21.2. Live GPS tracking
To activate live GPS tracking in QGIS, you need to select  GPS Information Panel or press Ctrl+0.
You will get a new docked window on the left side of the canvas.
GPS Information Panel or press Ctrl+0.
You will get a new docked window on the left side of the canvas.
There are three possible screens in this GPS tracking window:
 Position: GPS position coordinates and an interface for manually entering
vertices and features
Position: GPS position coordinates and an interface for manually entering
vertices and features Options:GPS options screen (see Fig. 21.5)
Options:GPS options screen (see Fig. 21.5)
With a plugged-in GPS receiver (has to be supported by your operating system), a simple click on Connect connects the GPS to QGIS. A second click (now on Disconnect) disconnects the GPS receiver from your computer. For GNU/Linux, gpsd support is integrated to support connection to most GPS receivers. Therefore, you first have to configure gpsd properly to connect QGIS to it.
With the Recenter button the map will jump to the current GPS position.
Warning
If you want to record your position to the canvas, you have to create a new vector layer first and switch it to editable status to be able to record your track.
When a GPS device is connected and the user moves the cursor over the map canvas, a live status bar message displays the distance and bearing from the cursor to the GPS position. Project distance and bearing settings are respected in this display.
Tip
Touch Screen Devices
On a touch screen device use a tap-and-hold event to trigger the live status bar message.
21.2.1. Position and additional attributes
 If the GPS is receiving signals from satellites, you will
see your position in latitude, longitude and altitude together with additional
attributes.
If the GPS is receiving signals from satellites, you will
see your position in latitude, longitude and altitude together with additional
attributes.
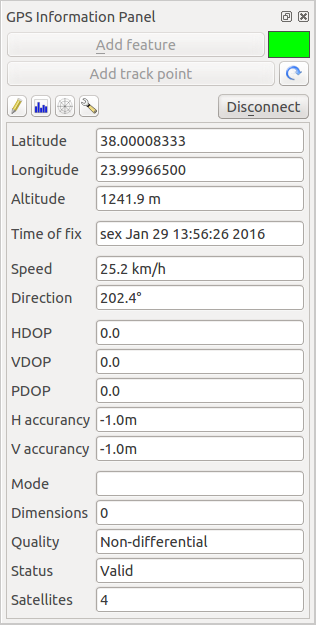
Fig. 21.3 GPS tracking position and additional attributes
21.2.2. GPS signal strength
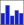 Here, you can see the signal strength of the satellites you
are receiving signals from.
Here, you can see the signal strength of the satellites you
are receiving signals from.
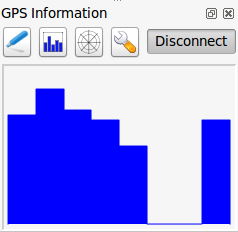
Fig. 21.4 GPS tracking signal strength
21.2.3. GPS options
Fig. 21.5 GPS tracking options window
Here you can specify:
Connection
Digitizing
You can activate
 when you are in editing mode. Or you can activate
when you are in editing mode. Or you can activate  Automatically add points to the map canvas with a certain width
and color.
Automatically add points to the map canvas with a certain width
and color.The Calculate bearing from travel direction can be used if the device reports faulty bearing measurements and it will calculate the GPS bearing based on the previous two recorded locations.
Cursor: you can use a slider
 to shrink
and grow the position cursor on the canvas.
to shrink
and grow the position cursor on the canvas.Filtering: You can also set an Acquisition interval (seconds) and a Distance threshold (meters) parameters to keep the cursor still active when the receiver is in static conditions.
Map Centering and Rotation
Activating
 Map centering allows you to decide in which
way the canvas will be updated. This includes ‘always’, ‘when leaving’, if your
recorded coordinates start to move out of the canvas, or ‘never’, to keep map
extent.
Map centering allows you to decide in which
way the canvas will be updated. This includes ‘always’, ‘when leaving’, if your
recorded coordinates start to move out of the canvas, or ‘never’, to keep map
extent.Activating Rotate map to match GPS direction will automatically rotate the map canvas so that it is oriented in the same direction as the GPS bearing.
Activating Show Bearing Line will show a line from the GPS location pointing in current path direction of the GPS.
Finally, you can activate
 Log file and define a path
and a file where log messages about the GPS tracking are logged.
Log file and define a path
and a file where log messages about the GPS tracking are logged.
If you want to set a feature manually, you have to go back to  Position and click on Add Point or Add Track Point.
Position and click on Add Point or Add Track Point.
21.2.4. Connect to a Bluetooth GPS for live tracking
With QGIS you can connect a Bluetooth GPS for field data collection. To perform this task you need a GPS Bluetooth device and a Bluetooth receiver on your computer.
At first you must let your GPS device be recognized and paired to the computer. Turn on the GPS, go to the Bluetooth icon on your notification area and search for a New Device.
On the right side of the Device selection mask make sure that all devices are selected so your GPS unit will probably appear among those available. In the next step a serial connection service should be available, select it and click on Configure button.
Remember the number of the COM port assigned to the GPS connection as resulting by the Bluetooth properties.
After the GPS has been recognized, make the pairing for the connection. Usually
the authorization code is 0000.
Now open GPS information panel and switch to  GPS
options screen. Select the COM port assigned to the GPS connection and click
the Connect. After a while a cursor indicating your position should
appear.
GPS
options screen. Select the COM port assigned to the GPS connection and click
the Connect. After a while a cursor indicating your position should
appear.
If QGIS can’t receive GPS data, then you should restart your GPS device, wait 5-10 seconds then try to connect again. Usually this solution work. If you receive again a connection error make sure you don’t have another Bluetooth receiver near you, paired with the same GPS unit.
21.2.5. Using GPSMAP 60cs
21.2.5.1. MS Windows
Easiest way to make it work is to use a middleware (freeware, not open) called GPSGate.
Launch the program, make it scan for GPS devices (works for both USB and BT
ones) and then in QGIS just click Connect in the Live tracking panel
using the  Autodetect mode.
Autodetect mode.
21.2.5.2. Ubuntu/Mint GNU/Linux
As for Windows the easiest way is to use a server in the middle, in this case GPSD, so
sudo apt install gpsd
Then load the garmin_gps kernel module
sudo modprobe garmin_gps
And then connect the unit. Then check with dmesg the actual device being
used bu the unit, for example /dev/ttyUSB0. Now you can launch gpsd
gpsd /dev/ttyUSB0
And finally connect with the QGIS live tracking tool.
21.2.6. Using BTGP-38KM datalogger (only Bluetooth)
Using GPSD (under Linux) or GPSGate (under Windows) is effortless.
21.2.7. Using BlueMax GPS-4044 datalogger (both BT and USB)
21.2.7.1. MS Windows
The live tracking works for both USB and BT modes, by using GPSGate or even
without it, just use the  Autodetect mode, or point
the tool the right port.
Autodetect mode, or point
the tool the right port.
21.2.7.2. Ubuntu/Mint GNU/Linux
For USB
The live tracking works both with GPSD
gpsd /dev/ttyACM3
or without it, by connecting the QGIS live tracking tool directly to the
device (for example /dev/ttyACM3).
For Bluetooth
The live tracking works both with GPSD
gpsd /dev/rfcomm0
or without it, by connecting the QGIS live tracking tool directly to the device
(for example /dev/rfcomm0).
