17.33. 처리 과정에서 R 스크립트 사용
Module contributed by Matteo Ghetta - funded by Scuola Superiore Sant’Anna
Processing (with the Processing R Provider plugin) makes it possible to write
and run R scripts inside QGIS.
경고
R has to be installed on your computer and the PATH has to be correctly set up. Moreover Processing just calls the external R packages, it is not able to install them. So be sure to install external packages directly in R. See the related chapter in the user manual.
참고
If you have package problems, it may be related to missing
mandatory packages required by Processing, like sp, rgdal and raster.
17.33.1. 스크립트 추가
Adding a script is simple.
The easiest way is to open the Processing toolbox and choose
from the R menu (labelled with an
R icon) at the top of the Processing Toolbox.
You can also create the script in for instance a text editor and save it in
your R scripts folder (processing/rscripts).
When it has been saved there, it will be available for editing by
right-clicking on the script name in the processing toolbox and then choose
).
참고
처리 과정에 R이 안 보일 경우, 메뉴에서 활성화시켜야 합니다.
스크립트 편집 창 이 열리는데, 여기에 스크립트 자체를 추가하기 전에 몇몇 파라미터들을 설정해줘야 합니다.
17.33.2. 그래프 생성
이번 예제에서 벡터 레이어 항목의 **상자 모양 그래프**를 생성할 것입니다.
Open the r_intro.qgs QGIS project under the
exercise_data/processing/r_intro/ folder.
스크립트 파라미터
편집기를 실행해서 첫 부분부터 입력을 시작하십시오.
스크립트 자체를 입력하기 전에 몇몇 파라미터들을 설정 해야 합니다.
The name of the group (plots in this case) in which you want to put your script (if the group does not exist, it will be created):
##plots=groupYou will find your script in the plots R group in the Processing toolbox.
You have to tell Processing that you want to display a plot (in this example):
##showplotsYou will then find a link to the plot in the Result Viewer panel (can be turned on / off in and with ).
You also need to tell Processing about your input data. In this example we want to create a plot from a field of a vector layer:
##Layer=vectorProcessing now knows that the input is a vector. The name Layer is not important, what matters is the vector parameter.
Finally, you have to specify the input field of the vector layer (using the name you have provided above - Layer):
##X=Field LayerProcessing now knows that you need a field of Layer, and that you will call it X.
It is also possible to define the name of your script using
name:##My box plot script=nameIf not defined, the file name will be used as the name of the script.
스크립트 자체
이제 스크립트의 *표제(heading)*를 설정했으니, 함수를 추가할 수 있습니다.
boxplot(Layer[[X]])
boxplot is the name of the R function, the parameter Layer is the name that you have defined for the input dataset and X is the name you have defined for the field of that dataset.
경고
The parameter X has to be within double square brackets ([[]]).
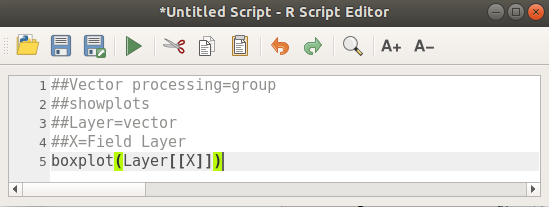
최종 스크립트는 다음과 같이 보일 겁니다.
##Vector processing=group
##showplots
##Layer=vector
##X=Field Layer
boxplot(Layer[[X]])
Save the script in the default path suggested by Processing (processing/rscripts).
If you have not defined a name in the script heading, the file name you
choose will become the name of the script in the Processing toolbox.
참고
You can save the script wherever you like, but Processing will then not be able to include it in the processing toolbox automatically, so you have to upload it manually.
이제 편집 창 최상단에 있는 버튼을 클릭해서 스크립트를 실행해보십시오.
Once the editor window has been closed, use the text box of Processing to find your script:
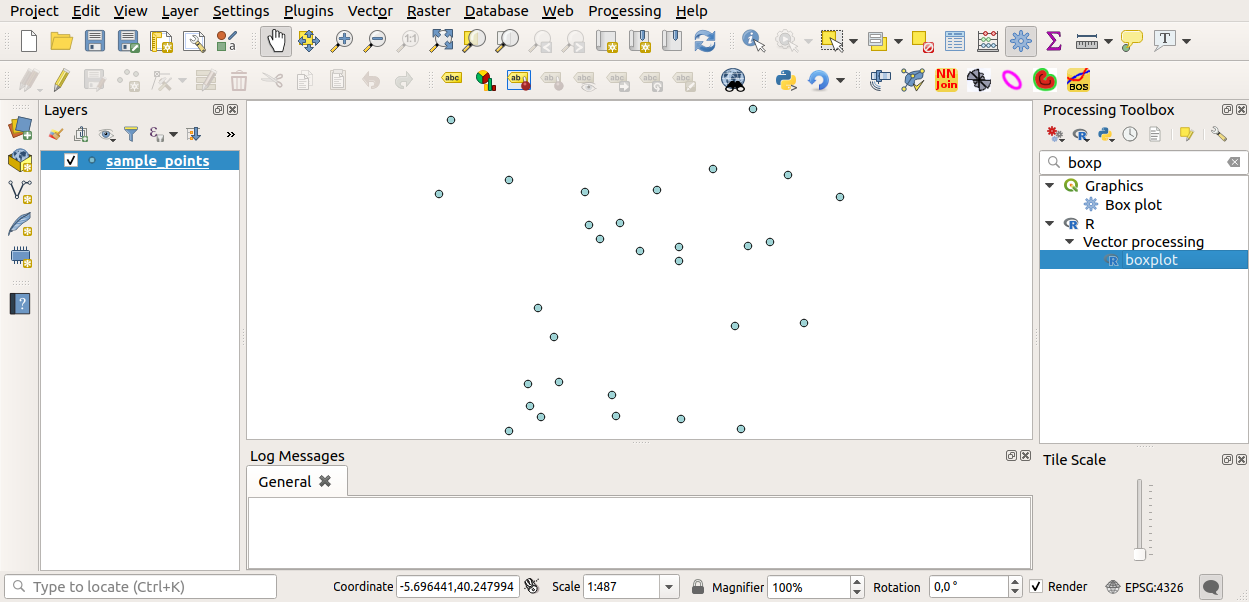
You can now fill the parameters required in the Processing algorithm window:
for Layer choose sample_points
for the X field choose value
Run 버튼을 클릭하십시오.
Result window 가 자동적으로 열릴 텐데, 열리지 않을 경우 메뉴를 클릭하면 됩니다.
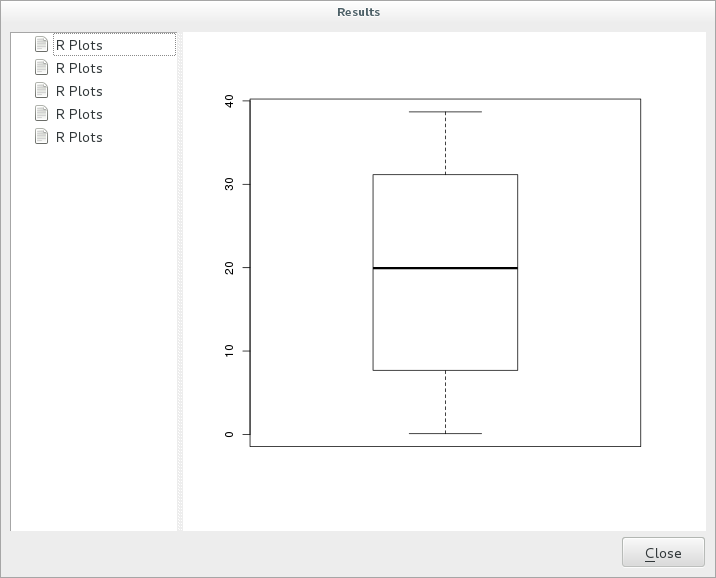
Click on the link in the viewer and you will see:
참고
You can open, copy and save the image by right clicking on the plot.
17.33.3. 벡터 생성
You can also create a vector layer and have it automatically loaded into QGIS.
The following example has been taken from the Random sampling grid
script that can be found in the online collection of R scripts
(the scripts in this online collection can be found in
https://github.com/qgis/QGIS-Processing/tree/master/rscripts).
The aim of this exercise is to create a random point vector layer
using an input vector layer to restrict the extent using the spsample
function of the sp package.
스크립트 파라미터
이전과 마찬가지로 스크립트 자체를 입력하기 전에 몇몇 파라미터들을 설정해줘야 합니다.
Specify the name of the group in which you want to put your script, in this case Point pattern analysis:
##Point pattern analysis=groupDefine an input parameter (a vector layer) that will constrain the placement of the random points:
##Layer=vectorSet an input parameter for the number of points that are going to be created (
Size, with a default value of10):##Size=number 10참고
Since a default value (
10) is defined, the user can change this number or can leave the parameter without a number.Specify that there is an output vector layer (called
Output):##Output=output vector
스크립트 자체
이제 함수 자체를 추가할 수 있습니다.
Use the
spsamplefunction:pts=spsample(Layer, Size, type="random")
The function uses the Layer to constrain the placement of the points (if it is a line layer, a points will have to be on one of the lines in the layer, if it is a polygon layer, a point will have to be within a polygon). The number of points is taken from the Size parameter. The sampling method is random.
Generate the output (the
Outputparameter):Output=SpatialPointsDataFrame(pts, as.data.frame(pts))
최종 스크립트는 다음과 같이 보일 겁니다.
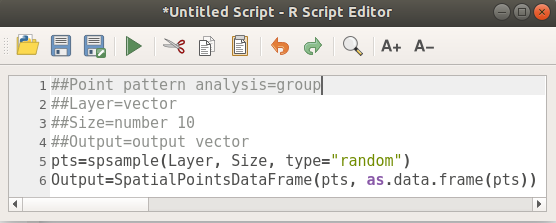
##Point pattern analysis=group
##Layer=vector
##Size=number 10
##Output=output vector
pts=spsample(Layer, Size, type="random")
Output=SpatialPointsDataFrame(pts, as.data.frame(pts))
Save it and run it, clicking on the run button.
새 창에서 정확한 파라미터들을 입력하십시오.
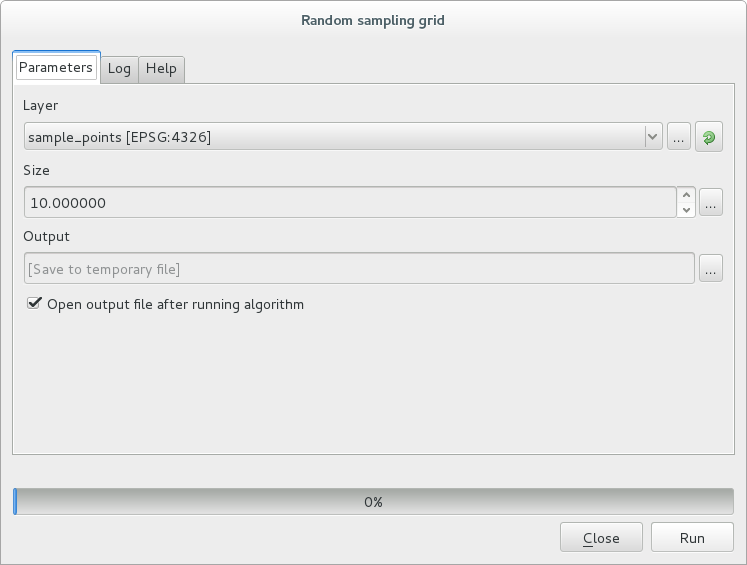
Run 버튼을 클릭합니다.
The result layer will be added to the table of contents and its points will be displayed on the map canvas:
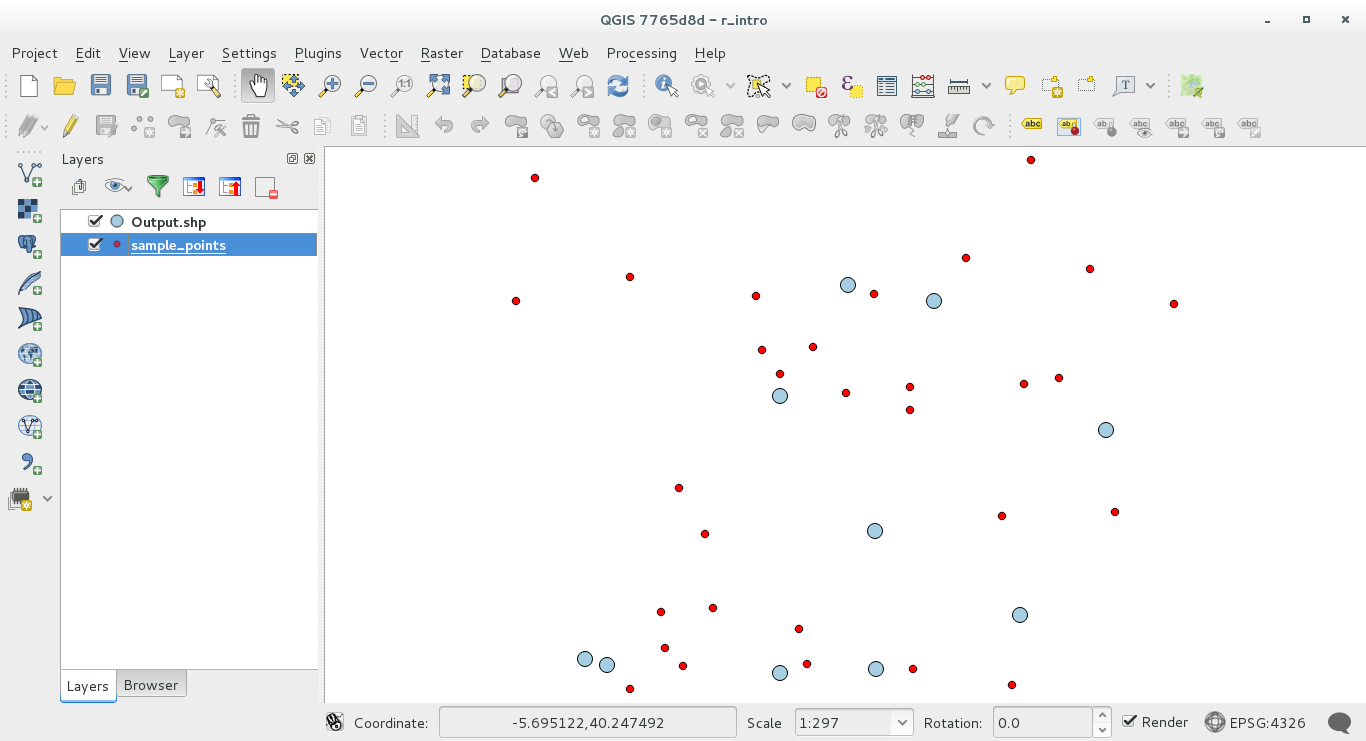
17.33.4. Text and graph output from R - syntax
Processing (with the Processing R Provider plugin) uses special
syntax to get the results out of R:
명령어 앞에
>lillie.test(Layer[[Field]])처럼>를 삽입하는 것은 결과를 R 산출물(Result viewer)로 보내야 한다는 의미입니다.+after a plot enables overlay plots. For exampleplot(Layer[[X]], Layer[[Y]]) + abline(h=mean(Layer[[X]]))