13. Comunicarea cu utilizatorul
Sugestie
The code snippets on this page need the following imports if you’re outside the pyqgis console:
1from qgis.core import (
2 QgsMessageLog,
3 QgsGeometry,
4)
5
6from qgis.gui import (
7 QgsMessageBar,
8)
9
10from qgis.PyQt.QtWidgets import (
11 QSizePolicy,
12 QPushButton,
13 QDialog,
14 QGridLayout,
15 QDialogButtonBox,
16)
Această secțiune prezintă câteva metode și elemente care ar trebui să fie utilizate pentru a comunica cu utilizatorul, în scopul menținerii coerenței interfaței cu utilizatorul.
13.1. Showing messages. The QgsMessageBar class
Folosirea casetelor de mesaje poate fi o idee rea, din punctul de vedere al experienței utilizatorului. Pentru a arăta o mică linie de informații sau un mesaj de avertizare/eroare, bara QGIS de mesaje este, de obicei, o opțiune mai bună.
Folosind referința către obiectul interfeței QGIS, puteți afișa un text în bara de mesaje, cu ajutorul următorului cod
from qgis.core import Qgis
iface.messageBar().pushMessage("Error", "I'm sorry Dave, I'm afraid I can't do that", level=Qgis.Critical)
Messages(2): Error : I'm sorry Dave, I'm afraid I can't do that
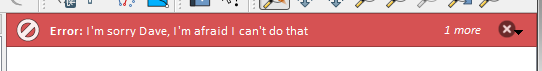
Fig. 13.33 Bara de mesaje a QGIS
Puteți seta o durată, pentru afișarea pentru o perioadă limitată de timp
iface.messageBar().pushMessage("Ooops", "The plugin is not working as it should", level=Qgis.Critical, duration=3)
Messages(2): Ooops : The plugin is not working as it should

Fig. 13.34 Bara de mesaje a QGIS, cu cronometru
Exemplele de mai sus prezintă o bară de eroare, dar parametrul level poate fi utilizat pentru a crea mesaje de avertizare sau informative, folosind enumerarea Qgis.MessageLevel. Se pot utiliza până la 4 niveluri diferite:
Info
Warning
Critical
Success
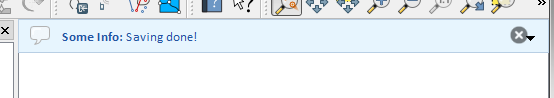
Fig. 13.35 Bara de mesaje a QGIS (info)
Widget-urile pot fi adăugate la bara de mesaje, cum ar fi, de exemplu, un buton pentru afișarea mai multor informații
1def showError():
2 pass
3
4widget = iface.messageBar().createMessage("Missing Layers", "Show Me")
5button = QPushButton(widget)
6button.setText("Show Me")
7button.pressed.connect(showError)
8widget.layout().addWidget(button)
9iface.messageBar().pushWidget(widget, Qgis.Warning)
Messages(1): Missing Layers : Show Me
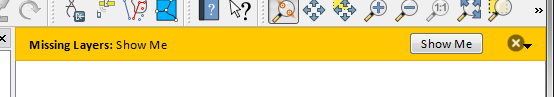
Fig. 13.36 Bara de mesaje a QGIS, cu un buton
Puteți utiliza o bară de mesaje chiar și în propria fereastră de dialog, în loc să apelați la o casetă de text, sau să arătați mesajul în fereastra principală a QGIS
1class MyDialog(QDialog):
2 def __init__(self):
3 QDialog.__init__(self)
4 self.bar = QgsMessageBar()
5 self.bar.setSizePolicy( QSizePolicy.Minimum, QSizePolicy.Fixed )
6 self.setLayout(QGridLayout())
7 self.layout().setContentsMargins(0, 0, 0, 0)
8 self.buttonbox = QDialogButtonBox(QDialogButtonBox.Ok)
9 self.buttonbox.accepted.connect(self.run)
10 self.layout().addWidget(self.buttonbox, 0, 0, 2, 1)
11 self.layout().addWidget(self.bar, 0, 0, 1, 1)
12 def run(self):
13 self.bar.pushMessage("Hello", "World", level=Qgis.Info)
14
15myDlg = MyDialog()
16myDlg.show()
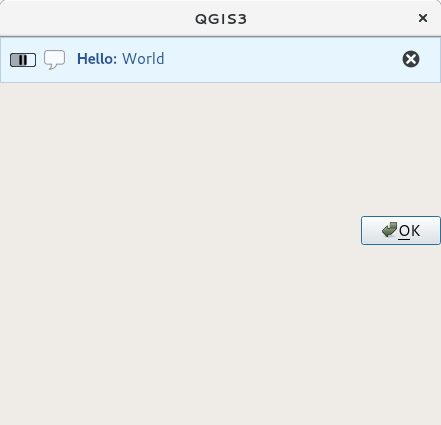
Fig. 13.37 Bara de mesaje a QGIS, într-o fereastră de dialog
13.2. Afișarea progresului
Barele de progres pot fi, de asemenea, incluse în bara de mesaje QGIS, din moment ce, așa cum am văzut, aceasta acceptă widget-uri. Iată un exemplu pe care îl puteți încerca în consolă.
1import time
2from qgis.PyQt.QtWidgets import QProgressBar
3from qgis.PyQt.QtCore import *
4progressMessageBar = iface.messageBar().createMessage("Doing something boring...")
5progress = QProgressBar()
6progress.setMaximum(10)
7progress.setAlignment(Qt.AlignLeft|Qt.AlignVCenter)
8progressMessageBar.layout().addWidget(progress)
9iface.messageBar().pushWidget(progressMessageBar, Qgis.Info)
10
11for i in range(10):
12 time.sleep(1)
13 progress.setValue(i + 1)
14
15iface.messageBar().clearWidgets()
Messages(0): Doing something boring...
Also, you can use the built-in status bar to report progress, as in the next example:
1vlayer = iface.activeLayer()
2
3count = vlayer.featureCount()
4features = vlayer.getFeatures()
5
6for i, feature in enumerate(features):
7 # do something time-consuming here
8 print('.') # printing should give enough time to present the progress
9
10 percent = i / float(count) * 100
11 # iface.mainWindow().statusBar().showMessage("Processed {} %".format(int(percent)))
12 iface.statusBarIface().showMessage("Processed {} %".format(int(percent)))
13
14iface.statusBarIface().clearMessage()
13.3. Jurnalizare
There are three different types of logging available in QGIS to log and save all the information about the execution of your code. Each has its specific output location. Please consider to use the correct way of logging for your purpose:
QgsMessageLogis for messages to communicate issues to the user. The output of the QgsMessageLog is shown in the Log Messages Panel.The python built in logging module is for debugging on the level of the QGIS Python API (PyQGIS). It is recommended for Python script developers that need to debug their python code, e.g. feature ids or geometries
QgsLoggeris for messages for QGIS internal debugging / developers (i.e. you suspect something is triggered by some broken code). Messages are only visible with developer versions of QGIS.
Examples for the different logging types are shown in the following sections below.
Atenționare
Use of the Python print statement is unsafe to do in any code which may be
multithreaded and extremely slows down the algorithm. This includes expression
functions, renderers,
symbol layers and Processing algorithms (amongst others). In these
cases you should always use the python logging module or thread safe classes
(QgsLogger
or QgsMessageLog) instead.
13.3.1. QgsMessageLog
# You can optionally pass a 'tag' and a 'level' parameters
QgsMessageLog.logMessage("Your plugin code has been executed correctly", 'MyPlugin', level=Qgis.Info)
QgsMessageLog.logMessage("Your plugin code might have some problems", level=Qgis.Warning)
QgsMessageLog.logMessage("Your plugin code has crashed!", level=Qgis.Critical)
MyPlugin(0): Your plugin code has been executed correctly
(1): Your plugin code might have some problems
(2): Your plugin code has crashed!
Notă
You can see the output of the QgsMessageLog
in the Log Messages Panel
13.3.2. The python built in logging module
1import logging
2formatter = '%(asctime)s - %(name)s - %(levelname)s - %(message)s'
3logfilename=r'c:\temp\example.log'
4logging.basicConfig(filename=logfilename, level=logging.DEBUG, format=formatter)
5logging.info("This logging info text goes into the file")
6logging.debug("This logging debug text goes into the file as well")
The basicConfig method configures the basic setup of the logging. In the above code the filename, logging level and the format are defined. The filename refers to where to write the logfile to, the logging level defines what levels to output and the format defines the format in which each message is output.
2020-10-08 13:14:42,998 - root - INFO - This logging text goes into the file
2020-10-08 13:14:42,998 - root - DEBUG - This logging debug text goes into the file as well
If you want to erase the log file every time you execute your script you can do something like:
if os.path.isfile(logfilename):
with open(logfilename, 'w') as file:
pass
Further resources on how to use the python logging facility are available at:
Atenționare
Please note that without logging to a file by setting a filename the logging may be multithreaded which heavily slows down the output.