Fontos
A fordítás közösségi munka eredménye, amelyhez itt tudsz csatlakozni. Ennek az oldalnak eddig a 10.26% részét fordítottuk le.
17.2. Raszter analízis
17.2.1. Raster Calculator
The in the menu allows you to perform calculations on the basis of existing raster pixel values (see 17.22. ábra). The results are written to a new raster layer in a GDAL-supported format.
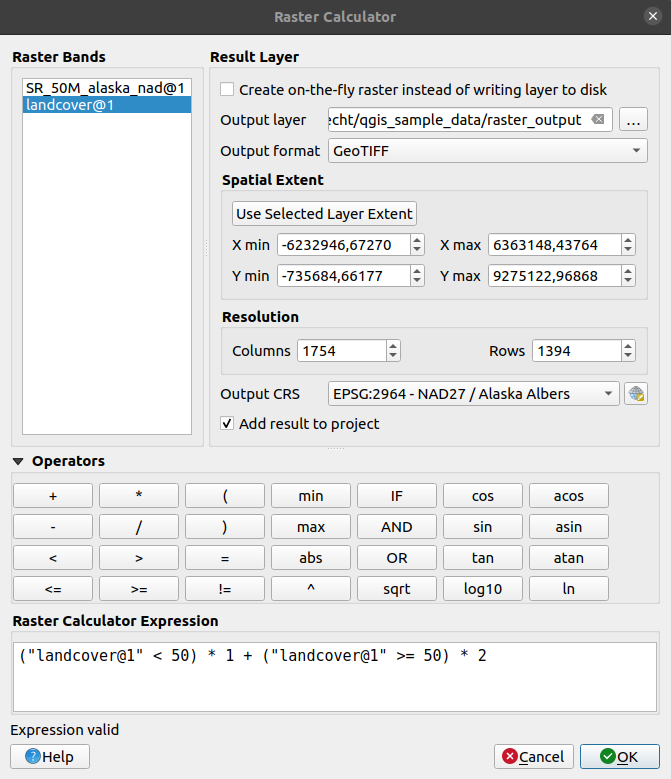
17.22. ábra Raster Calculator
The Raster bands list contains all loaded raster layers that can be used. To add a raster to the raster calculator expression field, double click its name in the Fields list. You can then use the operators to construct calculation expressions, or you can just type them into the box.
In the Result layer section, you will need to define an output layer. You can:
 Create on-the-fly raster instead of writing layer to disk:
Create on-the-fly raster instead of writing layer to disk:If unchecked, the output is stored on the disk as a new plain file. An Output layer path and an Output format are required.
If checked, a virtual raster layer, i.e. a raster layer defined by its URI and whose pixels are calculated on-the-fly, is created. It’s not a new file on disk; the virtual layer is still connected to the rasters used in the calculation meaning that deleting or moving these rasters would break it. A Layer name can be provided, otherwise the calculation expression is used as such. Removing the virtual layer from the project deletes it, and it can be made persistent in file using the layer contextual menu.
Define the Spatial extent of the calculation based on an input raster layer extent, or on custom X,Y coordinates
Set the Resolution of the layer using columns and rows number. If the input layer has a different resolution, the values will be resampled with the nearest neighbor algorithm.
With the
 Add result to project checkbox, the result layer
will automatically be added to the legend area and can be visualized.
Checked by default for virtual rasters.
Add result to project checkbox, the result layer
will automatically be added to the legend area and can be visualized.
Checked by default for virtual rasters.
The Operators section contains all available operators. To add an operator
to the raster calculator expression box, click the appropriate button. Mathematical
calculations (+, -, *, … ) and trigonometric functions (sin,
cos, tan, … ) are available. Conditional expressions (=, !=,
<, >=, … ) return either 0 for false or 1 for true, and therefore can be
used with other operators and functions.
Lásd még
Raster calculator and Raster calculator (virtual) algorithms
17.2.1.1. Raster calculator expression
The dialog
The Raster calculator expression dialog provides means to write expressions for pixels calculations between a set of raster layers.
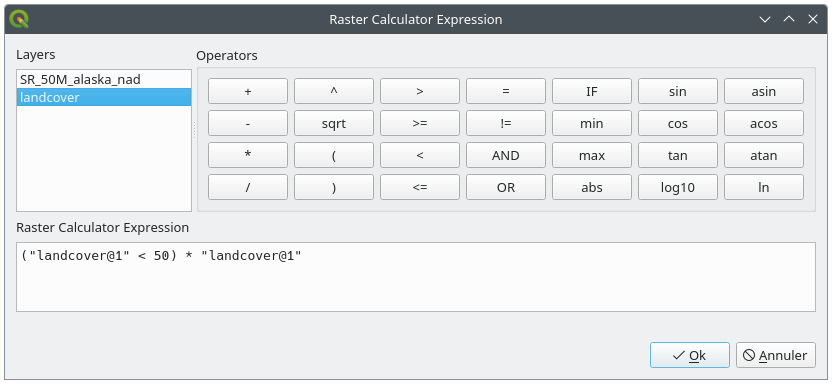
17.23. ábra Raster Expression Calculator
Layers: Shows the list of all raster layers loaded in the legend. These can be used to fill the expression box (double click to add). Raster layers are referred by their name and the number of the band:
layer_name@band_number. For instance, the first band from a layer namedDEMwill be referred asDEM@1.Operators: contains a number of calculation operators for pixels manipulation:
Arithmetical:
+,-,*,sqrt,abs,ln, …Trigonometric:
sin,cos,tan, …Comparison:
=,!=,<,>=, …Logical:
IF,AND,OR,(,)Statistical:
min,max
To add an operator to the raster calculator expression box, click the appropriate button.
Raster calculator expression is the area in which the expression is composed
Példák
Convert elevation values from meters to feet
Creating an elevation raster in feet from a raster in meters, you need to use the conversion factor for meters to feet: 3.28. The expression is:
"elevation@1" * 3.28
Using a mask
If you want to mask out parts of a raster – say, for instance, because you are only interested in elevations above 0 meters – you can use the following expression to create a mask and apply the result to a raster in one step.
("elevation@1" >= 0) * "elevation@1"
In other words, for every cell greater than or equal to 0 the conditional expression evaluates to 1, which keeps the original value by multiplying it by 1. Otherwise the conditional expression evaluates to 0, which sets the raster value to 0. This creates the mask on the fly.
Classify a Raster
If you want to classify a raster – say, for instance into two elevation classes, you can use the following expression to create a raster with two values 1 and 2 in one step.
("elevation@1" < 50) * 1 + ("elevation@1" >= 50) * 2
In other words, for every cell less than 50 set its value to 1. For every cell greater than or equal 50 set its value to 2.
Or you can use the IF operator.
if ( elevation@1 < 50 , 1 , 2 )