` `
Expresiones¶
- The Expression string builder
- Lista de funciones
- Operadores
- Conditionals
- Funciones Matemáticas
- Aggregates Functions
- Funciones de Color
- Funciones de conversión
- Funciones personalizadas
- Funciones de Fecha y Hora
- Campos y Valores
- Funciones Concordancia aproximada
- Funciones Generales
- Funciones de Geometría
- Record Functions
- Funciones de cadena
- Funciones recientes
- Variables Functions
- Editor de Funciones
Based on layer data and prebuilt or user defined functions, Expressions offer a powerful way to manipulate attribute value, geometry and variables in order to dynamically change the geometry style, the content or position of the label, the value for diagram, the height of a composer item, select some features, create virtual field ...
The Expression string builder¶
Main dialog to build expressions, the Expression string builder is available from many parts in QGIS and, can particularly be accessed when:
- clicking the
 button;
button; - selecting features with the
 Select By Expression... tool;
Select By Expression... tool; - editing attributes with e.g. the
 Field calculator tool;
Field calculator tool; - manipulating symbology, label or composer item parameters with the
 Data defined override tool (see Configuración de anulación definida por datos);
Data defined override tool (see Configuración de anulación definida por datos); - building a geometry generator symbol layer;
- doing some geoprocessing.
The Expression builder dialog offers access to the:
- Expression tab which, thanks to a list of predefined functions, helps to write and check the expression to use;
- Function Editor tab which helps to extend the list of functions by creating custom ones.
Some use cases of expressions:
From Field Calculator, calculate a “pop_density” field using existing “total_pop” and “area_km2” fields:
"total_pop" / "area_km2"
Update the field “density_level” with categories according to the “pop_density” values:
CASE WHEN "pop_density" < 50 THEN 'Low population density' WHEN "pop_density" >= 50 and "pop_density" < 150 THEN 'Medium population density' WHEN "pop_density" >= 150 THEN 'High population density' ENDApply a categorized style to all the features according to whether their average house price is smaller or higher than 10000€ per square metre:
"price_m2" > 10000
Using the “Select By Expression...” tool, select all the features representing areas of “High population density” and whose average house price is higher than 10000€ per square metre:
"density_level" = 'High population density' and "price_m2" > 10000
Likewise, the previous expression could also be used to define which features should be labeled or shown in the map.
Using expressions offers you a lot of possibilities.
Truco
Use named parameters to improve the expression reading
Some functions require many parameters to be set. The expression engine supports the use of named parameters. This means that instead of writing the cryptic expression clamp( 1, 2, 9), you can use clamp( min:=1, value:=2, max:=9). This also allows arguments to be switched, e.g. clamp( value:=2, max:=9, min:=1). Using named parameters helps clarify what the arguments for an expression function refer to, which is helpful when you are trying to interpret an expression at a later date!
Lista de funciones¶
The Expression tab provides the main interface to write expressions using functions, layer’s fields and values. It contains widgets to:
- type expressions using functions and/or fields. At the bottom of the dialog, is displayed the result of the expression evaluated on the first feature of the layer.
- select the appropriate function among a list, organized in groups. A search box is available to filter the list and quickly find a particular function or field. Double-clicking on the item’s name adds it to the expression being written.
- display help for each function selected. When a field is selected, this widget shows a sample of its values. Double-clicking a value adds it to the expression.
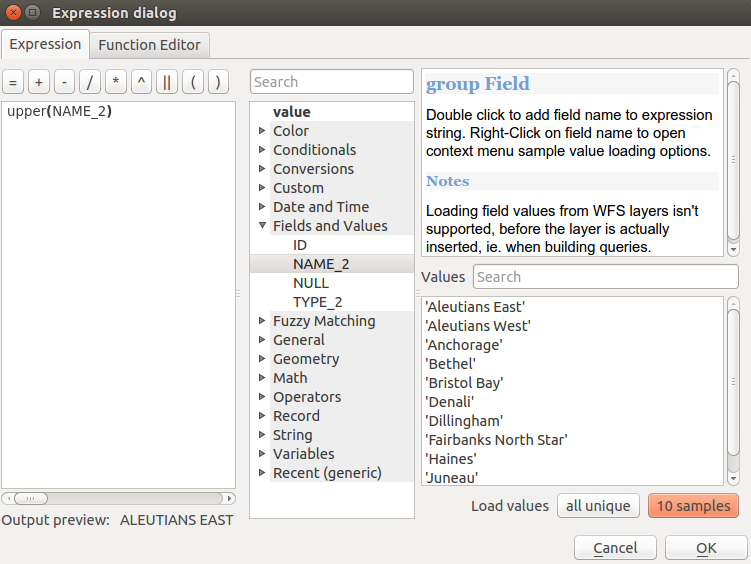
The Expression tab
Operadores¶
This group contains operators (e.g., +, -, *). Note that for most of the mathematical functions below, if one of the inputs is NULL then the result is NULL.
Función |
Descripción |
|---|---|
| a + b | Addition of two values (a plus b) |
| a - b | Subtraction of two values (a minus b). |
| a * b | Multiplication of two values (a multiplied by b) |
| a / b | División de dos valores (a dividido entre b) |
| a % b | Remainder of division of a by b (eg, 7 % 2 = 1, or 2 fits into 7 three times with remainder 1) |
| a ^ b | Power of two values (for example, 2^2=4 or 2^3=8) |
| a < b | Compares two values and evaluates to 1 if the left value is less than the right value (a is smaller than b) |
| a <= b | Compares two values and evaluates to 1 if the left value isless than or equal to the right value |
| a <> b | Compara dos valores y evalúa a 1 si no son iguales |
| a = b | Compara dos valores y evalúa a 1 si son iguales. |
| a != b | a and b are not equal |
| a > b | Compara dos valores y evalúa como 1 si el valor izquierdo es mayor que el valor derecho (a es mayor que b) |
| a >= b | Compara dos valores y evalúa a 1 si el valor de la izquierda es mayor que o igual que el valor de la derecha |
| a ~ b | a matches the regular expression b |
| || | Joins two values together into a string. If one of the values is NULL the result will be NULL |
| ‘\n’ | Inserta una nueva línea en una cadena |
| LIKE | Devuelve 1 si el primer parámetro coincide con el patrón provisto |
| ILIKE | Returns 1 if the first parameter matches case-insensitive the supplied pattern (ILIKE can be used instead of LIKE to make the match case-insensitive) |
| a IS b | Tests whether two values are identical. Returns 1 if a is the same as b |
| a OR b | Returns 1 when condition a or condition b is true |
| a AND b | Returns 1 when conditions a and b are true |
| NOT | Niega una condición |
| column name “column name” | Value of the field column name, take care to not be confused with simple quote, see below |
‘cadena’ |
a string value, take care to not be confused with double quote, see above |
| NULL | valor nulo |
| a IS NULL | a no tiene valor |
| a IS NOT NULL | a tiene valor |
| a IN (value[,value]) | a esta debajo de los valores listados |
a NOT IN (valor[,valor]) |
a no está debajo de los valores listados |
Nota
About fields concatenation
You can concatenate strings using either || or +. The latter also means sum up expression. So if you have an integer (field or numeric value) this can be error prone. In this case, you should use ||. If you concatenate two string values, you can use both.
Algún ejemplo:
Une una cadena de texto y un valor de un nombre de columna:
'My feature''s id is: ' || "gid" 'My feature''s id is: ' + "gid" => triggers an error as gid is an integer "country_name" + '(' + "country_code" + ')' "country_name" || '(' || "country_code" || ')'Test if the “description” attribute field starts with the ‘Hello’ string in the value (note the position of the % character):
"description" LIKE 'Hello%'
Conditionals¶
Este grupo contiene funciones para menejar comprobaciones condicionales en expresiones.
Función |
Descripción |
|---|---|
| CASE WHEN ... THEN ... END | Evalúa una expresión y devuelve un resultado si es verdadera. Puede probar múltiples condiciones |
| CASE WHEN ... THEN ... ELSE ... END | Evalúa una expresión y devuelva un resultado diferente sea verdadero o falso. Puede probar múltiples condiciones |
| coalesce | Devuelve el primer valor no-NULO de la lista de expresión |
si |
Prueba una condición y devuelve un resultado diferente dependiendo de la comprobación condicional |
| regexp_match | Returns true if any part of a string matches the supplied regular expression |
Algún ejemplo:
Send back a value if the first condition is true, else another value:
CASE WHEN "software" LIKE '%QGIS%' THEN 'QGIS' ELSE 'Other' END
Funciones Matemáticas¶
Este grupo contiene funciones matemáticas,por ejemplo raíz cuadrada, seno y coseno
Función |
Descripción |
|---|---|
| abs | Devuelve el valor absoluto de un número |
arcos |
Devuelve la inversa del coseno de un valor en radianes |
arcsen |
Devuelve la inversa del seno de un valor en radianes |
| atan | Returns the inverse tangent of a value in radians |
| atan2(y,x) | Returns the inverse tangent of y/x by using the signs of the two arguments to determine the quadrant of the result |
| azimuth(a,b) | Returns the north-based azimuth as the angle in radians measured clockwise from the vertical on point a to point b |
| ceil | Rounds a number upwards |
| clamp | Restricts an input value to a specified range |
| cos | Devuelve el coseno de un valor en radianes |
grados |
Convierte de radianes a grados |
| exp | Devuelve la exponencial de un valor |
| floor | Rounds a number downwards |
| ln | Returns the natural logarithm of the passed expression |
| log | Returns the value of the logarithm of the passed value and base |
| log10 | Returns the value of the base 10 logarithm of the passed expression |
máx |
Returns the largest value in a set of values |
mín |
Returns the smallest value in a set of values |
| pi | Returns the value of pi for calculations |
radianes |
Convierte de grados a radianes |
| rand | Returns the random integer within the range specified by the minimum and maximum argument (inclusive) |
| randf | Returns the random float within the range specified by the minimum and maximum argument (inclusive) |
| round | Rounds to number of decimal places |
| scale_exp | Transforma un valor dado de un dominio de entrada a un rango de salida usando una curva exponencial |
| scale_linear | Transforma un valor dado de un dominio de entrada a un rango de salida usando interpolación lineal |
sen |
Returns the sine of an angle |
raíz cuadrada |
Returns the square root of a value |
| tan | Devuelve la tangente de un ángulo |
Aggregates Functions¶
This group contains functions which aggregate values over layers and fields.
Función |
Descripción |
|---|---|
agregar |
Returns an aggregate value calculated using features from another layer |
concatenar |
Returns the all aggregated strings from a field or expression joined by a delimiter |
Número |
Returns the count of matching features |
| count_distinct | Returns the count of distinct values |
| count_missing | Returns the count of missing (null) values |
| iqr | Returns the calculated inter quartile range from a field or expression |
mayoría |
Returns the aggregate majority of values (most commonly occurring value) from a field or expression |
| max_length | Returns the maximum length of strings from a field or expression |
máximo |
Returns the aggregate maximum value from a field or expression |
media |
Returns the aggregate mean value from a field or expression |
mediana |
Returns the aggregate median value from a field or expression |
| min_length | Returns the minimum length of strings from a field or expression |
mínimo |
Returns the aggregate minimum value from a field or expression |
minoría |
Returns the aggregate minority of values (least commonly occurring value) from a field or expression |
| q1 | Returns the calculated first quartile from a field or expression |
| q3 | Devuelve el tercer cuartil calculado a partir de un campo o expresión |
intervalo |
Returns the aggregate range of values (maximum - minimum) from a field or expression |
| relation_aggregate | Returns an aggregate value calculated using all matching child features from a layer relation |
| stdev | Returns the aggregate standard deviation value from a field or expression |
| sum | Returns the aggregate summed value from a field or expression |
Ejemplos:
Return the maximum of the “passengers” field from features in the layer grouped by “station_class” field:
maximum("passengers", group_by:="station_class")Calculate the total number of passengers for the stations inside the current atlas feature:
aggregate('rail_stations','sum',"passengers", intersects(@atlas_geometry, $geometry))Return the mean of the “field_from_related_table” field for all matching child features using the ‘my_relation’ relation from the layer:
aggregate_relation('my_relation', 'mean', "field_from_related_table")
o:
aggregate_relation(relation:='my_relation', calculation := 'mean', expression := "field_from_related_table")
Funciones de Color¶
This group contains functions for manipulating colors.
Función |
Descripción |
|---|---|
| color_cmyk | Devuelve una representación en forma de cadena de un color en base a sus componentes cian, magenta, amarillo y negro |
| color_cmyka | Returns a string representation of a color based on its cyan, magenta, yellow, black and alpha (transparency) components |
| color_hsl | Returns a string representation of a color based on its hue, saturation, and lightness attributes |
| color_hsla | Devuelve una representación en forma de cadena de un color en base a sus atributos de matiz, saturación, luminosidad y canal alfa (transparencia). |
| color_hsv | Returns a string representation of a color based on its hue, saturation, and value attributes |
| color_hsva | Devuelve una representación en forma de cadena de un color en base a sus atributos de matiz, saturación, valor y canal alfa (transparencia) |
| color_part | Devuelve un componente específico de la cadena de un color, por ejemplo el componente rojo o el alfa |
| color_rgb | Returns a string representation of a color based on its red, green, and blue components |
| color_rgba | Returns a string representation of a color based on its red, green, blue, and alpha (transparency) components |
más oscuro |
Devuelve una cadena de color más oscura (o más clara) |
más claro |
Devuelve una cadena de color más clara (o más oscura) |
| project_color | Devuelve un color del esquema de color del proyecto |
| ramp_color | Devuelve una cadena que representa un color de una rampa de color |
| set_color_part | Sets a specific color component for a color string, eg the red component or alpha component |
Funciones de conversión¶
This group contains functions to convert one data type to another (e.g., string to integer, integer to string).
Función |
Descripción |
|---|---|
| to_date | Convierte una cadena de texto en un objeto fecha |
| to_datetime | Converts a string into a datetime object |
| to_int | Convierte una cadena de texto a número entero |
| to_interval | Converts a string to an interval type (can be used to take days, hours, months, etc. of a date) |
| to_real | Convierte una cadena de texto en número real |
| to_string | Convierte un número en cadena. |
| to_time | Converts a string into a time object |
Funciones personalizadas¶
This group contains functions created by the user. See Editor de Funciones for more details.
Funciones de Fecha y Hora¶
Este grupo contiene funciones para manipular datos de fecha y hora.
Función |
Descripción |
|---|---|
edad |
Returns as an interval the difference between two dates or datetimes |
día |
Extracts the day from a date or datetime, or the number of days from an interval |
| day_of_week | Returns a number corresponding to the day of the week for a specified date or datetime |
hora |
Extracts the hour from a datetime or time, or the number of hours from an interval |
minuto |
Extracts the minute from a datetime or time, or the number of minutes from an interval |
mes |
Extracts the month part from a date or datetime, or the number of months from an interval |
| now | Returns current date and time |
segundo |
Extracts the second from a datetime or time, or the number of seconds from an interval |
semana |
Extrae el número de la semana de una fecha o el número de semanas de un intervalo. |
| year | Extracts the year part from a date or datetime, or the number of years from an interval |
This group also shares several functions with the Funciones de conversión ( to_date, to_time, to_datetime, to_interval) and Funciones de cadena (format_date) groups.
Algún ejemplo:
Get today’s month and year in the “month_number/year” format:
format_date(now(),'MM/yyyy') -- Returns '03/2017'
Besides these functions, subtracting dates, datetimes or times using the - (minus) operator will return an interval.
Adding or subtracting an interval to dates, datetimes or times, using the + (plus) and - (minus) operators, will return a datetime.
Get the number of days until QGIS 3.0 release:
to_date('2017-09-29') - to_date(now()) -- Returns <interval: 203 days>
The same with time:
to_datetime('2017-09-29 12:00:00') - to_datetime(now()) -- Returns <interval: 202.49 days>
Get the datetime of 100 days from now:
now() + to_interval('100 days') -- Returns <datetime: 2017-06-18 01:00:00>
Nota
Storing date and datetime and intervals on fields
The ability to store date, time and datetime values directly on fields may depend on the data source’s provider (e.g., shapefiles accept date format, but not datetime or time format). The following are some suggestions to overcame this limitation.
date, Datetime and time can be stored in text type fields after using the to_format() function.
Intervals can be stored in integer or decimal type fields after using one of the date extraction functions (e.g., day() to get the interval expressed in days)
Campos y Valores¶
Contains a list of fields from the layer.
Generally, you can use the various fields, values and functions to construct the calculation expression, or you can just type it into the box.
To display the values of a field, you just click on the appropriate field and choose between Load top 10 unique values and Load all unique values. On the right side, the Field Values list opens with the unique values. At the top of the list, a search box helps filtering the values. To add a value to the expression you are writing, double click its name in the list.
Sample values can also be accessed via right-click. Select the field name from the list, then right-click to access a context menu with options to load sample values from the selected field.
Fields name should be double-quoted in the expression. Values or string should be simple-quoted.
Funciones Concordancia aproximada¶
This group contains functions for fuzzy comparisons between values.
Función |
Descripción |
|---|---|
| hamming_distance | Returns the number of characters at corresponding positions within the input strings where the characters are different |
| levensheim | Returns the minimum number of character edits (insertions, deletions or substitutions) required to change one string to another. Measure the similarity between two strings |
| longest_common_substring | Returns the longest common substring between two strings |
| soundex | Returns the Soundex representation of a string |
Funciones Generales¶
Este grupo contiene funciones generales variadas.
Función |
Descripción |
|---|---|
| eval | Evaluates an expression which is passed in a string. Useful to expand dynamic parameters passed as context variables or fields |
| layer_property | Returns a property of a layer or a value of its metadata. It can be layer name, crs, geometry type, feature count... |
| var | Returns the value stored within a specified variable. See variable functions below |
Funciones de Geometría¶
This group contains functions that operate on geometry objects (e.g., length, area).
Función |
Descripción |
|---|---|
| $area | Returns the area size of the current feature |
| $geometry | Returns the geometry of the current feature (can be used for processing with other functions) |
| $length | Returns the length of the current line feature |
| $perimeter | Returns the perimeter of the current polygon feature |
| $x | Returns the x coordinate of the current feature |
| $x_at(n) | Returns the x coordinate of the nth node of the current feature’s geometry |
| $y | Returns the y coordinate of the current feature |
| $y_at(n) | Returns the y coordinate of the nth node of the current feature’s geometry |
| angle_at_vertex | Returns the bisector angle (average angle) to the geometry for a specified vertex on a linestring geometry. Angles are in degrees clockwise from north |
| area | Devuelve el perímetro de un objeto de geometría poligonal. Los cálculos están en el Sistema de Referencia Espacial de esta geometría |
azimut |
Returns the north-based azimuth as the angle in radians measured clockwise from the vertical on point_a to point_b |
contorno |
Returns the closure of the combinatorial boundary of the geometry (ie the topological boundary of the geometry). |
límites |
Returns a geometry which represents the bounding box of an input geometry. Calculations are in the Spatial Reference System of this geometry |
| bounds_height | Returns the height of the bounding box of a geometry. Calculations are in the Spatial Reference System of this geometry |
| bounds_width | Devuelve la anchura del recuadro delimitador de una geometría. Los cálculos están en el Sistema de Referencia Espacial de esta geometría |
| buffer | Returns a geometry that represents all points whose distance from this geometry is less than or equal to distance. Calculations are in the Spatial Reference System of this geometry |
| centroid | Returns the geometric center of a geometry |
| closest_point | Returns the point on a geometry that is closest to a second geometry |
combinar |
Devuelve la combinación de dos geometrías |
| contains(a,b) | Returns 1 (true) if and only if no points of b lie in the exterior of a, and at least one point of the interior of b lies in the interior of a |
| convex_hull | Returns the convex hull of a geometry (this represents the minimum convex geometry that encloses all geometries within the set) |
cruza |
Returns 1 (true) if the supplied geometries have some, but not all, interior points in common |
| difference(a,b) | Returns a geometry that represents that part of geometry a that does not intersect with geometry b |
inconexo |
Returns 1 (true) if the geometries do not share any space together |
| distance | Returns the minimum distance (based on Spatial Reference System) between two geometries in projected units |
| distance_to_vertex | Returns the distance along the geometry to a specified vertex |
| end_point | Returns the last node from a geometry |
| exterior_ring | Returns a line string representing the exterior ring of a polygon geometry, or null if the geometry is not a polygon |
| extrude(geom,x,y) | Returns an extruded version of the input (Multi-) Curve or (Multi-)Linestring geometry with an extension specified by x and y |
| geom_from_gml | Returns a geometry created from a GML representation of geometry |
| geom_from_wkt | Returns a geometry created from a well-known text (WKT) representation |
| geom_to_wkt | Returns the well-known text (WKT) representation of the geometry without SRID metadata |
| geometry | Devuelve la geometría de un objeto |
| geometry_n | Returns the nth geometry from a geometry collection, or null if the input geometry is not a collection |
| interior_ring_n | Returns the geometry of the nth interior ring from a polygon geometry, or null if the geometry is not a polygon |
intersección |
Returns a geometry that represents the shared portion of two geometries |
intersecta |
Tests whether a geometry intersects another. Returns 1 (true) if the geometries spatially intersect (share any portion of space) and 0 if they don’t |
| intersects_bbox | Tests whether a geometry’s bounding box overlaps another geometry’s bounding box. Returns 1 (true) if the geometries spatially intersect (share any portion of space) their bounding box, or 0 if they don’t |
| is_closed | Returns true if a line string is closed (start and end points are coincident), false if a line string is not closed, or null if the geometry is not a line string |
longitud |
Returns length of a line geometry feature (or length of a string) |
| line_interpolate_angle | Returns the angle parallel to the geometry at a specified distance along a linestring geometry. Angles are in degrees clockwise from north. |
| line_interpolate_point | Returns the point interpolated by a specified distance along a linestring geometry. |
| line_locate_point | Returns the distance along a linestring corresponding to the closest position the linestring comes to a specified point geometry. |
| line_merge | Returns a (Multi-)LineString geometry, where any connected LineStrings from the input geometry have been merged into a single linestring. |
| m | Returns the m value of a point geometry |
| make_line | Crea una geometría de línea a partir de una serie de geometrías de puntos |
| make_point(x,y,z,m) | Returns a point geometry from x and y (and optional z or m) values |
| make_point_m(x,y,m) | Returns a point geometry from x and y coordinates and m values |
| make_polygon | Crea una geometría de polígono a partir de un anillo exterior y series opcionales de geometrías interiores de anillo |
| nodes_to_points | Returns a multipoint geometry consisting of every node in the input geometry |
| num_geometries | Devuelve el número de geometrías en una colección de geometrías o nulo si la geometría de entrada no es una colección |
| num_interior_rings | Devuelve el número de anillos interiores de un polígono o una colección de geometrías o nulo si la geometría de entrada no es un polígono o una colección |
| num_points | Devuelve el número de vértices de una geometría. |
| num_rings | Devuelve el número de anillos (incluidos los anillos exteriores) de un polígono o una colección de geometrías o nulo si la geometría de entrada no es un polígono o una colección |
| order_parts | Ordena las partes de una MultiGeometría por los criterios dados |
solapa |
Comprueba si una geometría solapa con otra. Devuelve 1(verdadero) si las geometrías comparten espacio, son de la misma dimensión, pero no están contenidas en la otra. |
perímetro |
Devuelve el perímetro de un objeto de geometría poligonal. Los cálculos están en el Sistema de Referencia Espacial de esta geometría. |
| point_n | Returns a specific node from a geometry |
| point_on_surface | Returns a point guaranteed to lie on the surface of a geometry |
proyecto |
Returns a point projected from a start point using a distance and bearing (azimuth) in radians |
| relate | Prueba o devuelve la representación del Modelo de Intersección 9 Extendido Dimensional (DE-9IM) de la relación entre dos geometrías. |
invertir |
Reverses the direction of a line string by reversing the order of its vertices |
| segments_to_lines | Returns a multi line geometry consisting of a line for every segment in the input geometry |
| shortest_line | Returns the shortest line joining two geometries. The resultant line will start at geometry 1 and end at geometry 2 |
| start_point | Returns the first node from a geometry |
| sym_difference | Returns a geometry that represents the portions of two geometries that do not intersect |
toca |
Tests whether a geometry touches another. Returns 1 (true) if the geometries have at least one point in common, but their interiors do not intersect |
Transformar |
Returns the geometry transformed from the source CRS to the destination CRS |
Convertir |
Returns a translated version of a geometry. Calculations are in the Spatial Reference System of this geometry |
unión |
Devuelve una geometría que representa el conjunto unión de los puntos de las geometrías. |
entre(a,b) |
Tests whether a geometry is within another. Returns 1 (true) if geometry a is completely inside geometry b |
| x | Returns the x coordinate of a point geometry, or the x coordinate of the centroid for a non-point geometry |
| x_min | Returns the minimum x coordinate of a geometry. Calculations are in the Spatial Reference System of this geometry |
| x_max | Returns the maximum x coordinate of a geometry. Calculations are in the Spatial Reference System of this geometry |
| y | Returns the y coordinate of a point geometry, or the y coordinate of the centroid for a non-point geometry |
| y_min | Returns the minimum y coordinate of a geometry. Calculations are in the Spatial Reference System of this geometry |
| y_max | Returns the maximum y coordinate of a geometry. Calculations are in the Spatial Reference System of this geometry |
| z | Returns the z coordinate of a point geometry |
Algún ejemplo:
You can manipulate the current geometry with the variable $geometry to create a buffer or get the point on surface:
buffer( $geometry, 10 ) point_on_surface( $geometry )
Return the x coordinate of the current feature’s centroid:
x( $geometry )
Send back a value according to feature’s area:
CASE WHEN $area > 10 000 THEN 'Larger' ELSE 'Smaller' END
Record Functions¶
Este grupo contiene funciones que operan sobre identificadores de registros.
Función |
Descripción |
|---|---|
| $currentfeature | Devuelve el objeto espacial que está siendo evaluado. Se puede usar con la función ‘attribute’ para evaluar los valores de atributo del objeto actual. |
| $id | Devuelve el ID del objeto de la fila actual |
| $map | Returns the id of the current map item if the map is being drawn in a composition, or “canvas” if the map is being drawn within the main QGIS window |
| $rownum | Returns the number of the current row |
| $scale | Returns the current scale of the map canvas |
atributo |
Devuelve el valor del atributo especificado de un objeto |
| get_feature | Devuelve el primer objeto de una capa que coincide con un valor de atributo dado |
| uuid | Generates a Universally Unique Identifier (UUID) for each row. Each UUID is 38 characters long. |
Algún ejemplo:
Return the first feature in layer “LayerA” whose field “id” has the same value as the field “name” of the current feature (a kind of jointure):
get_feature( 'layerA', 'id', attribute( $currentfeature, 'name') )
Calculate the area of the joined feature from the previous example:
area( geometry( get_feature( 'layerA', 'id', attribute( $currentfeature, 'name') ) ) )
Funciones de cadena¶
Este grupo contiene funciones que operan sobre cadenas, por ejemplo reemplazar, convertir a mayúsculas.
Función |
Descripción |
|---|---|
| char | Devuelve el carácter asociado con un código unicode |
| concat | Concatenates several strings to one |
| format | Da formato a una cadena usando los argumentos proporcionados. |
| format_date | Formats a date type or string into a custom string format |
| format_number | Devuelve un número formateado con el separador local de miles (también trunca el número al número de decimales indicado) |
| left(string, n) | Returns a substring that contains the n leftmost characters of the string |
longitud |
Returns length of a string (or length of a line geometry feature) |
| lower | Convierte una cadena a letras minúsculas. |
| lpad | Returns a string with supplied width padded using the fill character |
| regexp_replace | Devuelve una cadena en la que se ha remplazado la expresión regular proporcionada |
| regexp_substr | Devuelve la parte de una cadena que coincide con una expresión regular proporcionada |
remplazar |
Returns a string with the supplied string replaced |
right(cadena, n) |
Devuelve una subcadena que contiene los n caracteres más a la derecha de la cadena. |
| rpad | Returns a string with supplied width padded using the fill character |
| strpos | Returns the index of a regular expression in a string |
| substr | Devuelve una parte de una cadena. |
Título |
Convierte todas las palabras de una cadena a formato de título (todas las palabras en minúscula con la primera letra en mayúscula) |
| trim | Elimina todos los espacios en blanco (espacios, tabuladores, etc.) de comienzo y final de una cadena. |
| upper | Convierte una cadena a letras mayúsculas. |
| wordwrap | Devuelve una cadena ajustada un número de caracteres máximo/mínimo |
Funciones recientes¶
This group contains recently used functions. Any expression used in the Expression dialog is added to the list, sorted from the more recent to the less one. This helps to quickly retrieve any previous expression.
Variables Functions¶
This group contains dynamic variables related to the application, the project file and other settings. It means that some functions may not be available according to the context:
- from the
 Select by expression dialog
Select by expression dialog desde el diálogo de propiedades de la capa
- from the print composer
To use these functions in an expression, they should be preceded by @ character (e.g, @row_number). Are concerned:
Función |
Descripción |
|---|---|
| atlas_feature | Devuelve el objeto del atlas actual (como objeto espacial) |
| atlas_featureid | Devuelve el ID de objeto del atlas actual. |
| atlas_featurenumber | Returns the number of pages in composition |
| atlas_filename | Devuelve el nombre de archivo del atlas actual. |
| atlas_geometry | Devuelve la geometría de objeto del atlas actual |
| atlas_pagename | Devuelve el nombre de la página del atlas actual |
| atlas_totalfeatures | Devuelve el número total de objetos en el atlas. |
| grid_axis | Devuelve el eje de la anotación de la cuadrícula actual (ej.: ‘x’ para longitud, ‘y’ para latitud). |
| grid_number | Devuelve el valor de anotación de la cuadrícula actual. |
| item_id | Returns the composer item user ID (not necessarily unique) |
| item_uuid | Returns the composer item unique ID |
| layer_id | Devuelve el ID de la capa actual |
| layer_name | Devuelve el nombre de la capa actual |
| layout_dpi | Devulve la resolución de la composición (DPI). |
| layout_numpages | Returns the number of pages in the composition |
| layout_pageheight | Returns the composition height in mm |
| layout_pagewidth | Returns the composition width in mm |
| map_extent_center | Returns the point feature at the center of the map |
| map_extent_height | Devuelve la altura actual del mapa |
| map_extent_width | Devuelve el ancho actual del mapa |
| map_id | Returns the ID of current map destination. This will be ‘canvas’ for canvas renders, and the item ID for composer map renders |
| map_rotation | Devuelve la rotación actual del mapa |
| map_scale | Devuelve la escala actual del mapa |
| project_filename | Returns the filename of current project |
| project_folder | Returns the folder for current project |
| project_path | Returns the full path (including file name) of current project |
| project_title | Devuelve el Título del proyecto actual. |
| qgis_os_name | Devuelve el nombre del sistema operativo, ej. ‘Windows’, ‘Linux’ o ‘OSX’. |
| qgis_platform | Devuelve la plataforma de QGIS, ej. ‘Escritorio’ o ‘Servidor’. |
| qgis_release_name | Devuelve el nombre de la versión actual de QGIS |
| qgis_version | Devuelve la versión actual de QGIS como cadena |
| qgis_version_no | Devuelve la versión actual de QGIS como número |
| symbol_angle | Devuelve el ángulo del símbolo usado para representar el objeto (solo válido para símbolos de marcador). |
| symbol_color | Returns the color of the symbol used to render the feature |
| user_account_name | Devuelve el nombre de la cuenta del sistema operativo del usuario actual. |
| user_full_name | Devuelve el nombre de usuario del sistema operativo del usuario actual. |
| row_number | Guarda el número de la fila actual. |
Valor |
Devuelve el valor actual |
Editor de Funciones¶
With the Function Editor, you are able to define your own Python custom functions in a comfortable way.
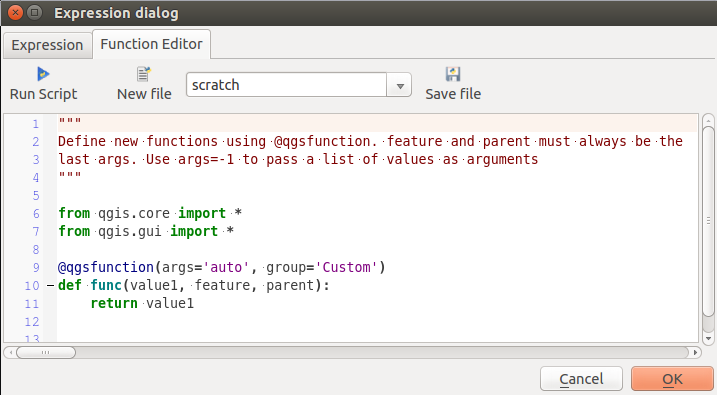
La pestaña Editor de funciones
The function editor will create new Python files in .qgis2\python\expressions folder and will auto load all functions defined when starting QGIS. Be aware that new functions are only saved in the expressions folder and not in the project file. If you have a project that uses one of your custom functions you will need to also share the .py file in the expressions folder.
Here’s a short example on how to create your own functions:
@qgsfunction(args="auto", group='Custom')
def myfunc(value1, value2, feature, parent):
pass
The short example creates a function myfunc that will give you a function with two values. When using the args='auto' function argument the number of function arguments required will be calculated by the number of arguments the function has been defined with in Python (minus 2 - feature, and parent).
This function then can be used with the following expression:
myfunc('test1', 'test2')
Your function will be implemented in the Custom functions group of the Expression tab after using the Run Script button.
Se puede encontrar más información sobre cómo crear código Python en:ref:PyQGIS-Developer-Cookbook.
The function editor is not only limited to working with the field calculator, it can be found whenever you work with expressions.