23.1.16. Vector overlay
23.1.16.1. Clip
Clips a vector layer using the features of an additional polygon layer.
Only the parts of the features in the input layer that fall within the polygons of the overlay layer will be added to the resulting layer.
Warning
Feature modification
The attributes of the features are not modified, although properties such as area or length of the features will be modified by the clipping operation. If such properties are stored as attributes, those attributes will have to be manually updated.
This algorithm uses spatial indexes on the providers, prepared geometries and apply a clipping operation if the geometry isn’t wholly contained by the mask geometry.
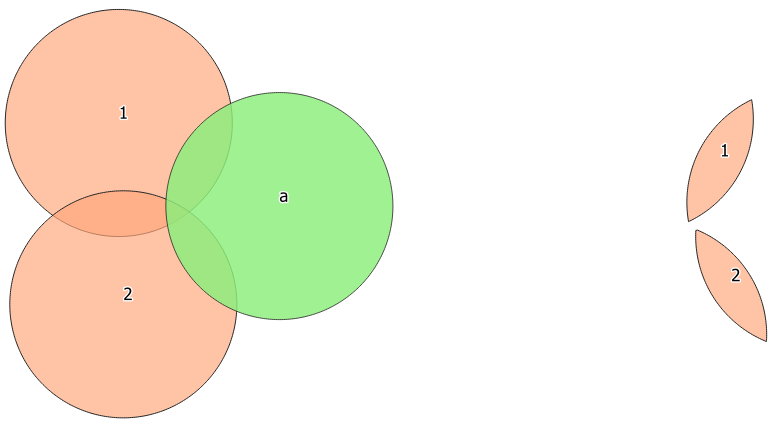
Fig. 23.78 Clipping operation between a two-features input layer and a single feature overlay layer (left) - resulting features are moved for clarity (right)
 Allows features in-place modification
Allows features in-place modification
Default menu:
See also
23.1.16.1.1. Parameters
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Input layer |
|
[vector: any] |
Layer containing the features to be clipped |
Overlay layer |
|
[vector: polygon] |
Layer containing the clipping features |
Clipped |
|
[same as input] Default: |
Specify the layer to contain the features from the input layer that are inside the overlay (clipping) layer. One of:
The file encoding can also be changed here. |
23.1.16.1.2. Outputs
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Clipped |
|
[same as input] |
Layer containing features from the input layer split by the overlay layer. |
23.1.16.1.3. Python code
Algorithm ID: qgis:clip
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
The algorithm id is displayed when you hover over the algorithm in the Processing Toolbox. The parameter dictionary provides the parameter NAMEs and values. See Using processing algorithms from the console for details on how to run processing algorithms from the Python console.
23.1.16.2. Difference
Extracts features from the input layer that don’t fall within the boundaries of the overlay layer.
Input layer features that partially overlap the overlay layer feature(s) are split along the boundary of those feature(s) and only the portions outside the overlay layer features are retained.
Attributes are not modified (see warning).
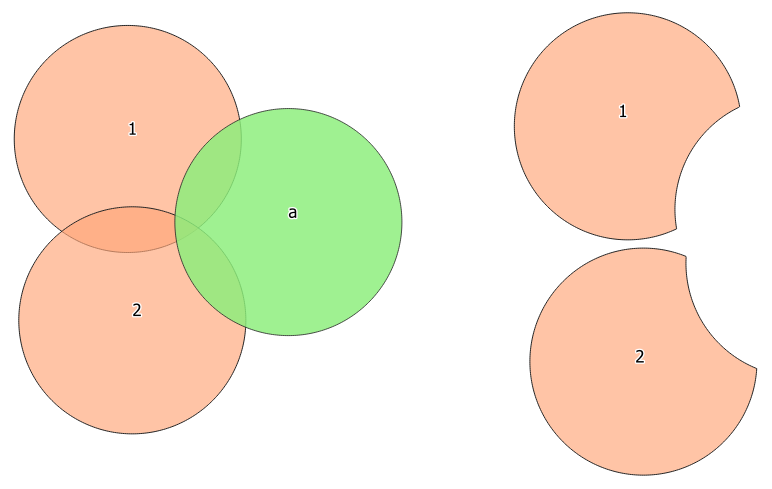
Fig. 23.79 Difference operation between a two-features input layer and a single feature overlay layer (left) - resulting features are moved for clarity (right)
 Allows features in-place modification
Allows features in-place modification
Default menu:
See also
23.1.16.2.1. Parameters
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Input layer |
|
[vector: any] |
Layer to extract (parts of) features from. |
Overlay layer |
|
[vector: any] |
Layer containing the geometries that will be subtracted from the input layer geometries. It is expected to have at least as many dimensions (point: 0D, line: 1D, polygon: 2D, volume: 3D) as the input layer geometries. |
Difference |
|
[same as input] Default: |
Specify the layer to contain the (parts of) features from the input layer that are not inside the overlay layer. One of:
The file encoding can also be changed here. |
23.1.16.2.2. Outputs
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Difference |
|
[same as input] |
Layer containing (parts of) features from the input layer not overlapping the overlay layer. |
23.1.16.2.3. Python code
Algorithm ID: qgis:difference
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
The algorithm id is displayed when you hover over the algorithm in the Processing Toolbox. The parameter dictionary provides the parameter NAMEs and values. See Using processing algorithms from the console for details on how to run processing algorithms from the Python console.
23.1.16.3. Extract/clip by extent
Creates a new vector layer that only contains features which fall within a specified extent.
Any features which intersect the extent will be included.
See also
23.1.16.3.1. Parameters
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Input layer |
|
[vector: any] |
Layer to extract (parts of) features from. |
Extent (xmin, xmax, ymin, ymax) |
|
[extent] |
Extent for clipping. |
Clip features to extent |
|
[boolean] Default: False |
If checked, output geometries will be automatically converted to multi geometries to ensure uniform output types. Moreover the geometries will be clipped to the extent chosen instead of taking the whole geometry as output. |
Extracted |
|
[same as input] Default: |
Specify the layer to contain the features from the input layer that are inside the clip extent. One of:
The file encoding can also be changed here. |
23.1.16.3.2. Outputs
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Extracted |
|
[same as input] |
Layer containing the clipped features. |
23.1.16.3.3. Python code
Algorithm ID: qgis:extractbyextent
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
The algorithm id is displayed when you hover over the algorithm in the Processing Toolbox. The parameter dictionary provides the parameter NAMEs and values. See Using processing algorithms from the console for details on how to run processing algorithms from the Python console.
23.1.16.4. Intersection
Extracts the portions of features from the input layer that overlap features in the overlay layer.
Features in the intersection layer are assigned the attributes of the overlapping features from both the input and overlay layers.
Attributes are not modified (see warning).
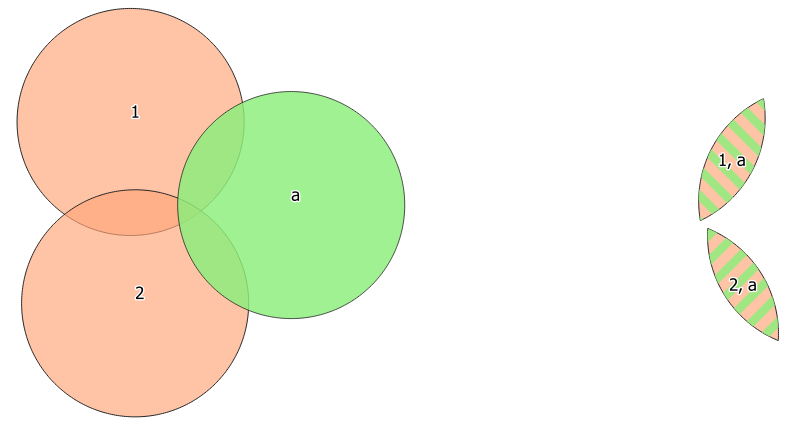
Fig. 23.80 The intersection operation: A two-features input layer and a single feature overlay layer (left) - resulting features are moved for clarity (right)
Default menu:
See also
23.1.16.4.1. Parameters
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Input layer |
|
[vector: any] |
Layer to extract (parts of) features from. |
Overlay layer |
|
[vector: any] |
Layer containing the features to check for overlap. Its features’ geometry is expected to have at least as many dimensions (point: 0D, line: 1D, polygon: 2D, volume: 3D) as the input layer’s. |
Input fields to keep (leave empty to keep all fields) Optional |
|
[tablefield: any] [list] Default: None |
Field(s) of the input layer to keep in the output. If no fields are chosen all fields are taken. |
Overlay fields to keep (leave empty to keep all fields) Optional |
|
[tablefield: any] [list] Default: None |
Field(s) of the overlay layer to keep in the output. If no fields are chosen all fields are taken. |
Overlay fields prefix Optional |
|
[string] |
Prefix to add to the field names of the intersect layer’s fields to avoid name collisions with fields in the input layer. |
Intersection |
|
[same as input] Default: |
Specify the layer to contain (the parts of) the features from the input layer that overlap one or more features from the overlay layer. One of:
The file encoding can also be changed here. |
23.1.16.4.2. Outputs
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Intersection |
|
[same as input] |
Layer containing (parts of) features from the input layer that overlap the overlay layer. |
23.1.16.4.3. Python code
Algorithm ID: qgis:intersection
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
The algorithm id is displayed when you hover over the algorithm in the Processing Toolbox. The parameter dictionary provides the parameter NAMEs and values. See Using processing algorithms from the console for details on how to run processing algorithms from the Python console.
23.1.16.5. Line intersections
Creates point features where the lines from the two layers intersect.

Fig. 23.81 Points of intersection
Default menu:
23.1.16.5.1. Parameters
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Input layer |
|
[vector: line] |
Input line layer. |
Intersect layer |
|
[vector: line] |
Layer to use to find line intersections. |
Input fields to keep (leave empty to keep all fields) Optional |
|
[tablefield: any] [list] Default: None |
Field(s) of the input layer to keep in the output. If no fields are chosen all fields are taken. |
Intersect fields to keep (leave empty to keep all fields) Optional |
|
[tablefield: any] [list] Default: None |
Field(s) of the intersect layer to keep in the output. If no fields are chosen all fields are taken. |
Intersect fields prefix Optional |
|
[string] |
Prefix to add to the field names of the intersect layer’s fields to avoid name collisions with fields in the input layer. |
Intersection |
|
[vector: point] Default: |
Specify the layer to contain the intersection points of the lines from the input and overlay layers. One of:
The file encoding can also be changed here. |
23.1.16.5.2. Outputs
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Intersections |
|
[vector: point] |
Point vector layer with the intersections. |
23.1.16.5.3. Python code
Algorithm ID: qgis:lineintersections
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
The algorithm id is displayed when you hover over the algorithm in the Processing Toolbox. The parameter dictionary provides the parameter NAMEs and values. See Using processing algorithms from the console for details on how to run processing algorithms from the Python console.
23.1.16.6. Split with lines
Splits the lines or polygons in one layer using the lines in another layer to define the breaking points. Intersection between geometries in both layers are considered as split points.
Output will contain multi geometries for split features.
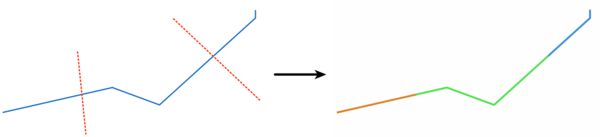
Fig. 23.82 Split lines
 Allows features in-place modification
Allows features in-place modification
23.1.16.6.1. Parameters
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Input layer |
|
[vector: line, polygon] |
Layer containing the lines or polygons to split. |
Split layer |
|
[vector: line] |
Line layer whose lines are used to define the breaking points. |
Split |
|
[same as input] Default: |
Specify the layer to contain the splitted (in case they are intersected by a line in the split layer) line/polygon features from the input layer. One of:
The file encoding can also be changed here. |
23.1.16.6.2. Outputs
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Split |
|
[same as input] |
Output vector layer with split lines or polygons from input layer. |
23.1.16.6.3. Python code
Algorithm ID: qgis:splitwithlines
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
The algorithm id is displayed when you hover over the algorithm in the Processing Toolbox. The parameter dictionary provides the parameter NAMEs and values. See Using processing algorithms from the console for details on how to run processing algorithms from the Python console.
23.1.16.7. Symmetrical difference
Creates a layer containing features from both the input and overlay layers but with the overlapping areas between the two layers removed.
The attribute table of the symmetrical difference layer contains attributes and fields from both the input and overlay layers.
Attributes are not modified (see warning).
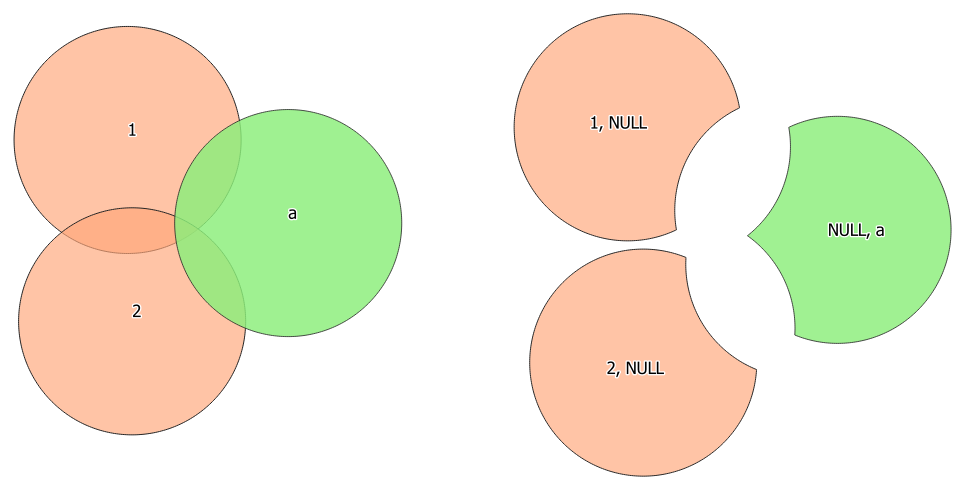
Fig. 23.83 Symmetrical difference operation between a two-features input layer and a single feature overlay layer (left) - resulting features are moved for clarity (right)
Default menu:
See also
23.1.16.7.1. Parameters
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Input layer |
|
[vector: any] |
First layer to extract (parts of) features from. |
Overlay layer |
|
[vector: any] |
Second layer to extract (parts of) features from. Ideally the geometry type should be the same as input layer. |
Overlay fields prefix Optional |
|
[string] |
Prefix to add to the field names of the overlay layer’s fields to avoid name collisions with fields in the input layer. |
Symmetrical difference |
|
[same as input] Default: |
Specify the layer to contain (the parts of) the features from the input and overlay layers that do not overlap features from the other layer. One of:
The file encoding can also be changed here. |
23.1.16.7.2. Outputs
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Symmetrical difference |
|
[same as input] |
Layer containing (parts of) features from each layer not overlapping the other layer. |
23.1.16.7.3. Python code
Algorithm ID: qgis:symmetricaldifference
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
The algorithm id is displayed when you hover over the algorithm in the Processing Toolbox. The parameter dictionary provides the parameter NAMEs and values. See Using processing algorithms from the console for details on how to run processing algorithms from the Python console.
23.1.16.8. Union
Checks overlaps between features within the input layer and creates separate features for overlapping and non-overlapping parts. The area of overlap will create as many identical overlapping features as there are features that participate in that overlap.
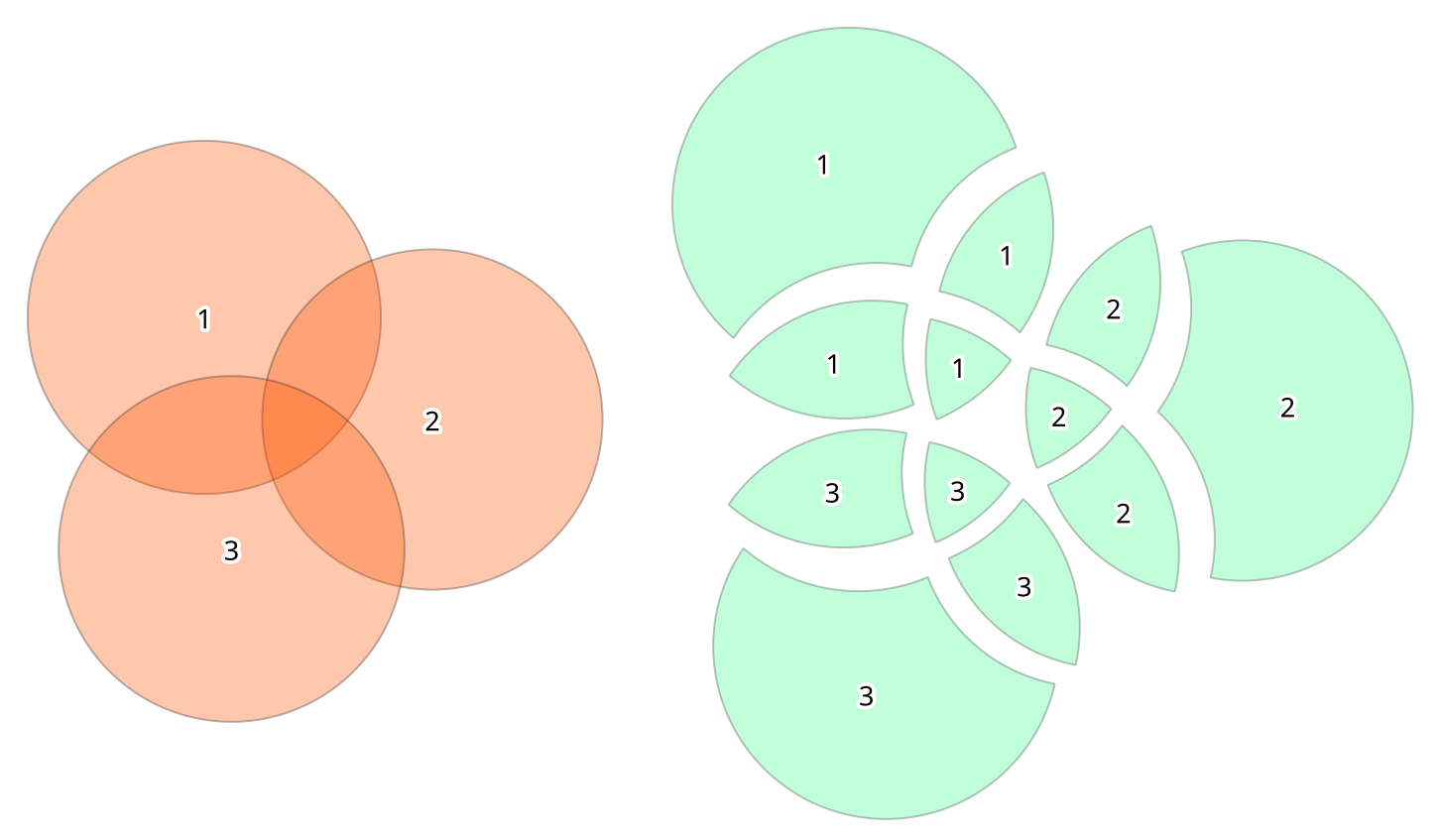
Fig. 23.84 Union operation with a single input layer of three overlapping features (left) - resulting features are moved for clarity (right)
An overlay layer can also be used, in which case features from each layer are split at their overlap with features from the other one, creating a layer containing all the portions from both input and overlay layers. The attribute table of the union layer is filled with attribute values from the respective original layer for non-overlapping features, and attribute values from both layers for overlapping features.
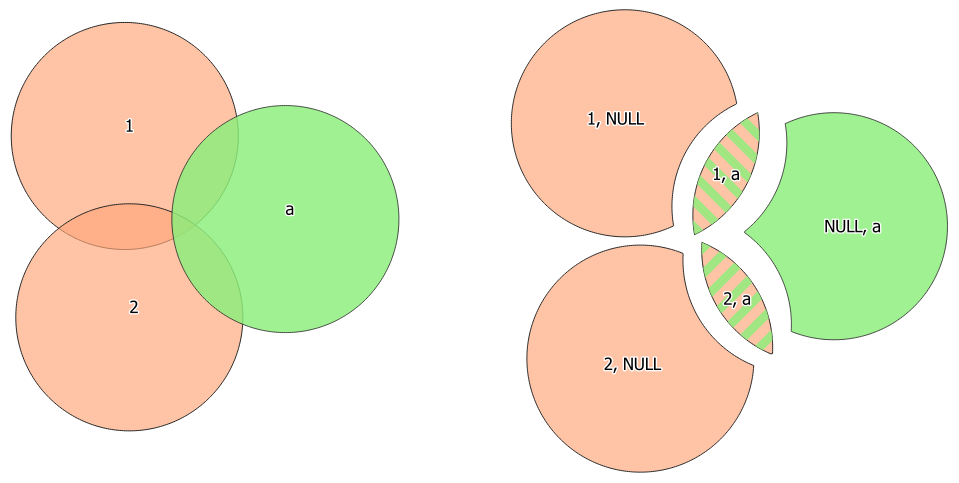
Fig. 23.85 Union operation between a two-features input layer and a single feature overlay layer (left) - resulting features are moved for clarity (right)
Note
For union(A,B) algorithm, if there are overlaps among
geometries of layer A or among geometries of layer B, these are not
resolved: you need to do union(union(A,B)) to resolve all
overlaps, i.e. run single layer union(X) on the produced result
X=union(A,B).
Default menu:
See also
23.1.16.8.1. Parameters
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Input layer |
|
[vector: any] |
Input vector layer to split at any intersections. |
Overlay layer Optional |
|
[vector: any] |
Layer that will be combined to the first one. Ideally the geometry type should be the same as input layer. |
Overlay fields prefix Optional |
|
[string] |
Prefix to add to the field names of the overlay layer’s fields to avoid name collisions with fields in the input layer. |
Union |
|
[same as input] Default: |
Specify the layer to contain the (split and duplicated) features from the input layer and the overlay layer. One of:
The file encoding can also be changed here. |
23.1.16.8.2. Outputs
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Union |
|
[same as input] |
Layer containing all the overlapping and non-overlapping parts from the processed layer(s). |
23.1.16.8.3. Python code
Algorithm ID: qgis:union
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
The algorithm id is displayed when you hover over the algorithm in the Processing Toolbox. The parameter dictionary provides the parameter NAMEs and values. See Using processing algorithms from the console for details on how to run processing algorithms from the Python console.