Importante
La traduzione è uno sforzo comunitario you can join. Questa pagina è attualmente tradotta al 100.00%.
20.1. Introduzione ai Dati GNSS/GPS
20.1.1. Cos’è un GPS?
GPS, il Global Positioning System, è un sistema satellitare che permette a chiunque abbia un ricevitore GPS di trovare la propria posizione esatta in qualsiasi parte del mondo. Il GPS è utilizzato come ausilio alla navigazione, ad esempio in aereo, in barca e dagli escursionisti. Il ricevitore GPS utilizza i segnali dei satelliti per calcolare la latitudine, la longitudine e (talvolta) l’elevazione. La maggior parte dei ricevitori ha anche la capacità di memorizzare:
posizioni (note come waypoints)
sequenze di posizioni che compongono una route pianificata
e un registro track del percorso del ricevitore nel tempo.
Waypoint, route e track sono i tre tipi di elementi di base dei dati GPS. QGIS visualizza i waypoint in layer di punti, mentre le route e le track sono visualizzate in layer di linee.
Nota
QGIS supporta anche ricevitori GNSS. Ma noi continuiamo a usare il termine GPS in questa documentazione.
20.1.2. Trasferire o caricare dati GPS
20.1.2.1. Caricamento di un file GPX
Ci sono una dozzina di formati di file diversi per memorizzare dati GPS. Il formato utilizzato da QGIS è chiamato GPX (GPS eXchange format), che è un formato standard di interscambio che può contenere svariati numeri di posizioni, percorsi e tracce nello stesso file.
Per caricare un file GPX:
Apri la scheda GPS nella finestra di dialogo Gestore delle Sorgenti Dati, ad es:
Usa il pulsante … Sfoglia accanto all’opzione Dataset GPX per selezionare il file GPX.
Utilizza le caselle di controllo per selezionare i Tipi di elementi che vuoi caricare dal file. Ogni tipo di elemento (Waypoints, Tracks o Routes) sarà caricato in un layer separato.
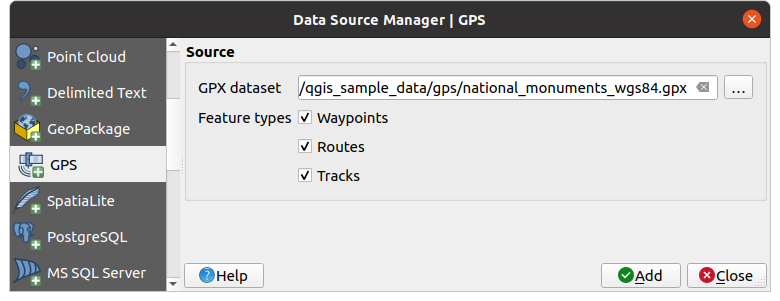
Fig. 20.1 Caricare finestra di dialogo Dati GPS
20.1.2.2. Caricamento da o verso un dispositivo
Esistono molti tipi diversi di dispositivi e formati GPS. Poiché QGIS utilizza file GPX, devi avere un modo per convertire altri formati di file GPS in GPX. QGIS può farlo utilizzando il programma gratuito GPSBabel. GPSBabel ti può aiutare a convertire waypoint, tracce e percorsi tra i ricevitori GPS più diffusi, come Garmin o Magellan, e programmi di mappatura come Google Earth o Basecamp. Sono supportati letteralmente centinaia di ricevitori e programmi GPS. Può anche trasferire dati GPS tra il computer e un dispositivo GPS.
In  :menuselection: Opzioni –>
:menuselection: Opzioni –> ![]()
![]() , QGIS ti permette di definire il tuo tipo di dispositivo e di impostare i parametri di conversione che potrebbero essere utilizzati in seguito da Processing GPS algorithms.
, QGIS ti permette di definire il tuo tipo di dispositivo e di impostare i parametri di conversione che potrebbero essere utilizzati in seguito da Processing GPS algorithms.
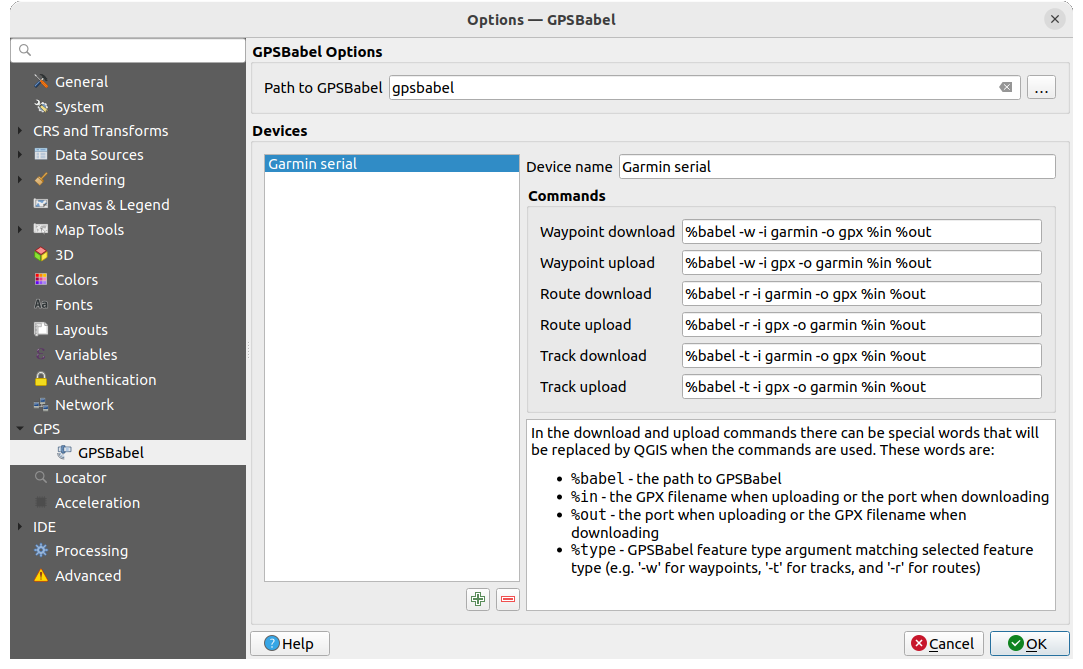
Fig. 20.2 Impostazioni GPS Babel
Per prima cosa devi definire il Percorso per GPSBabel.
A questo punto puoi aggiungere il dispositivo. Puoi aggiornare l’elenco dei dispositivi utilizzando il pulsante
 Aggiungi dispositivo o
Aggiungi dispositivo o  Rimuovi dispositivo.
Rimuovi dispositivo.Per ogni dispositivo:
fornisci un Nome dispositivo
puoi configurare diversi Comandi che QGIS utilizzerà durante l’interazione con esso, come ad esempio:
Scarica waypoint dal dispositivo
Carica waypoint sul dispositivo
Carica route dal dispositivo
Scarica route sul dispositivo
Carica track dal dispositivo
Scarica track sul dispositivo
Sebbene i comandi siano solitamente comandi GPSBabel, puoi anche utilizzare qualsiasi altro programma dalla linea di comando in grado di creare un file GPX. QGIS sostituirà le parole chiave
%type,%iin, and%outquando esegue il comando.Ad esempio, se crei un tipo di dispositivo con il comando di download
gpsbabel %type -i garmin -o gpx %iin %oute poi lo usi per scaricare waypoint dalla porta/dev/ttyS0al fileoutput.gpx, QGIS sostituirà le parole chiave ed eseguirà il comandogpsbabel -w -i garmin -o gpx /dev/ttyS0 output.gpx.Leggi il manuale di GPSBabel per le opzioni della linea di comando che possono essere specifiche per il tuo caso d’uso.
Una volta che hai creato un nuovo tipo di dispositivo, questo apparirà negli elenchi dei dispositivi per gli algoritmi di download e upload del GPS.
Nota
Le unità GPS consentono di memorizzare i dati in diversi sistemi di coordinate. Quando si scarica un file GPX (dall’unità GPS o da un sito web) e lo si carica in QGIS, assicurarsi che i dati memorizzati nel file GPX utilizzino il sistema WGS 84 (latitudine/longitudine). QGIS lo prevede ed è la specifica GPX ufficiale. Vedere GPX 1.1 Schema Documentation.

