3. QGIS GUI
The QGIS graphical user interface (GUI) is shown in the figure below (the numbers 1 through 5 in yellow circles indicate important elements of the QGIS GUI, and are discussed below).
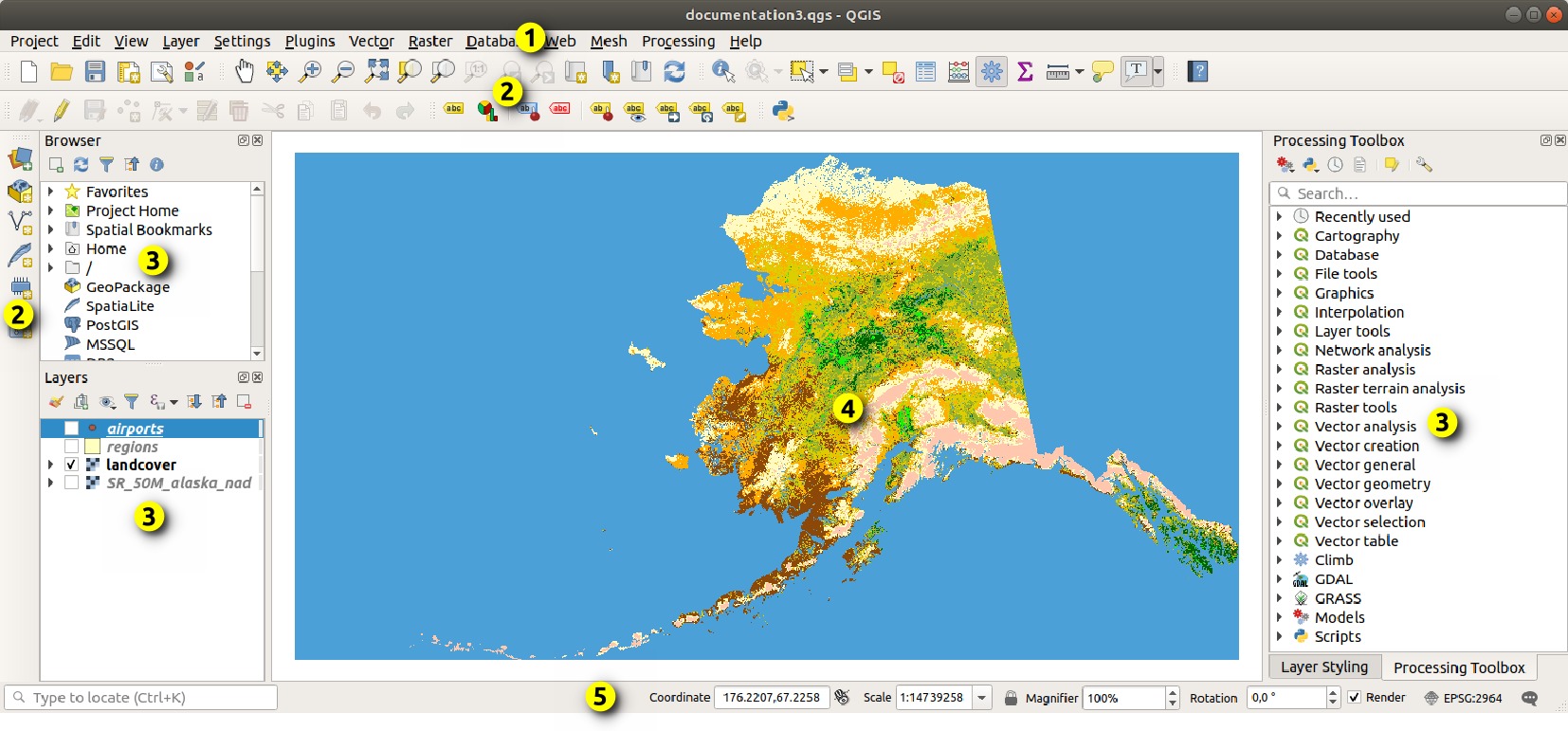
Fig. 3.1 QGIS GUI with Alaska sample data
Note
Your window decorations (title bar, etc.) may appear different depending on your operating system and window manager.
The main QGIS GUI (Fig. 3.1) consists of five components / component types:
Scroll down for detailed explanations of these.
3.2. Panels and Toolbars
From the menu (or  ),
you can switch QGIS widgets ()
and toolbars () on and off.
To (de)activate any of them, right-click the menu bar or toolbar and
choose the item you want.
Panels and toolbars can be moved and placed wherever you like within
the QGIS interface.
The list can also be extended with the activation of Core or
external plugins.
),
you can switch QGIS widgets ()
and toolbars () on and off.
To (de)activate any of them, right-click the menu bar or toolbar and
choose the item you want.
Panels and toolbars can be moved and placed wherever you like within
the QGIS interface.
The list can also be extended with the activation of Core or
external plugins.
3.2.1. Toolbars
The toolbars provide access to most of the functions in the menus, plus additional tools for interacting with the map. Each toolbar item has pop-up help available. Hover your mouse over the item and a short description of the tool’s purpose will be displayed.
Available toolbars are:
Toolbar name |
Main Reference for tools |
|---|---|
Advanced Digitizing |
|
Annotations |
|
Attributes |
|
Data Source Manager |
|
Database |
|
Digitizing |
|
GPS |
|
GRASS |
|
Help |
|
Label |
|
Manage Layers |
|
Map Navigation |
|
Mesh Digitizing |
|
Plugins |
|
Project |
Working with Project Files, Laying out the maps, The Style Library |
Processing Algorithms |
|
Raster |
|
Selection |
|
Shape digitizing |
|
Snapping |
|
Vector |
|
Web |
Note
Third-party plugins can extend the default toolbar with their own tools or provide their own toolbar.
Tip
Restoring toolbars
If you have accidentally hidden a toolbar, you can get it
back using
(or  ).
If, for some reason, a toolbar (or any other widget) totally
disappears from the interface, you’ll find tips to get it back at
restoring initial GUI.
).
If, for some reason, a toolbar (or any other widget) totally
disappears from the interface, you’ll find tips to get it back at
restoring initial GUI.
3.2.2. Panels
QGIS provides many panels. Panels are special widgets that you can interact with (selecting options, checking boxes, filling values…) to perform more complex tasks.
Below is a list of the default panels provided by QGIS:
Panel name |
Shortcut |
Reference |
|---|---|---|
Advanced Digitizing |
Ctrl+4 |
|
Browser |
Ctrl+2 |
|
Browser (2) |
||
Debugging/Development Tools |
F12 |
|
Elevation Profile |
||
Geometry Validation |
||
GPS Information |
Ctrl+0 |
|
GRASS Tools |
||
Layer Order |
Ctrl+9 |
|
Layer Styling |
Ctrl+3 |
|
Layers |
Ctrl+1 |
|
Log Messages |
||
Overview |
Ctrl+8 |
|
Processing Toolbox |
||
Results Viewer |
||
Snapping and Digitizing Options |
||
Spatial Bookmark Manager |
Ctrl+7 |
|
Statistics |
Ctrl+6 |
|
Temporal Controller |
||
Tile Scale |
||
Undo/Redo |
Ctrl+5 |
|
Vertex Editor |
3.3. Status Bar
The status bar provides you with general information about the map view and processed or available actions, and offers you tools to manage the map view.
3.3.1. Locator bar
On the left side of the status bar, the locator bar, a quick search widget, helps you find and run any feature or options in QGIS:
Click in the text widget to activate the locator search bar or press Ctrl+K.
Type a text associated with the item you are looking for (name, tag, keyword, …). By default, results are returned for the enabled locator filters, but you can limit the search to a certain scope by prefixing your text with the locator filters prefix, ie. typing
l cadwill return only the layers whose name containscad.The filter can also be selected with a double-click in the menu that shows when accessing the locator widget.
Click on a result to execute the corresponding action, depending on the type of item.
Tip
Limit the lookup to particular field(s) of the active layer
By default, a search with the “active layer features” filter (f) runs
through the whole attribute table of the layer. You can limit the search to
a particular field using the @ prefix. E.g., f @name sal or
@name sal returns only the features whose “name” attribute contains ‘sal’.
Text autocompletion is active when writing and the suggestion can be applied
using Tab key.
A more advanced control on the queried fields is possible from the layer Fields tab. Read Fields Properties for details.
Searching is handled using threads, so that results always become available as quickly as possible, even if slow search filters are installed. They also appear as soon as they are encountered by a filter, which means that e.g. a file search filter will show results one by one as the file tree is scanned. This ensures that the UI is always responsive, even if a very slow search filter is present (e.g. one which uses an online service).
Note
The Nominatim locator tool may behave differently (no autocompletion search, delay of fetching results, …) with respect to the OpenStreetMap Nominatim usage policy.
3.3.2. Reporting actions
In the area next to the locator bar, a summary of actions you’ve carried out will be shown when needed (such as selecting features in a layer, removing layer, pan distance and direction) or a long description of the tool you are hovering over (not available for all tools).
In case of lengthy operations, such as gathering of statistics in raster layers, executing Processing algorithms or rendering several layers in the map view, a progress bar is displayed in the status bar.
3.3.3. Control the map canvas
The ![]() Coordinate option shows the current
position of the mouse, following it while moving across the map view.
You can set the units (and precision) in the
tab.
Click on the small button at the left of the textbox to toggle between
the Coordinate option and the
Coordinate option shows the current
position of the mouse, following it while moving across the map view.
You can set the units (and precision) in the
tab.
Click on the small button at the left of the textbox to toggle between
the Coordinate option and the  Extents option
that displays the coordinates of the current bottom-left and top-right
corners of the map view in map units.
Extents option
that displays the coordinates of the current bottom-left and top-right
corners of the map view in map units.
Next to the coordinate display you will find the Scale display. It shows the scale of the map view. There is a scale selector, which allows you to choose between predefined and custom scales.
On the right side of the scale display, press the  button
to lock the scale to use the magnifier to zoom in or out.
The magnifier allows you to zoom in to a map without altering the map
scale, making it easier to tweak the positions of labels and symbols
accurately.
The magnification level is expressed as a percentage.
If the Magnifier has a level of 100%, then the current map
is not magnified, i.e. is rendered at accurate scale relative to the monitor’s resolution (DPI).
A default magnification value can be defined within
,
which is very useful for high-resolution screens to enlarge small
symbols. In addition, a setting in
controls whether QGIS respects each monitor’s physical DPI or uses the overall system logical DPI.
button
to lock the scale to use the magnifier to zoom in or out.
The magnifier allows you to zoom in to a map without altering the map
scale, making it easier to tweak the positions of labels and symbols
accurately.
The magnification level is expressed as a percentage.
If the Magnifier has a level of 100%, then the current map
is not magnified, i.e. is rendered at accurate scale relative to the monitor’s resolution (DPI).
A default magnification value can be defined within
,
which is very useful for high-resolution screens to enlarge small
symbols. In addition, a setting in
controls whether QGIS respects each monitor’s physical DPI or uses the overall system logical DPI.
To the right of the magnifier tool you can define a current clockwise rotation for your map view in degrees.
On the right side of the status bar, the  Render
checkbox can be used to temporarily suspend the map view rendering
(see section Controlling map rendering).
Render
checkbox can be used to temporarily suspend the map view rendering
(see section Controlling map rendering).
To the right of the  Render function, you find the
Render function, you find the
![]() EPSG:code button showing the current project CRS.
Clicking on this opens the Project Properties dialog and lets you
reproject the map view or adjust any other project property.
EPSG:code button showing the current project CRS.
Clicking on this opens the Project Properties dialog and lets you
reproject the map view or adjust any other project property.
Tip
Calculating the Correct Scale of Your Map Canvas
When you start QGIS, the default CRS is WGS 84 (EPSG 4326) and
units are degrees. This means that QGIS will interpret any
coordinate in your layer as specified in degrees.
To get correct scale values, you can either manually change this
setting in the General tab under
(e.g. to meters), or you
can use the ![]() EPSG:code icon seen above.
In the latter case, the units are set to what the project projection
specifies (e.g.,
EPSG:code icon seen above.
In the latter case, the units are set to what the project projection
specifies (e.g., +units=us-ft).
Note that CRS choice on startup can be set in .
3.3.4. Messaging
The  Messages button next to it opens the
Log Messages Panel which has information on underlying
processes (QGIS startup, plugins loading, processing tools…)
Messages button next to it opens the
Log Messages Panel which has information on underlying
processes (QGIS startup, plugins loading, processing tools…)