Important
Traducerea este un efort al comunității, la care puteți să vă alăturați. În prezent, această pagină este tradusă 19.51%.
29.2.2. Geometry Checker Plugin
Geometry Checker is a powerful core plugin to check and fix the geometry
validity of a layer. It is available from the
menu ( ).
).
29.2.2.1. Configuring the checks
The Check Geometries dialog shows different grouped settings in the first tab (Setup):
Input vector layers: to select the layers to check. A
 Only selected features checkbox can be used to restrict the
checking to the geometries of the selected features.
Only selected features checkbox can be used to restrict the
checking to the geometries of the selected features.Allowed geometry types gives the chance to restrict the geometry type of the input layer(s) to:
Geometry validity. Depending on geometry types you can choose between:
Geometry properties. Depending on geometry types, different options are available:
Geometry conditions. Allows you to add some condition to validate the geometries with:
Topology checks. Depending on geometry types, many different options are available:
Tolerance. You can define the tolerance of the check in map layer units.
Output vector layer gives the choice to:
When you are happy with the configuration, you can click on the Run button.
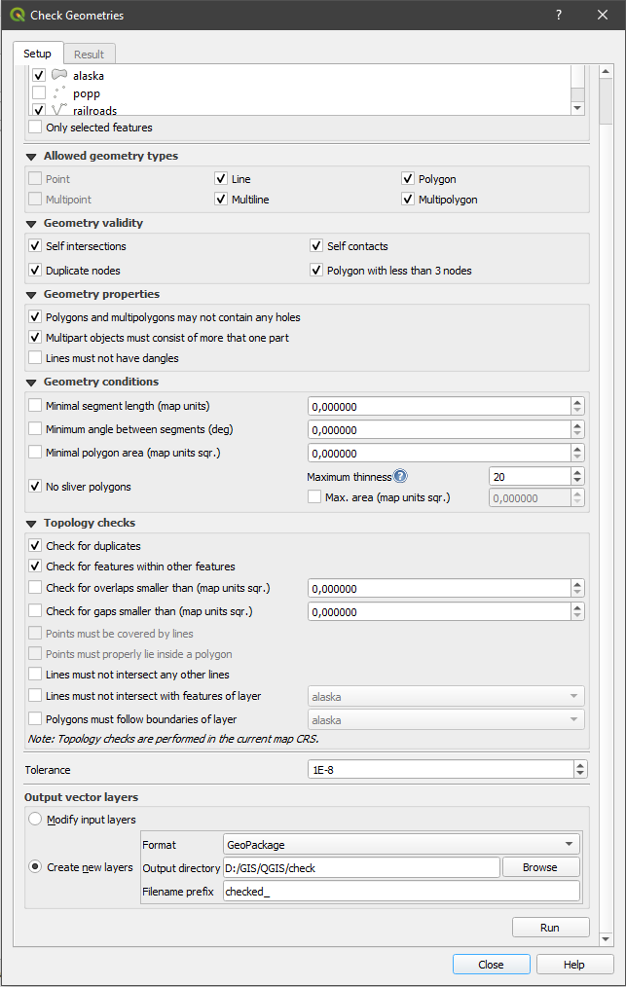
Fig. 29.6 The Geometry Checker Plugin
The Geometry Checker Plugin can find the following errors:
Self intersections: a polygon with a self intersection
Duplicate nodes: two duplicates nodes in a segment
Holes: hole in a polygon
Segment length: a segment length lower than a threshold
Minimum angle: two segments with an angle lower than a threshold
Minimum area: polygon area lower than a threshold
Silver polygon: this error come from very small polygon (with small area) with a large perimeter
Duplicates features
Feature within feature
Overlaps: polygon overlapping
Gaps: gaps between polygons
The following figure shows the different checks made by the plugin.
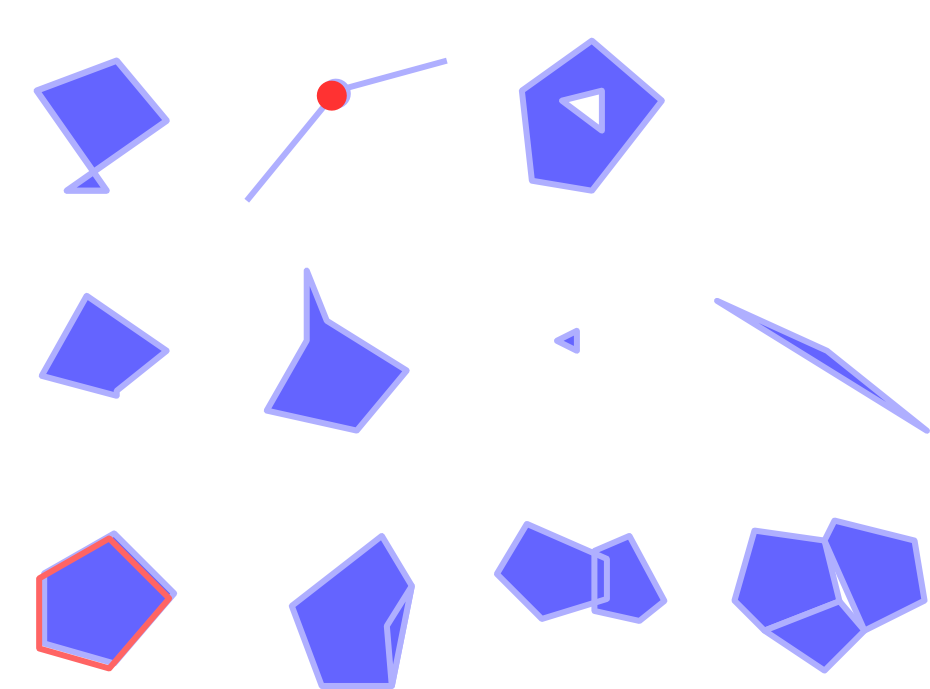
Fig. 29.7 Some checks supported by the plugin
29.2.2.2. Analysing the results
The results appear in the second tab (Result) and as an overview
layer of the errors in the canvas (its name has the default prefix
checked_).
A table lists the Geometry check result with one error per row and
columns containing: the layer name, an ID, the error type, then the coordinates
of the error, a value (depending on the type of the error) and finally the
resolution column which indicates the resolution of the error.
At the bottom of this table, you can Export the error into different file
formats. You also have a counter with the number of total errors and fixed ones.
You can select a row to see the location of the error. You can change this
behavior by selecting another action between  Error
(default),
Error
(default),  Feature,
Feature,  Don’t move, and
Don’t move, and  Highlight selected features.
Highlight selected features.
Below the zoom action when clicking on the table row, you can:
 Fix selected errors, prompt for resolution method
You will see a window to choose the resolution’s method among which:
Fix selected errors, prompt for resolution method
You will see a window to choose the resolution’s method among which:Merge with neighboring polygon with longest shared edge
Merge with neighboring polygon with largest area
Merge with neighboring polygon with identical attribute value, if any, or leave as is
Delete feature
No action
 Error resolution settings allows you to change the
default resolution method depending on the error type
Error resolution settings allows you to change the
default resolution method depending on the error type
Sfat
Fix multiple errors
You can fix multiple errors by selecting more than one row in the table with the CTRL + click action.
Finally, you can choose which Attribute to use when merging features by attribute value.