(array1, array2) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.2.15. array_last
Возвращает последнее значение массива.
Синтаксис |
array_last(array) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.2.16. array_length
Возвращает количество элементов массива.
Синтаксис |
array_length(array) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.2.17. array_majority
Возвращает наиболее распространенные значения в массиве.
Синтаксис |
array_majority(array, [option=“all“]) [] обозначает необязательные аргументы |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.2.18. array_max
Возвращает максимальное значение массива.
Синтаксис |
array_max(array) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.2.19. array_mean
Возвращает среднее арифметическое значение массива. Нечисловые значения в массиве игнорируются.
Синтаксис |
array_mean(array) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.2.20. array_median
Возвращает медиану арифметических значений в массиве. Неарифметические значения в массиве игнорируются.
Синтаксис |
array_median(array) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.2.21. array_min
Возвращает минимальное значение массива.
Синтаксис |
array_min(array) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.2.22. array_minority
Возвращает менее распространенные значения в массиве.
Синтаксис |
array_minority(array, [option=“all“]) [] обозначает необязательные аргументы |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.2.23. array_prepend
Возвращает массив с добавлением заданного значения в начало.
Синтаксис |
array_prepend(array, value) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.2.24. array_prioritize
Возвращает массив, отсортированный по порядку, указанному в другом массиве. Значения, которые присутствуют в первом массиве, но отсутствуют во втором, будут добавлены в конец результата.
Синтаксис |
array_prioritize(array, array_prioritize) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.2.25. array_remove_all
Возвращает массив, из которого удалены все элементы с заданным значением.
Синтаксис |
array_remove_all(array, value) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.2.26. array_remove_at
Возвращает массив, из которого удален элемент с указанным индексом. Поддерживает положительные (0 для первого элемента) и отрицательные (последнее -N-е значение, -1 для последнего элемента) индексы.
Синтаксис |
array_remove_at(array, pos) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.2.27. array_replace
Возвращает массив с замененным заданным значением, массивом или картой значений.
Вариант значения и массива
Возвращает массив, в котором указанное значение или массив значений заменено другим значением или массивом значений.
Синтаксис |
array_replace(array, before, after) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
Вариант карты
Возвращает массив, в котором ключи предоставленной карты заменены их сопряженными значениями.
Синтаксис |
array_replace(array, map) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
Дополнительная информация: replace, regexp_replace
9.2.2.28. array_reverse
Возвращает заданный массив со значениями массива в обратном порядке.
Синтаксис |
array_reverse(array) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.2.29. array_slice
Возвращает часть массива. Фрагмент определяется аргументами start_pos и end_pos.
Синтаксис |
array_slice(array, start_pos, end_pos) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.2.30. array_sort
Возвращает предоставленный массив с отсортированными элементами.
Синтаксис |
array_sort(array, [ascending=true]) [] обозначает необязательные аргументы |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.2.31. array_sum
Возвращает сумму арифметических значений в массиве. Нечисловые значения в массиве игнорируются.
Синтаксис |
array_sum(array) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.2.32. array_to_string
Объединяет элементы массива в строку, разделенную разделителем, и использует опциональную строку для пустых значений.
Синтаксис |
array_to_string(array, [delimiter=“,“], [empty_value=““]) [] обозначает необязательные аргументы |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
Дополнительная информация: string_to_array
9.2.2.33. generate_series
Создает массив, содержащий последовательность чисел.
Синтаксис |
generate_series(start, stop, [step=1]) [] обозначает необязательные аргументы |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.2.34. geometries_to_array
Разделяет геометрию на более простые геометрические фигуры в массиве.
Синтаксис |
geometries_to_array(geometry) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.2.35. regexp_matches
Возвращает массив всех строк, захваченных группами захвата, в том порядке, в котором сами группы появляются в предоставленном регулярном выражении по отношению к строке.
Синтаксис |
regexp_matches(string, regex, [empty_value=““]) [] обозначает необязательные аргументы |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
Дополнительная информация: substr, regexp_substr
9.2.2.36. string_to_array
Разделяет строку на массив, используя указанный разделитель и опциональную строку для пустых значений.
Синтаксис |
string_to_array(string, [delimiter=“,“], [empty_value=““]) [] обозначает необязательные аргументы |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
Дополнительная информация: array_to_string
9.2.3. Цветовые функции
Эта группа содержит функции для работы с цветами.
Показать/скрыть список функций
9.2.3.1. color_cmyk
Возвращает строковое представление цвета на основе его компонентов голубого, пурпурного, желтого и черного цветов.
Синтаксис |
color_cmyk(cyan, magenta, yellow, black) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.3.2. color_cmyka
Возвращает строковое представление цвета на основе его компонентов голубого, пурпурного, желтого, черного и альфа (прозрачность)
Синтаксис |
color_cmyka(cyan, magenta, yellow, black, alpha) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.3.3. color_cmykf
Возвращает объект цвета на основе его компонентов голубого, пурпурного, желтого, черного и альфа.
Синтаксис |
color_cmykf(голубой, пурпурный, желтый, черный, [альфа=1,0]) [] обозначает необязательные аргументы |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.3.4. color_grayscale_average
Применяет фильтр оттенков серого к цвету и возвращает его. Возвращаемый тип совпадает с аргументом цвета, т. е. представляет собой строковое представление цвета или объект цвета.
Синтаксис |
color_grayscale_average(color) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.3.5. color_hsl
Возвращает строковое представление цвета на основе его атрибутов оттенка, насыщенности и яркости.
Синтаксис |
color_hsl(hue, saturation, lightness) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.3.6. color_hsla
Возвращает строковое представление цвета на основе его атрибутов оттенка, насыщенности, яркости и альфа (прозрачности).
Синтаксис |
color_hsla(hue, saturation, lightness, alpha) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.3.7. color_hslf
Возвращает объект цвета на основе его атрибутов оттенка, насыщенности и яркости.
Синтаксис |
color_hslf(оттенок, насыщенность, яркость, [альфа=1,0]) [] обозначает необязательные аргументы |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.3.8. color_hsv
Возвращает строковое представление цвета на основе его атрибутов оттенка, насыщенности и яркости.
Синтаксис |
color_hsv(hue, saturation, value) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.3.9. color_hsva
Возвращает строковое представление цвета на основе его атрибутов оттенка, насыщенности, яркости и альфа-канала (прозрачности).
Синтаксис |
color_hsva(hue, saturation, value, alpha) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.3.10. color_hsvf
Возвращает объект цвета на основе его атрибутов оттенка, насыщенности и яркости.
Синтаксис |
color_hsvf(оттенок, насыщенность, значение, [альфа=1,0]) [] обозначает необязательные аргументы |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.3.11. color_mix
Возвращает цвет, смешивающий значения красного, зеленого, синего и альфа-канала двух заданных цветов на основе заданного соотношения. Возвращаемый тип совпадает с типами аргументов цвета, т. е. представляет собой строковое представление цвета или объект цвета.
Синтаксис |
color_mix(color1, color2, ratio) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.3.12. color_mix_rgb
Возвращает строку, представляющую цвет, полученный путем смешивания значений красного, зеленого, синего и альфа-канала двух заданных цветов в соответствии с заданным соотношением.
Синтаксис |
color_mix_rgb(color1, color2, ratio) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.3.13. color_part
Возвращает определенный компонент из цветовой строки или цветового объекта, например, красный компонент или альфа-компонент.
Синтаксис |
color_part(color, component) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.3.14. color_rgb
Возвращает строковое представление цвета на основе его красного, зеленого и синего компонентов.
Синтаксис |
color_rgb(red, green, blue) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.3.15. color_rgba
Возвращает строковое представление цвета на основе его красного, зеленого, синего и альфа-компонентов (прозрачности).
Синтаксис |
color_rgba(red, green, blue, alpha) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.3.16. color_rgbf
Возвращает объект цвета на основе его красного, зеленого, синего и альфа-компонентов.
Синтаксис |
color_rgbf(красный, зеленый, синий, [альфа=1,0]) [] обозначает необязательные аргументы |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.3.17. create_ramp
Возвращает градиентную рампу из карты цветовых строк и шагов.
Синтаксис |
create_ramp(map, [discrete=false]) [] обозначает необязательные аргументы |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.3.18. darker
Возвращает более темный (или более светлый) цвет. Возвращаемый тип совпадает с аргументами цвета, т. е. представляет собой строковое представление цвета или объект цвета.
Синтаксис |
darker(color, factor) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
Дополнительная информация: lighter
9.2.3.19. lighter
Возвращает более светлый (или более темный) цвет. Возвращаемый тип совпадает с аргументами цвета, т. е. представляет собой строковое представление цвета или объект цвета.
Синтаксис |
lighter(color, factor) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
Дополнительная информация: darker
9.2.3.20. project_color
Возвращает цвет из цветовой схемы проекта.
Синтаксис |
project_color(name) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
Дополнительная информация: :ref:`Настройка цветов проекта<project_colors> `
9.2.3.21. project_color_object
Возвращает цвет из цветовой схемы проекта. В отличие от project_color, который возвращает строковое представление цвета, project_color_object возвращает объект цвета.
Синтаксис |
project_color_object(name) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.3.22. ramp_color
Возвращает строку, представляющую цвет из цветовой гаммы.
Сохраненный вариант рампы
Возвращает строку, представляющую цвет из сохраненного градиента.
Синтаксис |
ramp_color(ramp_name, value) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
Примечание
Доступные цветовые градиенты различаются в зависимости от установки QGIS. Эта функция может не дать ожидаемых результатов, если вы перемещаете проект QGIS между установками.
Вариант рампы, созданный с помощью выражения
Возвращает строку, представляющую цвет из градиента, созданного выражением.
Синтаксис |
ramp_color(ramp, value) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
Дополнительная информация: Setting a Color Ramp, The color ramp drop-down shortcut
9.2.3.23. ramp_color_object
Возвращает объект цвета из цветовой шкалы. В отличие от ramp_color, который возвращает строковое представление цвета, ramp_color_object возвращает объект цвета.
Сохраненный вариант рампы
Возвращает объект цвета из сохраненного градиента
Синтаксис |
ramp_color_object(ramp_name, value) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
Примечание
Доступные цветовые градиенты различаются в зависимости от установки QGIS. Эта функция может не дать ожидаемых результатов, если вы перемещаете проект QGIS между установками.
Вариант рампы, созданный с помощью выражения
Возвращает объект цвета из градиента, созданного выражением.
Синтаксис |
ramp_color_object(ramp, value) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.3.24. set_color_part
Устанавливает определенный цветовой компонент для цветовой строки или цветового объекта, например, красный компонент или альфа-компонент.
Синтаксис |
set_color_part(color, component, value) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.4. Условные функции
Эта группа содержит функции для обработки условных проверок в выражениях.
Показать/скрыть список функций
9.2.4.1. CASE
CASE используется для оценки ряда условий и возврата результата для первого выполненного условия. Условия оцениваются последовательно, и если условие истинно, оценка останавливается и возвращается соответствующий результат. Если ни одно из условий не истинно, возвращается значение в предложении ELSE. Кроме того, если предложение ELSE не задано и ни одно из условий не выполняется, возвращается NULL.
CASE
КОГДА условие ТО результат
[ …n ]
[ ELSE результат ]
END
[ ] обозначает необязательные компоненты
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.4.2. coalesce
Возвращает первое значение, отличное от NULL, из списка выражений.
Эта функция может принимать любое количество аргументов.
Синтаксис |
coalesce(выражение1, выражение2, …) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.4.3. if
Проверяет условие и возвращает разный результат в зависимости от результата проверки.
Синтаксис |
if(condition, result_when_true, result_when_false) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.4.4. nullif
Returns a NULL value if value1 equals value2; otherwise it returns value1. This can be used to conditionally substitute values with NULL.
Синтаксис |
nullif(value1, value2) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.4.5. regexp_match
Return the first matching position matching a regular expression within an unicode string, or 0 if the substring is not found.
Синтаксис |
regexp_match(input_string, regex) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.4.6. try
Tries an expression and returns its value if error-free. If the expression returns an error, an alternative value will be returned when provided otherwise the function will return NULL.
Синтаксис |
try(expression, [alternative]) [] обозначает необязательные аргументы |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.5. Conversions Functions
This group contains functions to convert one data type to another (e.g., string from/to integer, binary from/to string, string to date, …).
Показать/скрыть список функций
9.2.5.1. from_base64
Decodes a string in the Base64 encoding into a binary value.
Синтаксис |
from_base64(string) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.5.2. hash
Creates a hash from a string with a given method. One byte (8 bits) is represented with two hex „“digits““, so „md4“ (16 bytes) produces a 16 * 2 = 32 character long hex string and „keccak_512“ (64 bytes) produces a 64 * 2 = 128 character long hex string.
Синтаксис |
hash(string, method) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.5.3. md5
Creates a md5 hash from a string.
Синтаксис |
md5(string) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.5.4. sha256
Creates a sha256 hash from a string.
Синтаксис |
sha256(string) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.5.5. to_base64
Encodes a binary value into a string, using the Base64 encoding.
Синтаксис |
to_base64(value) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.5.6. to_date
Converts a string into a date object. An optional format string can be provided to parse the string; see QDate::fromString or the documentation of the format_date function for additional documentation on the format. By default the current QGIS user locale is used.
Синтаксис |
to_date(string, [format], [language]) [] обозначает необязательные аргументы |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
Further reading: format_date
9.2.5.7. to_datetime
Converts a string into a datetime object. An optional format string can be provided to parse the string; see QDate::fromString, QTime::fromString or the documentation of the format_date function for additional documentation on the format. By default the current QGIS user locale is used.
Синтаксис |
to_datetime(string, [format], [language]) [] обозначает необязательные аргументы |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
Further reading: format_date
9.2.5.8. to_decimal
Converts a degree, minute, second coordinate to its decimal equivalent.
Синтаксис |
to_decimal(value) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.5.9. to_dm
Converts a coordinate to degree, minute.
Синтаксис |
to_dm(coordinate, axis, precision, [formatting=]) [] обозначает необязательные аргументы |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.5.10. to_dms
Converts a coordinate to degree, minute, second.
Синтаксис |
to_dms(coordinate, axis, precision, [formatting=]) [] обозначает необязательные аргументы |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.5.11. to_int
Converts a string to integer number. If a value cannot be converted to integer the expression is invalid (e.g „123asd“ is invalid).
Синтаксис |
to_int(string) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.5.12. to_interval
Converts a string to an interval type. Can be used to take days, hours, month, etc of a date.
Синтаксис |
to_interval(string) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.5.13. to_real
Converts a string to a real number. If a value cannot be converted to real the expression is invalid (e.g „123.56asd“ is invalid). Numbers are rounded after saving changes if the precision is smaller than the result of the conversion.
Синтаксис |
to_real(string) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.5.14. to_string
Converts a number to string.
Синтаксис |
to_string(number) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
Further reading: format_number
9.2.5.15. to_time
Converts a string into a time object. An optional format string can be provided to parse the string; see QTime::fromString for additional documentation on the format.
Синтаксис |
to_time(string, [format], [language]) [] обозначает необязательные аргументы |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
Further reading: format_date
9.2.6. Custom Functions
This group contains functions created by the user. See Редактор функций for more details.
9.2.7. Date and Time Functions
This group contains functions for handling date and time data. This group shares several functions with the Conversions Functions (to_date, to_time, to_datetime, to_interval) and String Functions (format_date) groups.
Примечание
Storing date, datetime and intervals on fields
The ability to store date, time and datetime values directly on fields depends on the data source’s provider (e.g., Shapefile accepts date format, but not datetime or time format). The following are some suggestions to overcome this limitation:
date, datetime and time can be converted and stored in text type fields using the format_date() function.
Intervals can be stored in integer or decimal type fields after using one of the date extraction functions (e.g., day() to get the interval expressed in days)
Показать/скрыть список функций
9.2.7.1. age
Returns the difference between two dates or datetimes.
The difference is returned as an Interval and needs to be used with one of the following functions in order to extract useful information:
yearmonthweekdayhourminutesecond
Синтаксис |
age(datetime1, datetime2) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.7.2. datetime_from_epoch
Returns a datetime whose date and time are the number of milliseconds, msecs, that have passed since 1970-01-01T00:00:00.000, Coordinated Universal Time (Qt.UTC), and converted to Qt.LocalTime.
Синтаксис |
datetime_from_epoch(int) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.7.3. day
Extracts the day from a date, or the number of days from an interval.
Date variant
Extracts the day from a date or datetime.
Синтаксис |
day(date) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
Interval variant
Calculates the length in days of an interval.
Синтаксис |
day(interval) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.7.4. day_of_week
Returns the day of the week for a specified date or datetime. The returned value ranges from 0 to 6, where 0 corresponds to a Sunday and 6 to a Saturday.
Синтаксис |
day_of_week(date) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.7.5. epoch
Returns the interval in milliseconds between the unix epoch and a given date value.
Синтаксис |
epoch(date) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.7.6. format_date
Formats a date type or string into a custom string format. Uses Qt date/time format strings. See QDateTime::toString.
Синтаксис |
format_date(datetime, format, [language]) [] обозначает необязательные аргументы |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Аргументы |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Примеры |
|
9.2.7.7. hour
Extracts the hour part from a datetime or time, or the number of hours from an interval.
Time variant
Extracts the hour part from a time or datetime.
Синтаксис |
hour(datetime) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
Interval variant
Calculates the length in hours of an interval.
Синтаксис |
hour(interval) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.7.8. make_date
Creates a date value from year, month and day numbers.
Синтаксис |
make_date(year, month, day) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.7.9. make_datetime
Creates a datetime value from year, month, day, hour, minute and second numbers.
Синтаксис |
make_datetime(year, month, day, hour, minute, second) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.7.10. make_interval
Creates an interval value from year, month, weeks, days, hours, minute and seconds values.
Синтаксис |
make_interval([years=0], [months=0], [weeks=0], [days=0], [hours=0], [minutes=0], [seconds=0]) [] обозначает необязательные аргументы |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.7.11. make_time
Creates a time value from hour, minute and second numbers.
Синтаксис |
make_time(hour, minute, second) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.7.12. minute
Extracts the minutes part from a datetime or time, or the number of minutes from an interval.
Time variant
Extracts the minutes part from a time or datetime.
Синтаксис |
minute(datetime) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
Interval variant
Calculates the length in minutes of an interval.
Синтаксис |
minute(interval) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.7.13. month
Extracts the month part from a date, or the number of months from an interval.
Date variant
Extracts the month part from a date or datetime.
Синтаксис |
month(date) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
Interval variant
Calculates the length in months of an interval.
Синтаксис |
month(interval) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.7.14. now
Returns the current date and time. The function is static and will return consistent results while evaluating. The time returned is the time when the expression is prepared.
Синтаксис |
now() |
Примеры |
|
9.2.7.15. second
Extracts the seconds part from a datetime or time, or the number of seconds from an interval.
Time variant
Extracts the seconds part from a time or datetime.
Синтаксис |
second(datetime) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
Interval variant
Calculates the length in seconds of an interval.
Синтаксис |
second(interval) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.7.16. to_date
Converts a string into a date object. An optional format string can be provided to parse the string; see QDate::fromString or the documentation of the format_date function for additional documentation on the format. By default the current QGIS user locale is used.
Синтаксис |
to_date(string, [format], [language]) [] обозначает необязательные аргументы |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
Further reading: format_date
9.2.7.17. to_datetime
Converts a string into a datetime object. An optional format string can be provided to parse the string; see QDate::fromString, QTime::fromString or the documentation of the format_date function for additional documentation on the format. By default the current QGIS user locale is used.
Синтаксис |
to_datetime(string, [format], [language]) [] обозначает необязательные аргументы |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
Further reading: format_date
9.2.7.18. to_interval
Converts a string to an interval type. Can be used to take days, hours, month, etc of a date.
Синтаксис |
to_interval(string) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.7.19. to_time
Converts a string into a time object. An optional format string can be provided to parse the string; see QTime::fromString for additional documentation on the format.
Синтаксис |
to_time(string, [format], [language]) [] обозначает необязательные аргументы |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
Further reading: format_date
9.2.7.20. week
Extracts the week number from a date, or the number of weeks from an interval.
Date variant
Extracts the week number from a date or datetime.
Синтаксис |
week(date) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
Interval variant
Calculates the length in weeks of an interval.
Синтаксис |
week(interval) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.7.21. year
Extracts the year part from a date, or the number of years from an interval.
Date variant
Extracts the year part from a date or datetime.
Синтаксис |
year(date) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
Interval variant
Calculates the length in years of an interval.
Синтаксис |
year(interval) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
Some examples:
Besides these functions, subtracting dates, datetimes or times using the
- (minus) operator will return an interval.
Adding or subtracting an interval to dates, datetimes or times, using the
+ (plus) and - (minus) operators, will return a datetime.
Get the number of days until QGIS 3.0 release:
to_date('2017-09-29') - to_date(now()) -- Returns <interval: 203 days>
The same with time:
to_datetime('2017-09-29 12:00:00') - now() -- Returns <interval: 202.49 days>
Get the datetime of 100 days from now:
now() + to_interval('100 days') -- Returns <datetime: 2017-06-18 01:00:00>
9.2.8. Fields and Values
Contains a list of fields from the active layer, and special values. Fields list includes the ones stored in the dataset, virtual and auxiliary ones as well as from joins.
Double-click a field name to have it added to your expression. You can also type the field name (preferably inside double quotes) or its alias.
To retrieve fields values to use in an expression, select the appropriate field and, in the shown widget, choose between 10 Samples and All Unique. Requested values are then displayed and you can use the Search box at the top of the list to filter the result. Sample values can also be accessed via right-clicking on a field.
To add a value to the expression you are writing, double-click on it in the list. If the value is of a string type, it should be simple quoted, otherwise no quote is needed.
Показать/скрыть список функций
9.2.8.1. NULL
Equates to a NULL value.
Синтаксис |
NULL |
Примеры |
|
Примечание
To test for NULL use an IS NULL or IS NOT NULL expression.
9.2.9. Files and Paths Functions
This group contains functions which manipulate file and path names.
Показать/скрыть список функций
9.2.9.1. base_file_name
Returns the base name of the file without the directory or file suffix.
Синтаксис |
base_file_name(path) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.9.2. exif
Retrieves exif tag values from an image file.
Синтаксис |
exif(path, [tag]) [] обозначает необязательные аргументы |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.9.3. file_exists
Returns TRUE if a file path exists.
Синтаксис |
file_exists(path) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.9.4. file_name
Returns the name of a file (including the file extension), excluding the directory.
Синтаксис |
file_name(path) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.9.5. file_path
Returns the directory component of a file path. This does not include the file name.
Синтаксис |
file_path(path) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.9.6. file_size
Returns the size (in bytes) of a file.
Синтаксис |
file_size(path) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.9.7. file_suffix
Returns the file suffix (extension) from a file path.
Синтаксис |
file_suffix(path) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.9.8. is_directory
Returns TRUE if a path corresponds to a directory.
Синтаксис |
is_directory(path) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.9.9. is_file
Returns TRUE if a path corresponds to a file.
Синтаксис |
is_file(path) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.10. Form Functions
This group contains functions that operate exclusively under the attribute form context. For example, in field’s widgets settings.
Показать/скрыть список функций
9.2.10.1. current_parent_value
Only usable in an embedded form context, this function returns the current, unsaved value of a field in the parent form currently being edited. This will differ from the parent feature’s actual attribute values for features which are currently being edited or have not yet been added to a parent layer. When used in a value-relation widget filter expression, this function should be wrapped into a „coalesce()“ that can retrieve the actual parent feature from the layer when the form is not used in an embedded context.
Синтаксис |
current_parent_value(field_name) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.10.2. current_value
Returns the current, unsaved value of a field in the form or table row currently being edited. This will differ from the feature’s actual attribute values for features which are currently being edited or have not yet been added to a layer.
Синтаксис |
current_value(field_name) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.11. Fuzzy Matching Functions
This group contains functions for fuzzy comparisons between values.
Показать/скрыть список функций
9.2.11.1. hamming_distance
Returns the Hamming distance between two strings. This equates to the number of characters at corresponding positions within the input strings where the characters are different. The input strings must be the same length, and the comparison is case-sensitive.
Синтаксис |
hamming_distance(string1, string2) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.11.2. levenshtein
Returns the Levenshtein edit distance between two strings. This equates to the minimum number of character edits (insertions, deletions or substitutions) required to change one string to another.
The Levenshtein distance is a measure of the similarity between two strings. Smaller distances mean the strings are more similar, and larger distances indicate more different strings. The distance is case sensitive.
Синтаксис |
levenshtein(string1, string2) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.11.3. longest_common_substring
Returns the longest common substring between two strings. This substring is the longest string that is a substring of the two input strings. For example, the longest common substring of «ABABC» and «BABCA» is «BABC». The substring is case sensitive.
Синтаксис |
longest_common_substring(string1, string2) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.11.4. soundex
Returns the Soundex representation of a string. Soundex is a phonetic matching algorithm, so strings with similar sounds should be represented by the same Soundex code.
Синтаксис |
soundex(string) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.12. General Functions
This group contains general assorted functions.
Показать/скрыть список функций
9.2.12.1. env
Gets an environment variable and returns its content as a string. If the variable is not found, NULL will be returned. This is handy to inject system specific configuration like drive letters or path prefixes. Definition of environment variables depends on the operating system, please check with your system administrator or the operating system documentation how this can be set.
Синтаксис |
env(name) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.12.2. eval
Evaluates an expression which is passed in a string. Useful to expand dynamic parameters passed as context variables or fields.
Синтаксис |
eval(expression) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.12.3. eval_template
Evaluates a template which is passed in a string. Useful to expand dynamic parameters passed as context variables or fields.
Синтаксис |
eval_template(template) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.12.4. is_layer_visible
Returns TRUE if a specified layer is visible.
Синтаксис |
is_layer_visible(layer) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.12.5. mime_type
Returns the mime type of the binary data.
Синтаксис |
mime_type(bytes) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.12.6. var
Returns the value stored within a specified variable.
Синтаксис |
var(name) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
Further reading: List of default variables
9.2.12.7. with_variable
This function sets a variable for any expression code that will be provided as 3rd argument. This is only useful for complicated expressions, where the same calculated value needs to be used in different places.
Синтаксис |
with_variable(name, value, expression) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.13. Geometry Functions
This group contains functions that operate on geometry objects (e.g. buffer, transform, $area).
Показать/скрыть список функций
9.2.13.1. affine_transform
Returns the geometry after an affine transformation. Calculations are in the Spatial Reference System of this geometry. The operations are performed in a scale, rotation, translation order. If there is a Z or M offset but the coordinate is not present in the geometry, it will be added.
Синтаксис |
affine_transform(geometry, delta_x, delta_y, rotation_z, scale_x, scale_y, [delta_z=0], [delta_m=0], [scale_z=1], [scale_m=1]) [] обозначает необязательные аргументы |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
Рис. 9.4 Vector point layer (green dots) before (left), and after (right) an affine transformation (translation).
9.2.13.2. angle_at_vertex
Returns the bisector angle (average angle) to the geometry for a specified vertex on a linestring geometry. Angles are in degrees clockwise from north.
Синтаксис |
angle_at_vertex(geometry, vertex) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.13.3. apply_dash_pattern
Applies a dash pattern to a geometry, returning a MultiLineString geometry which is the input geometry stroked along each line/ring with the specified pattern.
Синтаксис |
apply_dash_pattern(geometry, pattern, [start_rule=no_rule], [end_rule=no_rule], [adjustment=both], [pattern_offset=0]) [] обозначает необязательные аргументы |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.13.4. $area
Returns the area of the current feature. The area calculated by this function respects both the current project’s ellipsoid setting and area unit settings. For example, if an ellipsoid has been set for the project then the calculated area will be ellipsoidal, and if no ellipsoid is set then the calculated area will be planimetric.
Синтаксис |
$area |
Примеры |
|
9.2.13.5. area
Returns the area of a geometry polygon object. Calculations are always planimetric in the Spatial Reference System (SRS) of this geometry, and the units of the returned area will match the units for the SRS. This differs from the calculations performed by the $area function, which will perform ellipsoidal calculations based on the project’s ellipsoid and area unit settings.
Синтаксис |
area(geometry) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.13.6. azimuth
Returns the north-based azimuth as the angle in radians measured clockwise from the vertical on point_a to point_b.
Синтаксис |
azimuth(point_a, point_b) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.13.7. bearing
Returns the north-based bearing as the angle in radians measured clockwise on the ellipsoid from the vertical on point_a to point_b.
Синтаксис |
bearing(point_a, point_b, [source_crs], [ellipsoid]) [] обозначает необязательные аргументы |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.13.8. boundary
Returns the closure of the combinatorial boundary of the geometry (ie the topological boundary of the geometry). For instance, a polygon geometry will have a boundary consisting of the linestrings for each ring in the polygon. Some geometry types do not have a defined boundary, e.g., points or geometry collections, and will return NULL.
Синтаксис |
boundary(geometry) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
Рис. 9.5 Boundary (black dashed line) of the source polygon layer
Further reading: Boundary algorithm
9.2.13.9. bounds
Returns a geometry which represents the bounding box of an input geometry. Calculations are in the Spatial Reference System of this geometry.
Синтаксис |
bounds(geometry) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
Рис. 9.6 Black lines represent the bounding boxes of each polygon feature
Further reading: Bounding boxes algorithm
9.2.13.10. bounds_height
Returns the height of the bounding box of a geometry. Calculations are in the Spatial Reference System of this geometry.
Синтаксис |
bounds_height(geometry) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.13.11. bounds_width
Returns the width of the bounding box of a geometry. Calculations are in the Spatial Reference System of this geometry.
Синтаксис |
bounds_width(geometry) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.13.12. buffer
Returns a geometry that represents all points whose distance from this geometry is less than or equal to distance. Calculations are in the Spatial Reference System of this geometry.
Синтаксис |
buffer(geometry, distance, [segments=8], [cap=“round“], [join=“round“], [miter_limit=2]) [] обозначает необязательные аргументы |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
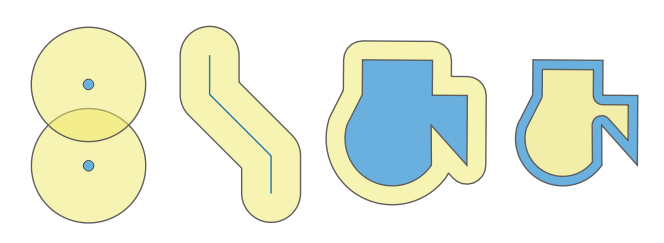
Рис. 9.7 Buffer (in yellow) of points, line, polygon with positive buffer, and polygon with negative buffer
Further reading: Buffer algorithm
9.2.13.13. buffer_by_m
Creates a buffer along a line geometry where the buffer diameter varies according to the m-values at the line vertices.
Синтаксис |
buffer_by_m(geometry, [segments=8]) [] обозначает необязательные аргументы |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
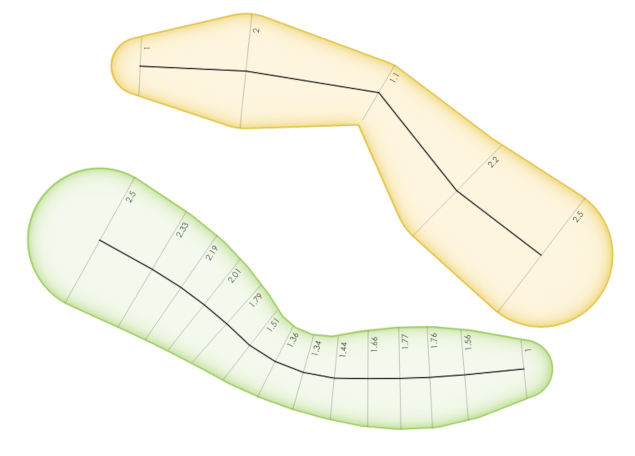
Рис. 9.8 Buffering line features using the m value on the vertices
Further reading: Variable width buffer (by M value) algorithm
9.2.13.14. centroid
Returns the geometric center of a geometry.
Синтаксис |
centroid(geometry) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
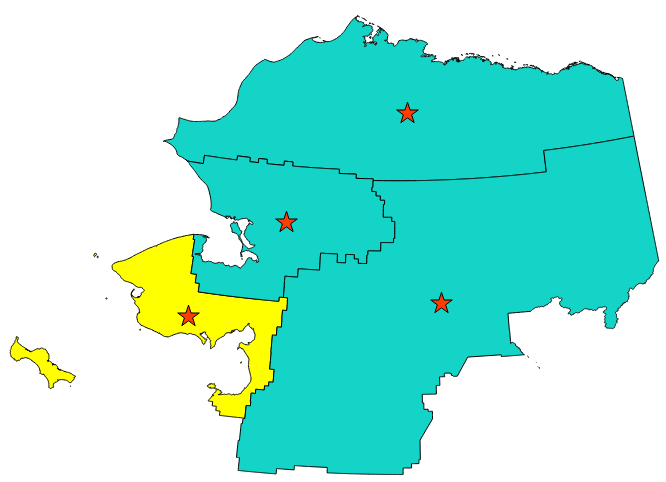
Рис. 9.9 The red stars represent the centroids of the features of the input layer.
Further reading: Centroids algorithm
9.2.13.15. close_line
Returns a closed line string of the input line string by appending the first point to the end of the line, if it is not already closed. If the geometry is not a line string or multi line string then the result will be NULL.
Синтаксис |
close_line(geometry) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.13.16. closest_point
Returns the point on geometry1 that is closest to geometry2.
Синтаксис |
closest_point(geometry1, geometry2) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.13.17. collect_geometries
Collects a set of geometries into a multi-part geometry object.
List of arguments variant
Geometry parts are specified as separate arguments to the function.
Синтаксис |
collect_geometries(geometry1, geometry2, …) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
Array variant
Geometry parts are specified as an array of geometry parts.
Синтаксис |
collect_geometries(array) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
Further reading: Collect geometries algorithm
9.2.13.18. combine
Returns the combination of two geometries.
Синтаксис |
combine(geometry1, geometry2) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.13.19. concave_hull
Returns a possibly concave polygon that contains all the points in the geometry
Синтаксис |
concave_hull(geometry, target_percent, [allow_holes=False]) [] обозначает необязательные аргументы |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
Рис. 9.10 Concave hulls with increasing target_percent parameter
Further reading: convex_hull, Concave hull algorithm
9.2.13.20. contains
Tests whether a geometry contains another. Returns TRUE if and only if no points of geometry2 lie in the exterior of geometry1, and at least one point of the interior of geometry2 lies in the interior of geometry1.
Синтаксис |
contains(geometry1, geometry2) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
Further reading: overlay_contains
9.2.13.21. convex_hull
Returns the convex hull of a geometry. It represents the minimum convex geometry that encloses all geometries within the set.
Синтаксис |
convex_hull(geometry) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
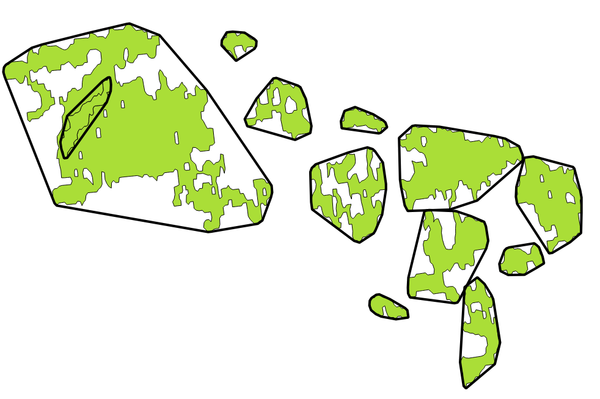
Рис. 9.11 Black lines identify the convex hull for each feature
Further reading: concave_hull, Convex hull algorithm
9.2.13.22. crosses
Tests whether a geometry crosses another. Returns TRUE if the supplied geometries have some, but not all, interior points in common.
Синтаксис |
crosses(geometry1, geometry2) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
Further reading: overlay_crosses
9.2.13.23. densify_by_count
Takes a polygon or line layer geometry and generates a new one in which the geometries have a larger number of vertices than the original one.
Синтаксис |
densify_by_count(geometry, vertices) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
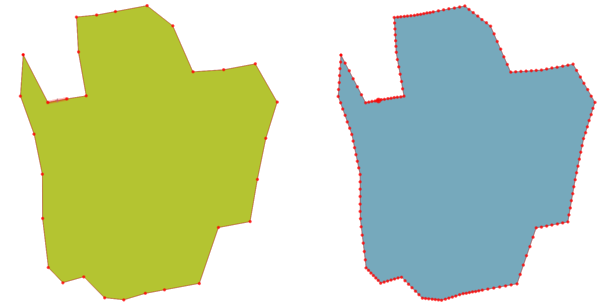
Рис. 9.12 Red points show the vertices before and after the densify
Further reading: Densify by count algorithm
9.2.13.24. densify_by_distance
Takes a polygon or line layer geometry and generates a new one in which the geometries are densified by adding additional vertices on edges that have a maximum distance of the specified interval distance.
Синтаксис |
densify_by_distance(geometry, distance) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
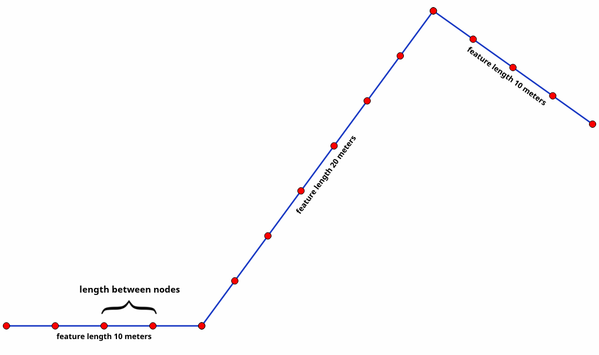
Рис. 9.13 Densify geometry at a given interval
Further reading: Densify by interval algorithm
9.2.13.25. difference
Returns a geometry that represents that part of geometry1 that does not intersect with geometry2.
Синтаксис |
difference(geometry1, geometry2) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
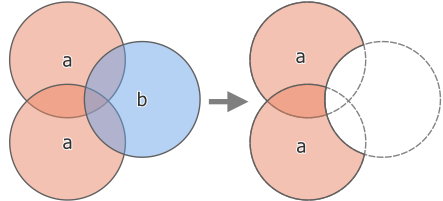
Рис. 9.14 Difference operation between a two-features input layer ‘a’ and a single feature overlay layer ‘b’ (left) - resulting in a new layer with the modified ‘a’ features (right)
Further reading: Difference algorithm
9.2.13.26. disjoint
Tests whether geometries do not spatially intersect. Returns TRUE if the geometries do not share any space together.
Синтаксис |
disjoint(geometry1, geometry2) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
Further reading: overlay_disjoint
9.2.13.27. distance
Returns the minimum distance (based on spatial reference) between two geometries in projected units.
Синтаксис |
distance(geometry1, geometry2) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.13.28. distance_to_vertex
Returns the distance along the geometry to a specified vertex.
Синтаксис |
distance_to_vertex(geometry, vertex) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.13.29. end_point
Returns the last node from a geometry.
Синтаксис |
end_point(geometry) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|

Рис. 9.15 End point of a line feature
Further reading: start_point, Extract specific vertices algorithm
9.2.13.30. exif_geotag
Creates a point geometry from the exif geotags of an image file.
Синтаксис |
exif_geotag(path) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.13.31. extend
Extends the start and end of a linestring geometry by a specified amount. Lines are extended using the bearing of the first and last segment in the line. For a multilinestring, all the parts are extended. Distances are in the Spatial Reference System of this geometry.
Синтаксис |
extend(geometry, start_distance, end_distance) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
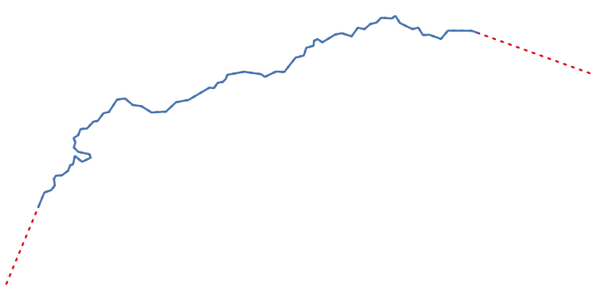
Рис. 9.16 The red dashes represent the initial and final extension of the original layer
Further reading: Extend lines algorithm
9.2.13.32. exterior_ring
Returns a line string representing the exterior ring of a polygon geometry. If the geometry is not a polygon then the result will be NULL.
Синтаксис |
exterior_ring(geometry) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
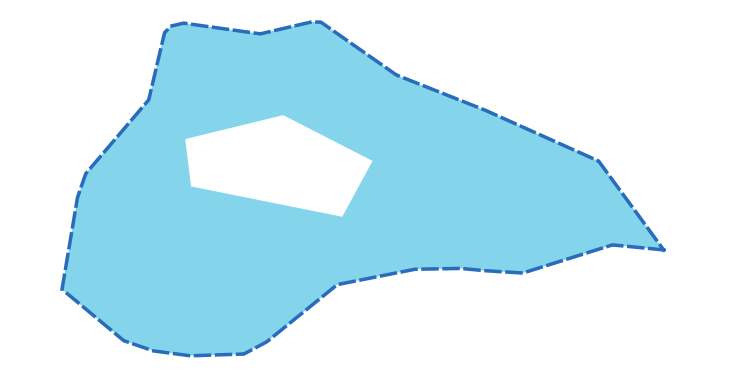
Рис. 9.17 The dashed line represents the exterior ring of the polygon
Further reading: Boundary algorithm, interior_ring_n
9.2.13.33. extrude
Returns an extruded version of the input (Multi-)Curve or (Multi-)Linestring geometry with an extension specified by x and y.
Синтаксис |
extrude(geometry, x, y) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
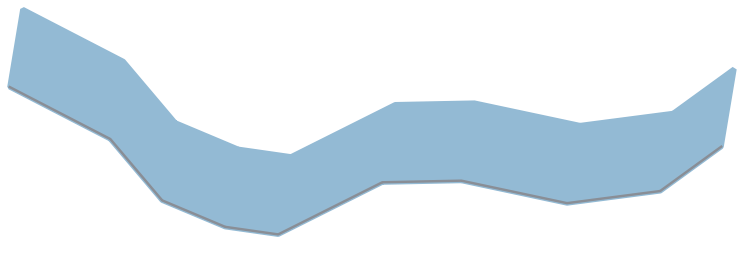
Рис. 9.18 Generating a polygon by extruding a line with offset in x and y directions
9.2.13.34. flip_coordinates
Returns a copy of the geometry with the x and y coordinates swapped. Useful for repairing geometries which have had their latitude and longitude values reversed.
Синтаксис |
flip_coordinates(geometry) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
Further reading: Swap X and Y coordinates algorithm
9.2.13.35. force_polygon_ccw
Forces a geometry to respect the convention where exterior rings are counter-clockwise, interior rings are clockwise.
Синтаксис |
force_polygon_ccw(geometry) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
Further reading: force_polygon_cw, force_rhr
9.2.13.36. force_polygon_cw
Forces a geometry to respect the convention where exterior rings are clockwise, interior rings are counter-clockwise.
Синтаксис |
force_polygon_cw(geometry) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
Further reading: force_polygon_ccw, force_rhr
9.2.13.37. force_rhr
Forces a geometry to respect the Right-Hand-Rule, in which the area that is bounded by a polygon is to the right of the boundary. In particular, the exterior ring is oriented in a clockwise direction and the interior rings in a counter-clockwise direction. Due to the inconsistency in the definition of the Right-Hand-Rule in some contexts it is recommended to use the explicit force_polygon_cw function instead.
Синтаксис |
force_rhr(geometry) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
Further reading: Force right-hand-rule algorithm, force_polygon_ccw, force_polygon_cw
9.2.13.38. geom_from_gml
Returns a geometry from a GML representation of geometry.
Синтаксис |
geom_from_gml(gml) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.13.39. geom_from_wkb
Returns a geometry created from a Well-Known Binary (WKB) representation.
Синтаксис |
geom_from_wkb(binary) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.13.40. geom_from_wkt
Returns a geometry created from a Well-Known Text (WKT) representation.
Синтаксис |
geom_from_wkt(text) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.13.41. geom_to_wkb
Returns the Well-Known Binary (WKB) representation of a geometry
Синтаксис |
geom_to_wkb(geometry) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.13.42. geom_to_wkt
Returns the Well-Known Text (WKT) representation of the geometry without SRID metadata.
Синтаксис |
geom_to_wkt(geometry, [precision=8]) [] обозначает необязательные аргументы |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.13.43. $geometry
Returns the geometry of the current feature. Can be used for processing with other functions. WARNING: This function is deprecated. It is recommended to use the replacement @geometry variable instead.
Синтаксис |
$geometry |
Примеры |
|
9.2.13.44. geometry
Returns a feature’s geometry.
Синтаксис |
geometry(feature) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.13.45. geometry_n
Returns a specific geometry from a geometry collection, or NULL if the input geometry is not a collection. Also returns a part from a multipart geometry.
Синтаксис |
geometry_n(geometry, index) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.13.46. geometry_type
Returns a string value describing the type of a geometry (Point, Line or Polygon)
Синтаксис |
geometry_type(geometry) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.13.47. hausdorff_distance
Returns the Hausdorff distance between two geometries. This is basically a measure of how similar or dissimilar 2 geometries are, with a lower distance indicating more similar geometries.
The function can be executed with an optional densify fraction argument. If not specified, an approximation to the standard Hausdorff distance is used. This approximation is exact or close enough for a large subset of useful cases. Examples of these are:
computing distance between Linestrings that are roughly parallel to each other, and roughly equal in length. This occurs in matching linear networks.
Testing similarity of geometries.
If the default approximate provided by this method is insufficient, specify the optional densify fraction argument. Specifying this argument performs a segment densification before computing the discrete Hausdorff distance. The parameter sets the fraction by which to densify each segment. Each segment will be split into a number of equal-length subsegments, whose fraction of the total length is closest to the given fraction. Decreasing the densify fraction parameter will make the distance returned approach the true Hausdorff distance for the geometries.
Синтаксис |
hausdorff_distance(geometry1, geometry2, [densify_fraction]) [] обозначает необязательные аргументы |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.13.48. inclination
Returns the inclination measured from the zenith (0) to the nadir (180) on point_a to point_b.
Синтаксис |
inclination(point_a, point_b) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.13.49. interior_ring_n
Returns a specific interior ring from a polygon geometry, or NULL if the geometry is not a polygon.
Синтаксис |
interior_ring_n(geometry, index) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
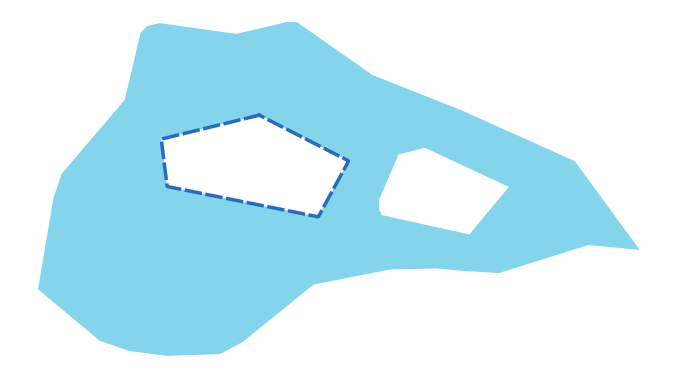
Рис. 9.19 The dashed line represents a specific interior ring of the polygon
Further reading: exterior_ring
9.2.13.50. intersection
Returns a geometry that represents the shared portion of two geometries.
Синтаксис |
intersection(geometry1, geometry2) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
Further reading: Intersection algorithm
9.2.13.51. intersects
Tests whether a geometry intersects another. Returns TRUE if the geometries spatially intersect (share any portion of space) and false if they do not.
Синтаксис |
intersects(geometry1, geometry2) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
Further reading: overlay_intersects
9.2.13.52. intersects_bbox
Tests whether a geometry’s bounding box overlaps another geometry’s bounding box. Returns TRUE if the geometries spatially intersect the bounding box defined and false if they do not.
Синтаксис |
intersects_bbox(geometry1, geometry2) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.13.53. is_closed
Returns TRUE if a line string is closed (start and end points are coincident), or false if a line string is not closed. If the geometry is not a line string then the result will be NULL.
Синтаксис |
is_closed(geometry) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.13.54. is_empty
Returns TRUE if a geometry is empty (without coordinates), false if the geometry is not empty and NULL if there is no geometry. See also is_empty_or_null.
Синтаксис |
is_empty(geometry) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
Further reading: is_empty_or_null
9.2.13.55. is_empty_or_null
Returns TRUE if a geometry is NULL or empty (without coordinates) or false otherwise. This function is like the expression „@geometry IS NULL or is_empty(@geometry)“
Синтаксис |
is_empty_or_null(geometry) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.13.56. is_multipart
Returns TRUE if the geometry is of Multi type.
Синтаксис |
is_multipart(geometry) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.13.57. is_valid
Returns TRUE if a geometry is valid; if it is well-formed in 2D according to the OGC rules.
Синтаксис |
is_valid(geometry) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
Further reading: make_valid, Check validity algorithm
9.2.13.58. $length
Returns the length of a linestring. If you need the length of a border of a polygon, use $perimeter instead. The length calculated by this function respects both the current project’s ellipsoid setting and distance unit settings. For example, if an ellipsoid has been set for the project then the calculated length will be ellipsoidal, and if no ellipsoid is set then the calculated length will be planimetric.
Синтаксис |
$length |
Примеры |
|
9.2.13.59. length
Returns the number of characters in a string or the length of a geometry linestring.
String variant
Returns the number of characters in a string.
Синтаксис |
length(string) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
Geometry variant
Calculate the length of a geometry line object. Calculations are always planimetric in the Spatial Reference System (SRS) of this geometry, and the units of the returned length will match the units for the SRS. This differs from the calculations performed by the $length function, which will perform ellipsoidal calculations based on the project’s ellipsoid and distance unit settings.
Синтаксис |
length(geometry) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
Further reading: straight_distance_2d
9.2.13.60. length3D
Calculates the 3D length of a geometry line object. If the geometry is not a 3D line object, it returns its 2D length. Calculations are always planimetric in the Spatial Reference System (SRS) of this geometry, and the units of the returned length will match the units for the SRS. This differs from the calculations performed by the $length function, which will perform ellipsoidal calculations based on the project’s ellipsoid and distance unit settings.
Синтаксис |
length3D(geometry) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.13.61. line_interpolate_angle
Returns the angle parallel to the geometry at a specified distance along a linestring geometry. Angles are in degrees clockwise from north.
Синтаксис |
line_interpolate_angle(geometry, distance) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.13.62. line_interpolate_point
Returns the point interpolated by a specified distance along a linestring geometry.
Синтаксис |
line_interpolate_point(geometry, distance) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
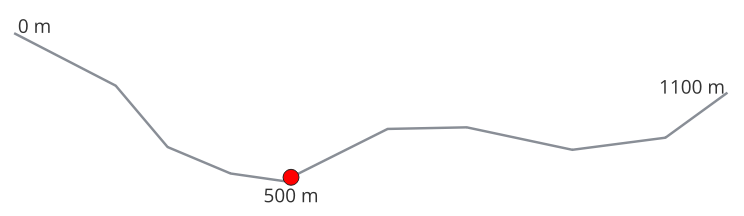
Рис. 9.20 Interpolated point at 500m of the beginning of the line
Further reading: Interpolate point on line algorithm
9.2.13.63. line_interpolate_point_by_m
Returns the point interpolated by a matching M value along a linestring geometry.
Синтаксис |
line_interpolate_point_by_m(geometry, m, [use_3d_distance=false]) [] обозначает необязательные аргументы |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.13.64. line_locate_m
Returns the distance along a linestring corresponding to the first matching interpolated M value.
Синтаксис |
line_locate_m(geometry, m, [use_3d_distance=false]) [] обозначает необязательные аргументы |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.13.65. line_locate_point
Returns the distance along a linestring corresponding to the closest position the linestring comes to a specified point geometry.
Синтаксис |
line_locate_point(geometry, point) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.13.66. line_merge
Returns a LineString or MultiLineString geometry, where any connected LineStrings from the input geometry have been merged into a single linestring. This function will return NULL if passed a geometry which is not a LineString/MultiLineString.
Синтаксис |
line_merge(geometry) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.13.67. line_substring
Returns the portion of a line (or curve) geometry which falls between the specified start and end distances (measured from the beginning of the line). Z and M values are linearly interpolated from existing values.
Синтаксис |
line_substring(geometry, start_distance, end_distance) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
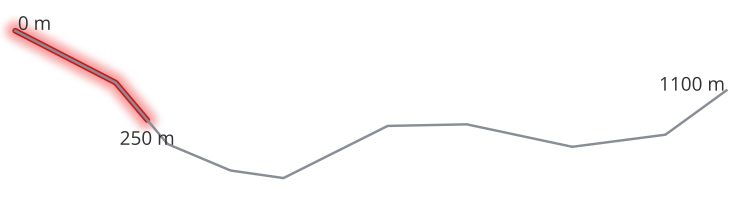
Рис. 9.21 Substring line with starting distance set at 0 meters and the ending distance at 250 meters.
Further reading: Line substring algorithm
9.2.13.68. m
Returns the m (measure) value of a point geometry.
Синтаксис |
m(geometry) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.13.69. m_at
Retrieves a m coordinate of the geometry, or NULL if the geometry has no m value.
Синтаксис |
m_at(geometry, vertex) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.13.70. m_max
Returns the maximum m (measure) value of a geometry.
Синтаксис |
m_max(geometry) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.13.71. m_min
Returns the minimum m (measure) value of a geometry.
Синтаксис |
m_min(geometry) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.13.72. main_angle
Returns the angle of the long axis (clockwise, in degrees from North) of the oriented minimal bounding rectangle, which completely covers the geometry.
Синтаксис |
main_angle(geometry) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.13.73. make_circle
Creates a circular polygon.
Синтаксис |
make_circle(center, radius, [segments=36]) [] обозначает необязательные аргументы |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.13.74. make_ellipse
Creates an elliptical polygon.
Синтаксис |
make_ellipse(center, semi_major_axis, semi_minor_axis, azimuth, [segments=36]) [] обозначает необязательные аргументы |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.13.75. make_line
Creates a line geometry from a series of point geometries.
List of arguments variant
Line vertices are specified as separate arguments to the function.
Синтаксис |
make_line(point1, point2, …) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
Array variant
Line vertices are specified as an array of points.
Синтаксис |
make_line(array) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.13.76. make_point
Creates a point geometry from an x and y (and optional z and m) value.
Синтаксис |
make_point(x, y, [z], [m]) [] обозначает необязательные аргументы |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.13.77. make_point_m
Creates a point geometry from an x, y coordinate and m value.
Синтаксис |
make_point_m(x, y, m) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.13.78. make_polygon
Creates a polygon geometry from an outer ring and optional series of inner ring geometries.
Синтаксис |
make_polygon(outerRing, [innerRing1], [innerRing2], …) [] обозначает необязательные аргументы |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.13.79. make_rectangle_3points
Creates a rectangle from 3 points.
Синтаксис |
make_rectangle_3points(point1, point2, point3, [option=0]) [] обозначает необязательные аргументы |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.13.80. make_regular_polygon
Creates a regular polygon.
Синтаксис |
make_regular_polygon(center, radius, number_sides, [circle=0]) [] обозначает необязательные аргументы |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.13.81. make_square
Creates a square from a diagonal.
Синтаксис |
make_square(point1, point2) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.13.82. make_triangle
Creates a triangle polygon.
Синтаксис |
make_triangle(point1, point2, point3) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.13.83. make_valid
Returns a valid geometry or an empty geometry if the geometry could not be made valid.
Синтаксис |
make_valid(geometry, [method=structure], [keep_collapsed=false]) [] обозначает необязательные аргументы |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
Further reading: is_valid, Fix geometries algorithm
9.2.13.84. minimal_circle
Returns the minimal enclosing circle of a geometry. It represents the minimum circle that encloses all geometries within the set.
Синтаксис |
minimal_circle(geometry, [segments=36]) [] обозначает необязательные аргументы |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
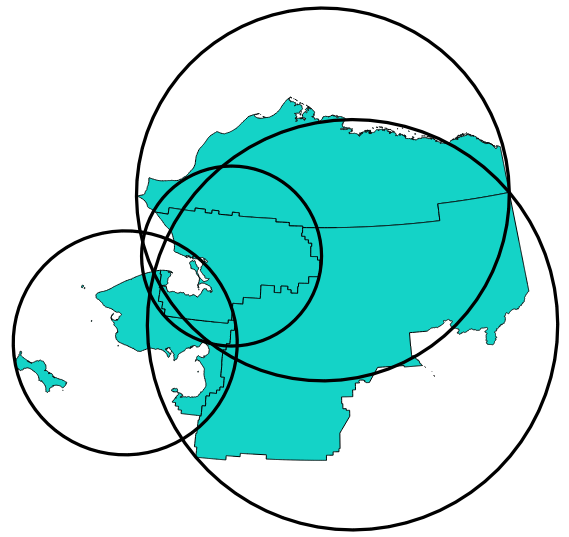
Рис. 9.22 Minimal enclosing circle of each feature
Further reading: Minimum enclosing circles algorithm
9.2.13.85. nodes_to_points
Returns a multipoint geometry consisting of every node in the input geometry.
Синтаксис |
nodes_to_points(geometry, [ignore_closing_nodes=false]) [] обозначает необязательные аргументы |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
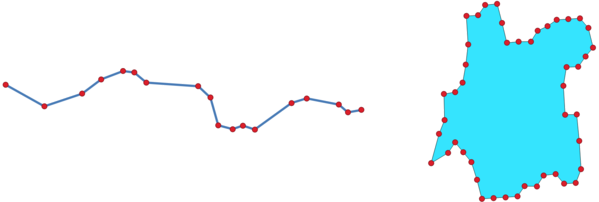
Рис. 9.23 Multi-point feature extracted from vertices
Further reading: Extract vertices algorithm
9.2.13.86. num_geometries
Returns the number of geometries in a geometry collection, or the number of parts in a multi-part geometry. The function returns NULL if the input geometry is not a collection.
Синтаксис |
num_geometries(geometry) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.13.87. num_interior_rings
Returns the number of interior rings in a polygon or geometry collection, or NULL if the input geometry is not a polygon or collection.
Синтаксис |
num_interior_rings(geometry) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.13.88. num_points
Returns the number of vertices in a geometry.
Синтаксис |
num_points(geometry) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.13.89. num_rings
Returns the number of rings (including exterior rings) in a polygon or geometry collection, or NULL if the input geometry is not a polygon or collection.
Синтаксис |
num_rings(geometry) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.13.90. offset_curve
Returns a geometry formed by offsetting a linestring geometry to the side. Distances are in the Spatial Reference System of this geometry.
Синтаксис |
offset_curve(geometry, distance, [segments=8], [join=1], [miter_limit=2.0]) [] обозначает необязательные аргументы |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
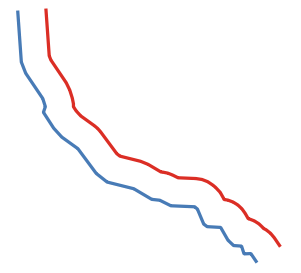
Рис. 9.24 In blue the source layer, in red the offset one
Further reading: Offset lines algorithm
9.2.13.91. order_parts
Orders the parts of a MultiGeometry by a given criteria
Синтаксис |
order_parts(geometry, orderby, [ascending=true]) [] обозначает необязательные аргументы |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.13.92. oriented_bbox
Returns a geometry which represents the minimal oriented bounding box of an input geometry.
Синтаксис |
oriented_bbox(geometry) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
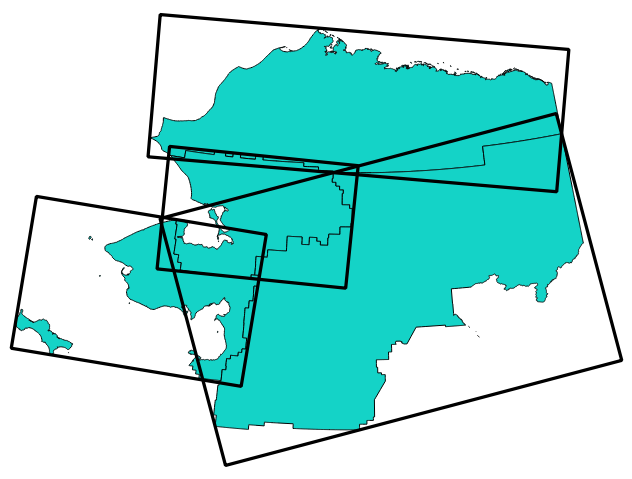
Рис. 9.25 Oriented minimum bounding box
Further reading: Oriented minimum bounding box algorithm
9.2.13.93. overlaps
Tests whether a geometry overlaps another. Returns TRUE if the geometries share space, are of the same dimension, but are not completely contained by each other.
Синтаксис |
overlaps(geometry1, geometry2) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.13.94. overlay_contains
Returns whether the current feature spatially contains at least one feature from a target layer, or an array of expression-based results for the features in the target layer contained in the current feature.
Read more on the underlying GEOS «Contains» predicate, as described in PostGIS ST_Contains function.
Синтаксис |
overlay_contains(layer, [expression], [filter], [limit], [cache=false]) [] обозначает необязательные аргументы |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
Further reading: contains, array manipulation, Select by location algorithm
9.2.13.95. overlay_crosses
Returns whether the current feature spatially crosses at least one feature from a target layer, or an array of expression-based results for the features in the target layer crossed by the current feature.
Read more on the underlying GEOS «Crosses» predicate, as described in PostGIS ST_Crosses function.
Синтаксис |
overlay_crosses(layer, [expression], [filter], [limit], [cache=false]) [] обозначает необязательные аргументы |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
Further reading: crosses, array manipulation, Select by location algorithm
9.2.13.96. overlay_disjoint
Returns whether the current feature is spatially disjoint from all the features of a target layer, or an array of expression-based results for the features in the target layer that are disjoint from the current feature.
Read more on the underlying GEOS «Disjoint» predicate, as described in PostGIS ST_Disjoint function.
Синтаксис |
overlay_disjoint(layer, [expression], [filter], [limit], [cache=false]) [] обозначает необязательные аргументы |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
Further reading: disjoint, array manipulation, Select by location algorithm
9.2.13.97. overlay_equals
Returns whether the current feature spatially equals to at least one feature from a target layer, or an array of expression-based results for the features in the target layer that are spatially equal to the current feature.
Read more on the underlying GEOS «Equals» predicate, as described in PostGIS ST_Equals function.
Синтаксис |
overlay_equals(layer, [expression], [filter], [limit], [cache=false]) [] обозначает необязательные аргументы |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
Further reading: array manipulation, Select by location algorithm
9.2.13.98. overlay_intersects
Returns whether the current feature spatially intersects at least one feature from a target layer, or an array of expression-based results for the features in the target layer intersected by the current feature.
Read more on the underlying GEOS «Intersects» predicate, as described in PostGIS ST_Intersects function.
Синтаксис |
overlay_intersects(layer, [expression], [filter], [limit], [cache=false], [min_overlap], [min_inscribed_circle_radius], [return_details], [sort_by_intersection_size]) [] обозначает необязательные аргументы |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
Further reading: intersects, array manipulation, Select by location algorithm
9.2.13.99. overlay_nearest
Returns whether the current feature has feature(s) from a target layer within a given distance, or an array of expression-based results for the features in the target layer within a distance from the current feature.
Note: This function can be slow and consume a lot of memory for large layers.
Синтаксис |
overlay_nearest(layer, [expression], [filter], [limit=1], [max_distance], [cache=false]) [] обозначает необязательные аргументы |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
Further reading: array manipulation, Join attributes by nearest algorithm
9.2.13.100. overlay_touches
Returns whether the current feature spatially touches at least one feature from a target layer, or an array of expression-based results for the features in the target layer touched by the current feature.
Read more on the underlying GEOS «Touches» predicate, as described in PostGIS ST_Touches function.
Синтаксис |
overlay_touches(layer, [expression], [filter], [limit], [cache=false]) [] обозначает необязательные аргументы |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
Further reading: touches, array manipulation, Select by location algorithm
9.2.13.101. overlay_within
Returns whether the current feature is spatially within at least one feature from a target layer, or an array of expression-based results for the features in the target layer that contain the current feature.
Read more on the underlying GEOS «Within» predicate, as described in PostGIS ST_Within function.
Синтаксис |
overlay_within(layer, [expression], [filter], [limit], [cache=false]) [] обозначает необязательные аргументы |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
Further reading: within, array manipulation, Select by location algorithm
9.2.13.102. $perimeter
Returns the perimeter length of the current feature. The perimeter calculated by this function respects both the current project’s ellipsoid setting and distance unit settings. For example, if an ellipsoid has been set for the project then the calculated perimeter will be ellipsoidal, and if no ellipsoid is set then the calculated perimeter will be planimetric.
Синтаксис |
$perimeter |
Примеры |
|
9.2.13.103. perimeter
Returns the perimeter of a geometry polygon object. Calculations are always planimetric in the Spatial Reference System (SRS) of this geometry, and the units of the returned perimeter will match the units for the SRS. This differs from the calculations performed by the $perimeter function, which will perform ellipsoidal calculations based on the project’s ellipsoid and distance unit settings.
Синтаксис |
perimeter(geometry) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.13.104. point_n
Returns a specific node from a geometry.
Синтаксис |
point_n(geometry, index) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
Further reading: Extract specific vertices algorithm
9.2.13.105. point_on_surface
Returns a point guaranteed to lie on the surface of a geometry.
Синтаксис |
point_on_surface(geometry) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
Further reading: Point on Surface algorithm
9.2.13.106. pole_of_inaccessibility
Calculates the approximate pole of inaccessibility for a surface, which is the most distant internal point from the boundary of the surface. This function uses the „polylabel“ algorithm (Vladimir Agafonkin, 2016), which is an iterative approach guaranteed to find the true pole of inaccessibility within a specified tolerance. More precise tolerances require more iterations and will take longer to calculate.
Синтаксис |
pole_of_inaccessibility(geometry, tolerance) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
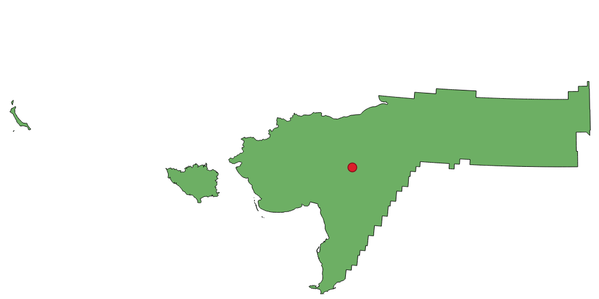
Рис. 9.26 Pole of inaccessibility
Further reading: Pole of inaccessibility algorithm
9.2.13.107. project
Returns a point projected from a start point using a distance, a bearing (azimuth) and an elevation in radians.
Синтаксис |
project(point, distance, azimuth, [elevation]) [] обозначает необязательные аргументы |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
Further reading: Project points (Cartesian) algorithm
9.2.13.108. relate
Tests the Dimensional Extended 9 Intersection Model (DE-9IM) representation of the relationship between two geometries.
Relationship variant
Returns the Dimensional Extended 9 Intersection Model (DE-9IM) representation of the relationship between two geometries.
Синтаксис |
relate(geometry, geometry) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
Pattern match variant
Tests whether the DE-9IM relationship between two geometries matches a specified pattern.
Синтаксис |
relate(geometry, geometry, pattern) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.13.109. reverse
Reverses the direction of a line string by reversing the order of its vertices.
Синтаксис |
reverse(geometry) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
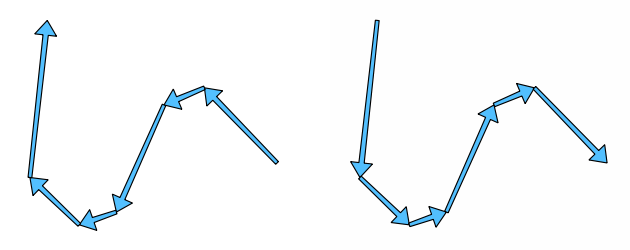
Рис. 9.27 Reversing line direction
Further reading: Reverse line direction algorithm
9.2.13.110. rotate
Returns a rotated version of a geometry. Calculations are in the Spatial Reference System of this geometry.
Синтаксис |
rotate(geometry, rotation, [center=NULL], [per_part=false]) [] обозначает необязательные аргументы |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
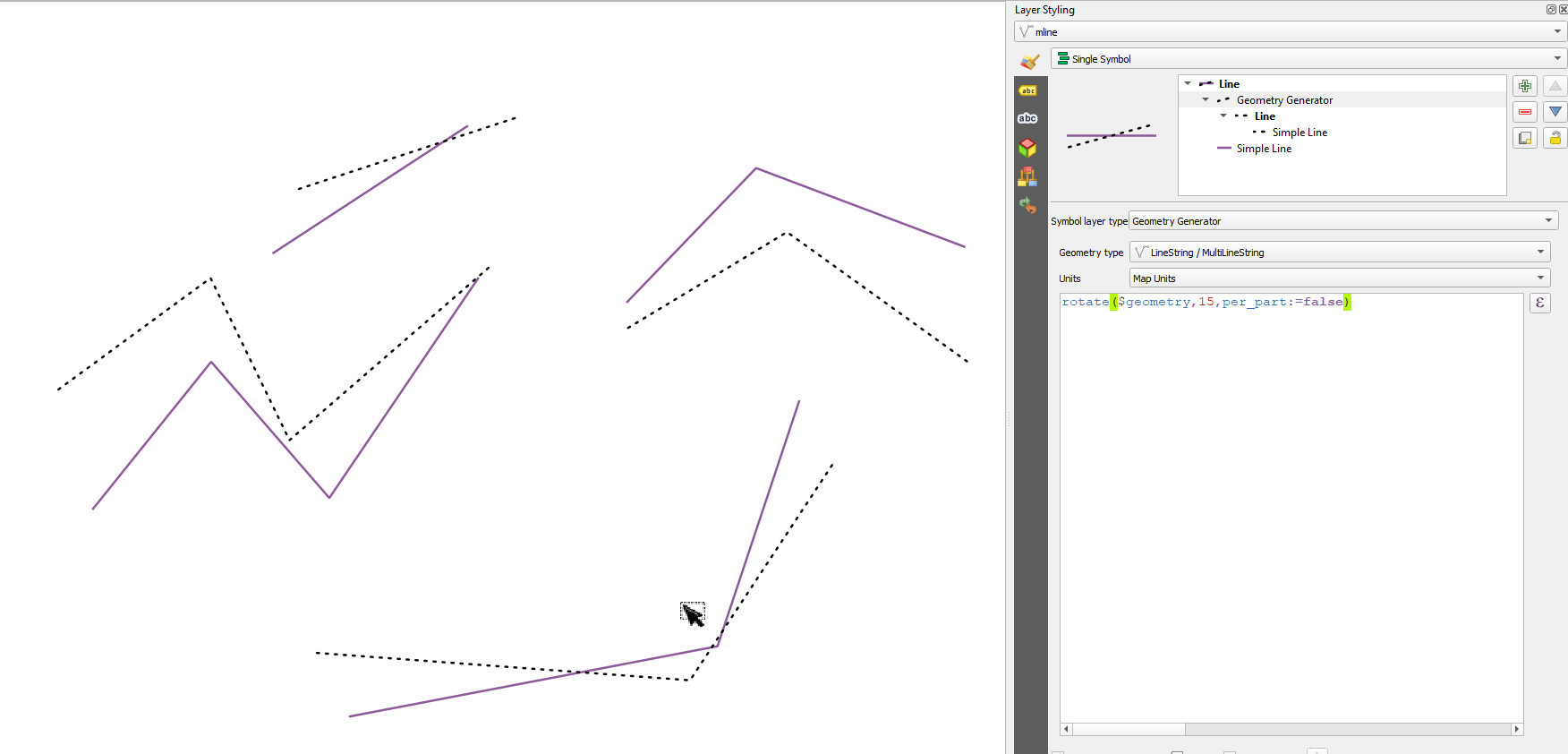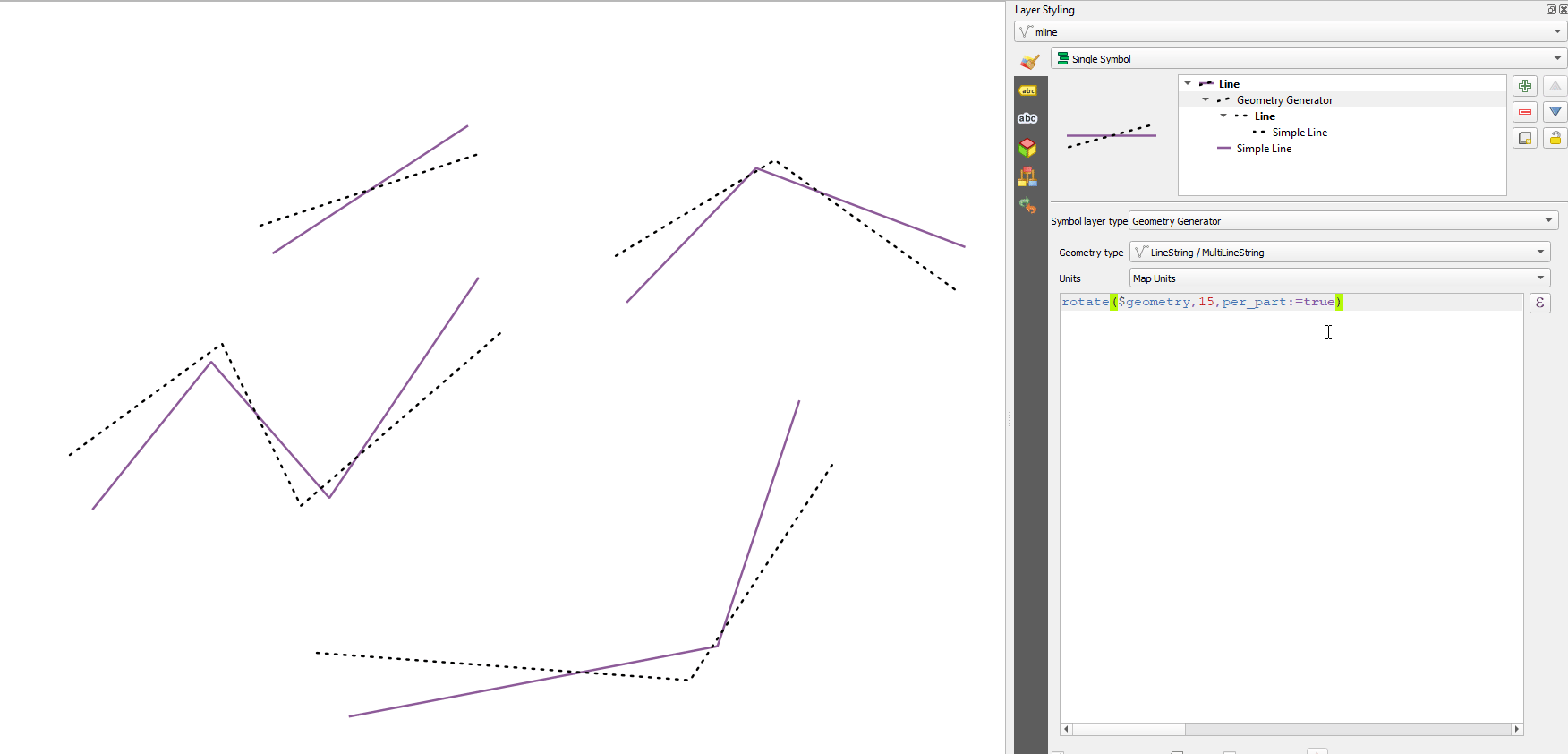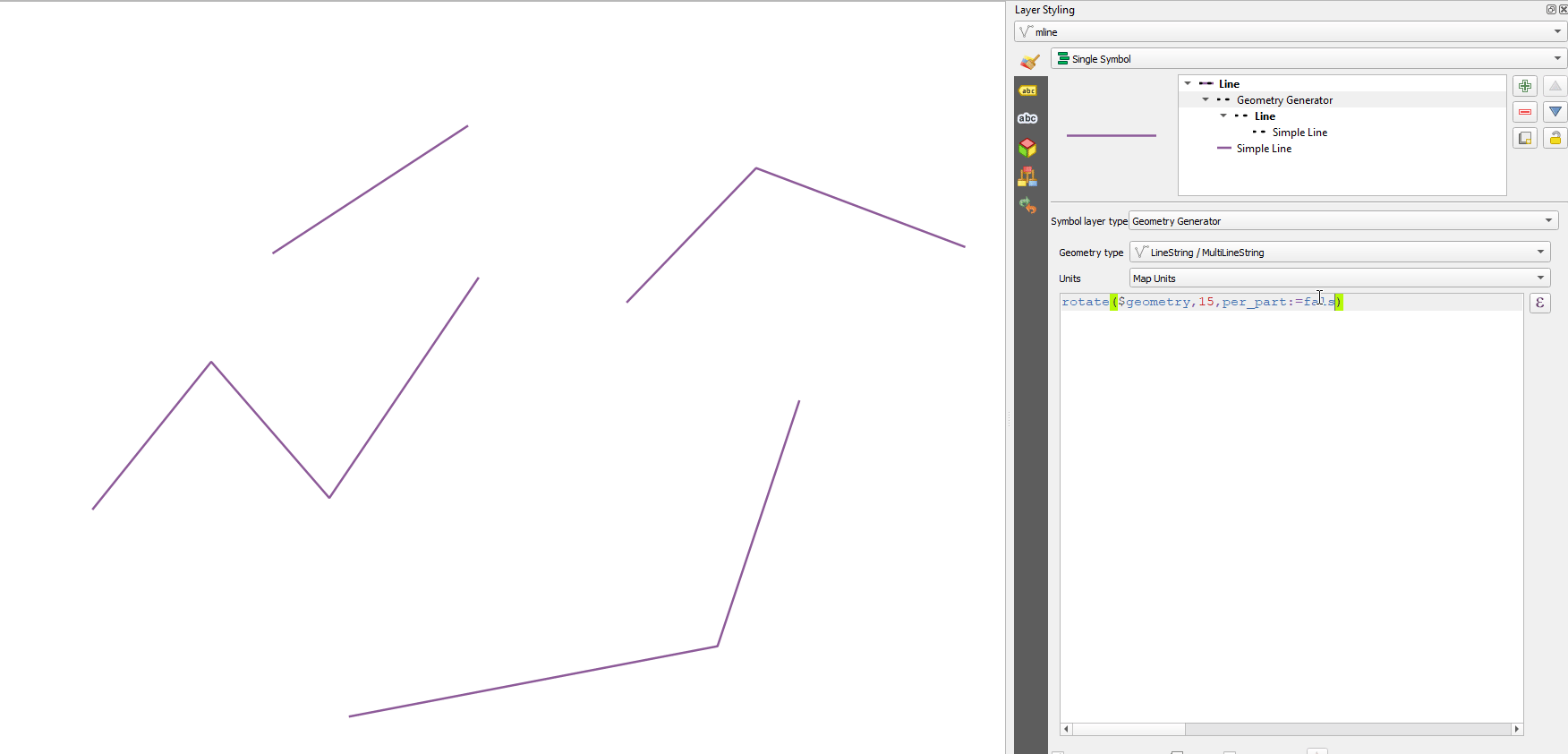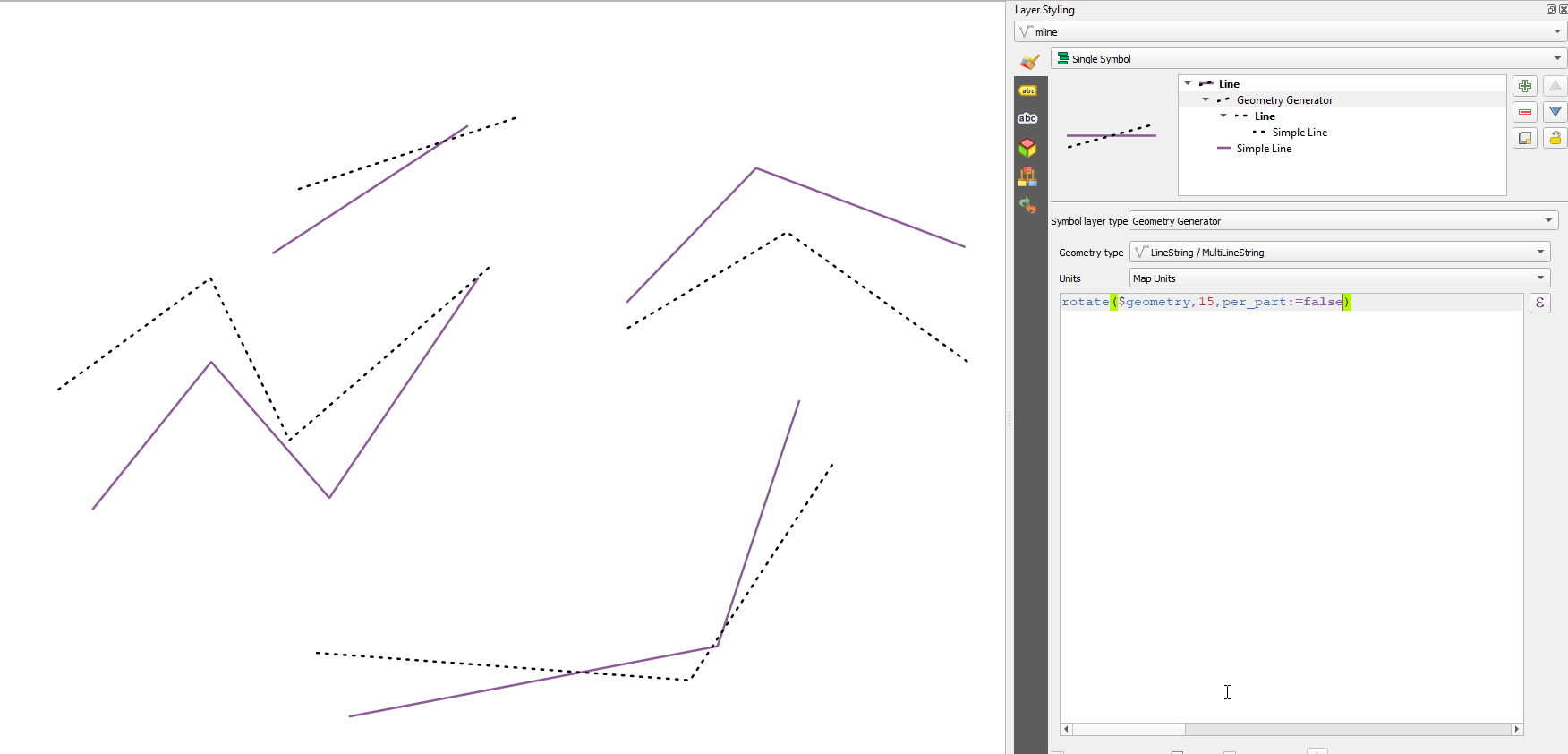
Рис. 9.28 Rotating features
9.2.13.111. roundness
Calculates how close a polygon shape is to a circle. The function returns 1 when the polygon shape is a perfect circle and 0 when it is completely flat.
Синтаксис |
roundness(geometry) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
Further reading: Roundness algorithm
9.2.13.112. scale
Returns a scaled version of a geometry. Calculations are in the Spatial Reference System of this geometry.
Синтаксис |
scale(geometry, x_scale, y_scale, [center]) [] обозначает необязательные аргументы |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.13.113. segments_to_lines
Returns a multi line geometry consisting of a line for every segment in the input geometry.
Синтаксис |
segments_to_lines(geometry) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
Further reading: Explode lines algorithm
9.2.13.115. shortest_line
Returns the shortest line joining geometry1 to geometry2. The resultant line will start at geometry1 and end at geometry2.
Синтаксис |
shortest_line(geometry1, geometry2) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.13.116. simplify
Simplifies a geometry by removing nodes using a distance based threshold (ie, the Douglas Peucker algorithm). The algorithm preserves large deviations in geometries and reduces the number of vertices in nearly straight segments.
Синтаксис |
simplify(geometry, tolerance) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
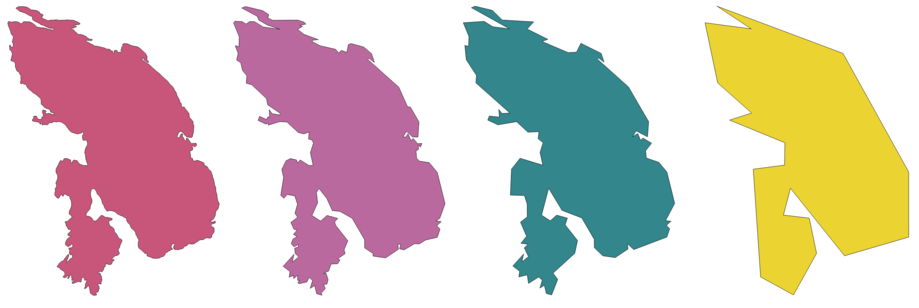
Рис. 9.29 From left to right, source layer and increasing simplification tolerances
Further reading: Simplify algorithm
9.2.13.117. simplify_vw
Simplifies a geometry by removing nodes using an area based threshold (ie, the Visvalingam-Whyatt algorithm). The algorithm removes vertices which create small areas in geometries, e.g., narrow spikes or nearly straight segments.
Синтаксис |
simplify_vw(geometry, tolerance) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
Further reading: Simplify algorithm
9.2.13.118. single_sided_buffer
Returns a geometry formed by buffering out just one side of a linestring geometry. Distances are in the Spatial Reference System of this geometry.
Синтаксис |
single_sided_buffer(geometry, distance, [segments=8], [join=1], [miter_limit=2.0]) [] обозначает необязательные аргументы |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
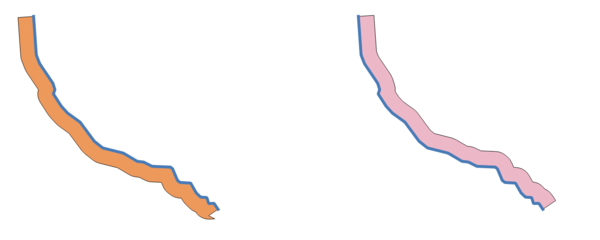
Рис. 9.30 Left versus right side buffer on the same vector line layer
Further reading: Single sided buffer algorithm
9.2.13.119. sinuosity
Returns the sinuosity of a curve, which is the ratio of the curve length to the straight (2D) distance between its endpoints.
Синтаксис |
sinuosity(geometry) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.13.120. smooth
Smooths a geometry by adding extra nodes which round off corners in the geometry. If input geometries contain Z or M values, these will also be smoothed and the output geometry will retain the same dimensionality as the input geometry.
Синтаксис |
smooth(geometry, [iterations=1], [offset=0.25], [min_length=-1], [max_angle=180]) [] обозначает необязательные аргументы |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|

Рис. 9.31 Increasing number of iterations causes smoother geometries
Further reading: Smooth algorithm
9.2.13.121. square_wave
Constructs square/rectangular waves along the boundary of a geometry.
Синтаксис |
square_wave(geometry, wavelength, amplitude, [strict=False]) [] обозначает необязательные аргументы |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
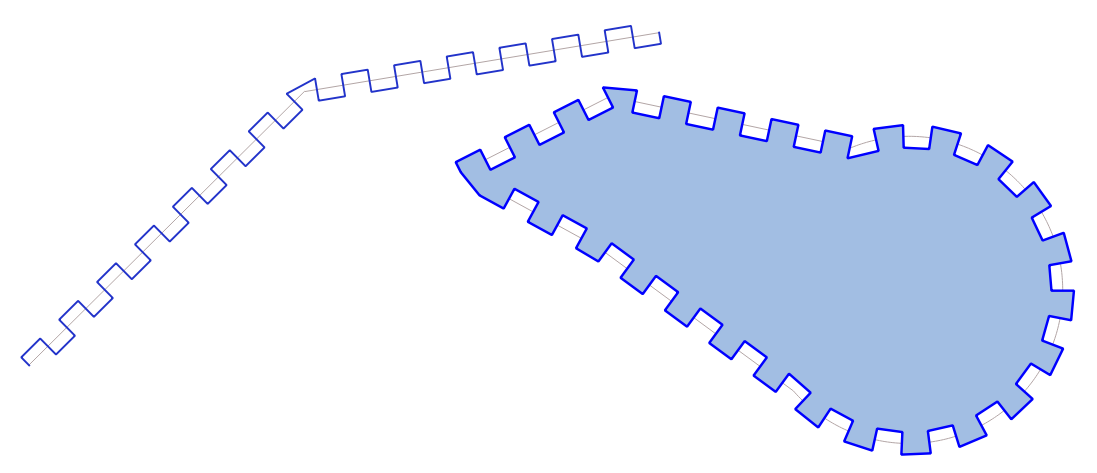
Рис. 9.32 Symbolizing features with square waves
9.2.13.122. square_wave_randomized
Constructs randomized square/rectangular waves along the boundary of a geometry.
Синтаксис |
square_wave_randomized(geometry, min_wavelength, max_wavelength, min_amplitude, max_amplitude, [seed=0]) [] обозначает необязательные аргументы |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
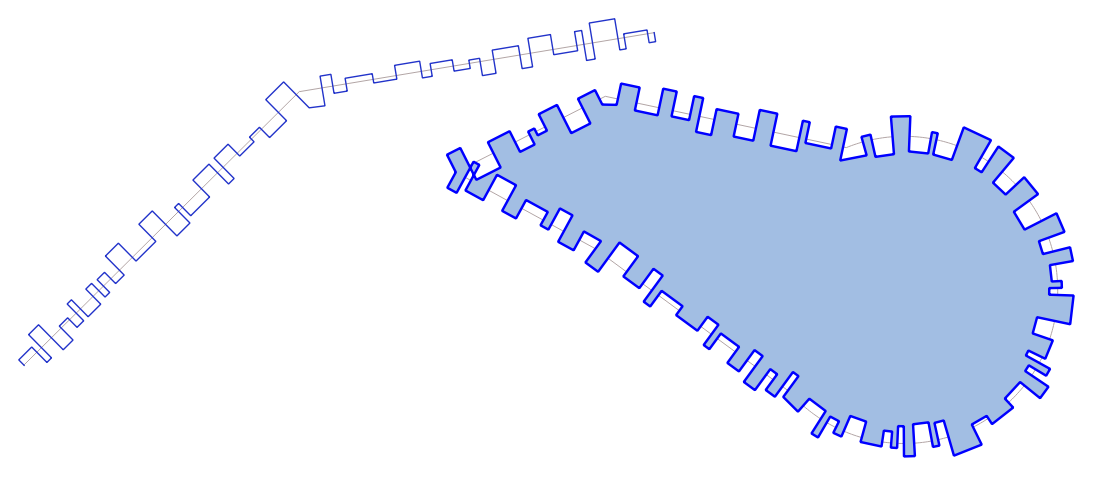
Рис. 9.33 Symbolizing features with square randomized waves
9.2.13.123. start_point
Returns the first node from a geometry.
Синтаксис |
start_point(geometry) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|

Рис. 9.34 Starting point of a line feature
Further reading: end_point, Extract specific vertices algorithm
9.2.13.124. straight_distance_2d
Returns the direct/euclidean distance between the first and last vertex of a geometry. The geometry must be a curve (circularstring, linestring).
Синтаксис |
straight_distance_2d(geometry) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
Further reading: length
9.2.13.125. sym_difference
Returns a geometry that represents the portions of two geometries that do not intersect.
Синтаксис |
sym_difference(geometry1, geometry2) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
Further reading: Symmetrical difference algorithm
9.2.13.126. tapered_buffer
Creates a buffer along a line geometry where the buffer diameter varies evenly over the length of the line.
Синтаксис |
tapered_buffer(geometry, start_width, end_width, [segments=8]) [] обозначает необязательные аргументы |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
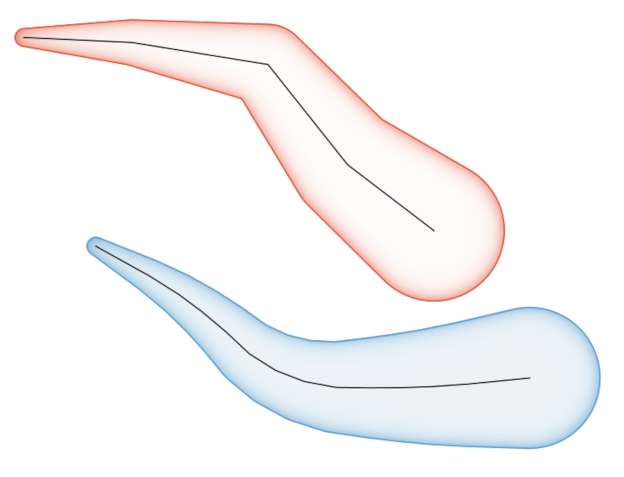
Рис. 9.35 Tapered buffer on line features
Further reading: Tapered buffers algorithm
9.2.13.127. touches
Tests whether a geometry touches another. Returns TRUE if the geometries have at least one point in common, but their interiors do not intersect.
Синтаксис |
touches(geometry1, geometry2) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
Further reading: overlay_touches
9.2.13.128. transform
Returns the geometry transformed from a source CRS to a destination CRS.
Синтаксис |
transform(geometry, source_auth_id, dest_auth_id) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
Further reading: Reproject layer algorithm
9.2.13.129. translate
Returns a translated version of a geometry. Calculations are in the Spatial Reference System of this geometry.
Синтаксис |
translate(geometry, dx, dy) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
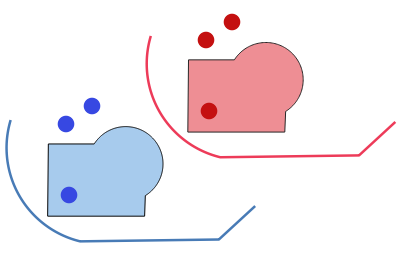
Рис. 9.36 Translating features
Further reading: Перевод algorithm
9.2.13.130. triangular_wave
Constructs triangular waves along the boundary of a geometry.
Синтаксис |
triangular_wave(geometry, wavelength, amplitude, [strict=False]) [] обозначает необязательные аргументы |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
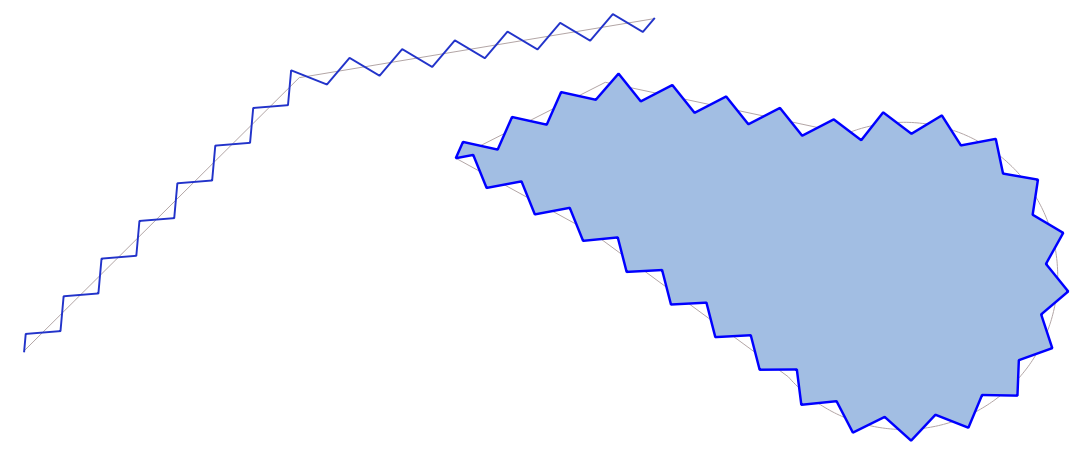
Рис. 9.37 Symbolizing features with triangular waves
9.2.13.131. triangular_wave_randomized
Constructs randomized triangular waves along the boundary of a geometry.
Синтаксис |
triangular_wave_randomized(geometry, min_wavelength, max_wavelength, min_amplitude, max_amplitude, [seed=0]) [] обозначает необязательные аргументы |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
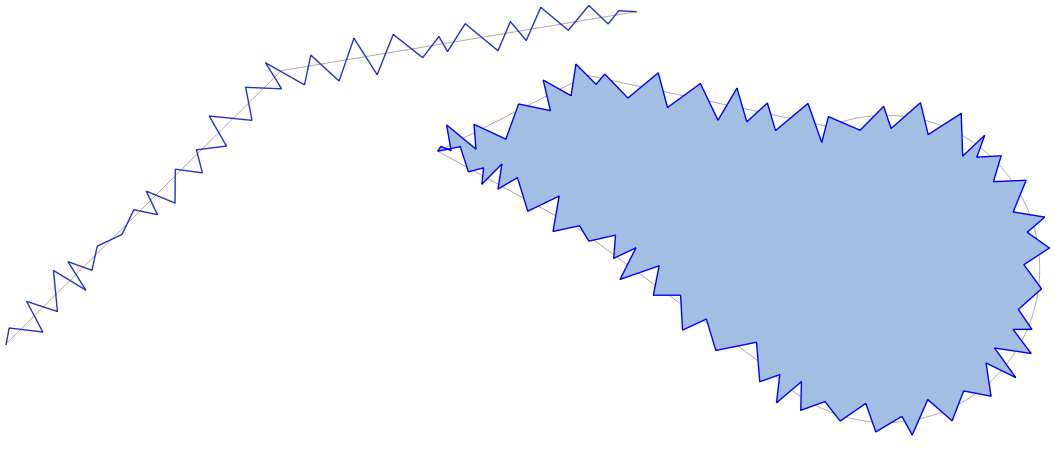
Рис. 9.38 Symbolizing features with triangular randomized waves
9.2.13.132. union
Returns a geometry that represents the point set union of the geometries.
Синтаксис |
union(geometry1, geometry2) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.13.133. wave
Constructs rounded (sine-like) waves along the boundary of a geometry.
Синтаксис |
wave(geometry, wavelength, amplitude, [strict=False]) [] обозначает необязательные аргументы |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
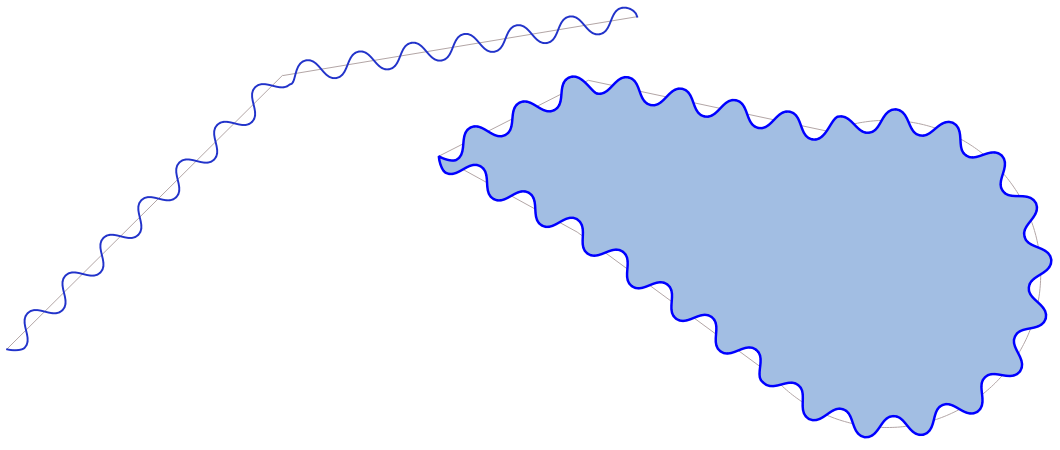
Рис. 9.39 Symbolizing features with waves
9.2.13.134. wave_randomized
Constructs randomized curved (sine-like) waves along the boundary of a geometry.
Синтаксис |
wave_randomized(geometry, min_wavelength, max_wavelength, min_amplitude, max_amplitude, [seed=0]) [] обозначает необязательные аргументы |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
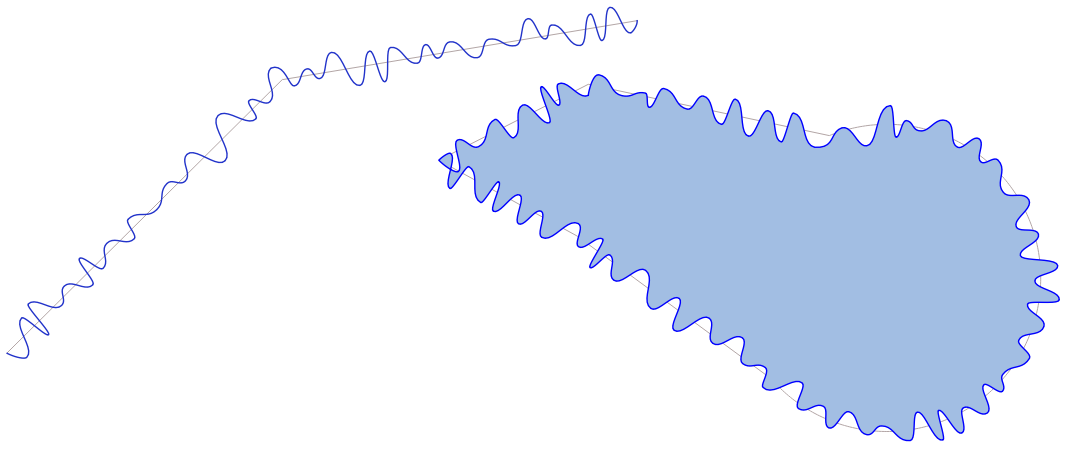
Рис. 9.40 Symbolizing features with randomized waves
9.2.13.135. wedge_buffer
Returns a wedge shaped buffer originating from a point geometry.
Синтаксис |
wedge_buffer(center, azimuth, width, outer_radius, [inner_radius=0.0]) [] обозначает необязательные аргументы |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|

Рис. 9.41 Wedge buffering features
Further reading: Create wedge buffers algorithm
9.2.13.136. within
Tests whether a geometry is within another. Returns TRUE if the geometry1 is completely within geometry2.
Синтаксис |
within(geometry1, geometry2) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
Further reading: overlay_within
9.2.13.137. $x
Returns the x coordinate of the current point feature. If the feature is a multipoint feature, then the x-coordinate of the first point will be returned. WARNING: This function is deprecated. It is recommended to use the replacement x() function with @geometry variable instead.
Синтаксис |
$x |
Примеры |
|
Further reading: x
9.2.13.138. x
Returns the x coordinate of a point geometry, or the x coordinate of the centroid for a non-point geometry.
Синтаксис |
x(geometry) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.13.139. $x_at
Retrieves a x coordinate of the current feature’s geometry. WARNING: This function is deprecated. It is recommended to use the replacement x_at function with @geometry variable instead.
Синтаксис |
$x_at(vertex) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
Further reading: x_at
9.2.13.140. x_at
Retrieves a x coordinate of the geometry.
Синтаксис |
x_at(geometry, vertex) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.13.141. x_max
Returns the maximum x coordinate of a geometry. Calculations are in the spatial reference system of this geometry.
Синтаксис |
x_max(geometry) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.13.142. x_min
Returns the minimum x coordinate of a geometry. Calculations are in the spatial reference system of this geometry.
Синтаксис |
x_min(geometry) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.13.143. $y
Returns the y coordinate of the current point feature. If the feature is a multipoint feature, then the y-coordinate of the first point will be returned. WARNING: This function is deprecated. It is recommended to use the replacement y() function with @geometry variable instead.
Синтаксис |
$y |
Примеры |
|
Further reading: y
9.2.13.144. y
Returns the y coordinate of a point geometry, or the y coordinate of the centroid for a non-point geometry.
Синтаксис |
y(geometry) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.13.145. $y_at
Retrieves a y coordinate of the current feature’s geometry. WARNING: This function is deprecated. It is recommended to use the replacement y_at function with @geometry variable instead.
Синтаксис |
$y_at(vertex) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
Further reading: y_at
9.2.13.146. y_at
Retrieves a y coordinate of the geometry.
Синтаксис |
y_at(geometry, vertex) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.13.147. y_max
Returns the maximum y coordinate of a geometry. Calculations are in the spatial reference system of this geometry.
Синтаксис |
y_max(geometry) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.13.148. y_min
Returns the minimum y coordinate of a geometry. Calculations are in the spatial reference system of this geometry.
Синтаксис |
y_min(geometry) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.13.149. $z
Returns the z value of the current point feature if it is 3D. If the feature is a multipoint feature, then the z value of the first point will be returned. WARNING: This function is deprecated. It is recommended to use the replacement z() function with @geometry variable instead.
Синтаксис |
$z |
Примеры |
|
9.2.13.150. z
Returns the z coordinate of a point geometry, or NULL if the geometry has no z value.
Синтаксис |
z(geometry) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.13.151. z_at
Retrieves a z coordinate of the geometry, or NULL if the geometry has no z value.
Синтаксис |
z_at(geometry, vertex) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.13.152. z_max
Returns the maximum z coordinate of a geometry, or NULL if the geometry has no z value.
Синтаксис |
z_max(geometry) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.13.153. z_min
Returns the minimum z coordinate of a geometry, or NULL if the geometry has no z value.
Синтаксис |
z_min(geometry) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.14. Layout Functions
This group contains functions to manipulate print layout items properties.
Показать/скрыть список функций
9.2.14.1. item_variables
Returns a map of variables from a layout item inside this print layout.
Синтаксис |
item_variables(id) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
Further reading: List of default variables
9.2.14.2. map_credits
Returns a list of credit (usage rights) strings for the layers shown in a layout, or specific layout map item.
Синтаксис |
map_credits([id], [include_layer_names=false], [layer_name_separator=“: „]) [] обозначает необязательные аргументы |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
This function requires the Access metadata properties of the layers to have been filled.
9.2.15. Map Layers
This group contains a list of the available layers in the current project and, for each layer, their fields (stored in the dataset, virtual or auxiliary ones as well as from joins). The fields can be interacted the same way as mentioned in Fields and Values, except that a double-click will add the name as a string (single quoted) to the expression instead of as a field reference given that they do not belong to the active layer. This offers a convenient way to write expressions referring to different layers, such as when performing aggregates, attribute or spatial queries.
It also provides some convenient functions to manipulate layers.
Показать/скрыть список функций
9.2.15.1. decode_uri
Takes a layer and decodes the uri of the underlying data provider. It depends on the dataprovider, which data is available.
Синтаксис |
decode_uri(layer, [part]) [] обозначает необязательные аргументы |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.15.2. layer_property
Returns a matching layer property or metadata value.
Синтаксис |
layer_property(layer, property) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.15.3. load_layer
Loads a layer by source URI and provider name.
Синтаксис |
load_layer(uri, provider) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.16. Maps Functions
This group contains functions to create or manipulate keys and values of map data structures (also known as dictionary objects, key-value pairs, or associative arrays). Unlike the list data structure where values order matters, the order of the key-value pairs in the map object is not relevant and values are identified by their keys.
Показать/скрыть список функций
9.2.16.1. from_json
Loads a JSON formatted string.
Синтаксис |
from_json(string) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.16.2. hstore_to_map
Creates a map from a hstore-formatted string.
Синтаксис |
hstore_to_map(string) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.16.3. map
Returns a map containing all the keys and values passed as pair of parameters.
Синтаксис |
map(key1, value1, key2, value2, …) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.16.4. map_akeys
Returns all the keys of a map as an array.
Синтаксис |
map_akeys(map) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.16.5. map_avals
Returns all the values of a map as an array.
Синтаксис |
map_avals(map) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.16.6. map_concat
Returns a map containing all the entries of the given maps. If two maps contain the same key, the value of the second map is taken.
Синтаксис |
map_concat(map1, map2, …) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.16.7. map_delete
Returns a map with the given key and its corresponding value deleted.
Синтаксис |
map_delete(map, key) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.16.8. map_exist
Returns TRUE if the given key exists in the map.
Синтаксис |
map_exist(map, key) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.16.9. map_get
Returns the value of a map, given its key. Returns NULL if the key does not exist.
Синтаксис |
map_get(map, key) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
Подсказка
You can also use the index operator ([]) to get a value from a map.
9.2.16.10. map_insert
Returns a map with an added key/value. If the key already exists, its value is overridden.
Синтаксис |
map_insert(map, key, value) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.16.11. map_prefix_keys
Returns a map with all keys prefixed by a given string.
Синтаксис |
map_prefix_keys(map, prefix) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.16.12. map_to_hstore
Merge map elements into a hstore-formatted string.
Синтаксис |
map_to_hstore(map) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.16.13. map_to_html_dl
Merge map elements into a HTML definition list string.
Синтаксис |
map_to_html_dl(map) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.16.14. map_to_html_table
Merge map elements into a HTML table string.
Синтаксис |
map_to_html_table(map) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.16.15. to_json
Create a JSON formatted string from a map, array or other value.
Синтаксис |
to_json(value) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.16.16. url_encode
Returns an URL encoded string from a map. Transforms all characters in their properly-encoded form producing a fully-compliant query string.
Note that the plus sign „+“ is not converted.
Синтаксис |
url_encode(map) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.17. Mathematical Functions
This group contains math functions (e.g., square root, sin and cos).
Показать/скрыть список функций
9.2.17.1. abs
Returns the absolute value of a number.
Синтаксис |
abs(value) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.17.2. acos
Returns the inverse cosine of a value in radians.
Синтаксис |
acos(value) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.17.3. asin
Returns the inverse sine of a value in radians.
Синтаксис |
asin(value) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.17.4. atan
Returns the inverse tangent of a value in radians.
Синтаксис |
atan(value) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.17.5. atan2
Returns the inverse tangent of dy/dx by using the signs of the two arguments to determine the quadrant of the result.
Синтаксис |
atan2(dy, dx) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.17.6. ceil
Rounds a number upwards.
Синтаксис |
ceil(value) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.17.7. clamp
Restricts an input value to a specified range.
Синтаксис |
clamp(minimum, input, maximum) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.17.8. cos
Returns cosine of an angle.
Синтаксис |
cos(angle) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.17.9. degrees
Converts from radians to degrees.
Синтаксис |
degrees(radians) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.17.10. exp
Returns exponential of an value.
Синтаксис |
exp(value) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.17.11. floor
Rounds a number downwards.
Синтаксис |
floor(value) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.17.12. ln
Returns the natural logarithm of a value.
Синтаксис |
ln(value) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.17.13. log
Returns the value of the logarithm of the passed value and base.
Синтаксис |
log(base, value) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.17.14. log10
Returns the value of the base 10 logarithm of the passed expression.
Синтаксис |
log10(value) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.17.15. max
Returns the largest value in a set of values.
Синтаксис |
max(value1, value2, …) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.17.16. min
Returns the smallest value in a set of values.
Синтаксис |
min(value1, value2, …) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.17.17. pi
Returns value of pi for calculations.
Синтаксис |
pi() |
Примеры |
|
9.2.17.18. radians
Converts from degrees to radians.
Синтаксис |
radians(degrees) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.17.19. rand
Returns a random integer within the range specified by the minimum and maximum argument (inclusive). If a seed is provided, the returned will always be the same, depending on the seed.
Синтаксис |
rand(min, max, [seed=NULL]) [] обозначает необязательные аргументы |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.17.20. randf
Returns a random float within the range specified by the minimum and maximum argument (inclusive). If a seed is provided, the returned will always be the same, depending on the seed.
Синтаксис |
randf([min=0.0], [max=1.0], [seed=NULL]) [] обозначает необязательные аргументы |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.17.21. round
Rounds a number to number of decimal places.
Синтаксис |
round(value, [places=0]) [] обозначает необязательные аргументы |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.17.22. scale_exponential
Transforms a given value from an input domain to an output range using an exponential curve. This function can be used to ease values in or out of the specified output range.
Синтаксис |
scale_exponential(value, domain_min, domain_max, range_min, range_max, exponent) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.17.23. scale_linear
Transforms a given value from an input domain to an output range using linear interpolation.
Синтаксис |
scale_linear(value, domain_min, domain_max, range_min, range_max) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.17.24. scale_polynomial
Transforms a given value from an input domain to an output range using a polynomial curve. This function can be used to ease values in or out of the specified output range.
Синтаксис |
scale_polynomial(value, domain_min, domain_max, range_min, range_max, exponent) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.17.25. sin
Returns the sine of an angle.
Синтаксис |
sin(angle) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.17.26. sqrt
Returns square root of a value.
Синтаксис |
sqrt(value) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.17.27. tan
Returns the tangent of an angle.
Синтаксис |
tan(angle) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.18. Meshes Functions
This group contains functions which calculate or return mesh related values.
Показать/скрыть список функций
9.2.18.1. $face_area
Returns the area of the current mesh face. The area calculated by this function respects both the current project’s ellipsoid setting and area unit settings. For example, if an ellipsoid has been set for the project then the calculated area will be ellipsoidal, and if no ellipsoid is set then the calculated area will be planimetric.
Синтаксис |
$face_area |
Примеры |
|
9.2.18.2. $face_index
Returns the index of the current mesh face.
Синтаксис |
$face_index |
Примеры |
|
9.2.18.3. $vertex_as_point
Returns the current vertex as a point geometry.
Синтаксис |
$vertex_as_point |
Примеры |
|
9.2.18.4. $vertex_index
Returns the index of the current mesh vertex.
Синтаксис |
$vertex_index |
Примеры |
|
9.2.18.5. $vertex_x
Returns the X coordinate of the current mesh vertex.
Синтаксис |
$vertex_x |
Примеры |
|
9.2.18.6. $vertex_y
Returns the Y coordinate of the current mesh vertex.
Синтаксис |
$vertex_y |
Примеры |
|
9.2.18.7. $vertex_z
Returns the Z value of the current mesh vertex.
Синтаксис |
$vertex_z |
Примеры |
|
9.2.19. Operators
This group contains operators (e.g., +, -, *). Note that for most of the mathematical functions below, if one of the inputs is NULL then the result is NULL.
Показать/скрыть список функций
9.2.19.1. %
Remainder of division. Takes the sign of the dividend.
Синтаксис |
a % b |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.19.2. *
Multiplication of two values
Синтаксис |
a * b |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.19.3. +
Addition of two values. If one of the values is NULL the result will be NULL.
Синтаксис |
a + b |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.19.4. -
Subtraction of two values. If one of the values is NULL the result will be NULL.
Синтаксис |
a - b |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.19.5. /
Division of two values
Синтаксис |
a / b |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.19.6. //
Floor division of two values
Синтаксис |
a // b |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.19.7. <
Compares two values and evaluates to 1 if the left value is less than the right value.
Синтаксис |
a < b |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.19.8. <=
Compares two values and evaluates to 1 if the left value is less or equal than the right value.
Синтаксис |
a <= b |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.19.9. <>
Compares two values and evaluates to 1 if they are not equal.
Синтаксис |
a <> b |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.19.10. =
Compares two values and evaluates to 1 if they are equal.
Синтаксис |
a = b |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.19.11. >
Compares two values and evaluates to 1 if the left value is greater than the right value.
Синтаксис |
a > b |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.19.12. >=
Compares two values and evaluates to 1 if the left value is greater or equal than the right value.
Синтаксис |
a >= b |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.19.13. AND
Returns TRUE when conditions a and b are true.
Синтаксис |
a AND b |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.19.14. BETWEEN
Returns TRUE if value is within the specified range. The range is considered inclusive of the bounds. To test for exclusion NOT BETWEEN can be used.
Синтаксис |
value BETWEEN lower_bound AND higher_bound |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
Примечание
value BETWEEN lower_bound AND higher_bound is the same as «value >= lower_bound AND value <= higher_bound».
Further reading: NOT BETWEEN
9.2.19.15. ILIKE
Returns TRUE if the first parameter matches case-insensitive the supplied pattern. LIKE can be used instead of ILIKE to make the match case-sensitive. Works with numbers also.
Синтаксис |
string/number ILIKE pattern |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.19.16. IN
Returns TRUE if value is found within a list of values.
Синтаксис |
a IN b |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.19.17. IS
Returns TRUE if a is the same as b.
Синтаксис |
a IS b |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.19.18. IS NOT
Returns TRUE if a is not the same as b.
Синтаксис |
a IS NOT b |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.19.19. LIKE
Returns TRUE if the first parameter matches the supplied pattern. Works with numbers also.
Синтаксис |
string/number LIKE pattern |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.19.20. NOT
Negates a condition.
Синтаксис |
NOT a |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.19.21. NOT BETWEEN
Returns TRUE if value is not within the specified range. The range is considered inclusive of the bounds.
Синтаксис |
value NOT BETWEEN lower_bound AND higher_bound |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
Примечание
value NOT BETWEEN lower_bound AND higher_bound is the same as «value < lower_bound OR value > higher_bound».
Further reading: BETWEEN
9.2.19.22. OR
Returns TRUE when condition a or b is true.
Синтаксис |
a OR b |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.19.23. []
Index operator. Returns an element from an array or map value.
Синтаксис |
[index] |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.19.24. ^
Power of two values.
Синтаксис |
a ^ b |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.19.25. ||
Joins two values together into a string.
If one of the values is NULL the result will be NULL. See the CONCAT function for a different behavior.
Синтаксис |
a || b |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.19.26. ~
Performs a regular expression match on a string value. Backslash characters must be double escaped (e.g., «\\s» to match a white space character).
Синтаксис |
string ~ regex |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
Further reading: regexp_match
9.2.20. Processing Functions
This group contains functions that operate on processing algorithms.
Показать/скрыть список функций
9.2.20.1. parameter
Returns the value of a processing algorithm input parameter.
Синтаксис |
parameter(name) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.21. Rasters Functions
This group contains functions to operate on raster layer.
Показать/скрыть список функций
9.2.21.1. raster_attributes
Returns a map with the fields names as keys and the raster attribute table values as values from the attribute table entry that matches the given raster value.
Синтаксис |
raster_attributes(layer, band, value) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.21.2. raster_statistic
Returns statistics from a raster layer.
Синтаксис |
raster_statistic(layer, band, property) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.21.3. raster_value
Returns the raster value found at the provided point.
Синтаксис |
raster_value(layer, band, point) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.22. Record and Attributes Functions
This group contains functions that operate on record identifiers.
Показать/скрыть список функций
9.2.22.1. attribute
Returns an attribute from a feature.
Variant 1
Returns the value of an attribute from the current feature.
Синтаксис |
attribute(attribute_name) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
Variant 2
Allows the target feature and attribute name to be specified.
Синтаксис |
attribute(feature, attribute_name) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.22.2. attributes
Returns a map containing all attributes from a feature, with field names as map keys.
Variant 1
Returns a map of all attributes from the current feature.
Синтаксис |
attributes() |
Примеры |
|
Variant 2
Allows the target feature to be specified.
Синтаксис |
attributes(feature) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
Further reading: Maps Functions
9.2.22.3. $currentfeature
Returns the current feature being evaluated. This can be used with the „attribute“ function to evaluate attribute values from the current feature. WARNING: This function is deprecated. It is recommended to use the replacement @feature variable instead.
Синтаксис |
$currentfeature |
Примеры |
|
9.2.22.4. display_expression
Returns the display expression for a given feature in a layer. The expression is evaluated by default. Can be used with zero, one or more arguments, see below for details.
No parameters
If called with no parameters, the function will evaluate the display expression of the current feature in the current layer.
Синтаксис |
display_expression() |
Примеры |
|
One „feature“ parameter
If called with a „feature“ parameter only, the function will evaluate the specified feature from the current layer.
Синтаксис |
display_expression(feature) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
Layer and feature parameters
If the function is called with both a layer and a feature, it will evaluate the specified feature from the specified layer.
Синтаксис |
display_expression(layer, feature, [evaluate=true]) [] обозначает необязательные аргументы |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.22.5. feature_id
Returns a feature’s unique ID, or NULL if the feature is not valid.
Синтаксис |
feature_id(feature) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
Further reading: get_feature_by_id
9.2.22.6. get_feature
Returns the first feature of a layer matching a given attribute value.
Single value variant
Along with the layer ID, a single column and value are specified.
Синтаксис |
get_feature(layer, attribute, value) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
Вариант карты
Along with the layer ID, a map containing the columns (key) and their respective value to be used.
Синтаксис |
get_feature(layer, attribute) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.22.7. get_feature_by_id
Returns the feature with an id on a layer.
Синтаксис |
get_feature_by_id(layer, feature_id) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
Further reading: feature_id
9.2.22.8. $id
Returns the feature id of the current row. WARNING: This function is deprecated. It is recommended to use the replacement @id variable instead.
Синтаксис |
$id |
Примеры |
|
Further reading: feature_id, get_feature_by_id
9.2.22.9. is_attribute_valid
Returns TRUE if a specific feature attribute meets all constraints.
Синтаксис |
is_attribute_valid(attribute, [feature], [layer], [strength]) [] обозначает необязательные аргументы |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
Further reading: Constraints
9.2.22.10. is_feature_valid
Returns TRUE if a feature meets all field constraints.
Синтаксис |
is_feature_valid([feature], [layer], [strength]) [] обозначает необязательные аргументы |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
Further reading: Constraints
9.2.22.11. is_selected
Returns TRUE if a feature is selected. Can be used with zero, one or two arguments, see below for details.
No parameters
If called with no parameters, the function will return TRUE if the current feature in the current layer is selected.
Синтаксис |
is_selected() |
Примеры |
|
One „feature“ parameter
If called with a „feature“ parameter only, the function returns TRUE if the specified feature from the current layer is selected.
Синтаксис |
is_selected(feature) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
Two parameters
If the function is called with both a layer and a feature, it will return TRUE if the specified feature from the specified layer is selected.
Синтаксис |
is_selected(layer, feature) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.22.12. maptip
Returns the maptip for a given feature in a layer. The expression is evaluated by default. Can be used with zero, one or more arguments, see below for details.
No parameters
If called with no parameters, the function will evaluate the maptip of the current feature in the current layer.
Синтаксис |
maptip() |
Примеры |
|
One „feature“ parameter
If called with a „feature“ parameter only, the function will evaluate the specified feature from the current layer.
Синтаксис |
maptip(feature) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
Layer and feature parameters
If the function is called with both a layer and a feature, it will evaluate the specified feature from the specified layer.
Синтаксис |
maptip(layer, feature, [evaluate=true]) [] обозначает необязательные аргументы |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.22.13. num_selected
Returns the number of selected features on a given layer. By default works on the layer on which the expression is evaluated.
Синтаксис |
num_selected([layer=current layer]) [] обозначает необязательные аргументы |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.22.14. represent_attributes
Returns a map with the attribute names as keys and the configured representation values as values. The representation value for the attributes depends on the configured widget type for each attribute. Can be used with zero, one or more arguments, see below for details.
No parameters
If called with no parameters, the function will return the representation of the attributes of the current feature in the current layer.
Синтаксис |
represent_attributes() |
Примеры |
|
One „feature“ parameter
If called with a „feature“ parameter only, the function will return the representation of the attributes of the specified feature from the current layer.
Синтаксис |
represent_attributes(feature) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
Layer and feature parameters
If called with a „layer“ and a „feature“ parameter, the function will return the representation of the attributes of the specified feature from the specified layer.
Синтаксис |
represent_attributes(layer, feature) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
Further reading: represent_value
9.2.22.15. represent_value
Returns the configured representation value for a field value. It depends on the configured widget type. Often, this is useful for „Value Map“ widgets.
Синтаксис |
represent_value(value, [fieldName]) [] обозначает необязательные аргументы |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
Further reading: widget types, represent_attributes
9.2.22.16. sqlite_fetch_and_increment
Manage autoincrementing values in sqlite databases.
SQlite default values can only be applied on insert and not prefetched.
This makes it impossible to acquire an incremented primary key via AUTO_INCREMENT before creating the row in the database. Sidenote: with postgres, this works via the option evaluate default values.
When adding new features with relations, it is really nice to be able to already add children for a parent, while the parents form is still open and hence the parent feature uncommitted.
To get around this limitation, this function can be used to manage sequence values in a separate table on sqlite based formats like gpkg.
The sequence table will be filtered for a sequence id (filter_attribute and filter_value) and the current value of the id_field will be incremented by 1 and the incremented value returned.
If additional columns require values to be specified, the default_values map can be used for this purpose.
Note
This function modifies the target sqlite table. It is intended for usage with default value configurations for attributes.
When the database parameter is a layer and the layer is in transaction mode, the value will only be retrieved once during the lifetime of a transaction and cached and incremented. This makes it unsafe to work on the same database from several processes in parallel.
Синтаксис |
sqlite_fetch_and_increment(database, table, id_field, filter_attribute, filter_value, [default_values]) [] обозначает необязательные аргументы |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
Further reading: Data Sources Properties, Setting relations between multiple layers
9.2.22.17. uuid
Generates a Universally Unique Identifier (UUID) for each row using the Qt QUuid::createUuid method.
Синтаксис |
uuid([format=“WithBraces“]) [] обозначает необязательные аргументы |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.23. Relations
This group contains the list of the relations available in the current project, with their description. It provides a quick access to the relation ID for writing an expression (with e.g. the relation_aggregate function) or customizing a form.
9.2.24. Sensors Functions
This group contains functions to interact with sensors.
Показать/скрыть список функций
9.2.24.1. sensor_data
Returns the last captured value (or values as a map for sensors which report multiple values) from a registered sensor.
Синтаксис |
sensor_data(name, [expiration]) [] обозначает необязательные аргументы |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.25. String Functions
This group contains functions that operate on strings (e.g., that replace, convert to upper case).
Показать/скрыть список функций
9.2.25.1. ascii
Returns the unicode code associated with the first character of a string.
Синтаксис |
ascii(string) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.25.2. char
Returns the character associated with a unicode code.
Синтаксис |
char(code) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.25.3. concat
Concatenates several strings to one. NULL values are converted to empty strings. Other values (like numbers) are converted to strings.
Синтаксис |
concat(string1, string2, …) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
About fields concatenation
You can also concatenate strings or field values using either || or +
operators, with some special characteristics:
The
+operator also means sum up expression, so if you have an integer (field or numeric value) operand, this can be error prone and you better use the others:'My feature id is: ' + "gid" => triggers an error as gid returns an integer
When any of the arguments is a NULL value, either
||or+will return a NULL value. To return the other arguments regardless the NULL value, you may want to use theconcatorarray_to_stringfunction:'My feature id is: ' + NULL ==> NULL 'My feature id is: ' || NULL => NULL concat('My feature id is: ', NULL) => 'My feature id is: ' array_to_string( array('My feature id is: ', NULL) ) => 'My feature id is: '
further reading: array_to_string, ||, +
9.2.25.4. format
Format a string using supplied arguments.
Синтаксис |
format(string, arg1, arg2, …) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.25.5. format_date
Formats a date type or string into a custom string format. Uses Qt date/time format strings. See QDateTime::toString.
Синтаксис |
format_date(datetime, format, [language]) [] обозначает необязательные аргументы |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Аргументы |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Примеры |
|
9.2.25.6. format_number
Returns a number formatted with the locale separator for thousands. By default the current QGIS user locale is used. Also truncates the decimal places to the number of supplied places.
Синтаксис |
format_number(number, [places=0], [language], [omit_group_separators=false], [trim_trailing_zeroes=false]) [] обозначает необязательные аргументы |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.25.7. left
Returns a substring that contains the n leftmost characters of the string.
Синтаксис |
left(string, length) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
Further reading: right
9.2.25.8. length
Returns the number of characters in a string or the length of a geometry linestring.
String variant
Returns the number of characters in a string.
Синтаксис |
length(string) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
Geometry variant
Calculate the length of a geometry line object. Calculations are always planimetric in the Spatial Reference System (SRS) of this geometry, and the units of the returned length will match the units for the SRS. This differs from the calculations performed by the $length function, which will perform ellipsoidal calculations based on the project’s ellipsoid and distance unit settings.
Синтаксис |
length(geometry) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.25.9. lower
Converts a string to lower case letters.
Синтаксис |
lower(string) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.25.10. lpad
Returns a string padded on the left to the specified width, using a fill character. If the target width is smaller than the string’s length, the string is truncated.
Синтаксис |
lpad(string, width, fill) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
Further reading: rpad
9.2.25.11. ltrim
Removes the longest string containing only the specified characters (a space by default) from the start of string.
Синтаксис |
ltrim(string, [characters=“ „]) [] обозначает необязательные аргументы |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.25.12. regexp_match
Return the first matching position matching a regular expression within an unicode string, or 0 if the substring is not found.
Синтаксис |
regexp_match(input_string, regex) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
Further reading: strpos
9.2.25.13. regexp_replace
Returns a string with the supplied regular expression replaced.
Синтаксис |
regexp_replace(input_string, regex, replacement) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
Further reading: replace, array_replace
9.2.25.14. regexp_substr
Returns the portion of a string which matches a supplied regular expression.
Синтаксис |
regexp_substr(input_string, regex) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
Further reading: substr, regexp_matches
9.2.25.15. replace
Returns a string with the supplied string, array, or map of strings replaced.
String & array variant
Returns a string with the supplied string or array of strings replaced by a string or an array of strings.
Синтаксис |
replace(string, before, after) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
Вариант карты
Returns a string with the supplied map keys replaced by paired values. Longer map keys are evaluated first.
Синтаксис |
replace(string, map) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
Further reading: regexp_replace, array_replace
9.2.25.16. right
Returns a substring that contains the n rightmost characters of the string.
Синтаксис |
right(string, length) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
Further reading: left
9.2.25.17. rpad
Returns a string padded on the right to the specified width, using a fill character. If the target width is smaller than the string’s length, the string is truncated.
Синтаксис |
rpad(string, width, fill) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
Further reading: lpad
9.2.25.18. rtrim
Removes the longest string containing only the specified characters (a space by default) from the end of string.
Синтаксис |
rtrim(string, [characters=“ „]) [] обозначает необязательные аргументы |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.25.19. strpos
Return the first matching position of a substring within another string, or 0 if the substring is not found.
Синтаксис |
strpos(haystack, needle) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
Further reading: regexp_match
9.2.25.20. substr
Returns a part of a string.
Синтаксис |
substr(string, start, [length]) [] обозначает необязательные аргументы |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
Further reading: regexp_substr, regexp_matches
9.2.25.21. title
Converts all words of a string to title case (all words lower case with leading capital letter).
Синтаксис |
title(string) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.25.22. to_string
Converts a number to string.
Синтаксис |
to_string(number) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
Further reading: format_number
9.2.25.23. trim
Removes all leading and trailing whitespace (spaces, tabs, etc) from a string.
Синтаксис |
trim(string) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.25.24. upper
Converts a string to upper case letters.
Синтаксис |
upper(string) |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.25.25. wordwrap
Returns a string wrapped to a maximum/minimum number of characters.
Синтаксис |
wordwrap(string, wrap_length, [delimiter_string]) [] обозначает необязательные аргументы |
Аргументы |
|
Примеры |
|
9.2.26. User Expressions
This group contains the expressions saved as user expressions.
9.2.27. Переменные
This group contains dynamic variables related to the application, the project file and other settings. The availability of variables depends on the context:
from the layer properties dialog
from the print layout
To use these variables in an expression, they should be preceded by the
@ character (e.g, @row_number).
Variable |
Описание |
|---|---|
algorithm_id |
The unique ID of an algorithm |
animation_end_time |
End of the animation’s overall temporal time range (as a datetime value) |
animation_interval |
Duration of the animation’s overall temporal time range (as an interval value) |
animation_start_time |
Start of the animation’s overall temporal time range (as a datetime value) |
atlas_feature |
The current atlas feature (as feature object) |
atlas_featureid |
The current atlas feature ID |
atlas_featurenumber |
The current atlas feature number in the layout |
atlas_filename |
The current atlas file name |
atlas_geometry |
The current atlas feature geometry |
atlas_layerid |
The current atlas coverage layer ID |
atlas_layername |
The current atlas coverage layer name |
atlas_pagename |
The current atlas page name |
atlas_totalfeatures |
The total number of features in atlas |
band |
The number of the band in the raster layer |
band_description |
The description of the band in the raster layer |
band_name |
The name of the band in the raster layer |
canvas_cursor_point |
The last cursor position on the canvas in the project’s geographical coordinates |
cluster_color |
The color of symbols within a cluster, or NULL if symbols have mixed colors |
cluster_size |
The number of symbols contained within a cluster |
current_feature |
The feature currently being edited in the attribute form or table row |
current_geometry |
The geometry of the feature currently being edited in the form or the table row |
current_parent_feature |
represents the feature currently being edited in the parent form. Only usable in an embedded form context. |
current_parent_geometry |
represents the geometry of the feature currently being edited in the parent form. Only usable in an embedded form context. |
form_mode |
What the form is used for, like AddFeatureMode, SingleEditMode, MultiEditMode, SearchMode, AggregateSearchMode or IdentifyMode as string. |
feature |
The current feature being evaluated. This can be used with the „attribute“ function to evaluate attribute values from the current feature. |
frame_duration |
Temporal duration of each animation frame (as an interval value) |
frame_number |
Current frame number during animation playback |
frame_rate |
Number of frames per second during animation playback |
fullextent_maxx |
Maximum x value from full canvas extent (including all layers) |
fullextent_maxy |
Maximum y value from full canvas extent (including all layers) |
fullextent_minx |
Minimum x value from full canvas extent (including all layers) |
fullextent_miny |
Minimum y value from full canvas extent (including all layers) |
geometry |
The geometry of the current feature being evaluated |
geometry_part_count |
The number of parts in rendered feature’s geometry |
geometry_part_num |
The current geometry part number for feature being rendered |
geometry_point_count |
The number of points in the rendered geometry’s part |
geometry_point_num |
The current point number in the rendered geometry’s part |
geometry_ring_num |
Current geometry ring number for feature being rendered (for polygon features only). The exterior ring has a value of 0. |
grid_axis |
The current grid annotation axis (eg, „x“ for longitude, „y“ for latitude) |
grid_number |
The current grid annotation value |
id |
The ID of the current feature being evaluated |
item_id |
The layout item user ID (not necessarily unique) |
item_uuid |
The layout item unique ID |
layer |
The current layer |
layer_crs |
The Coordinate Reference System Authority ID of the current layer |
layer_crs_ellipsoid |
The ellipsoid Authority ID of the current layer CRS |
layer_cursor_point |
Point geometry under the mouse position in map canvas (or the GetFeatureInfo position in context of QGIS Server), in active layer’s CRS |
layer_id |
The ID of current layer |
layer_ids |
The IDs of all the map layers in the current project as a list |
layer_name |
The name of current layer |
layer_vertical_crs |
The Identifier for the vertical coordinate reference system of the layer (e.g., „EPSG:5703“) |
layer_vertical_crs_definition |
The full definition of the vertical Coordinate reference system of the layer |
layer_vertical_crs_description |
The name of the vertical Coordinate reference system of the layer |
layer_vertical_crs_wkt |
The WKT definition of the vertical Coordinate reference system of the current layer |
layers |
All the map layers in the current project as a list |
layout_dpi |
The composition resolution (DPI) |
layout_name |
The layout name |
layout_numpages |
The number of pages in the layout |
layout_page |
The page number of the current item in the layout |
layout_pageheight |
The active page height in the layout (in mm for standard paper sizes, or whatever unit was used for custom paper size) |
layout_pageoffsets |
Array of Y coordinate of the top of each page. Allows to dynamically position items on pages in a context where page sizes may change |
layout_pagewidth |
The active page width in the layout (in mm for standard paper sizes, or whatever unit was used for custom paper size) |
legend_column_count |
The number of columns in the legend |
legend_filter_by_map |
Indicates if the content of the legend is filtered by the map |
legend_filter_out_atlas |
Indicates if the atlas is filtered out of the legend |
legend_split_layers |
Indicates if layers can be split in the legend |
legend_title |
The title of the legend |
legend_wrap_string |
The character(s) used to wrap the legend text |
map_crs |
The Coordinate reference system of the current map |
map_crs_acronym |
The acronym of the Coordinate reference system of the current map |
map_crs_definition |
The full definition of the Coordinate reference system of the current map |
map_crs_description |
The name of the Coordinate reference system of the current map |
map_crs_ellipsoid |
The acronym of the ellipsoid of the Coordinate reference system of the current map |
map_crs_proj4 |
The Proj4 definition of the Coordinate reference system of the current map |
map_crs_projection |
The descriptive name of the projection method used by the Coordinate reference system of the map (e.g. „Albers Equal Area“) |
map_crs_wkt |
The WKT definition of the Coordinate reference system of the current map |
map_end_time |
The end of the map’s temporal time range (as a datetime value) |
map_extent |
The geometry representing the current extent of the map |
map_extent_center |
The point feature at the center of the map |
map_extent_height |
The current height of the map |
map_extent_width |
The current width of the map |
map_id |
The ID of current map destination. This will be „canvas“ for canvas renders, and the item ID for layout map renders |
map_interval |
The duration of the map’s temporal time range (as an interval value) |
map_layer_ids |
The list of map layer IDs visible in the map |
map_layers |
The list of map layers visible in the map |
map_rotation |
The current rotation of the map |
map_scale |
The current scale of the map |
map_start_time |
The start of the map’s temporal time range (as a datetime value) |
map_units |
The units of map measurements |
map_z_range_lower |
Lower elevation of the map’s elevation range |
map_z_range_upper |
Upper elevation of the map’s elevation range |
model_path |
Full path (including file name) of current model (or project path if model is embedded in a project). |
model_folder |
Folder containing current model (or project folder if model is embedded in a project). |
model_name |
Name of current model |
model_group |
Group for current model |
notification_message |
Content of the notification message sent by the provider (available only for actions triggered by provider notifications). |
parent |
Refers to the current feature in the parent layer, providing access to its attributes and geometry when filtering an aggregate function |
plot_axis |
The associated plot axis, e.g. „x“ or „y“. |
plot_axis_value |
The current value for the plot axis. |
project_abstract |
The project abstract, taken from project metadata |
project_area_units |
The area unit for the current project, used when calculating areas of geometries |
project_author |
The project author, taken from project metadata |
project_basename |
The basename of current project’s filename (without path and extension) |
project_creation_date |
The project creation date, taken from project metadata |
project_crs |
Identifier for the coordinate reference system of the project (e.g., „EPSG:4326“) |
project_crs_arconym |
The acronym of the Coordinate reference system of the project |
project_crs_definition |
The full definition of the Coordinate reference system of the project |
project_crs_description |
The description of the Coordinate reference system of the project |
project_crs_ellipsoid |
The ellipsoid of the Coordinate reference system of the project |
project_crs_proj4 |
The Proj4 representation of the Coordinate reference system of the project |
project_crs_wkt |
The WKT (well known text) representation of the coordinate reference system of the project |
project_distance_units |
The distance unit for the current project, used when calculating lengths of geometries and distances |
project_ellipsoid |
The name of the ellipsoid of the current project, used when calculating geodetic areas or lengths of geometries |
project_filename |
The filename of the current project |
project_folder |
The folder of the current project |
project_home |
The home path of the current project |
project_identifier |
The project identifier, taken from the project’s metadata |
project_keywords |
The project keywords, taken from the project’s metadata |
project_last_saved |
Date/time when project was last saved. |
project_path |
The full path (including file name) of the current project |
project_title |
The title of current project |
project_units |
The units of the project’s CRS |
project_vertical_crs |
Identifier for the vertical Coordinate reference system of the project (e.g., „EPSG:5703“) |
project_vertical_crs_definition |
The full definition of the vertical coordinate reference system of the project |
project_vertical_crs_description |
The description of the vertical coordinate reference system of the project |
project_vertical_crs_wkt |
The WKT (well known text) representation of the vertical coordinate reference system of the project |
qgis_locale |
The current language of QGIS |
qgis_os_name |
The current Operating system name, eg „windows“, „linux“ or „osx“ |
qgis_platform |
The QGIS platform, eg „desktop“ or „server“ |
qgis_release_name |
The current QGIS release name |
qgis_short_version |
The current QGIS version short string |
qgis_version |
The current QGIS version string |
qgis_version_no |
The current QGIS version number |
row_number |
Stores the number of the current row |
snapping_results |
Gives access to snapping results while digitizing a feature (only available in add feature) |
scale_value |
The current scale bar distance value |
selected_file_path |
Selected file path from file widget selector when uploading a file with an external storage system |
symbol_angle |
The angle of the symbol used to render the feature (valid for marker symbols only) |
symbol_color |
The color of the symbol used to render the feature |
symbol_count |
The number of features represented by the symbol (in the layout legend) |
symbol_frame |
The frame number (for animated symbols only) |
symbol_id |
The Internal ID of the symbol (in the layout legend) |
symbol_label |
The label for the symbol (either a user defined label or the default autogenerated label - in the layout legend) |
symbol_layer_count |
Total number of symbol layers in the symbol |
symbol_layer_index |
Current symbol layer index |
symbol_marker_column |
Column number for marker (valid for point pattern fills only). |
symbol_marker_row |
Row number for marker (valid for point pattern fills only). |
user_account_name |
The current user’s operating system account name |
user_full_name |
The current user’s operating system user name |
value |
The current value |
vector_tile_zoom |
Exact vector tile zoom level of the map that is being rendered (derived from the current map scale). Normally in interval [0, 20]. Unlike @zoom_level, this variable is a floating point value which can be used to interpolate values between two integer zoom levels. |
with_variable |
Allows setting a variable for usage within an expression and avoid recalculating the same value repeatedly |
zoom_level |
Vector tile zoom level of the map that is being rendered (derived from the current map scale). Normally in interval [0, 20]. |
Some examples:
Return the X coordinate of a map item center in layout:
x( map_get( item_variables( 'map1'), 'map_extent_center' ) )
Return, for each feature in the current layer, the number of overlapping airport features:
aggregate( layer:='airport', aggregate:='count', expression:="code", filter:=intersects( $geometry, geometry( @parent ) ) )Get the object_id of the first snapped point of a line:
with_variable( 'first_snapped_point', array_first( @snapping_results ), attribute( get_feature_by_id( map_get( @first_snapped_point, 'layer' ), map_get( @first_snapped_point, 'feature_id' ) ), 'object_id' ) )
9.2.28. Recent Functions
This group contains recently used functions. Depending on the context of its usage (feature selection, field calculator, generic), recently applied expressions are added to the corresponding list (up to ten expressions), sorted from more to less recent. This makes it easy to quickly retrieve and reapply previously used expressions.