Important
La traduction est le fruit d’un effort communautaire auquel vous pouvez vous joindre. Cette page est actuellement traduite à 35.56%.
20.1. Introducing GNSS/GPS Data
20.1.1. Qu’est ce que le GPS ?
GPS, the Global Positioning System, is a satellite-based system that allows anyone with a GPS receiver to find their exact position anywhere in the world. GPS is used as an aid in navigation, for example in airplanes, in boats and by hikers. The GPS receiver uses the signals from the satellites to calculate its latitude, longitude and (sometimes) elevation. Most receivers also have the capability to store:
locations (known as waypoints)
sequences of locations that make up a planned route
and a track log of the receiver’s movement over time.
Waypoints, routes and tracks are the three basic feature types in GPS data. QGIS displays waypoints in point layers, while routes and tracks are displayed in linestring layers.
Note
QGIS gère aussi les récepteurs GNSS. Mais nous utiliserons le terme GPS tout au long de la documentation.
20.1.2. Transferring or loading GPS data
20.1.2.1. Loading a GPX file
Il y a des dizaines de formats de fichier différent pour stocker des données GPS. Le format que QGIS utilise est appelé GPX (GPS eXchange format), qui est un format d’échange standard qui peut contenir n’importe quel nombre de waypoints, itinéraires et tracks dans un même fichier.
To load a GPX file:
Open the GPS tab in the Data Source Manager dialog, i.e.:
Use the … Browse button next to the GPX dataset option to select the GPX file
Use the check boxes to select the Feature types you want to load from the file. Each feature type (Waypoints, Tracks or Routes) will be loaded in a separate layer.
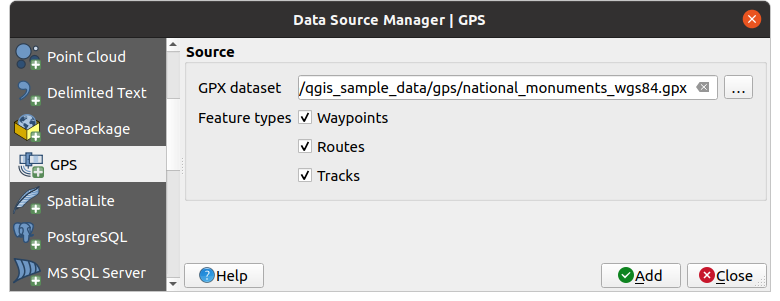
Fig. 20.1 Fenêtre de chargement de données GPS
20.1.2.2. Loading to or from a device
There are lots of different types of GPS devices and formats. Since QGIS uses GPX files, you need a way to convert other GPS file formats to GPX. QGIS can do that using the free program GPSBabel. GPSBabel can help you convert waypoints, tracks, and routes between popular GPS receivers such as Garmin or Magellan and mapping programs like Google Earth or Basecamp. Literally hundreds of GPS receivers and programs are supported. It can also transfer GPS data between your computer and a GPS device.
Under 
![]()
![]() ,
QGIS allows you to define your own device type and set parameters of conversion
that could later be used by the Processing GPS algorithms.
,
QGIS allows you to define your own device type and set parameters of conversion
that could later be used by the Processing GPS algorithms.
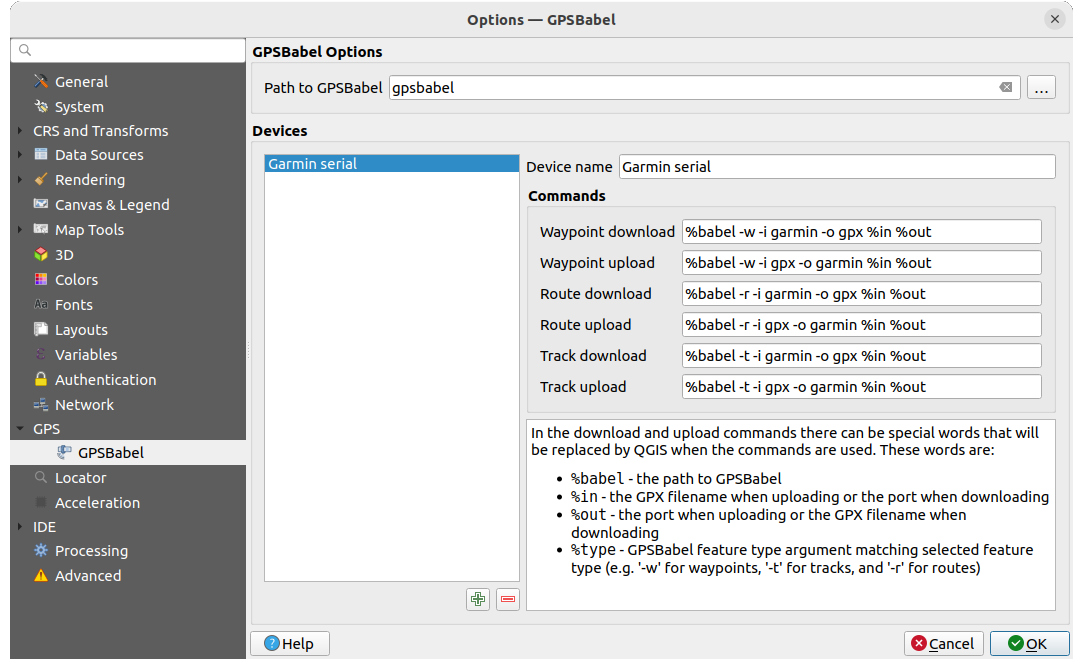
Fig. 20.2 GPS Babel
First you have to define the Path to GPSBabel binaries.
Then you may want to add your device. You can update devices list using
 Add new device
or
Add new device
or  Remove device button.
Remove device button.Pour chaque appareil :
vous indiquez un Nom de l’appareil
you configure different Commands QGIS will use while interacting with it, such as:
Waypoint download from the device
Waypoint upload to the device
Route download from the device
Route upload to the device
Track download from the device
Track upload to the device
While the commands are usually GPSBabel commands, you can also use any other command line program that can create a GPX file. QGIS will replace the keywords
%type,%in, and%outwhen it runs the command.As an example, if you create a device type with the download command
gpsbabel %type -i garmin -o gpx %in %outand then use it to download waypoints from port/dev/ttyS0to the fileoutput.gpx, QGIS will replace the keywords and run the commandgpsbabel -w -i garmin -o gpx /dev/ttyS0 output.gpx.Pensez à consulter le manuel de GPSBabel sur les options de ligne de commande qui pourraient être spécifiques à votre cas.
Une fois le nouveau type de périphérique créé, celui-ci apparaîtra dans les listes de périphériques des outils de téléchargement et d’upload GPS.
Note
GPS units allow you to store data in different coordinate systems. When downloading a GPX file (from your GPS unit or a web site) and then loading it in QGIS, be sure that the data stored in the GPX file uses WGS 84 (latitude/longitude). QGIS expects this, and it is the official GPX specification. See GPX 1.1 Schema Documentation.

