Pyqgis konsolunun dışındaysanız, bu sayfadaki kod parçacıkları aşağıdaki içe aktarmalara ihtiyaç duyar:
1from qgis.core import (
2 QgsMessageLog,
3 QgsGeometry,
4)
5
6from qgis.gui import (
7 QgsMessageBar,
8)
9
10from qgis.PyQt.QtWidgets import (
11 QSizePolicy,
12 QPushButton,
13 QDialog,
14 QGridLayout,
15 QDialogButtonBox,
16)
13. Kullanıcı iletişim arayüzü
Bu bölüm kullanıcı ile iletişim kurmamızı sağlayan metod ve bileşenlerin kullanımını içerir.
13.1. Mesajları gösterme. QgsMessageBar sınıfı
Mesaj kutuları kullanarak mesajlarımızı göstermek kullanıcı açısından kötü bir deneyim oluşturur. Bunun yerine uyarı ve hata mesajlarını bilgi çubuğu, mesaj satırı bölmesinde göstermek QGIS için daha mantıklı bir yöntemdir. Toplu işlemlerde yüzlerce hata ve uyarı mesajı oluşabilir.
QGIS arayüzünde mesaj satırı kısmını kullanarak mesaj göstermek için kullanılacak kod örneği:
from qgis.core import Qgis
iface.messageBar().pushMessage("Error", "I'm sorry Dave, I'm afraid I can't do that", level=Qgis.Critical)
Messages(2): Error : I'm sorry Dave, I'm afraid I can't do that
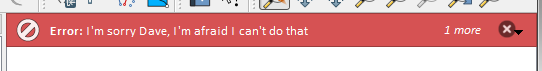
Şekil 13.25 QGIS Mesaj çubuğu
Mesajların belirli bir süre gösterilip ardından mesaj çubuğunun kaybolmasını sağlamak için süre sınırı koyabilirsiniz.
iface.messageBar().pushMessage("Ooops", "The plugin is not working as it should", level=Qgis.Critical, duration=3)
Messages(2): Ooops : The plugin is not working as it should

Şekil 13.26 QGIS Mesaj çubuğu, zaman sınırlaması ile
Yukarıdaki örnekte hata mesajı görülmekte, fakat level parametresi uyarı veya bilgi mesajı tipi olabilir. Qgis.MessageLevel seçenekleri kullanılabilir. 4 farklı seviye öntanımlıdır:
Bilgi
Uyarı
Kritik
Başarılı
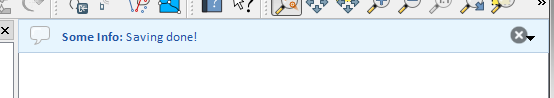
Şekil 13.27 QGIS Mesaj çubuğu (bilgi)
Mesaj çubuğuna araçlar eklenebilir, örneğin daha fazla bilgi göstermek için bir buton
1def showError():
2 pass
3
4widget = iface.messageBar().createMessage("Missing Layers", "Show Me")
5button = QPushButton(widget)
6button.setText("Show Me")
7button.pressed.connect(showError)
8widget.layout().addWidget(button)
9iface.messageBar().pushWidget(widget, Qgis.Warning)
Messages(1): Missing Layers : Show Me
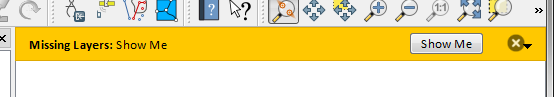
Şekil 13.28 Butonlu bir QGIS Mesaj çubuğu
Bu şekilde mesaj çubuğunu kendi mesaj kutunuzu göstermek için kullanabilirsiniz yada mesaj kutusu göstermek zorunlu değilse kullanılabilir.
1class MyDialog(QDialog):
2 def __init__(self):
3 QDialog.__init__(self)
4 self.bar = QgsMessageBar()
5 self.bar.setSizePolicy( QSizePolicy.Minimum, QSizePolicy.Fixed )
6 self.setLayout(QGridLayout())
7 self.layout().setContentsMargins(0, 0, 0, 0)
8 self.buttonbox = QDialogButtonBox(QDialogButtonBox.Ok)
9 self.buttonbox.accepted.connect(self.run)
10 self.layout().addWidget(self.buttonbox, 0, 0, 2, 1)
11 self.layout().addWidget(self.bar, 0, 0, 1, 1)
12 def run(self):
13 self.bar.pushMessage("Hello", "World", level=Qgis.Info)
14
15myDlg = MyDialog()
16myDlg.show()
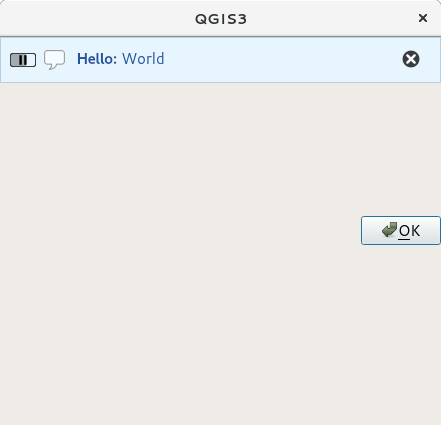
Şekil 13.29 QGIS, özel bileşenli mesaj çubuğu
13.2. İlerleme durumu gösterme
İlerleme durum çubukları QGIS mesaj çubuğu içinde gösterilebilir. İşte burada konsolda deneyebileceğiniz örnek bir kod.
1import time
2from qgis.PyQt.QtWidgets import QProgressBar
3from qgis.PyQt.QtCore import *
4progressMessageBar = iface.messageBar().createMessage("Doing something boring...")
5progress = QProgressBar()
6progress.setMaximum(10)
7progress.setAlignment(Qt.AlignLeft|Qt.AlignVCenter)
8progressMessageBar.layout().addWidget(progress)
9iface.messageBar().pushWidget(progressMessageBar, Qgis.Info)
10
11for i in range(10):
12 time.sleep(1)
13 progress.setValue(i + 1)
14
15iface.messageBar().clearWidgets()
Messages(0): Doing something boring...
Ayrıca entegre ilerleme durum çubuğunu kullanabilirsiniz. İşte sonraki örnek kod:
1vlayer = iface.activeLayer()
2
3count = vlayer.featureCount()
4features = vlayer.getFeatures()
5
6for i, feature in enumerate(features):
7 # do something time-consuming here
8 print('.') # printing should give enough time to present the progress
9
10 percent = i / float(count) * 100
11 # iface.mainWindow().statusBar().showMessage("Processed {} %".format(int(percent)))
12 iface.statusBarIface().showMessage("Processed {} %".format(int(percent)))
13
14iface.statusBarIface().clearMessage()
13.3. Loglama
Kodunuzun çalıştırılmasıyla ilgili tüm bilgileri günlüğe kaydetmek için QGIS’te üç farklı günlük kaydı türü vardır. Her birinin kendine özgü çıktı konumu vardır. Lütfen amacınız için doğru günlük kaydı yöntemini kullanmayı düşünün:
QgsMessageLogis for messages to communicate issues to the user. The output of the QgsMessageLog is shown in the Log Messages Panel.The python built in logging module is for debugging on the level of the QGIS Python API (PyQGIS). It is recommended for Python script developers that need to debug their python code, e.g. feature ids or geometries
QgsLoggeris for messages for QGIS internal debugging / developers (i.e. you suspect something is triggered by some broken code). Messages are only visible with developer versions of QGIS.
Examples for the different logging types are shown in the following sections below.
Uyarı
Use of the Python print statement is unsafe to do in any code which may be
multithreaded and extremely slows down the algorithm. This includes expression
functions, renderers,
symbol layers and Processing algorithms (amongst others). In these
cases you should always use the python logging module or thread safe classes
(QgsLogger
or QgsMessageLog) instead.
13.3.1. QgsMessageLog
# You can optionally pass a 'tag' and a 'level' parameters
QgsMessageLog.logMessage("Your plugin code has been executed correctly", 'MyPlugin', level=Qgis.Info)
QgsMessageLog.logMessage("Your plugin code might have some problems", level=Qgis.Warning)
QgsMessageLog.logMessage("Your plugin code has crashed!", level=Qgis.Critical)
MyPlugin(0): Your plugin code has been executed correctly
(1): Your plugin code might have some problems
(2): Your plugin code has crashed!
Not
QgsMessageLog sınıfının çıktılarını Log Messages Panel içerisinde görebilirsiniz.
13.3.2. The python built in logging module
1import logging
2formatter = '%(asctime)s - %(name)s - %(levelname)s - %(message)s'
3logfilename=r'c:\temp\example.log'
4logging.basicConfig(filename=logfilename, level=logging.DEBUG, format=formatter)
5logging.info("This logging info text goes into the file")
6logging.debug("This logging debug text goes into the file as well")
The basicConfig method configures the basic setup of the logging. In the above code the filename, logging level and the format are defined. The filename refers to where to write the logfile to, the logging level defines what levels to output and the format defines the format in which each message is output.
2020-10-08 13:14:42,998 - root - INFO - This logging text goes into the file
2020-10-08 13:14:42,998 - root - DEBUG - This logging debug text goes into the file as well
If you want to erase the log file every time you execute your script you can do something like:
if os.path.isfile(logfilename):
with open(logfilename, 'w') as file:
pass
Further resources on how to use the python logging facility are available at:
Uyarı
Please note that without logging to a file by setting a filename the logging may be multithreaded which heavily slows down the output.