24.1.18. Raster tools
24.1.18.1. Align raster
Aligns raster by resampling it to the same cell size and reprojecting to the same CRS as a reference raster.
Warning
This algorithm is ONLY available in the Model Designer context. For other contexts, use instead Align rasters.
Parameters
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Input layer |
|
[raster] |
Input raster layer to align |
Resampling method |
|
[enumeration] Default: 0 |
Method to use for input layer resampling.
|
Rescale values according to the cell size |
|
[boolean] Default: No |
|
Reference layer |
|
[raster] |
A raster layer that will be used to fetch extent, cell size and CRS that will be applied to input layers. |
Override reference CRS Optional |
|
[crs] |
CRS to be used instead of the reference layer’s |
Override reference cell size X Optional |
|
[numeric: double] |
Cell size in X direction to be used instead of the reference layer’s |
Override reference cell size Y Optional |
|
[numeric: double] |
Cell size in Y direction to be used instead of the reference layer’s |
Override reference grid offset X Optional |
|
[numeric: double] |
Offset in X direction to apply to cells grid |
Override reference grid offset Y Optional |
|
[numeric: double] |
Offset in Y direction to apply to cells grid |
Clip to extent Optional |
|
[extent] |
Specify the extent of the output raster layer. It will internally be extended to a multiple of the tile size. Available methods are:
|
Aligned raster |
|
[raster] |
output raster with pixels resampled |
Outputs
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Aligned raster |
|
[raster] |
output raster with pixels resampled |
Python code
Algorithm ID: native:alignsingleraster
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
The algorithm id is displayed when you hover over the algorithm in the Processing Toolbox. The parameter dictionary provides the parameter NAMEs and values. See Using processing algorithms from the console for details on how to run processing algorithms from the Python console.
24.1.18.2. Align rasters
Aligns rasters by resampling them to the same cell size and reprojecting to the same CRS as a reference raster.
Warning
This algorithm is NOT available in the Model Designer context. Use instead Align raster.
Parameters
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Input layers |
|
[raster] [list] |
List of input raster layers with resampling options associated
(filled as a
Rescale values according to the cell size [boolean] ( |
Reference layer |
|
[raster] |
A raster layer that will be used to fetch extent, cell size and CRS that will be applied to input layers. |
Override reference CRS Optional |
|
[crs] |
CRS to be used instead of the reference layer’s |
Override reference cell size X Optional |
|
[numeric: double] |
Cell size in X direction to be used instead of the reference layer’s |
Override reference cell size Y Optional |
|
[numeric: double] |
Cell size in Y direction to be used instead of the reference layer’s |
Override reference grid offset X Optional |
|
[numeric: double] |
Offset in X direction to apply to cells grid |
Override reference grid offset Y Optional |
|
[numeric: double] |
Offset in Y direction to apply to cells grid |
Clip to extent Optional |
|
[extent] |
Specify the extent of the output raster layer. It will internally be extended to a multiple of the tile size. Available methods are:
|
Outputs
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Aligned rasters |
|
[raster] [list] |
output rasters with pixels resampled |
Python code
Algorithm ID: native:alignrasters
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
The algorithm id is displayed when you hover over the algorithm in the Processing Toolbox. The parameter dictionary provides the parameter NAMEs and values. See Using processing algorithms from the console for details on how to run processing algorithms from the Python console.
24.1.18.3. Convert map to raster
Creates a raster image of map canvas content.
A map theme can be selected to render a predetermined set of layers with a defined style for each layer.
Alternatively, a single layer can be selected if no map theme is set.
If neither map theme nor layer is set, the current map content will be rendered. The minimum extent entered will internally be extended to be a multiple of the tile size.
Parameters
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Minimum extent to render (xmin, xmax, ymin, ymax) |
|
[extent] |
Specify the extent of the output raster layer. It will internally be extended to a multiple of the tile size. Available methods are:
|
Tile size |
|
[numeric: integer] Default: 1024 |
Size of the tile of the output raster layer. Minimum value: 64. |
Map units per pixel |
|
[numeric: double] Default: 100.0 |
Pixel size (in map units). Minimum value: 0.0 |
Make background transparent |
|
[boolean] Default: False |
Allows exporting the map with a transparent background.
Outputs an RGBA (instead of RGB) image if set to |
Map theme to render Optional |
|
[enumeration] |
Use an existing map theme for the rendering. |
Single layer to render Optional |
|
[enumeration] |
Choose a single layer for the rendering |
Output layer |
|
[raster] Default: |
Specification of the output raster. One of:
|
Outputs
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Output layer |
|
[raster] |
Output raster layer |
Python code
Algorithm ID: native:rasterize
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
The algorithm id is displayed when you hover over the algorithm in the Processing Toolbox. The parameter dictionary provides the parameter NAMEs and values. See Using processing algorithms from the console for details on how to run processing algorithms from the Python console.
24.1.18.4. Fill NoData cells
Resets the NoData values in the input raster to a chosen value, resulting in raster dataset with no NoData pixels.
The algorithm respects the input raster data type, e.g. a floating point fill value will be truncated when applied to an integer raster.
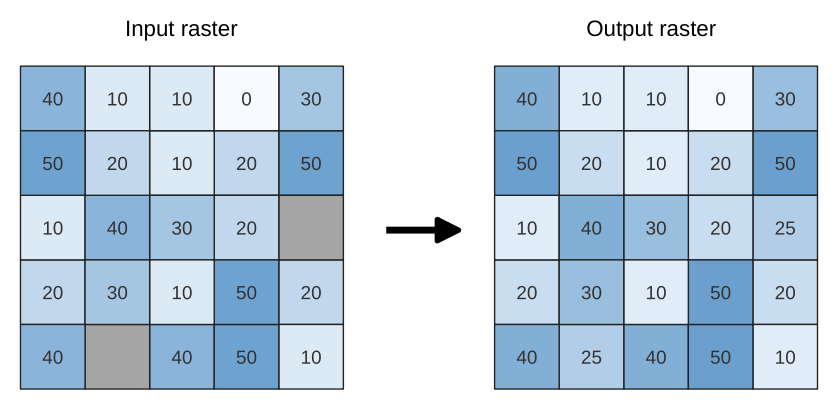
Fig. 24.39 Filling NoData values (in grey) of a raster
Parameters
Basic parameters
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Input raster |
|
[raster] |
The raster to process. |
Band number |
|
[raster band] Default: 1 |
The band of the raster |
Fill value |
|
[numeric: double] Default: 1.0 |
Set the value to use for the NoData pixels |
Output raster |
|
[raster] Default: |
Specification of the output raster. One of:
|
Advanced parameters
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Creation options Optional |
|
[string] Default: ‘’ |
For adding one or more creation options that control the raster to be created (colors, block size, file compression…). For convenience, you can rely on predefined profiles (see GDAL driver options section). Batch Process and Model Designer: separate multiple options with a pipe
character ( |
Outputs
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Output raster |
|
[raster] |
The output raster layer with filled data cells. |
Python code
Algorithm ID: native:fillnodata
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
The algorithm id is displayed when you hover over the algorithm in the Processing Toolbox. The parameter dictionary provides the parameter NAMEs and values. See Using processing algorithms from the console for details on how to run processing algorithms from the Python console.
24.1.18.5. Generate XYZ tiles (Directory)
Generates raster “XYZ” tiles using the current QGIS project as individual images to a directory structure.
Optionally, a Leaflet HTML output file using the generated tiles as a map layer could be created.
Parameters
Basic parameters
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Extent (xmin, xmax, ymin, ymax) |
|
[extent] |
Specify the extent of the tiles. It will internally be extended to a multiple of the tile size. Available methods are:
|
Minimum zoom |
|
[numeric: integer] Default: 12 |
Minimum 0, maximum 25. |
Maximum zoom |
|
[numeric: integer] Default: 12 |
Minimum 0, maximum 25. |
DPI |
|
[numeric: integer] Default: 96 |
Minimum 48, maximum 600. |
Background color Optional |
|
[color] Default: QColor(0, 0, 0, 0) |
Choose the background color for the tiles |
Enable antialiasing |
|
[boolean] Default: True |
Determines if antialiasing should be enabled |
Tile format |
|
[enumeration] Default: 0 |
One of:
|
Quality (JPG only) Optional |
|
[numeric: integer] Default: 75 |
Minimum 1, maximum 100. |
Metatile size Optional |
|
[numeric: integer] Default: 4 |
Specify a custom metatile size when generating XYZ tiles. Larger values may speed up the rendering of tiles and provide better labelling (fewer gaps without labels) at the expense of using more memory. Minimum 1, maximum 20. |
Tile width Optional |
|
[numeric: integer] Default: 256 |
Minimum 1, maximum 4096. |
Tile height Optional |
|
[numeric: integer] Default: 256 |
Minimum 1, maximum 4096. |
Use inverted tile Y axis (TMS conventions) |
|
[boolean] Default: False |
|
Output directory |
|
[folder] Default: |
Specification of the output directory (for the tiles). One of:
|
Output html (Leaflet) Optional |
|
[html] Default: |
Specification of the output HTML file. One of:
|
Advanced parameters
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Leaflet HTML output title Optional |
|
[string] Default: Not set |
HTML <title>-tag used for the Leaflet HTML output file. |
Leaflet HTML output attribution Optional |
|
[string] Default: Not set |
Custom map attribution used for the Leaflet HTML output file. HTML links are possible. |
Include OpenStreetMap basemap in Leaflet HTML output |
|
[boolean] Default: False |
An OpenStreetMap basemap layer (source: https://tile.openstreetmap.org) is included in the Leaflet HTML output file. Proper map attribution is added automatically. |
Outputs
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Output directory |
|
[folder] |
Output directory (for the tiles) |
Output html (Leaflet) |
|
[html] |
The output HTML (Leaflet) file |
Python code
Algorithm ID: native:tilesxyzdirectory
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
The algorithm id is displayed when you hover over the algorithm in the Processing Toolbox. The parameter dictionary provides the parameter NAMEs and values. See Using processing algorithms from the console for details on how to run processing algorithms from the Python console.
24.1.18.6. Generate XYZ tiles (MBTiles)
Generates raster “XYZ” tiles using the current QGIS project as a single file in the “MBTiles” format.
Parameters
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Extent (xmin, xmax, ymin, ymax) |
|
[extent] |
Specify the extent of the tiles. It will internally be extended to a multiple of the tile size. Available methods are:
|
Minimum zoom |
|
[numeric: integer] Default: 12 |
Minimum 0, maximum 25. |
Maximum zoom |
|
[numeric: integer] Default: 12 |
Minimum 0, maximum 25. |
DPI |
|
[numeric: integer] Default: 96 |
Minimum 48, maximum 600. |
Background color Optional |
|
[color] Default: QColor(0, 0, 0, 0) |
Choose the background color for the tiles |
Enable antialiasing |
|
[boolean] Default: True |
Determines if antialiasing should be enabled |
Tile format |
|
[enumeration] Default: 0 |
One of:
|
Quality (JPG only) Optional |
|
[numeric: integer] Default: 75 |
Minimum 1, maximum 100. |
Metatile size Optional |
|
[numeric: integer] Default: 4 |
Specify a custom metatile size when generating XYZ tiles. Larger values may speed up the rendering of tiles and provide better labelling (fewer gaps without labels) at the expense of using more memory. Minimum 1, maximum 20. |
Output file (for MBTiles) |
|
[file] Default: |
Specification of the output file. One of:
|
Outputs
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Output file (for MBTiles) |
|
[file] |
The output file. |
Python code
Algorithm ID: native:tilesxyzmbtiles
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
The algorithm id is displayed when you hover over the algorithm in the Processing Toolbox. The parameter dictionary provides the parameter NAMEs and values. See Using processing algorithms from the console for details on how to run processing algorithms from the Python console.