` `
Accedere ai dati¶
- Il Pannello Browser
- Il DB Manager
- Strumenti di caricamento per specifici provider di dati
- Formati QGIS personalizzati
- Connessione a web services
Facendo parte di un ecosistema Software Open Source QGIS è costruito su diverse librerie che, unitamente agli specifici provider, offrono la capacità di leggere e spesso scrivere molti formati:
- Vector data formats include ESRI formats (shapefiles, geodatabases...), MapInfo and MicroStation file formats, AutoCAD DWG/DXF, GeoPackage, GeoJSON, GRASS, GPX, KML, Comma Separated Values, and many more... Read the complete list of OGR vector supported formats;
- Raster data formats include ArcInfo Binary Grid, ArcInfo ASCII Grid, JPEG, GeoTIFF, ERDAS IMAGINE, MBTiles, R or Idrisi rasters, ASCII Gridded XYZ, GDAL Virtual, SRTM, Sentinel Data, and many more... Read the complete list of raster supported formats;
- Database formats include PostgreSQL/PostGIS, SQLite/SpatiaLite, Oracle, DB2 or MSSQL Spatial, MySQL...;
- Support of web data services (WM(T)S, WFS, WCS, CSW, ArcGIS Servers...) is also handled by QGIS providers (see QGIS come client di dati OGC);
Puoi anche leggere i files supportati dalle cartelle archiviate e utilizzare formati nativi di QGIS come i layer virtuali e i layer in memoria.
As of the date of this document, more than 80 vector and 140 raster formats are supported by the GDAL/OGR and QGIS native providers.
Nota
Non tutti i formati in elenco possono funzionare in QGIS per vari motivi. Ad esempio, alcuni richiedono librerie proprietarie esterne o il sistema operativo in uso potrebbe non essere tra quelli previsti per l’installazione del formato GDAL/OGR che tu desideri utilizzare. Per avere un elenco di formati disponibili, eseguire la linea di comando ogrinfo --formats (per i vettori) o vedere il menu Impostazioni ‣ Opzioni ‣ GDAL (per i raster) in QGIS.
Il Pannello Browser¶
QGIS Browser is one of the main panels of QGIS that lets you quickly and easily add your data to projects. It helps you navigate in your filesystem and manage geodata, regardless the type of layer (raster, vector, table), or the datasource format (plain or compressed files, database, web services).
To add a layer into a project:
- right-click on QGIS toolbar and check
 Browser Panel
to activate it or select it from the menu View ‣ Panels
(or
Browser Panel
to activate it or select it from the menu View ‣ Panels
(or  Settings ‣ Panels);
Settings ‣ Panels); - a browser tree with your filesystem, databases and web services is displayed;
- find the layer in the list;
- right-click on its name and select Add selected layer(s). Your layer is now added to the Layers Panel and can be viewed in the map canvas.
Nota
You can also add a layer or open a QGIS project directly from the Browser panel by double-clicking its name or by drag-and-drop into the map canvas.
Una volta caricato un file, puoi ingrandirlo utilizzando gli strumenti di navigazione della mappa. Per modificare lo stile di un layer, apri la finestra di dialogo Proprietà Layer facendo doppio clic sul nome del layer o facendo clic con il pulsante destro del mouse sul nome nella legenda e scegliendo Proprietà nel menu contestuale. Vedi la sezione Style Properties per ulteriori informazioni sull’impostazione di simbologia dei layer vettoriali.
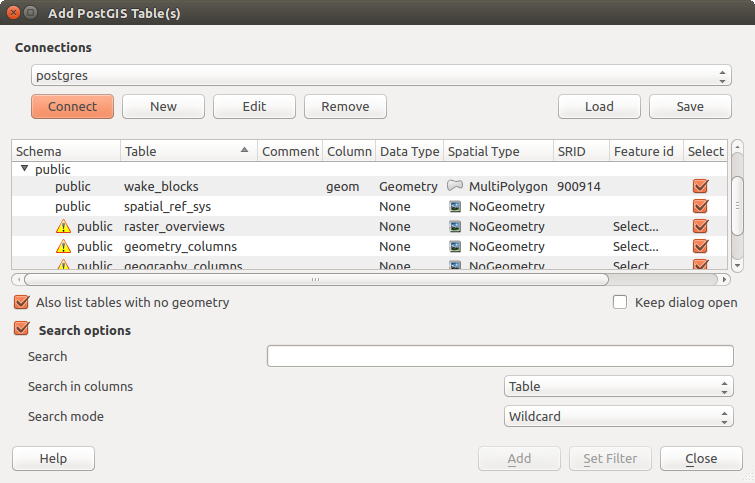
Nella parte superiore del Browser panel trovi alcune icone che ti aiutano a:
 Aggiungi layer selezionati: puoi aggiungere dati nella mappa anche selezionando Aggiungi layer selezionato dal menu contestuale del layer;
Aggiungi layer selezionati: puoi aggiungere dati nella mappa anche selezionando Aggiungi layer selezionato dal menu contestuale del layer; Browser filtro per cercare dati specifici. Immetti una parola di ricerca o un carattere jolly e il browser visualizzerà l’albero per visualizzare solo i percorsi corrispondenti a tabelle DB, file o cartelle DB - altri dati o cartelle non verranno visualizzate. Vedi l’esempio del Pannello di Browser (2) sulla figura figure_browser_panels. La ricerca può essere sensibile alla distinzione tra maiuscole e minuscole o meno. Può anche essere impostata su:
Browser filtro per cercare dati specifici. Immetti una parola di ricerca o un carattere jolly e il browser visualizzerà l’albero per visualizzare solo i percorsi corrispondenti a tabelle DB, file o cartelle DB - altri dati o cartelle non verranno visualizzate. Vedi l’esempio del Pannello di Browser (2) sulla figura figure_browser_panels. La ricerca può essere sensibile alla distinzione tra maiuscole e minuscole o meno. Può anche essere impostata su:normale: restituisce qualsiasi elemento contenente il testo cercato;
utilizzando il/i carattere(i) jolly: confermare la ricerca utilizzando ? e/o * per specificare la posizione del testo cercato;
usando una espressione regolare.
 Enable/disable properties widget: when toggled on,
a new widget is added at the bottom of the panel showing, if applicable,
metadatas of the selected item.
Enable/disable properties widget: when toggled on,
a new widget is added at the bottom of the panel showing, if applicable,
metadatas of the selected item.
Click destro su un elemento nell’albero del browser ti aiuta a:
in caso di un file o di una tabella, visualizzarne i metadati o aprirli nel tuo progetto. Le tabelle possono anche essere rinominate, cancellate o troncate;
in caso di cartella, definirla come segnalibro nei preferiti, nasconderla dall’albero del browser. Le cartelle nascoste possono essere gestite dalla scheda Impostazioni ‣ Opzioni ‣ Origine dati;
creare collegamento a database o server web;
aggiornare, rinominare o eliminare la scelta.
Puoi anche importare i files nei database o copiare le tabelle da uno schema/database a un altro con un semplice trascinamento drag-and-drop. C’è un secondo pannello del browser disponibile per evitare lunghi scorrimenti durante il trascinamento. Basta selezionare il file e fare drag-and-drop da un pannello all’altro.
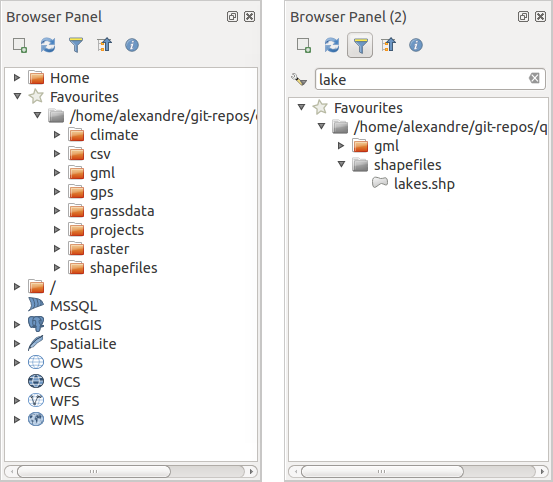
Pannelli QGIS Browser affiancati
Suggerimento
Aggiungi layers a QGIS con un semplice drag-and-drop dal visualizzatore file del tuo sistema operativo
Puoi anche aggiungere i file al progetto trascinandoli dal proprio visualizzatore di file del sistema operativo in uso al Panello Layer o all’area di visualizzazione mappa.
Il DB Manager¶
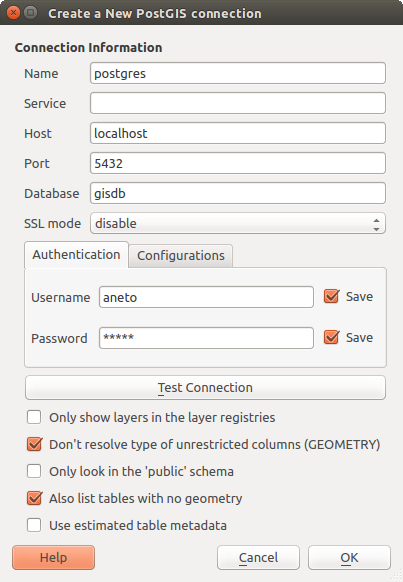
Il Plugin DB Manager è un altro degli strumenti principali e nativi per integrare e gestire i formati di database spaziali supportati da QGIS (PostGIS, SpatiaLite, GeoPackage, Oracle Spatial, MSSQL, DB2, Virtual layers) in un’interfaccia utente. Può essere attivato dal menu Plugins ‣ Gestisci ed installa Plugins....
Il Plugin  DB Manager offre diverse funzionalità:
DB Manager offre diverse funzionalità:
collegarsi a database e visualizzare la struttura e il contenuto;
anteprima di tabelle di database;
aggiungere layers alla visualizzazione mappa, sia con un doppio clic che con trascina e rilascia;
aggiungere layers a un database da QGIS Browser o da un altro database;
creare e aggiungere l’output delle query SQL alla visualizzazione mappa;
creare virtual layers.
Ulteriori informazioni sulle funzionalità di DB Manager sono esposte in Plugin DB Manager.
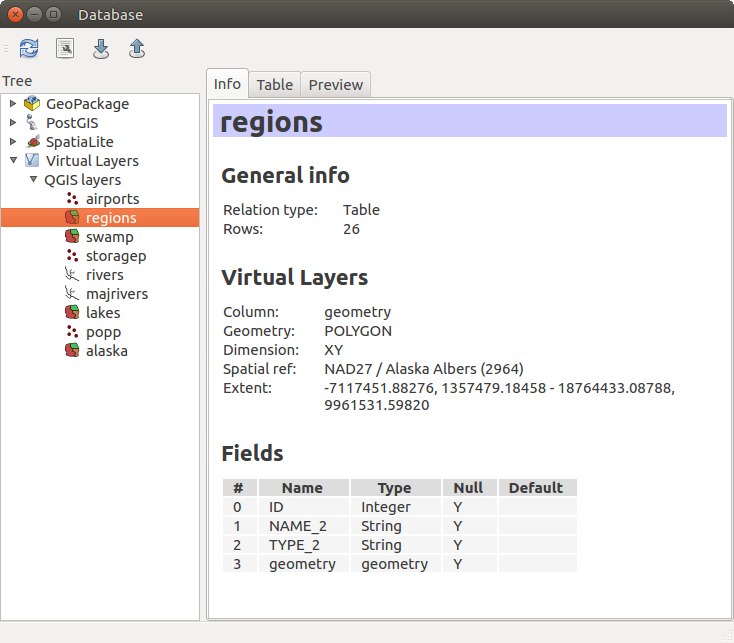
Finestra di dialogo DB Manager
Strumenti di caricamento per specifici provider di dati¶
Oltre a Pannello Browser e DB Manager che sono gli strumenti di base forniti da QGIS per aggiungere layers a prescindere dal formato, puoi anche trovate strumenti che sono specifici ai fornitore di dati.
Nota
Alcuni external plugins propongono anche strumenti per aprire file di formato specifico in QGIS..
Caricare un layer da un file¶
Per caricare un layer da un file, puoi:
for vector data (like Shapefile, Mapinfo or dxf layer), click on
 Add Vector Layer toolbar button, select the
Layer ‣ Add Layer ‣
Add Vector Layer toolbar button, select the
Layer ‣ Add Layer ‣  Add Vector
Layer menu option or press Ctrl+Shift+V.
This will bring up a new window (see figure_vector_add) from which you can
check
Add Vector
Layer menu option or press Ctrl+Shift+V.
This will bring up a new window (see figure_vector_add) from which you can
check  File and click on [Browse]. You can
also specify the encoding for the file if desired.
File and click on [Browse]. You can
also specify the encoding for the file if desired.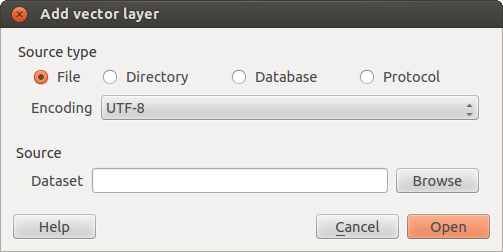
Finestra di dialogo aggiungi vettore
per i layer raster, clicca sull’icona
 Aggiungi raster, selezione l’opzione del menu Layer ‣ Aggiungi layer ‣ o digita Ctrl+Shift+R.
Aggiungi raster, selezione l’opzione del menu Layer ‣ Aggiungi layer ‣ o digita Ctrl+Shift+R.
Verrà visualizzata una finestra di dialogo standard per i file aperti (vedi figure_vector_open), che ti consente di navigare nel file system e caricare uno shapefile, un geotiff o un’altra fonte dati supportata. La casella di selezione Filtro  ti consente di preselezionare alcuni formati di file supportati. Solo i formati che sono stati ben testati appaiono nella lista. Altri formati non testati possono essere caricati selezionando Tutti i file (*. *) .
ti consente di preselezionare alcuni formati di file supportati. Solo i formati che sono stati ben testati appaiono nella lista. Altri formati non testati possono essere caricati selezionando Tutti i file (*. *) .
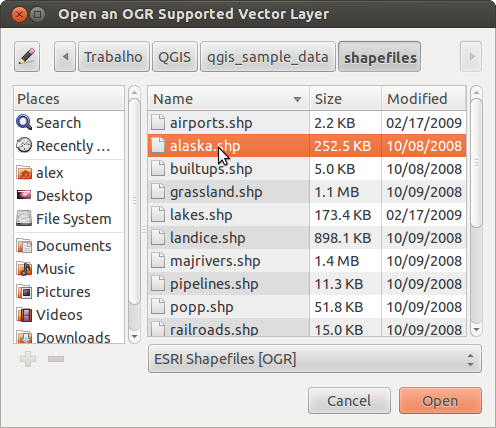
Aprire una finestra di dialogo di un layer vettoriale supportato OGR
Selecting a file from the list and clicking [Open] loads it into QGIS. More than one layer can be loaded at the same time by holding down the Ctrl or Shift key and clicking on multiple items in the dialog. Figure_vector_loaded shows QGIS after loading the alaska.shp file.
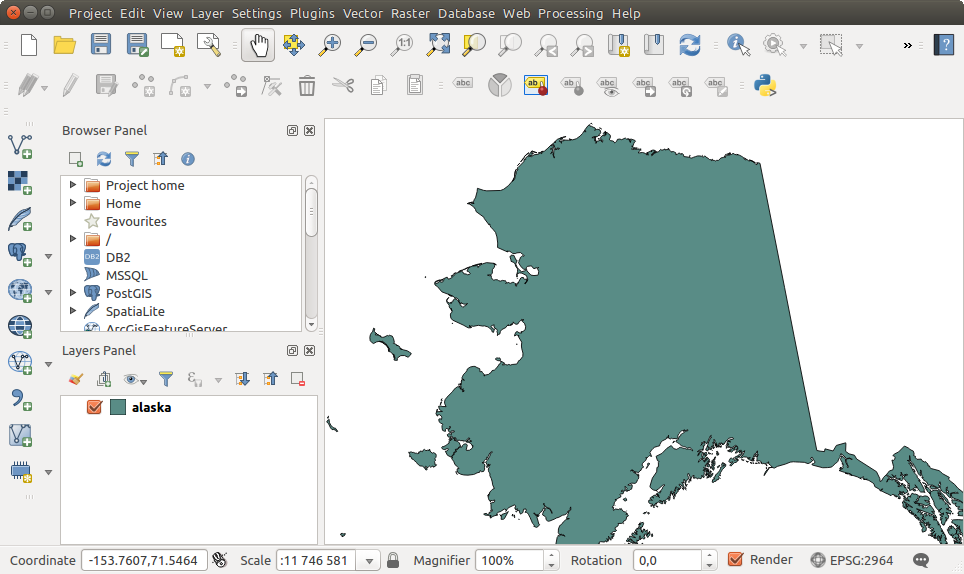
QGIS con il caricamento dello Shapefile Alaska
Nota
Poiché alcuni formati come MapInfo (ad esempio .tab) o Autocad (.dxf) consentono di mescolare diversi tipi di geometrie in un singolo file, il caricamento di tale formato in QGIS apre una finestra di dialogo per selezionare le geometrie da utilizzare in modo da ricavare un layer a singola tipologia geometrica.
Using the  Add Vector Layer tool:
Add Vector Layer tool:
You can also load specific formats like ArcInfo Binary Coverage, UK. National Transfer Format, as well as the raw TIGER format of the US Census Bureau or OpenfileGDB. To do that, you’d need to select
 Directory as Source type. In this case
a directory can be selected in the dialog after pressing [Browse].
Directory as Source type. In this case
a directory can be selected in the dialog after pressing [Browse].With the
 Database source type you can select an
existing database connection or create one to the selected database type.
Available database types are ODBC, OGDI Vectors, Esri Personal
Geodatabase, MySQL as well as PostgreSQL or MSSQL.
Database source type you can select an
existing database connection or create one to the selected database type.
Available database types are ODBC, OGDI Vectors, Esri Personal
Geodatabase, MySQL as well as PostgreSQL or MSSQL.Pressing the [New] button opens the Create a New OGR Database Connection dialog whose parameters are among the ones you can find in Creazione della connessione. Pressing [Open] you can select from the available tables for example of the PostGIS enabled database.
The last source type,
 Protocol, enables to open
data from the web using for example GeoJSON or CouchDB format. After
selecting the type you have to fill URI of the source.
Protocol, enables to open
data from the web using for example GeoJSON or CouchDB format. After
selecting the type you have to fill URI of the source.
Suggerimento
Caricare layers e progetti da unità esterne montate su macOS
On macOS, portable drives that are mounted beside the primary hard drive do not show up as expected under File ‣ Open Project. We are working on a more macOS-native open/save dialog to fix this. As a workaround, you can type /Volumes in the File name box and press Enter. Then you can navigate to external drives and network mounts.
Importare file di testo delimitato¶
Delimited text file (e.g. .csv, .txt) can be loaded in QGIS
using the tools described above. However, loaded this way, it’ll show up like a
simple table data. Sometimes, delimited text files can contain geometric data
you’d want to visualize; this is what the  Add
Delimited Text Layer is designed for.
Add
Delimited Text Layer is designed for.
Click the toolbar icon  Add Delimited Text Layer in the
Manage layers toolbar to open the Create a Layer from a
Delimited Text File dialog, as shown in figure_delimited_text.
Add Delimited Text Layer in the
Manage layers toolbar to open the Create a Layer from a
Delimited Text File dialog, as shown in figure_delimited_text.

Finestra di dialogo Testo Delimitato
First, select the file to import (e.g., qgis_sample_data/csv/elevp.csv) by clicking on the [Browse] button. Once the file is selected, QGIS attempts to parse the file with the most recently used delimiter. To enable QGIS to properly parse the file, it is important to select the correct delimiter. You can specify a delimiter by activating:
 CSV (comma separated values);
CSV (comma separated values); Delimitatori personalizzati, scegliendo tra alcuni delimitatori predefiniti come comma, spazio, TAB`, punto e virgola...;
Delimitatori personalizzati, scegliendo tra alcuni delimitatori predefiniti come comma, spazio, TAB`, punto e virgola...;o
 Delimitatore espressione regolare e inserendo un testo nel campo Espressione. Per esempio se vuoi usare TAB come delimitatore usa \t (questa è l’espressione regolare usata per TAB).
Delimitatore espressione regolare e inserendo un testo nel campo Espressione. Per esempio se vuoi usare TAB come delimitatore usa \t (questa è l’espressione regolare usata per TAB).
Once the file is parsed, set Geometry definition to
 Point coordinates and choose the X and Y
fields from the dropdown lists. If the coordinates are defined as
degrees/minutes/seconds, activate the
Point coordinates and choose the X and Y
fields from the dropdown lists. If the coordinates are defined as
degrees/minutes/seconds, activate the  DMS coordinates
checkbox.
DMS coordinates
checkbox.
Finally, enter a layer name (e.g., elevp), as shown in figure_delimited_text. To add the layer to the map, click [OK]. The delimited text file now behaves as any other map layer in QGIS.
There is also a helper option that allows you to trim leading and trailing
spaces from fields —  Trim fields. Also, it is possible
to
Trim fields. Also, it is possible
to  Discard empty fields. If necessary, you can force a
comma to be the decimal separator by activating
Discard empty fields. If necessary, you can force a
comma to be the decimal separator by activating  Decimal
separator is comma.
Decimal
separator is comma.
If spatial information is represented by WKT, activate the  Well Known Text option and select the field with the WKT definition
for point, line or polygon objects. If the file contains non-spatial data,
activate
Well Known Text option and select the field with the WKT definition
for point, line or polygon objects. If the file contains non-spatial data,
activate  No geometry (attribute only table) and it
will be loaded as an ordinal table.
No geometry (attribute only table) and it
will be loaded as an ordinal table.
Puoi anche attivare:
Importare file DXF o DWG¶
DXF and DWG files can be added to QGIS by simple drag-and-drop from the common Browser Panel. You’ll be prompted to select the sublayers you’d like to add to the project. Layers are added with random style properties.
Nota
Per i file DXF contenenti diversi tipi di geometria (punto, linea e/o poligono) il nome del layer verrà ricavato da <filename.dxf> entities <geometry type>.
To keep the dxf/dwg structure and its symbology in QGIS, you may want to use the dedicated Project ‣ DWG/DXF Import... tool. Indeed, the DWG/DXF Import dialog allows you to import into GeoPackage database any element of the drawing file.
In the dialog, you have to:
- Input a location for a GeoPackage file, that will be created to store the DWG/DXF content to;
- Specify which coordinate system the data in the DWG data is in;
- Then use the [Import] button to select the DWG/DXF file to use (one per geopackage). The GeoPackage database will be automatically populated with the drawing file content. Depending on the size of the *CAD file, this could take some time;
- The
 Expand block references will transform the existing
blocks into normal elements;
Expand block references will transform the existing
blocks into normal elements; - the
 Use curves promotes the output layers geometry type
to a curved one.
Use curves promotes the output layers geometry type
to a curved one.
After the .dwg or .dxf data is imported into the GeoPackage database the frame in the lower half of the dialog is populated with the list of layers from the imported file. There you can select which layers to add to the QGIS project:
- At the top, set a Group name to group the drawing files in the project;
- Check layers to show: Each selected layer is added to an ad hoc group which contains vector layers for the point, line, label and area features of the drawing layer. The style of each layer is setup so that it resembles the look it originally had in *CAD;
- Check whether layer should be visible at opening;
- Alternatively using the
 Merge layers option places all
layers in a single group;
Merge layers option places all
layers in a single group; - Press [OK] to open the layers in QGIS.
Importare vettori OpenStreetMap¶
Negli ultimi anni il progetto OpenStreetMap ha guadagnato popolarità perché in molti Paesi non sono disponibili dati geodati gratuiti quali mappe stradali digitali. L’obiettivo del progetto OSM è quello di creare una mappa liberamente modificabile del mondo da dati GPS, fotografia aerea o conoscenze locali. Per supportare questo obiettivo, QGIS fornisce il supporto per i dati OSM.
Utilizzando il Browser Panel, puoi caricare un file .osm sulla mappa, nel qual caso ti verrà visualizzata una finestra di dialogo per selezionare i sublayers in base al tipo di geometria. I layers caricati conterrano tutti i dati di quella tipologia di geometria presenti nel file e manterranno la struttura dati del file osm.
To avoid working with a such complex data structure, and be able to select only features you need based on their tags, QGIS provides a core and fully integrated OpenStreetMap import tool:
- To connect to the OSM server and download data, open the menu Vector ‣ OpenStreetMap ‣ Download data.... You can skip this step if you already obtained an .osm XML file using JOSM, Overpass API or any other source;
- The menu Vector ‣ OpenStreetMap ‣ Import Topology from XML... will convert your .osm file into a SpatiaLite database and create a corresponding database connection;
- The menu Vector ‣ OpenStreetMap ‣ Export Topology to
SpatiaLite... then allows you to open the database connection, select the
type of data you want (points, lines, or polygons) and choose tags to import.
This creates a SpatiaLite geometry layer that you can add to your
project by clicking on the
 Add SpatiaLite Layer toolbar button or by selecting the
Add SpatiaLite Layer toolbar button or by selecting the
 Add SpatiaLite Layer... option
from the Layer menu (see section SpatiaLite Layers).
Add SpatiaLite Layer... option
from the Layer menu (see section SpatiaLite Layers).
GPS¶
Il caricamento dei dati GPS in QGIS può essere effettuato utilizzando il plugin di base: Strumenti GPS. Le istruzioni sono descritte nel paragrafo Plugin GPS.
GRASS¶
Lavorare con i dati vettoriali GRASS è descritto nel capitolo Integrazione con GRASS GIS.
SpatiaLite Layers¶
 La prima volta che carichi i dati da un database di SpatiaLite, inizia da:
La prima volta che carichi i dati da un database di SpatiaLite, inizia da:
facendo clic sul pulsante
 Aggiungi vettore SpatiaLite della barra degli strumenti;
Aggiungi vettore SpatiaLite della barra degli strumenti;selezionando l’opzione
 Aggiungi vettore SpatiaLite... dal menu Layer ‣ Aggiungi Layer;
Aggiungi vettore SpatiaLite... dal menu Layer ‣ Aggiungi Layer;o digitando Ctrl+Shift+L.
This will bring up a window that will allow you either to connect to a SpatiaLite database already known to QGIS, which you can choose from the drop-down menu, or to define a new connection to a new database. To define a new connection, click on [New] and use the file browser to point to your SpatiaLite database, which is a file with a .sqlite extension.
QGIS supporta anche viste modificabili in SpatiaLite.
Formati QGIS personalizzati¶
QGIS dispone di due formati personalizzati che puoi caricare nell’applicazione utilizzando l’appropriato strumento di caricamento:
Layer temporaneo: un layer in memoria associato al progetto con il quale viene aperto (vedi Creazione di un nuovo Layer temporaneo per ulteriori informazioni)
Layers virtuali: un layer risultante da una query su altro(i) layer(s) (per ulteriori informazioni, vedi Layers virtuali)
Connessione a web services¶
Con QGIS puoi accedere a diversi tipi di servizi web OGC (WM(T)S, WFS(-T), CSW ...). Grazie a QGIS Server, puoi anche pubblicare questi servizi. La descrizione di queste funzionalità e le istruzioni per l’uso sono fornite nel capitolo Lavorare con i dati OGC.