25.3. QGIS Python console
As you will see later in this chapter, QGIS has been designed with a plugin architecture. Plugins can be written in Python, a very famous language in the geospatial world.
QGIS brings a Python API (see PyQGIS Developer Cookbook for some code sample) to let the user interact with its objects (layers, feature or interface). QGIS also has a Python console.
The QGIS Python Console is an interactive shell for Python command executions.
It also has a Python file editor that allows you to edit and save your Python scripts.
Both console and editor are based on PyQScintilla2 package.
To open the console go to (Ctrl+Alt+P) or
click on the ![]() Python Console icon in the Plugins toolbar.
Python Console icon in the Plugins toolbar.
25.3.1. The Interactive Console
The console is a Python interpreter that allows you to execute Python commands. Modules from QGIS (analysis, core, gui, server, processing, 3d) and Qt (QtCore, QtGui, QtNetwork, QtWidgets, QtXml) as well as Python’s math, os, re and sys modules are already imported and can be used directly.
The interactive console is composed of a toolbar, an input area and an output one.
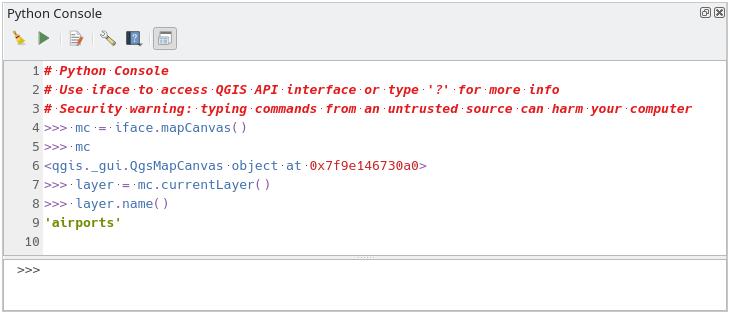
Fig. 25.17 The Python Console
25.3.1.1. Toolbar
The toolbar proposes the following tools:
 Run Command available in the input area: same as
pressing Enter;
Run Command available in the input area: same as
pressing Enter; Show Editor: toggles The Code Editor
visibility;
Show Editor: toggles The Code Editor
visibility; Options…: opens a dialog to configure console properties;
Options…: opens a dialog to configure console properties; Help… provides a menu to access various documentation:
Help… provides a menu to access various documentation:Python Console Help (the current page)
 Dock Code Editor to dock or undock the panel in QGIS interface
Dock Code Editor to dock or undock the panel in QGIS interface
25.3.1.2. Input area
The Console input area main features are:
Code completion, highlighting syntax and calltips for the following APIs:
Python
PyQGIS
PyQt6
QScintilla2
osgeo-gdal-ogr
osgeo-geos
Ctrl+Alt+Space to view the auto-completion list if enabled in the Python settings;
Execute code snippets from the input area by typing and pressing Enter or Run Command;
Execute code snippets from the output area using the Enter Selected from the contextual menu or pressing Ctrl+E;
Browse the command history from the input area using the Up and Down arrow keys and execute the command you want;
Ctrl+Shift+Space to view the command history: double-clicking a row will execute the command. The Command History dialog can also be accessed from context menu of input area;
Save and clear the command history. The history will be saved into the
console_history.txtfile under the active user profile folder;Type the following special commands:
?to show a help of the Python Console_apito open QGIS C++ API documentation or_api(object)for a specific object documentation (in QGIS C++ API or Qt API documentation)_pyqgisto open QGIS Python API documentation or_pyqgis(object)for a specific object documentation (in QGIS Python API or Qt API documentation)_cookbookto open PyQGIS Cookbook.!followed by a command to execute Shell commands from the Python Console. The console will start a subprocess, and forward its output to the Python Console Output. While the subprocess is running, the Python Console Input switches to STDIN mode and forwards entered character to the child process. This makes it possible to send confirmation when the child program asks for it. When the Console is in STDIN mode, pressing Ctrl+C kills the subprocess. It is also possible to affect the result of a command to a variable with the syntaxvar = !cmd>>> !echo QGIS Rocks! QGIS Rocks >>> !gdalinfo --version GDAL 3.10.3, released 2025/04/01 >>> !pip install black # Install black python formatter using pip (if available) >>> sql_formats = !ogrinfo --formats | grep SQL >>> sql_formats ['SQLite -vector- (rw+v): SQLite / Spatialite', ' MSSQLSpatial -vector- (rw+): Microsoft SQL Server Spatial Database', ' PostgreSQL -vector- (rw+): PostgreSQL/PostGIS', ' MySQL -vector- (rw+): MySQL', ' PGDUMP -vector- (w+v): PostgreSQL SQL dump']
Tip
Reuse executed commands from the output panel
You can execute code snippets from the output panel by selecting some text and
pressing Ctrl+E. No matter if selected text contains the interpreter
prompt (>>>, ...).
25.3.2. The Code Editor
Use the ![]() Show Editor button in the Interactive Console to enable the editor widget.
It allows editing and saving Python scripts and offers advanced functionalities
to manage your code.
Depending on the enabled settings,
it provides various capabilities for easier code writing,
such as code completion, highlighting syntax and calltips for supported APIs.
Automatic indentation, parenthesis insertion, code commenting and syntax checking are also available.
Show Editor button in the Interactive Console to enable the editor widget.
It allows editing and saving Python scripts and offers advanced functionalities
to manage your code.
Depending on the enabled settings,
it provides various capabilities for easier code writing,
such as code completion, highlighting syntax and calltips for supported APIs.
Automatic indentation, parenthesis insertion, code commenting and syntax checking are also available.
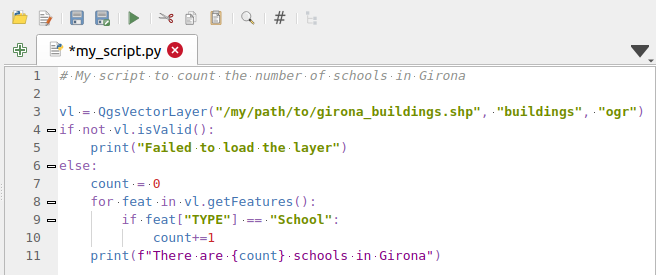
Fig. 25.18 The Python Console editor
The code editor area allows to simultaneously work on different scripts, each in a specific tab.
Press  New editor to add a new tab.
You can run partially or totally a script from the Code Editor
and output the result in the Interactive Console output area.
New editor to add a new tab.
You can run partially or totally a script from the Code Editor
and output the result in the Interactive Console output area.
Tip
Press Ctrl+Space to view the auto-completion list.
At the top of the dialog, a toolbar provides access to a few commands. Right-clicking the editor area provides some more options. All available tools are described in the following table.
Tool name |
Function |
Location |
|---|---|---|
Loads a Python file in the code editor dialog, as a new tab |
Toolbar |
|
Opens a saved Python script in the default external program set for Python file editing |
||
Saves the current script |
||
Saves the current script as a new file |
||
Executes the whole script in the Interactive console
(this creates a byte-compiled file with the extension |
Toolbar & Contextual menu |
|
Executes in the Interactive console the lines selected in the script |
||
Cuts selected text to the clipboard |
||
Copies selected text to the clipboard |
||
Pastes a cut or copied text |
||
Allows to search and replace a text in the script.
|
||
|
Comments out or uncomment selected lines, by adding or removing |
|
Allows to manually apply various formatting rules (sort imports, indentation, line length,…) to the code, following user-defined settings. This may require installation of additional Python modules. |
||
Shows and hides a dedicated browser with a tree structure for classes and functions available in the script. Click an item fo a quick access to its definition. The tool requires an activation from the Python settings - Run and Debug. |
||
Hide editor |
Hides the Python code editor block.
To make it visible again, press |
Contextual menu |
Browses the code and reports syntax errors, such as missing parenthesis, colons, wrong indentation,… |
||
Undoes the latest action |
||
Reverts undone actions to a more recent |
||
Select all (Ctrl+A) |
Selects the whole script |
|
Shares the script as a Secret Gist or Public Gist on GitHub, provided a GitHub access token. |
||
Opens the Python settings dialog. |