27.1.13. Raster terrain analysis
27.1.13.1. Aspect
Calculates the aspect of the Digital Terrain Model in input. The final aspect raster layer contains values from 0 to 360 that express the slope direction, starting from north (0°) and continuing clockwise.
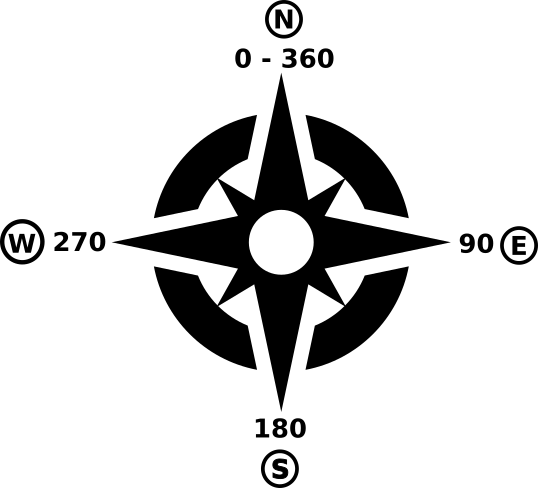
Рис. 27.21 Aspect values
The following picture shows the aspect layer reclassified with a color ramp:
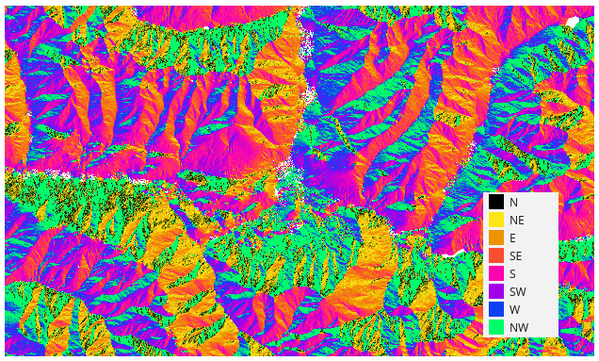
Рис. 27.22 Aspect layer reclassified
Параметры
Ярлык |
Имя |
Тип |
Описание |
|---|---|---|---|
Elevation layer |
|
[растр] |
Digital Terrain Model raster layer |
Z factor |
|
[number] Default: 1.0 |
Vertical exaggeration. This parameter is useful when the Z units differ from the X and Y units, for example feet and meters. You can use this parameter to adjust for this. The default is 1 (no exaggeration). |
Aspect |
|
[растр] По умолчанию: |
Specify the output aspect raster layer. One of:
|
Результаты
Ярлык |
Имя |
Тип |
Описание |
|---|---|---|---|
Aspect |
|
[растр] |
The output aspect raster layer |
Код на Python
Algorithm ID: qgis:aspect
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
ID алгоритма отображается при наведении мыши на алгоритм в Инструментах анализа. Словарь parameter dictionary содержит ключи параметров и их значения. См. Изпользование алгоритмов геообработки в консоли для детального описания того, как запускать алгоритмы анализа из консоли Python.
27.1.13.2. Hillshade
Calculates the hillshade raster layer given an input Digital Terrain Model.
The shading of the layer is calculated according to the sun position: you have the options to change both the horizontal angle (azimuth) and the vertical angle (sun elevation) of the sun.
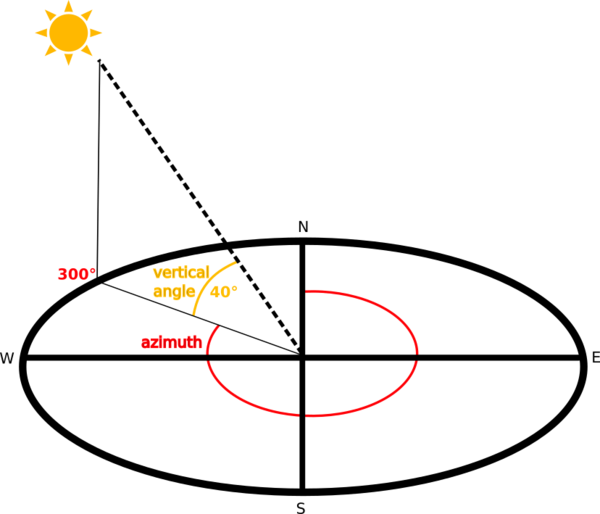
Рис. 27.23 Azimuth and vertical angle
The hillshade layer contains values from 0 (complete shadow) to 255 (complete sun). Hillshade is used usually to better understand the relief of the area.

Рис. 27.24 Hillshade layer with azimuth 300 and vertical angle 45
Particularly interesting is to give the hillshade layer a transparency value and overlap it with the elevation raster:
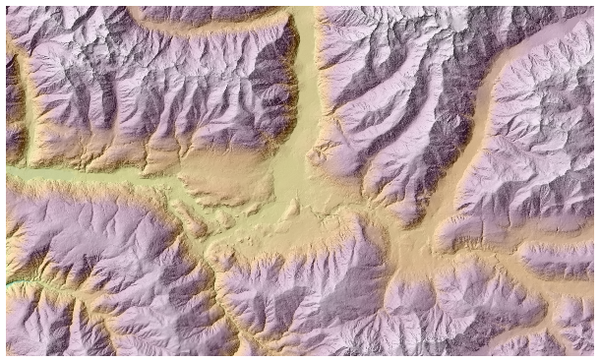
Рис. 27.25 Overlapping the hillshade with the elevation layer
Параметры
Ярлык |
Имя |
Тип |
Описание |
|---|---|---|---|
Elevation layer |
|
[растр] |
Digital Terrain Model raster layer |
Z factor |
|
[number] Default: 1.0 |
Vertical exaggeration. This parameter is useful when the Z units differ from the X and Y units, for example feet and meters. You can use this parameter to adjust for this. Increasing the value of this parameter will exaggerate the final result (making it look more «hilly»). The default is 1 (no exaggeration). |
Azimuth (horizontal angle) |
|
[number] Default: 300.0 |
Set the horizontal angle (in degrees) of the sun (clockwise direction). Range: 0 to 360. 0 is north. |
Vertical angle |
|
[number] Default: 40.0 |
Set the vertical angle (in degrees) of the sun, that is the height of the sun. Values can go from 0 (minimum elevation) to 90 (maximum elevation). |
Hillshade |
|
[растр] Default: |
Specify the output hillshade raster layer. One of:
|
Результаты
Ярлык |
Имя |
Тип |
Описание |
|---|---|---|---|
Hillshade |
|
[растр] |
The output hillshade raster layer |
Код на Python
Algorithm ID: qgis:hillshade
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
ID алгоритма отображается при наведении мыши на алгоритм в Инструментах анализа. Словарь parameter dictionary содержит ключи параметров и их значения. См. Изпользование алгоритмов геообработки в консоли для детального описания того, как запускать алгоритмы анализа из консоли Python.
27.1.13.3. Hypsometric curves
Calculates hypsometric curves for an input Digital Elevation Model. Curves are produced as CSV files in an output folder specified by the user.
A hypsometric curve is a cumulative histogram of elevation values in a geographical area.
You can use hypsometric curves to detect differences in the landscape due to the geomorphology of the territory.
Параметры
Ярлык |
Имя |
Тип |
Описание |
|---|---|---|---|
DEM to analyze |
|
[растр] |
Digital Terrain Model raster layer to use for calculating altitudes |
Boundary layer |
|
[vector: polygon] |
Polygon vector layer with boundaries of areas used to calculate hypsometric curves |
Step |
|
[number] Default: 100.0 |
Vertical distance between curves |
Use % of area instead of absolute value |
|
[логическое значение] По умолчанию: Ложь |
Write area percentage to “Area” field of the CSV file instead of the absolute area |
Hypsometric curves |
|
[folder] |
Specify the output folder for the hypsometric curves. One of:
|
Результаты
Ярлык |
Имя |
Тип |
Описание |
|---|---|---|---|
Hypsometric curves |
|
[folder] |
Directory containing the files with the hypsometric curves. For each feature from the input vector layer, a CSV file with area and altitude values will be created. The file names start with |
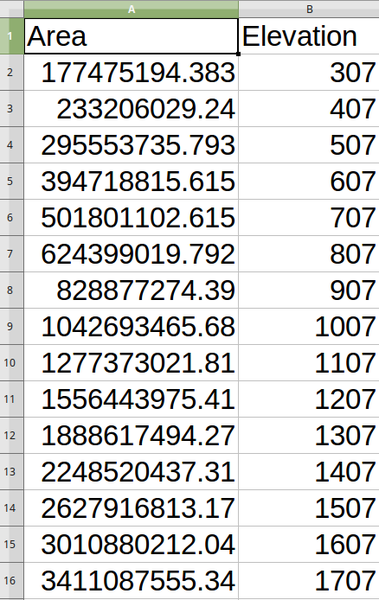
Код на Python
Algorithm ID: qgis:hypsometriccurves
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
ID алгоритма отображается при наведении мыши на алгоритм в Инструментах анализа. Словарь parameter dictionary содержит ключи параметров и их значения. См. Изпользование алгоритмов геообработки в консоли для детального описания того, как запускать алгоритмы анализа из консоли Python.
27.1.13.4. Relief
Creates a shaded relief layer from digital elevation data. You can specify the relief color manually, or you can let the algorithm choose automatically all the relief classes.
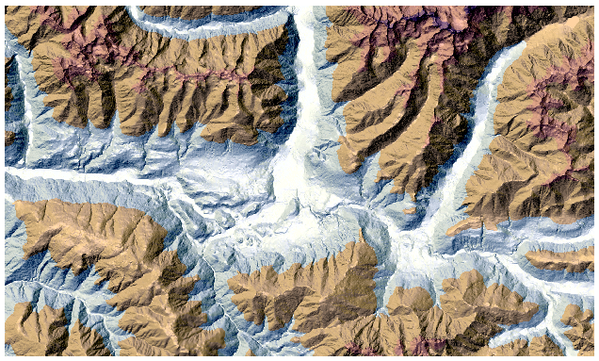
Рис. 27.26 Relief layer
Параметры
Ярлык |
Имя |
Тип |
Описание |
|---|---|---|---|
Elevation layer |
|
[растр] |
Digital Terrain Model raster layer |
Z factor |
|
[number] Default: 1.0 |
Vertical exaggeration. This parameter is useful when the Z units differ from the X and Y units, for example feet and meters. You can use this parameter to adjust for this. Increasing the value of this parameter will exaggerate the final result (making it look more «hilly»). The default is 1 (no exaggeration). |
Generate relief classes automatically |
|
[логическое значение] По умолчанию: Ложь |
If you check this option the algorithm will create all the relief color classes automatically |
Relief colors Optional |
|
[table widget] |
Use the table widget if you want to choose the relief colors manually. You can add as many color classes as you want: for each class you can choose the lower and upper bound and finally by clicking on the color row you can choose the color thanks to the color widget. 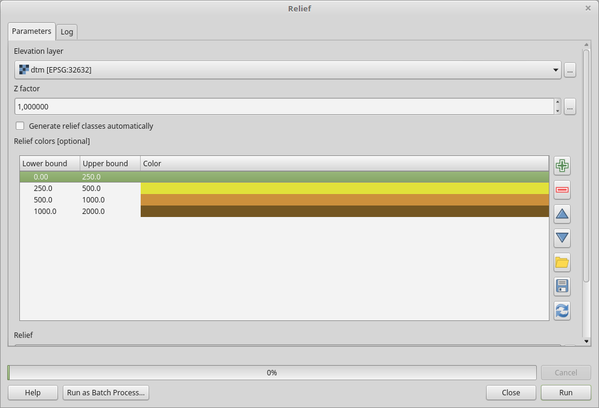
Рис. 27.27 Manually setting of relief color classes The buttons in the right side panel give you the chance to: add or remove color classes, change the order of the color classes already defined, open an existing file with color classes and save the current classes as file. |
Relief |
|
[растр] По умолчанию: |
Specify the output relief raster layer. One of:
|
Frequency distribution Optional |
|
[таблица] Default: |
Specify the CSV table for the output frequency distribution. One of:
|
Результаты
Ярлык |
Имя |
Тип |
Описание |
|---|---|---|---|
Relief |
|
[растр] |
The output relief raster layer |
Frequency distribution |
|
[таблица] |
The output frequency distribution |
Код на Python
Algorithm ID: qgis:relief
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
ID алгоритма отображается при наведении мыши на алгоритм в Инструментах анализа. Словарь parameter dictionary содержит ключи параметров и их значения. См. Изпользование алгоритмов геообработки в консоли для детального описания того, как запускать алгоритмы анализа из консоли Python.
27.1.13.5. Ruggedness index
Calculates the quantitative measurement of terrain heterogeneity described by Riley et al. (1999). It is calculated for every location, by summarizing the change in elevation within the 3x3 pixel grid.
Each pixel contains the difference in elevation from a center cell and the 8 cells surrounding it.
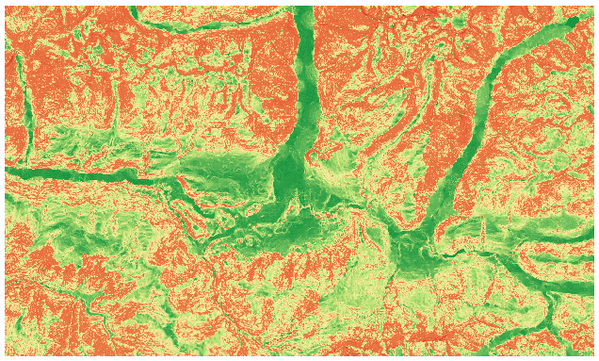
Рис. 27.28 Ruggedness layer from low (red) to high values (green)
Параметры
Ярлык |
Имя |
Тип |
Описание |
|---|---|---|---|
Elevation layer |
|
[растр] |
Digital Terrain Model raster layer |
Z factor |
|
[number] Default: 1.0 |
Vertical exaggeration. This parameter is useful when the Z units differ from the X and Y units, for example feet and meters. You can use this parameter to adjust for this. Increasing the value of this parameter will exaggerate the final result (making it look more rugged). The default is 1 (no exaggeration). |
Ruggedness |
|
[растр] По умолчанию: |
Specify the output ruggedness raster layer. One of:
|
Результаты
Ярлык |
Имя |
Тип |
Описание |
|---|---|---|---|
Ruggedness |
|
[растр] |
The output ruggedness raster layer |
Код на Python
Algorithm ID: qgis:ruggednessindex
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
ID алгоритма отображается при наведении мыши на алгоритм в Инструментах анализа. Словарь parameter dictionary содержит ключи параметров и их значения. См. Изпользование алгоритмов геообработки в консоли для детального описания того, как запускать алгоритмы анализа из консоли Python.
27.1.13.6. Уклон
Calculates the slope from an input raster layer. The slope is the angle of inclination of the terrain and is expressed in degrees.
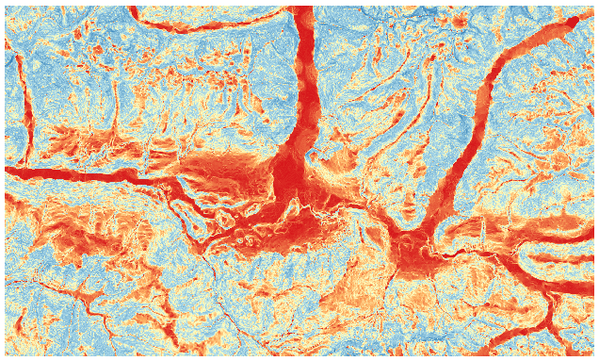
Рис. 27.29 Flat areas in red, steep areas in blue
Параметры
Ярлык |
Имя |
Тип |
Описание |
|---|---|---|---|
Elevation layer |
|
[растр] |
Digital Terrain Model raster layer |
Z factor |
|
[number] Default: 1.0 |
Vertical exaggeration. This parameter is useful when the Z units differ from the X and Y units, for example feet and meters. You can use this parameter to adjust for this. Increasing the value of this parameter will exaggerate the final result (making it steeper). The default is 1 (no exaggeration). |
Slope |
|
[растр] По умолчанию: |
Specify the output slope raster layer. One of:
|
Результаты
Ярлык |
Имя |
Тип |
Описание |
|---|---|---|---|
Slope |
|
[растр] |
The output slope raster layer |
Код на Python
Algorithm ID: qgis:slope
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
ID алгоритма отображается при наведении мыши на алгоритм в Инструментах анализа. Словарь parameter dictionary содержит ключи параметров и их значения. См. Изпользование алгоритмов геообработки в консоли для детального описания того, как запускать алгоритмы анализа из консоли Python.