25.1.13. Análise espacial Raster (Matricial)
25.1.13.1. Exposição/Orientação de Encostas
Calculates the aspect of the Digital Terrain Model in input. The final aspect raster layer contains values from 0 to 360 that express the slope direction, starting from north (0°) and continuing clockwise.
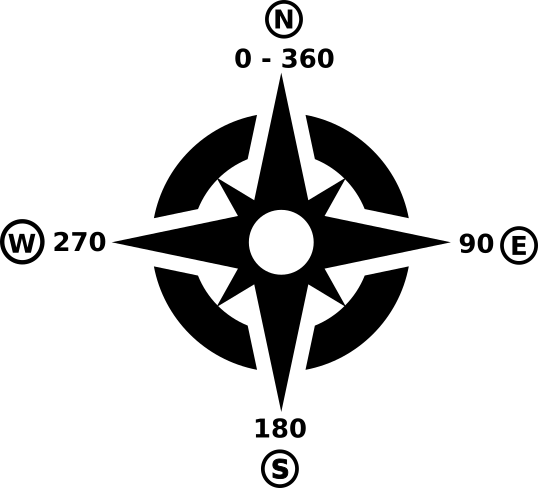
Fig. 25.21 Gama de valores da Exposição
A figura seguinte apresenta a camada de orientações reclassificada através de uma paleta (de cores).
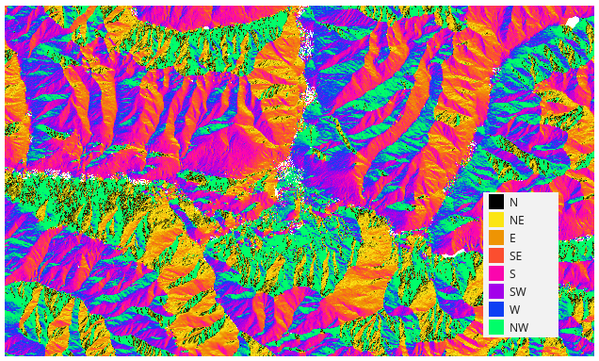
Fig. 25.22 Camada de Exposição reclassificada
Parâmetros
Label |
Nome |
Type |
Descrição |
|---|---|---|---|
Elevation layer |
|
[raster] |
Digital Terrain Model raster layer |
Z factor |
|
[number] Default: 1.0 |
Vertical exaggeration. This parameter is useful when the Z units differ from the X and Y units, for example feet and meters. You can use this parameter to adjust for this. The default is 1 (no exaggeration). |
Aspect |
|
[raster] |
Specify the output aspect raster layer. One of:
The file encoding can also be changed here. |
Resultados
Label |
Nome |
Type |
Descrição |
|---|---|---|---|
Aspect |
|
[raster] |
The output aspect raster layer |
Python code
Algorithm ID: qgis:aspect
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
The algorithm id is displayed when you hover over the algorithm in the Processing Toolbox. The parameter dictionary provides the parameter NAMEs and values. See Usando os algoritmos do processamento a partir da consola for details on how to run processing algorithms from the Python console.
25.1.13.2. Sombreados
Calculates the hillshade raster layer given an input Digital Terrain Model.
O sombreado da camada é calculado de acordo com a posição do sol com a opção de escolha, quer do seu ângulo horizontal (azimute), quer do seu ângulo vertical (elevação).
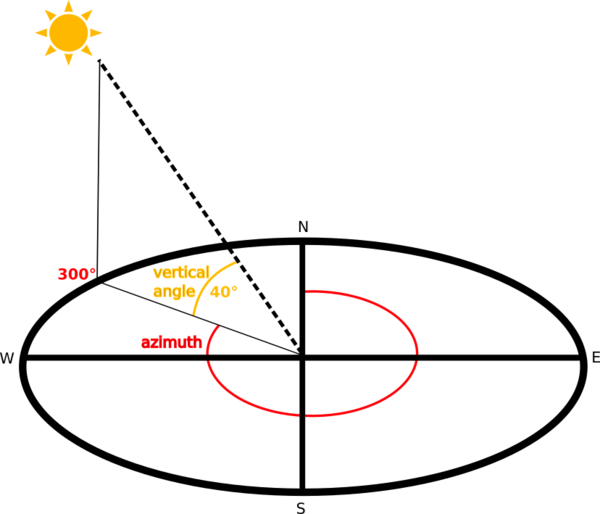
Fig. 25.23 Azimute e ângulo vertical
A camada de sombreados compreende valores entre 0 (sombra total) até 255 (claridade total). O método dos sombreados é habitualmente utilizado para aumentar a percepção do relevo do terreno.

Fig. 25.24 Camada de sombreados de azimute 300 e ângulo vertical 45
É particularmente interessante atribuir à camada de sombreados um nível de transparência que possibilite sobrepô-la ao raster de altitudes:
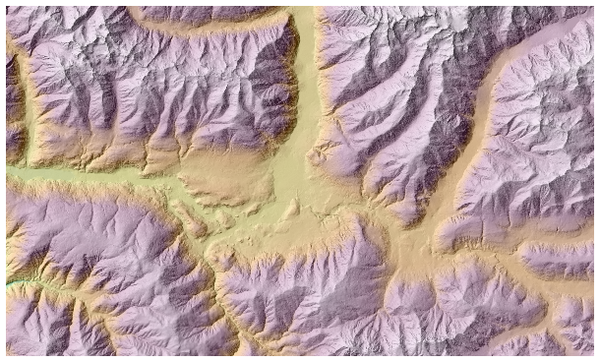
Fig. 25.25 Sobreposição dos sombreados à camada de altitudes
Parâmetros
Label |
Nome |
Type |
Descrição |
|---|---|---|---|
Elevation layer |
|
[raster] |
Digital Terrain Model raster layer |
Z factor |
|
[number] Default: 1.0 |
Vertical exaggeration. This parameter is useful when the Z units differ from the X and Y units, for example feet and meters. You can use this parameter to adjust for this. Increasing the value of this parameter will exaggerate the final result (making it look more «hilly»). The default is 1 (no exaggeration). |
Azimuth (horizontal angle) |
|
[number] Default: 300.0 |
Set the horizontal angle (in degrees) of the sun (clockwise direction). Range: 0 to 360. 0 is north. |
Vertical angle |
|
[number] Default: 40.0 |
Define o ângulo vertical (graus) ou altura do sol. Os valores variam entre 0 (altura mínima) e 90 (altura máxima). |
Hillshade |
|
[raster] |
Specify the output hillshade raster layer. One of:
The file encoding can also be changed here. |
Resultados
Label |
Nome |
Type |
Descrição |
|---|---|---|---|
Hillshade |
|
[raster] |
The output hillshade raster layer |
Python code
Algorithm ID: qgis:hillshade
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
The algorithm id is displayed when you hover over the algorithm in the Processing Toolbox. The parameter dictionary provides the parameter NAMEs and values. See Usando os algoritmos do processamento a partir da consola for details on how to run processing algorithms from the Python console.
25.1.13.3. Curvas Hipsométricas
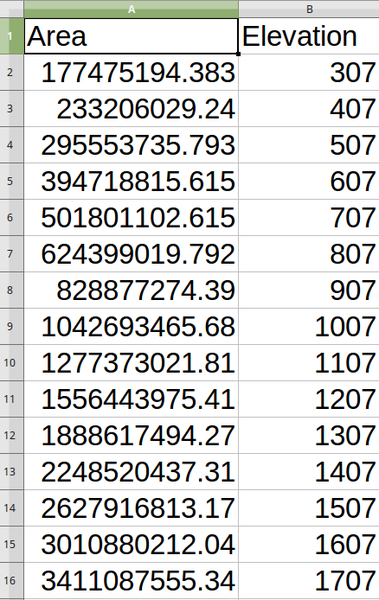
Calculates hypsometric curves for an input Digital Elevation Model. Curves are produced as CSV files in an output folder specified by the user.
A hypsometric curve is a cumulative histogram of elevation values in a geographical area.
You can use hypsometric curves to detect differences in the landscape due to the geomorphology of the territory.
Parâmetros
Label |
Nome |
Type |
Descrição |
|---|---|---|---|
DEM to analyze |
|
[raster] |
Digital Terrain Model raster layer to use for calculating altitudes |
Boundary layer |
|
[vector: polygon] |
Polygon vector layer with boundaries of areas used to calculate hypsometric curves |
Step |
|
[number] Default: 100.0 |
Vertical distance between curves |
Use % of area instead of absolute value |
|
[boolean] Default: False |
Write area percentage to “Area” field of the CSV file instead of the absolute area |
Hypsometric curves |
|
[folder] |
Specify the output folder for the hypsometric curves. One of:
The file encoding can also be changed here. |
Resultados
Label |
Nome |
Type |
Descrição |
|---|---|---|---|
Hypsometric curves |
|
[folder] |
Directory containing the files with the hypsometric curves. For each feature from the input vector layer, a CSV file with area and altitude values will be created. The file names start with |
Python code
Algorithm ID: qgis:hypsometriccurves
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
The algorithm id is displayed when you hover over the algorithm in the Processing Toolbox. The parameter dictionary provides the parameter NAMEs and values. See Usando os algoritmos do processamento a partir da consola for details on how to run processing algorithms from the Python console.
25.1.13.4. Relevo
Creates a shaded relief layer from digital elevation data. You can specify the relief color manually, or you can let the algorithm choose automatically all the relief classes.
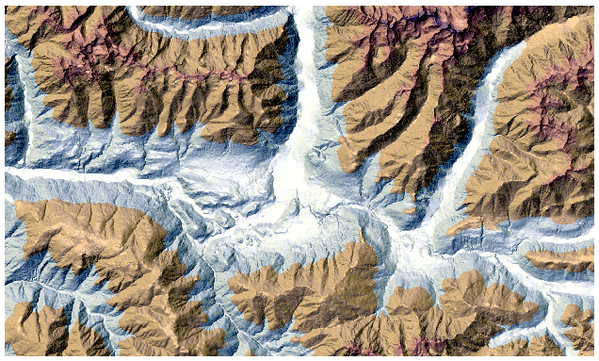
Fig. 25.26 Camada de relevo
Parâmetros
Label |
Nome |
Type |
Descrição |
|---|---|---|---|
Elevation layer |
|
[raster] |
Digital Terrain Model raster layer |
Z factor |
|
[number] Default: 1.0 |
Vertical exaggeration. This parameter is useful when the Z units differ from the X and Y units, for example feet and meters. You can use this parameter to adjust for this. Increasing the value of this parameter will exaggerate the final result (making it look more «hilly»). The default is 1 (no exaggeration). |
Generate relief classes automatically |
|
[boolean] Default: False |
If you check this option the algorithm will create all the relief color classes automatically |
Relief colors Opcional |
|
[table widget] |
Use the table widget if you want to choose the relief colors manually. You can add as many color classes as you want: for each class you can choose the lower and upper bound and finally by clicking on the color row you can choose the color thanks to the color widget. 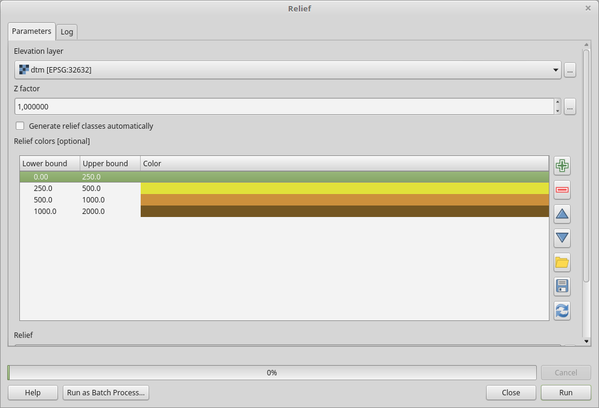
Fig. 25.27 Manually setting of relief color classes The buttons in the right side panel give you the chance to: add or remove color classes, change the order of the color classes already defined, open an existing file with color classes and save the current classes as file. |
Relief |
|
[raster] Default: |
Specify the output relief raster layer. One of:
The file encoding can also be changed here. |
Frequency distribution |
|
[table] Default: |
Specify the CSV table for the output frequency distribution. One of:
The file encoding can also be changed here. |
Resultados
Label |
Nome |
Type |
Descrição |
|---|---|---|---|
Relief |
|
[raster] |
The output relief raster layer |
Frequency distribution |
|
[table] |
The output frequency distribution |
Python code
Algorithm ID: qgis:relief
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
The algorithm id is displayed when you hover over the algorithm in the Processing Toolbox. The parameter dictionary provides the parameter NAMEs and values. See Usando os algoritmos do processamento a partir da consola for details on how to run processing algorithms from the Python console.
25.1.13.5. Acidentado do Terreno/Índice de Rugosidade
Determina a medida quantitativa da heterogeneidade do terreno descrita por Riley et al. (1999). É calculado para cada ponto analisando as diferenças de elevação existentes na grelha de células 3x3 em cujo centro está contido (ponto).
Cada célula contêm o somatório das diferenças absolutas de elevação entre uma célula central e as oito que a envolvem.
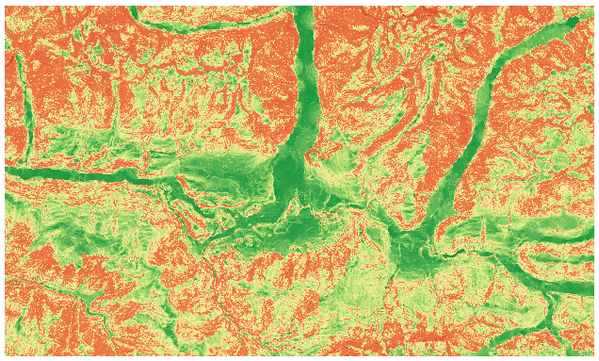
Fig. 25.28 Camada do Acidentado do Terreno desenvolvendo-se dos baixos (vermelho) para os altos (verde) índices.
Parâmetros
Label |
Nome |
Type |
Descrição |
|---|---|---|---|
Elevation layer |
|
[raster] |
Digital Terrain Model raster layer |
Z factor |
|
[number] Default: 1.0 |
Vertical exaggeration. This parameter is useful when the Z units differ from the X and Y units, for example feet and meters. You can use this parameter to adjust for this. Increasing the value of this parameter will exaggerate the final result (making it look more rugged). The default is 1 (no exaggeration). |
Ruggedness |
|
[raster] Default: |
Specify the output ruggedness raster layer. One of:
The file encoding can also be changed here. |
Resultados
Label |
Nome |
Type |
Descrição |
|---|---|---|---|
Ruggedness |
|
[raster] |
The output ruggedness raster layer |
Python code
Algorithm ID: qgis:ruggednessindex
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
The algorithm id is displayed when you hover over the algorithm in the Processing Toolbox. The parameter dictionary provides the parameter NAMEs and values. See Usando os algoritmos do processamento a partir da consola for details on how to run processing algorithms from the Python console.
25.1.13.6. Declives (ângulos)
Calcula os declives (em unidades angulares) de uma dada camada raster. O declive, aqui entendido como o ângulo de inclinação do terreno, é expresso em graus.
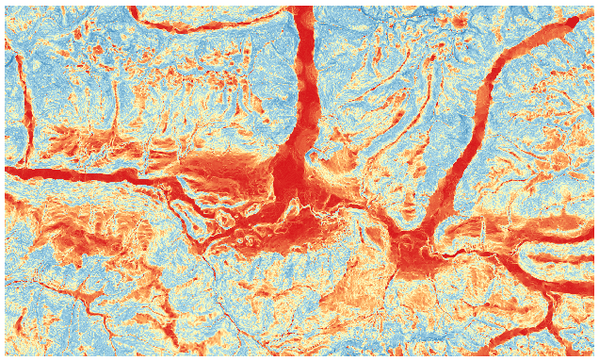
Fig. 25.29 Áreas planas a vermelho, áreas inclinadas a azul
Parâmetros
Label |
Nome |
Type |
Descrição |
|---|---|---|---|
Elevation layer |
|
[raster] |
Digital Terrain Model raster layer |
Z factor |
|
[number] Default: 1.0 |
Vertical exaggeration. This parameter is useful when the Z units differ from the X and Y units, for example feet and meters. You can use this parameter to adjust for this. Increasing the value of this parameter will exaggerate the final result (making it steeper). The default is 1 (no exaggeration). |
Slope |
|
[raster] Default: |
Specify the output slope raster layer. One of:
The file encoding can also be changed here. |
Resultados
Label |
Nome |
Type |
Descrição |
|---|---|---|---|
Slope |
|
[raster] |
The output slope raster layer |
Python code
Algorithm ID: qgis:slope
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
The algorithm id is displayed when you hover over the algorithm in the Processing Toolbox. The parameter dictionary provides the parameter NAMEs and values. See Usando os algoritmos do processamento a partir da consola for details on how to run processing algorithms from the Python console.