중요
번역은 여러분이 참여할 수 있는 커뮤니티 활동입니다. 이 페이지는 현재 100.00% 번역되었습니다.
25.2.5. 위상 점검기 플러그인
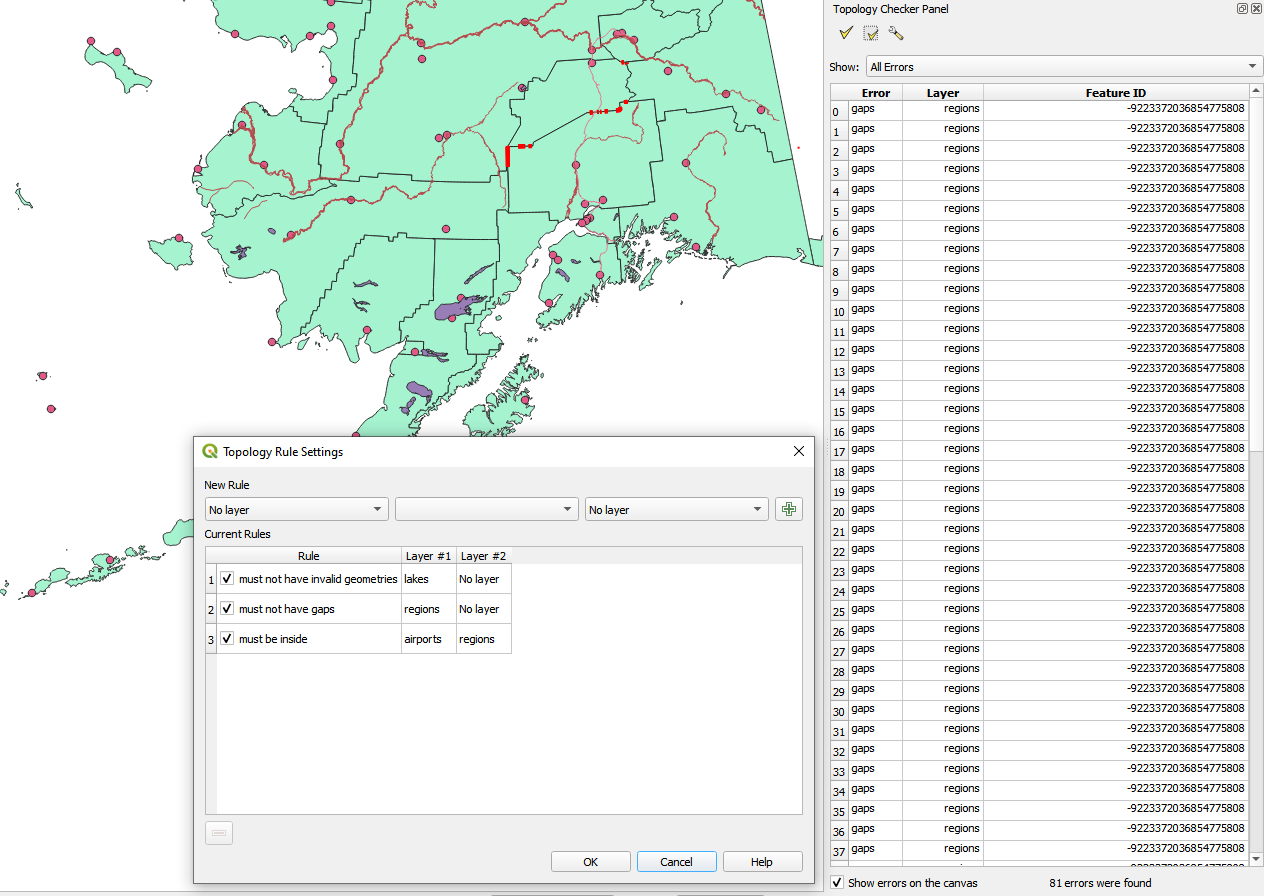
그림 25.14 위상 점검기 플러그인
위상(topology)이란 지리적 지역의 객체를 표현하는 포인트, 라인 및 폴리곤 간의 관계를 말합니다. 위상 점검기 플러그인을 사용해서 사용자 벡터 파일을 살펴보고 여러 위상 규칙을 기준으로 위상을 점검할 수 있습니다. 이런 규칙들은 사용자 객체가 서로 ‘동등(equal)’ 한지, ‘포함(contain)’ 하는지, ‘커버(cover)’ 하는지, ‘커버되는(CoveredBy)’ 지, ‘공간교차(cross)’ 하는지, ‘분절(disjoint)’ 되는지, ‘교차(intersect)’ 하는지, ‘중첩(overlap)’ 하는지, ‘접촉(touch)’ 하는지, 또는 서로의 ‘내부(within)’ 에 있는지 그 공간 관계를 점검합니다. 이 관계는 사용자 벡터 데이터에 개별적으로 어느 위상 규칙을 적용하느냐에 따라 달라집니다. (예를 들면, 일반적으로 라인 레이어에서는 오버슛(overshoot)을 허용하지 않지만, 오버슛이 막다른 길을 표현하는 경우 사용자 벡터 레이어에서 제거하지 않을 것입니다.)
QGIS는 위상 편집 기능을 내장하고 있는데, 오류가 없는 새 객체를 생성하는 데 매우 유용합니다. 그러나 기존 데이터의 오류 및 사용자가 발생시킨 오류를 찾기란 어렵습니다. 이 플러그인을 사용하면 일련의 규칙을 통해 그런 오류들을 찾을 수 있습니다.
Topology checker 플러그인을 활성화하려면:
Plugins 메뉴로 가십시오.
 Manage and Install plugins 플러그인 관리자를 연 다음
Manage and Install plugins 플러그인 관리자를 연 다음  Installed 설치된 플러그인을 선택하십시오.
Installed 설치된 플러그인을 선택하십시오.Plugin manager 대화창을 닫으십시오. Vector 메뉴에
 Topology checker 항목이 추가되었습니다.
Topology checker 항목이 추가되었습니다.
 Topology checker 를 활성화시킨 다음, 위상 점검기를 열고
Topology checker 를 활성화시킨 다음, 위상 점검기를 열고  Configure 를 선택해서 사용자의 위상 규칙을 생성하십시오.
Configure 를 선택해서 사용자의 위상 규칙을 생성하십시오.
포인트 레이어 상에서 다음 규칙들을 사용할 수 있습니다:
Must be covered by: 사용자 프로젝트에서 벡터 레이어를 선택할 수 있습니다. 지정한 벡터 레이어로 커버되지 않는 포인트를 ‘오류’ 항목으로 분류합니다.
Must be covered by endpoints of: 사용자 프로젝트에서 라인 레이어를 선택할 수 있습니다.
Must be inside: 사용자 프로젝트에서 폴리곤 레이어를 선택할 수 있습니다. 포인트가 폴리곤 내부에 들어가야만 합니다. QGIS는 들어가지 않는 포인트에 ‘오류’를 작성합니다.
Must not have duplicates: 어느 포인트가 두 번 이상 표현되는 경우, 해당 포인트를 ‘오류’ 항목으로 분류합니다.
Must not have invalid geometries: 도형이 무결한지 여부를 점검합니다.
Must not have multi-part-geometries: 모든 다중 부분 포인트를 ‘오류’로 분류합니다.
라인 레이어 상에서 다음 규칙들을 사용할 수 있습니다:
End points must be covered by: 사용자 프로젝트에서 포인트 레이어를 선택할 수 있습니다.
Must not have dangles: 라인 레이어에 있는 오버슛을 표시할 것입니다.
Must not have duplicates: 어느 라인 피처가 두 번 이상 표현되는 경우, 해당 라인을 ‘오류’ 항목으로 분류합니다.
Must not have invalid geometries: 도형이 무결한지 여부를 점검합니다.
Must not have multi-part geometries: 도형 한 개가 실제로는 단순(단일 부분, single-part) 도형의 집합인 경우가 종종 있습니다. 이런 도형을 다중 부분(multi-part) 도형이라고 합니다. 다중 부분 도형이 한 가지 유형의 단순 도형으로만 이루어져 있을 경우 멀티포인트, 멀티라인스트링, 멀티폴리곤이라 부릅니다. 모든 다중 부분 라인을 ‘오류’로 분류합니다.
Must not have pseudos: 라인 도형의 종단점이 다른 두 도형의 종단점과 연결돼 있어야 합니다. 종단점이 다른 한 도형의 종단점과만 연결돼 있는 경우, 이런 종단점을 유사(pseudo) 노드라고 합니다.
폴리곤 레이어 상에서 다음 규칙들을 사용할 수 있습니다:
Must contain: 폴리곤 레이어가 두 번째 레이어의 포인트 도형을 적어도 하나 포함해야만 합니다.
Must not have duplicates: 어떤 폴리곤과 동일한 폴리곤이 동일 레이어에 있어서는 안 됩니다. 어떤 폴리곤이 두 번 이상 표현되는 경우, 해당 폴리곤을 ‘오류’로 분류합니다.
Must not have gaps: 인접한 폴리곤 사이에 틈이 있어서는 안 됩니다. 행정구역 경계를 그 예로 들 수 있습니다. (미국의 주(州) 폴리곤들 사이엔 아무 틈도 존재하지 않습니다.)
Must not have invalid geometries: 도형이 무결한지 여부를 점검합니다. 다음은 무결한 도형을 정의하는 규칙 가운데 일부입니다:
폴리곤 고리는 닫혀 있어야만 합니다.
구멍을 정의하는 고리는 외부 경계선을 정의하는 고리 내부에 있어야만 합니다.
고리들이 자체 교차해서는 안 됩니다. (서로 접하거나 공간교차해서는 안 됩니다.)
고리는 한 포인트에서 접촉하는 경우 외엔 서로 접해서는 안 됩니다.
Must not have multi-part geometries: 도형 한 개가 실제로는 단순(단일 부분, single-part) 도형의 집합인 경우가 종종 있습니다. 이런 도형을 다중 부분(multi-part) 도형이라고 합니다. 다중 부분 도형이 한 가지 유형의 단순 도형으로만 이루어져 있을 경우 멀티포인트, 멀티라인스트링, 멀티폴리곤이라 부릅니다. 예를 들어 여러 개의 섬으로 이루어진 국가라면 멀티폴리곤으로 표현할 수 있습니다.
Must not overlap: 인접한 폴리곤들이 공통 영역을 공유해서는 안 됩니다.
Must not overlap with: 한 레이어에서 인접한 폴리곤들이 또다른 레이어의 폴리곤들과 공통 영역을 공유해서는 안 됩니다.
New rule 을 생성할 때, Current rules 에 새 규칙을 추가하려면  Add rule 아이콘을 클릭하십시오. 체크박스를 클릭하면 규칙을 하나하나 활성화시키거나 비활성화시킬 수 있습니다. 규칙을 오른쪽 클릭하면 다음과 같은 옵션들을 설정할 수 있습니다:
Add rule 아이콘을 클릭하십시오. 체크박스를 클릭하면 규칙을 하나하나 활성화시키거나 비활성화시킬 수 있습니다. 규칙을 오른쪽 클릭하면 다음과 같은 옵션들을 설정할 수 있습니다:
Select All: 규칙들을 모두 선택합니다.
Activate 또는 Deactivate: 선택한 규칙을 활성화 또는 비활성화시킵니다.
Toggle activation: 선택한 규칙의 활성화 상태를 켜고끕니다.
Delete: 선택한 규칙을 삭제합니다.
 Delete selected rules 버튼으로도 삭제할 수 있습니다.
Delete selected rules 버튼으로도 삭제할 수 있습니다.
OK 를 클릭한 다음 Topology checker 패널에서 다음을 선택하십시오:
또는
 Validate Extent: 현재 맵 캔버스 안에 있는 해당 레이어(들)의 피처에 활성화된 규칙들을 적용합니다. 이 버튼은 눌린 상태로 유지되어 맵 캔버스 범위가 변할 때마다 그 결과를 업데이트할 것입니다.
Validate Extent: 현재 맵 캔버스 안에 있는 해당 레이어(들)의 피처에 활성화된 규칙들을 적용합니다. 이 버튼은 눌린 상태로 유지되어 맵 캔버스 범위가 변할 때마다 그 결과를 업데이트할 것입니다.
오류는 오류 유형, 레이어 ID 및 피처 ID를 담고 있는 결과 테이블에 나타날 것입니다. 오류들을 특정 오류 유형으로 필터링하려면 Filter errors by rule 메뉴를 사용하십시오.
 Show errors on the canvas 옵션을 체크하면 캔버스 상에 오류 위치를 표시합니다. 테이블에서 행을 하나 클릭하면 맵 캔버스를 해당 피처로 확대/축소할 것입니다. 이때 QGIS 디지타이즈 작업 도구 를 사용해서 해당 피처의 오류를 고칠 수 있습니다.
Show errors on the canvas 옵션을 체크하면 캔버스 상에 오류 위치를 표시합니다. 테이블에서 행을 하나 클릭하면 맵 캔버스를 해당 피처로 확대/축소할 것입니다. 이때 QGIS 디지타이즈 작업 도구 를 사용해서 해당 피처의 오류를 고칠 수 있습니다.
