14.1. The Vector Properties Dialog
The Layer Properties dialog for a vector layer provides general settings to manage appearance of layer features in the map (symbology, labeling, diagrams), interaction with the mouse (actions, map tips, form design). It also provides information about the layer.
To access the Layer Properties dialog:
In the Layers panel, double-click the layer or right-click and select Properties… from the pop-up menu;
Go to menu when the layer is selected.
The vector Layer Properties dialog provides the following sections:
|
||
|
|
|
External plugins[2] tabs |
[1] Also available in the Layer styling panel
[2] External plugins you install can optionally add tabs to this dialog. Those are not presented in this document. Refer to their documentation.
Tip
Share full or partial properties of the layer styles
The menu at the bottom of the dialog allows you to import or export these or part of these properties from/to several destination (file, clipboard, database). See Managing Custom Styles.
Note
Because properties (symbology, label, actions, default values, forms…) of embedded layers (see Nesting Projects) are pulled from the original project file and to avoid changes that may break this behavior, the layer properties dialog is made unavailable for these layers.
14.1.1. Information Properties
 The Information tab is read-only and represents an interesting
place to quickly grab summarized information and metadata on the current layer.
Provided information are:
The Information tab is read-only and represents an interesting
place to quickly grab summarized information and metadata on the current layer.
Provided information are:
based on the provider of the layer (format of storage, path, geometry type, data source encoding, extent…);
picked from the filled metadata (access, links, contacts, history…);
or related to its geometry (spatial extent, CRS…) or its attributes (number of fields, characteristics of each…).
14.1.2. Source Properties
 Use this tab to define general settings for the vector layer.
Use this tab to define general settings for the vector layer.
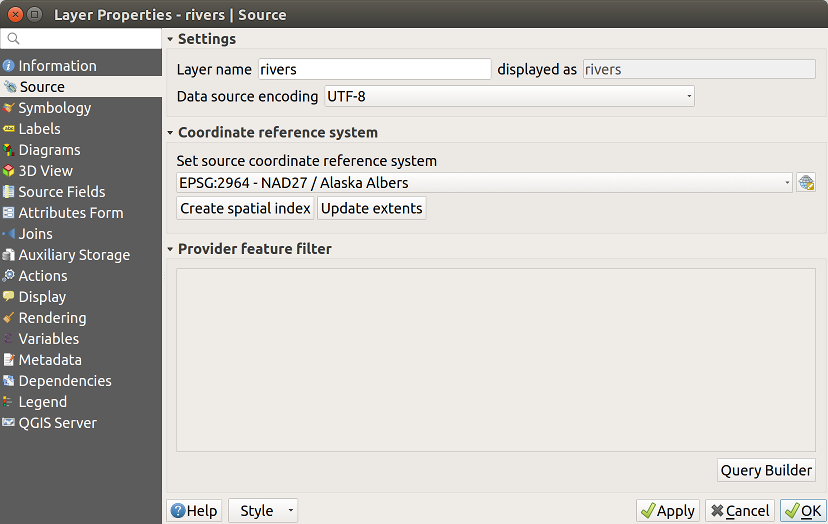
Fig. 14.1 Source tab in vector Layer Properties dialog
Other than setting the Layer name to display in the Layers Panel, available options include:
14.1.2.1. Coordinate Reference System
Displays the layer’s Coordinate Reference System (CRS). You can change the layer’s CRS, selecting a recently used one in the drop-down list or clicking on
 Select CRS button
(see Coordinate Reference System Selector). Use this process only if the CRS applied to the
layer is a wrong one or if none was applied.
If you wish to reproject your data into another CRS, rather use layer reprojection
algorithms from Processing or Save it into another layer.
Select CRS button
(see Coordinate Reference System Selector). Use this process only if the CRS applied to the
layer is a wrong one or if none was applied.
If you wish to reproject your data into another CRS, rather use layer reprojection
algorithms from Processing or Save it into another layer.Create spatial index (only for OGR-supported formats).
Update extents information for a layer.
14.1.2.2. Query Builder
The Query Builder dialog is accessible through the eponym button at the bottom of the Source tab in the Layer Properties dialog, under the Provider feature filter group.
The Query Builder provides an interface that allows you to define a subset of the features in the layer using a SQL-like WHERE clause and to display the result in the main window. As long as the query is active, only the features corresponding to its result are available in the project.
You can use one or more layer attributes to define the filter in the Query
Builder.
The use of more than one attribute is shown in Figure_vector_querybuilder.
In the example, the filter combines the attributes
toa(DateTimefield:cast("toa" as character) > '2017-05-17'andcast("toa" as character) < '2019-12-24T18:00:00'),name(Stringfield:"name" > 'S') andFID(Integerfield:FID > 10)
using the AND, OR and NOT operators and parenthesis.
This syntax (including the DateTime format for the toa field) works for
GeoPackage datasets.
The filter is made at the data provider (OGR, PostgreSQL, MSSQL…) level. So the syntax depends on the data provider (DateTime is for instance not supported for the ESRI Shapefile format). The complete expression:
cast("toa" as character) > '2017-05-17' AND
cast("toa" as character) < '2019-12-24T18:00:00' AND
NOT ("name" > 'S' OR FID > 10)
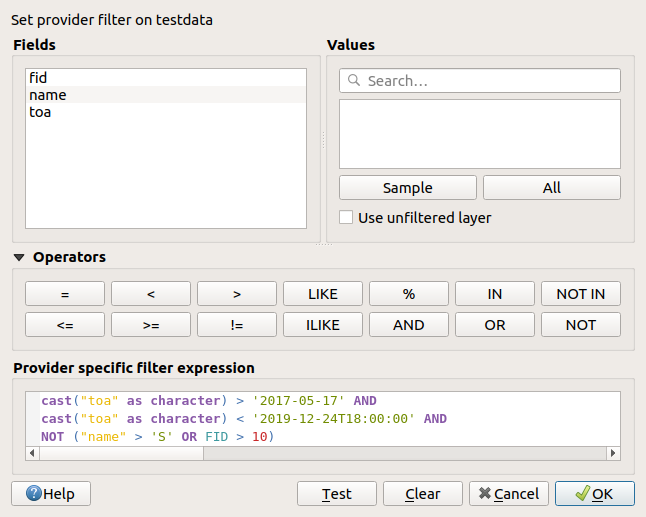
Fig. 14.2 Query Builder
You can also open the Query Builder dialog using the Filter… option from the menu or the layer contextual menu. The Fields, Values and Operators sections in the dialog help you to construct the SQL-like query exposed in the Provider specific filter expression box.
The Fields list contains all the fields of the layer. To add an attribute column to the SQL WHERE clause field, double-click its name or just type it into the SQL box.
The Values frame lists the values of the currently selected field. To list all unique values of a field, click the All button. To instead list the first 25 unique values of the column, click the Sample button. To add a value to the SQL WHERE clause field, double click its name in the Values list. You can use the search box at the top of the Values frame to easily browse and find attribute values in the list.
The Operators section contains all usable operators. To add an operator to
the SQL WHERE clause field, click the appropriate button. Relational operators
( = , > , …), string comparison operator (LIKE), and logical
operators (AND, OR, …) are available.
The Test button helps you check your query and displays a message box with the number of features satisfying the current query. Use the Clear button to wipe the SQL query and revert the layer to its original state (ie, fully load all the features).
When a filter is applied,
QGIS treats the resulting subset acts as if it were the entire layer. For
example if you applied the filter above for ‘Borough’ ("TYPE_2" = 'Borough'),
you can not display, query, save or edit Anchorage, because that is a
‘Municipality’ and therefore not part of the subset.
14.1.3. Symbology Properties
 The Symbology tab provides you with a comprehensive tool for
rendering and symbolizing your vector data. You can use tools that are
common to all vector data, as well as special symbolizing tools that were
designed for the different kinds of vector data. However all types share the
following dialog structure: in the upper part, you have a widget that helps
you prepare the classification and the symbol to use for features and at
the bottom the Layer rendering widget.
The Symbology tab provides you with a comprehensive tool for
rendering and symbolizing your vector data. You can use tools that are
common to all vector data, as well as special symbolizing tools that were
designed for the different kinds of vector data. However all types share the
following dialog structure: in the upper part, you have a widget that helps
you prepare the classification and the symbol to use for features and at
the bottom the Layer rendering widget.
Tip
Switch quickly between different layer representations
Using the menu at the bottom of the Layer Properties dialog, you can save as many styles as needed. A style is the combination of all properties of a layer (such as symbology, labeling, diagram, fields form, actions…) as you want. Then, simply switch between styles from the context menu of the layer in Layers Panel to automatically get different representations of your data.
Tip
Export vector symbology
You have the option to export vector symbology from QGIS into Google *.kml, *.dxf and MapInfo *.tab files. Just open the right mouse menu of the layer and click on to specify the name of the output file and its format. In the dialog, use the menu to save the symbology either as or as . If you have used symbol layers, it is recommended to use the second setting.
14.1.3.1. Features rendering
The renderer is responsible for drawing a feature together with the correct symbol. Regardless layer geometry type, there are four common types of renderers: single symbol, categorized, graduated and rule-based. For point layers, there are a point displacement and a heatmap renderers available while polygon layers can also be rendered with the inverted polygons and 2.5 D renderers.
There is no continuous color renderer, because it is in fact only a special case of the graduated renderer. The categorized and graduated renderers can be created by specifying a symbol and a color ramp - they will set the colors for symbols appropriately. For each data type (points, lines and polygons), vector symbol layer types are available. Depending on the chosen renderer, the dialog provides different additional sections.
Note
If you change the renderer type when setting the style of a vector layer the settings you made for the symbol will be maintained. Be aware that this procedure only works for one change. If you repeat changing the renderer type the settings for the symbol will get lost.
14.1.3.1.1. Single Symbol Renderer
The  Single Symbol renderer is used to render
all features of the layer using a single user-defined symbol.
See The Symbol Selector for further information about symbol representation.
Single Symbol renderer is used to render
all features of the layer using a single user-defined symbol.
See The Symbol Selector for further information about symbol representation.
Fig. 14.3 Single symbol line properties
14.1.3.1.2. No Symbols Renderer
The  No Symbols renderer is a special use case of the
Single Symbol renderer as it applies the same rendering to all features.
Using this renderer, no symbol will be drawn for features,
but labeling, diagrams and other non-symbol parts will still be shown.
No Symbols renderer is a special use case of the
Single Symbol renderer as it applies the same rendering to all features.
Using this renderer, no symbol will be drawn for features,
but labeling, diagrams and other non-symbol parts will still be shown.
Selections can still be made on the layer in the canvas and selected features will be rendered with a default symbol. Features being edited will also be shown.
This is intended as a handy shortcut for layers which you only want to show labels or diagrams for, and avoids the need to render symbols with totally transparent fill/border to achieve this.
14.1.3.1.3. Categorized Renderer
The  Categorized renderer is used to render the
features of a layer, using a user-defined symbol whose aspect reflects the
discrete values of a field or an expression.
Categorized renderer is used to render the
features of a layer, using a user-defined symbol whose aspect reflects the
discrete values of a field or an expression.
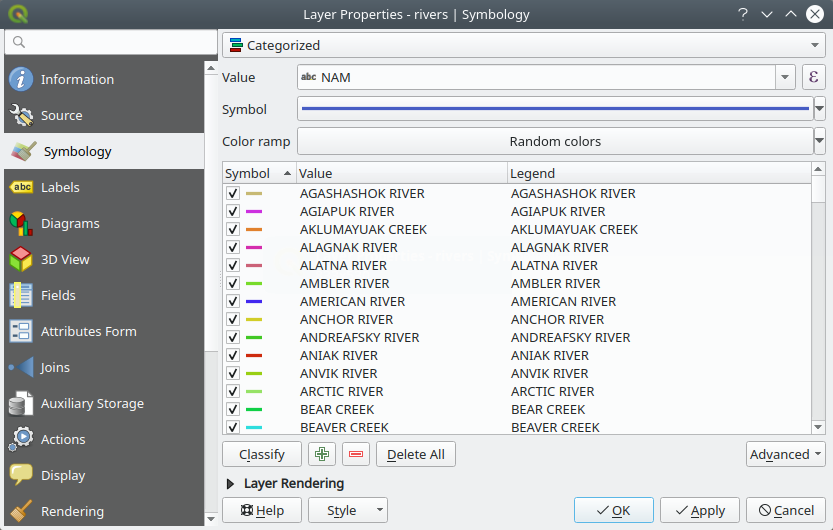
Fig. 14.4 Categorized Symbolizing options
To use categorized symbology for a layer:
Select the Value of classification: it can be an existing field or an expression you can type in the box or build using the associated
 button. Using expressions for categorizing
avoids the need to create an ad hoc field for symbology purposes (eg, if your
classification criteria are derived from one or more attributes).
button. Using expressions for categorizing
avoids the need to create an ad hoc field for symbology purposes (eg, if your
classification criteria are derived from one or more attributes).The expression used to classify features can be of any type; eg, it can:
be a comparison. In this case, QGIS returns values
1(True) and0(False). Some examples:myfield >= 100 $id = @atlas_featureid myfield % 2 = 0 within( $geometry, @atlas_geometry )
combine different fields:
concat( field_1, ' ', field_2 )
be a calculation on fields:
myfield % 2 year( myfield ) field_1 + field_2 substr( field_1, -3 )
be used to transform linear values to discrete classes, e.g.:
CASE WHEN x > 1000 THEN 'Big' ELSE 'Small' END
combine several discrete values into a single category, e.g.:
CASE WHEN building IN ('residence', 'mobile home') THEN 'residential' WHEN building IN ('commercial', 'industrial') THEN 'Commercial and Industrial' END
Tip
While you can use any kind of expression to categorize features, for some complex expressions it might be simpler to use rule-based rendering.
Configure the Symbol, which will be used as base symbol for all the classes;
Indicate the Color ramp, ie the range of colors from which the color applied to each symbol is selected.
Besides the common options of the color ramp widget, you can apply a
 Random Color Ramp to the categories.
You can click the Shuffle Random Colors entry to regenerate a new set
of random colors if you are not satisfied.
Random Color Ramp to the categories.
You can click the Shuffle Random Colors entry to regenerate a new set
of random colors if you are not satisfied.Then click on the Classify button to create classes from the distinct values of the provided field or expression.
Apply the changes if the live update is not in use and each feature on the map canvas will be rendered with the symbol of its class.
By default, QGIS appends an all other values class to the list. While empty at the beginning, this class is used as a default class for any feature not falling into the other classes (eg, when you create features with new values for the classification field / expression).
Further tweaks can be done to the default classification:
You can
 Add new categories,
Add new categories,  Remove
selected categories or Delete All of them.
Remove
selected categories or Delete All of them.A class can be disabled by unchecking the checkbox to the left of the class name; the corresponding features are hidden on the map.
Drag-and-drop the rows to reorder the classes
To change the symbol, the value or the legend of a class, double click the item.
Right-clicking over selected item(s) shows a contextual menu to:
Copy Symbol and Paste Symbol, a convenient way to apply the item’s representation to others
Change Color… of the selected symbol(s)
Change Opacity… of the selected symbol(s)
Change Output Unit… of the selected symbol(s)
Change Width… of the selected line symbol(s)
Change Size… of the selected point symbol(s)
Change Angle… of the selected point symbol(s)
Merge Categories: Groups multiple selected categories into a single one. This allows simpler styling of layers with a large number of categories, where it may be possible to group numerous distinct categories into a smaller and more manageable set of categories which apply to multiple values.
Tip
Since the symbol kept for the merged categories is the one of the topmost selected category in the list, you may want to move the category whose symbol you wish to reuse to the top before merging.
Unmerge Categories that were previously merged
Match to saved symbols: Using the symbols library, assigns to each category a symbol whose name represents the classification value of the category
Match to symbols from file…: Provided a file with symbols, assigns to each category a symbol whose name represents the classification value of the category
Symbol levels… to define the order of symbols rendering.
Tip
Edit categories directly from the Layers panel
When a layer symbology is based on a categorized, graduated or rule-based symbology mode, you can edit each of the categories from the Layers Panel. Right-click on a sub-item of the layer and you will:
Modify the symbol color thanks to the color selector wheel
Edit symbol… from the symbol selector dialog
Copy symbol
Paste symbol
14.1.3.1.4. Graduated Renderer
The  Graduated renderer is used to render
all the features from a layer, using an user-defined symbol whose color or size
reflects the assignment of a selected feature’s attribute to a class.
Graduated renderer is used to render
all the features from a layer, using an user-defined symbol whose color or size
reflects the assignment of a selected feature’s attribute to a class.
Like the Categorized Renderer, the Graduated Renderer allows you to define rotation and size scale from specified columns.
Also, analogous to the Categorized Renderer, it allows you to select:
The value (using the fields listbox or the
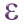 Set value expression function)
Set value expression function)The symbol (using the Symbol selector dialog)
The legend format and the precision
The method to use to change the symbol: color or size
The colors (using the color Ramp list) if the color method is selected
The size (using the size domain and its unit)
Then you can use the Histogram tab which shows an interactive histogram of the values from the assigned field or expression. Class breaks can be moved or added using the histogram widget.
Note
You can use Statistical Summary panel to get more information on your vector layer. See Statistical Summary Panel.
Back to the Classes tab, you can specify the number of classes and also the mode for classifying features within the classes (using the Mode list). The available modes are:
Equal Interval: each class has the same size (e.g. values from 0 to 16 and 4 classes, each class has a size of 4).
Quantile: each class will have the same number of element inside (the idea of a boxplot).
Natural Breaks (Jenks): the variance within each class is minimal while the variance between classes is maximal.
Standard Deviation: classes are built depending on the standard deviation of the values.
Pretty Breaks: Computes a sequence of about n+1 equally spaced nice values which cover the range of the values in x. The values are chosen so that they are 1, 2 or 5 times a power of 10. (based on pretty from the R statistical environment https://astrostatistics.psu.edu/datasets/R/html/base/html/pretty.html)
The listbox in the center part of the Symbology tab lists the classes together with their ranges, labels and symbols that will be rendered.
Click on Classify button to create classes using the chosen mode. Each classes can be disabled unchecking the checkbox at the left of the class name.
To change symbol, value and/or label of the class, just double click on the item you want to change.
Right-clicking over selected item(s) shows a contextual menu to:
Copy Symbol and Paste Symbol, a convenient way to apply the item’s representation to others
Change Color… of the selected symbol(s)
Change Opacity… of the selected symbol(s)
Change Output Unit… of the selected symbol(s)
Change Width… of the selected line symbol(s)
Change Size… of the selected point symbol(s)
Change Angle… of the selected point symbol(s)
The example in figure_graduated_symbology shows the graduated rendering dialog for the major_rivers layer of the QGIS sample dataset.
Fig. 14.5 Graduated Symbolizing options
Tip
Thematic maps using an expression
Categorized and graduated thematic maps can be created using the result
of an expression. In the properties dialog for vector layers, the attribute
chooser is extended with a ![]() Set column expression function.
So you don’t need to write the classification attribute
to a new column in your attribute table if you want the classification
attribute to be a composite of multiple fields, or a formula of some sort.
Set column expression function.
So you don’t need to write the classification attribute
to a new column in your attribute table if you want the classification
attribute to be a composite of multiple fields, or a formula of some sort.
14.1.3.1.5. Proportional Symbol and Multivariate Analysis
Proportional Symbol and Multivariate Analysis are not rendering types available from the Symbology rendering drop-down list. However with the data-defined override options applied over any of the previous rendering options, QGIS allows you to display your point and line data with such representation.
Creating proportional symbol
To apply a proportional rendering:
First apply to the layer the single symbol renderer.
Then set the symbol to apply to the features.
Select the item at the upper level of the symbol tree, and use the
 Data-defined override button next
to the Size (for point layer) or Width (for line
layer) option.
Data-defined override button next
to the Size (for point layer) or Width (for line
layer) option.Select a field or enter an expression, and for each feature, QGIS will apply the output value to the property and proportionally resize the symbol in the map canvas.
If need be, use the Size assistant… option of the
 menu to apply some transformation (exponential, flannery…) to the symbol
size rescaling (see Using the data-defined assistant interface for more details).
menu to apply some transformation (exponential, flannery…) to the symbol
size rescaling (see Using the data-defined assistant interface for more details).
You can choose to display the proportional symbols in the Layers panel and the print layout legend item: unfold the Advanced drop-down list at the bottom of the main dialog of the Symbology tab and select Data-defined size legend… to configure the legend items (see Data-defined size legend for details).
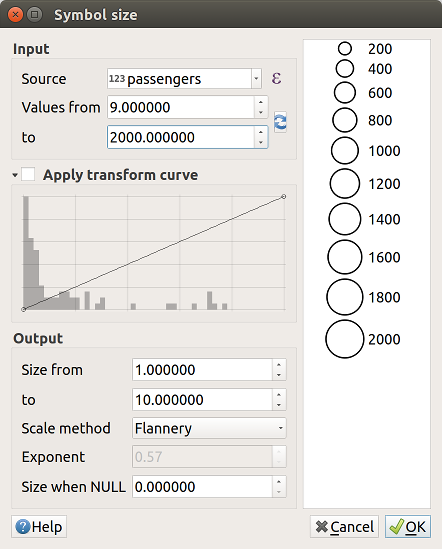
Fig. 14.6 Scaling airports size based on elevation of the airport
Creating multivariate analysis
A multivariate analysis rendering helps you evaluate the relationship between two or more variables e.g., one can be represented by a color ramp while the other is represented by a size.
The simplest way to create multivariate analysis in QGIS is to:
First apply a categorized or graduated rendering on a layer, using the same type of symbol for all the classes.
Then, apply a proportional symbology on the classes:
Click on the Change button above the classification frame: you get the The Symbol Selector dialog.
Rescale the size or width of the symbol layer using the
 data defined override widget as seen above.
data defined override widget as seen above.
Like the proportional symbol, the scaled symbology can be added to the layer tree, on top of the categorized or graduated classes symbols using the data defined size legend feature. And both representation are also available in the print layout legend item.
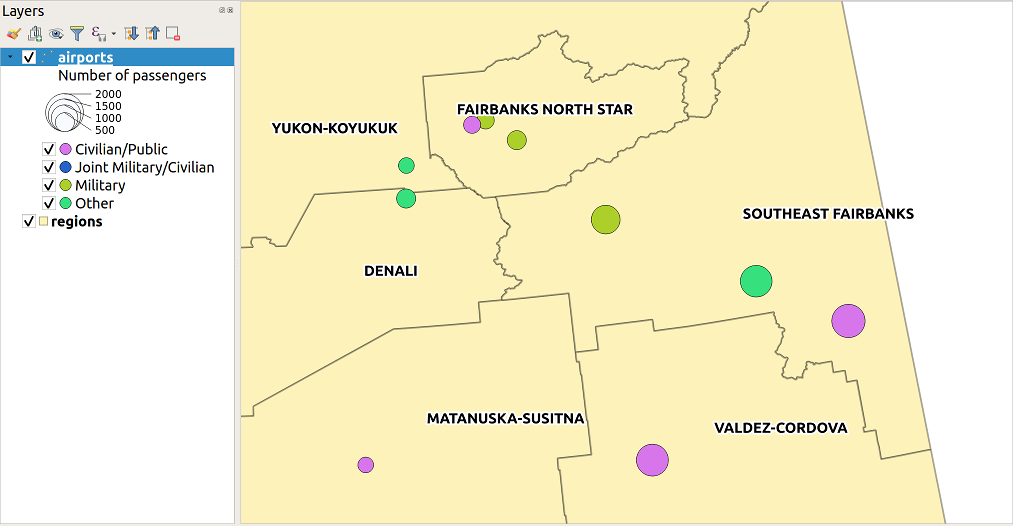
Fig. 14.7 Multivariate example with scaled size legend
14.1.3.1.6. Rule-based Renderer
The  Rule-based renderer is used to render
all the features from a layer,
using rule-based symbols whose aspect reflects the assignment of a selected
feature’s attribute to a class. The rules are based on SQL statements and can
be nested.
The dialog allows rule grouping by filter or scale, and you can decide
if you want to enable symbol levels or use only the first-matched rule.
Rule-based renderer is used to render
all the features from a layer,
using rule-based symbols whose aspect reflects the assignment of a selected
feature’s attribute to a class. The rules are based on SQL statements and can
be nested.
The dialog allows rule grouping by filter or scale, and you can decide
if you want to enable symbol levels or use only the first-matched rule.
To create a rule:
Activate an existing row by double-clicking it (by default, QGIS adds a symbol without a rule when the rendering mode is enabled) or click the
 Edit rule or
Edit rule or  Add rule button.
Add rule button.In the Edit Rule dialog that opens, you can define a label to help you identify each rule. This is the label that will be displayed in the Layers Panel and also in the print composer legend.
Manually enter an expression in the text box next to the
 Filter option or press the
Filter option or press the  button next to it to open
the expression string builder dialog.
button next to it to open
the expression string builder dialog.Use the provided functions and the layer attributes to build an expression to filter the features you’d like to retrieve. Press the Test button to check the result of the query.
You can enter a longer label to complete the rule description.
You can use the
 Scale Range option to set scales at which
the rule should be applied.
Scale Range option to set scales at which
the rule should be applied.Finally, configure the symbol to use for these features.
And press OK.
A new row summarizing the rule is added to the Layer Properties dialog. You can create as many rules as necessary following the steps above or copy pasting an existing rule. Drag-and-drop the rules on top of each other to nest them and refine the upper rule features in subclasses.
Selecting a rule, you can also organize its features in subclasses using the Refine selected rules drop-down menu. Automated rule refinement can be based on:
scales;
categories: applying a categorized renderer;
or ranges: applying a graduated renderer.
Refined classes appear like sub-items of the rule, in a tree hierarchy and like above, you can set symbology of each class.
In the Edit rule dialog, you can avoid writing all the rules and
make use of the  Else option to catch all the
features that do not match any of the other rules, at the same level. This
can also be achieved by writing
Else option to catch all the
features that do not match any of the other rules, at the same level. This
can also be achieved by writing Else in the Rule column of the
dialog.
Right-clicking over selected item(s) shows a contextual menu to:
Copy and Paste, a convenient way to create new item(s) based on existing item(s)
Copy Symbol and Paste Symbol, a convenient way to apply the item’s representation to others
Change Color… of the selected symbol(s)
Change Opacity… of the selected symbol(s)
Change Output Unit… of the selected symbol(s)
Change Width… of the selected line symbol(s)
Change Size… of the selected point symbol(s)
Change Angle… of the selected point symbol(s)
Refine Current Rule: open a submenu that allows to refine the current rule with scales, categories (categorized renderer) or Ranges (graduated renderer).
The created rules also appear in a tree hierarchy in the map legend. Double-click the rules in the map legend and the Symbology tab of the layer properties appears showing the rule that is the background for the symbol in the tree.
The example in figure_rule_based_symbology shows the rule-based rendering dialog for the rivers layer of the QGIS sample dataset.
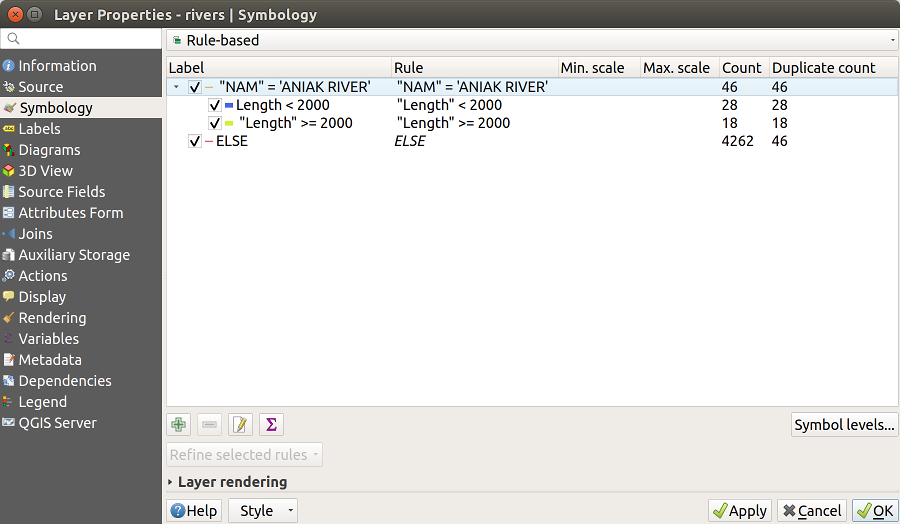
Fig. 14.8 Rule-based Symbolizing options
14.1.3.1.7. Point displacement Renderer
The  Point Displacement renderer works to
visualize all features of a point layer, even if they have the same location.
To do this, the renderer takes the points falling in a given Distance
tolerance from each other and places them around their barycenter following
different Placement methods:
Point Displacement renderer works to
visualize all features of a point layer, even if they have the same location.
To do this, the renderer takes the points falling in a given Distance
tolerance from each other and places them around their barycenter following
different Placement methods:
Ring: places all the features on a circle whose radius depends on the number of features to display.
Concentric rings: uses a set of concentric circles to show the features.
Grid: generates a regular grid with a point symbol at each intersection.
The Center symbol widget helps you customize the symbol and color of the middle point. For the distributed points symbols, you can apply any of the No symbols, Single symbol, Categorized, Graduated or Rule-based renderer using the Renderer drop-down list and customize them using the Renderer Settings… button.
While the minimal spacing of the Displacement lines depends on the point symbol renderer’s, you can still customize some of its settings such as the Stroke width, Stroke color and Size adjustment (eg, to add more spacing between the rendered points).
Use the Labels group options to perform points labeling: the labels are placed near the displaced position of the symbol, and not at the feature real position. Other than the Label attribute, Label font and Label color, you can set the Minimum map scale to display the labels.
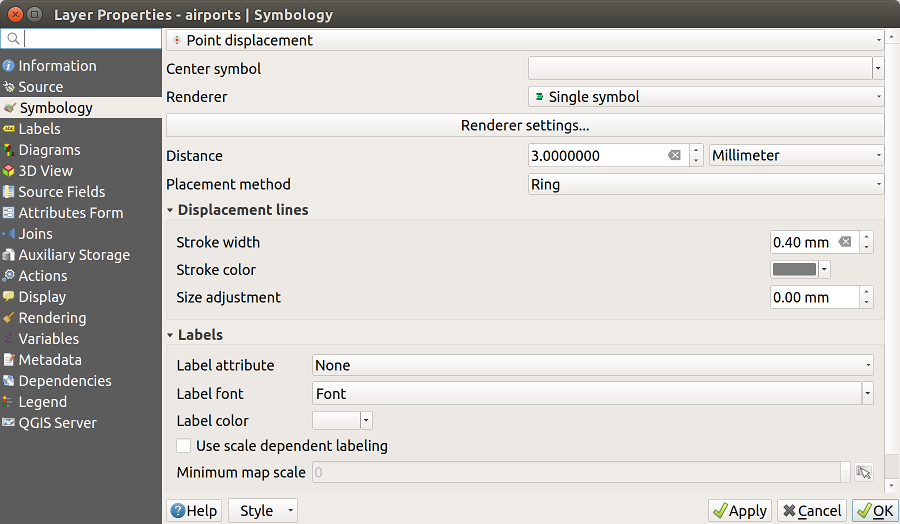
Fig. 14.9 Point displacement dialog
Note
Point Displacement renderer does not alter feature geometry, meaning that points are not moved from their position. They are still located at their initial place. Changes are only visual, for rendering purpose. Use instead the Processing Points displacement algorithm if you want to create displaced features.
14.1.3.1.8. Point Cluster Renderer
Unlike the  Point Displacement renderer
which blows up nearest or overlaid point features placement, the
Point Displacement renderer
which blows up nearest or overlaid point features placement, the  Point Cluster renderer groups nearby points into a single
rendered marker symbol. Based on a specified Distance, points
that fall within from each others are merged into a single symbol.
Points aggregation is made based on the closest group being formed, rather
than just assigning them the first group within the search distance.
Point Cluster renderer groups nearby points into a single
rendered marker symbol. Based on a specified Distance, points
that fall within from each others are merged into a single symbol.
Points aggregation is made based on the closest group being formed, rather
than just assigning them the first group within the search distance.
From the main dialog, you can:
set the symbol to represent the point cluster in the Cluster symbol; the default rendering displays the number of aggregated features thanks to the
@cluster_sizevariable on Font marker symbol layer.use the Renderer drop-down list to apply any of the other feature rendering types to the layer (single, categorized, rule-based…). Then, push the Renderer Settings… button to configure features’ symbology as usual. Note that this renderer is only visible on features that are not clustered. Also, when the symbol color is the same for all the point features inside a cluster, that color sets the
@cluster_colorvariable of the cluster.
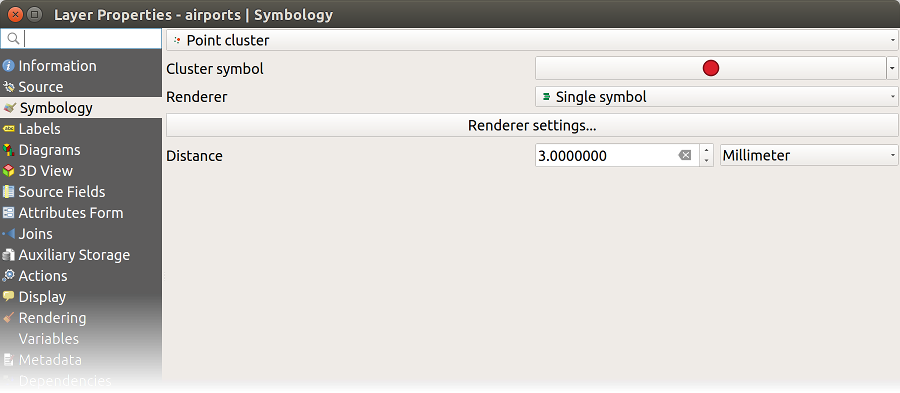
Fig. 14.10 Point Cluster dialog
Note
Point Cluster renderer does not alter feature geometry, meaning that points are not moved from their position. They are still located at their initial place. Changes are only visual, for rendering purpose. Use instead the Processing K-means clustering or DBSCAN clustering algorithm if you want to create cluster-based features.
14.1.3.1.9. Inverted Polygon Renderer
The  Inverted Polygon renderer allows user
to define a symbol to fill in
outside of the layer’s polygons. As above you can select subrenderers, namely
Single symbol, Graduated, Categorized, Rule-Based or 2.5D renderer.
Inverted Polygon renderer allows user
to define a symbol to fill in
outside of the layer’s polygons. As above you can select subrenderers, namely
Single symbol, Graduated, Categorized, Rule-Based or 2.5D renderer.
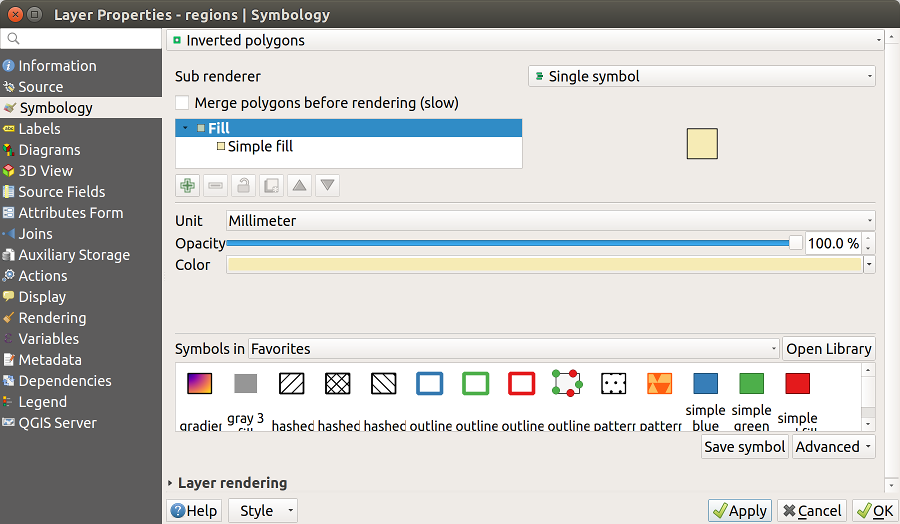
Fig. 14.11 Inverted Polygon dialog
14.1.3.1.10. Heatmap Renderer
With the  Heatmap renderer you can create live
dynamic heatmaps for (multi)point layers.
You can specify the heatmap radius in millimeters, points, pixels, map units or
inches, choose and edit a color ramp for the heatmap style and use a slider for
selecting a trade-off between render speed and quality. You can also define a
maximum value limit and give a weight to points using a field or an expression.
When adding or removing a feature the heatmap renderer updates the heatmap style
automatically.
Heatmap renderer you can create live
dynamic heatmaps for (multi)point layers.
You can specify the heatmap radius in millimeters, points, pixels, map units or
inches, choose and edit a color ramp for the heatmap style and use a slider for
selecting a trade-off between render speed and quality. You can also define a
maximum value limit and give a weight to points using a field or an expression.
When adding or removing a feature the heatmap renderer updates the heatmap style
automatically.
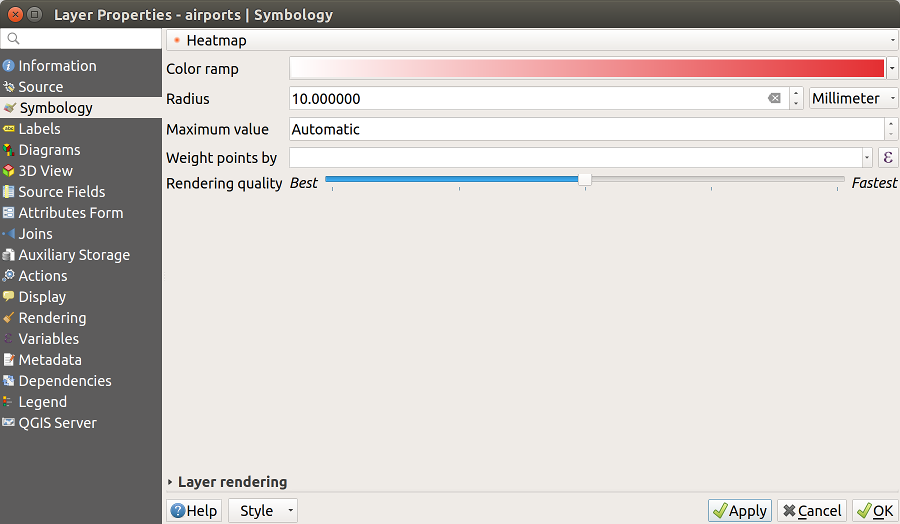
Fig. 14.12 Heatmap dialog
14.1.3.1.11. 2.5D Renderer
Using the  2.5D renderer it’s possible to create
a 2.5D effect on your layer’s features.
You start by choosing a Height value (in map units). For that
you can use a fixed value, one of your layer’s fields, or an expression. You also
need to choose an Angle (in degrees) to recreate the viewer position
(0° means west, growing in counter clock wise). Use advanced configuration options
to set the Roof Color and Wall Color. If you would like
to simulate solar radiation on the features walls, make sure to check the
2.5D renderer it’s possible to create
a 2.5D effect on your layer’s features.
You start by choosing a Height value (in map units). For that
you can use a fixed value, one of your layer’s fields, or an expression. You also
need to choose an Angle (in degrees) to recreate the viewer position
(0° means west, growing in counter clock wise). Use advanced configuration options
to set the Roof Color and Wall Color. If you would like
to simulate solar radiation on the features walls, make sure to check the
 Shade walls based on aspect option. You can also
simulate a shadow by setting a Color and Size (in map
units).
Shade walls based on aspect option. You can also
simulate a shadow by setting a Color and Size (in map
units).
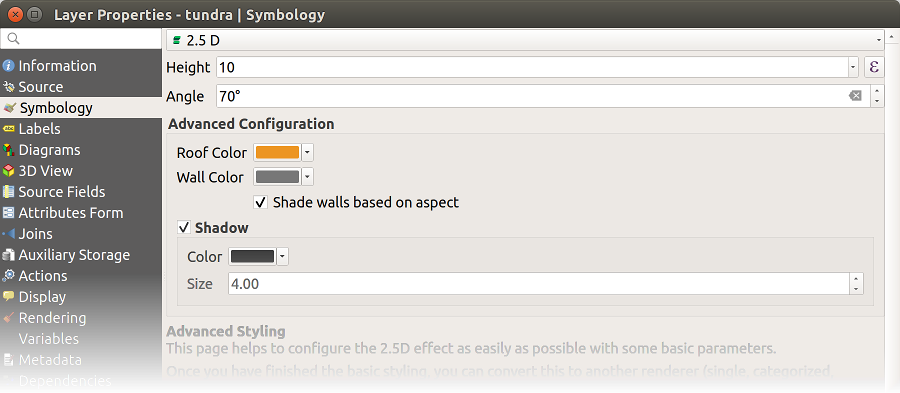
Fig. 14.13 2.5D dialog
Tip
Using 2.5D effect with other renderers
Once you have finished setting the basic style on the 2.5D renderer, you can convert this to another renderer (single, categorized, graduated). The 2.5D effects will be kept and all other renderer specific options will be available for you to fine tune them (this way you can have for example categorized symbols with a nice 2.5D representation or add some extra styling to your 2.5D symbols). To make sure that the shadow and the “building” itself do not interfere with other nearby features, you may need to enable Symbols Levels ( ). The 2.5D height and angle values are saved in the layer’s variables, so you can edit it afterwards in the variables tab of the layer’s properties dialog.
14.1.3.2. Layer rendering
From the Symbology tab, you can also set some options that invariably act on all features of the layer:
Opacity
 : You can make the underlying layer in
the map canvas visible with this tool. Use the slider to adapt the visibility
of your vector layer to your needs. You can also make a precise definition of
the percentage of visibility in the menu beside the slider.
: You can make the underlying layer in
the map canvas visible with this tool. Use the slider to adapt the visibility
of your vector layer to your needs. You can also make a precise definition of
the percentage of visibility in the menu beside the slider.Blending mode at the Layer and Feature levels: You can achieve special rendering effects with these tools that you may previously only know from graphics programs. The pixels of your overlaying and underlaying layers are mixed through the settings described in Blending Modes.
Apply paint effects on all the layer features with the Draw Effects button.
Control feature rendering order allows you, using features attributes, to define the z-order in which they shall be rendered. Activate the checkbox and click on the
 button beside.
You then get the Define Order dialog in which you:
button beside.
You then get the Define Order dialog in which you:Choose a field or build an expression to apply to the layer features.
Set in which order the fetched features should be sorted, i.e. if you choose Ascending order, the features with lower value are rendered under those with higher value.
Define when features returning NULL value should be rendered: first (bottom) or last (top).
Repeat the above steps as many times as rules you wish to use.
The first rule is applied to all the features in the layer, z-ordering them according to their returned value. Then, within each group of features with the same value (including those with NULL value) and thus the same z-level, the next rule is applied to sort them. And so on…
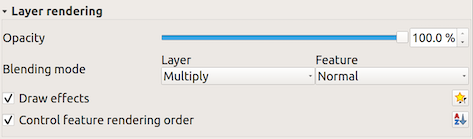
Fig. 14.14 Layer rendering options
14.1.3.3. Other Settings
14.1.3.3.1. Symbol levels
For renderers that allow stacked symbol layers (only heatmap doesn’t) there is an option to control the rendering order of each symbol’s levels.
For most of the renderers, you can access the Symbols levels option by clicking the Advanced button below the saved symbols list and choosing Symbol levels. For the Rule-based Renderer the option is directly available through Symbols Levels… button, while for Point displacement Renderer renderer the same button is inside the Rendering settings dialog.
To activate symbols levels, select the  Enable symbol
levels. Each row will show up a small sample of the combined symbol, its label
and the individual symbols layer divided into columns with a number next to it.
The numbers represent the rendering order level in which the symbol layer
will be drawn. Lower values levels are drawn first, staying at the bottom, while
higher values are drawn last, on top of the others.
Enable symbol
levels. Each row will show up a small sample of the combined symbol, its label
and the individual symbols layer divided into columns with a number next to it.
The numbers represent the rendering order level in which the symbol layer
will be drawn. Lower values levels are drawn first, staying at the bottom, while
higher values are drawn last, on top of the others.
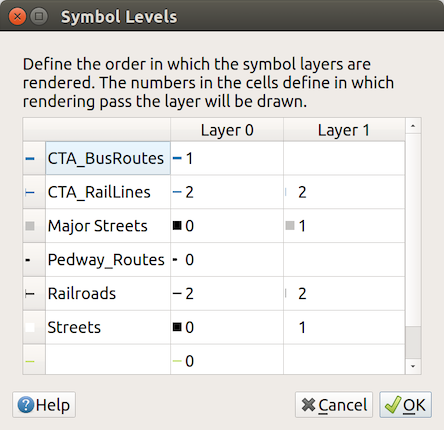
Fig. 14.15 Symbol levels dialog
Note
If symbols levels are deactivated, the complete symbols will be drawn according to their respective features order. Overlapping symbols will simply obfuscate to other below. Besides, similar symbols won’t “merge” with each other.
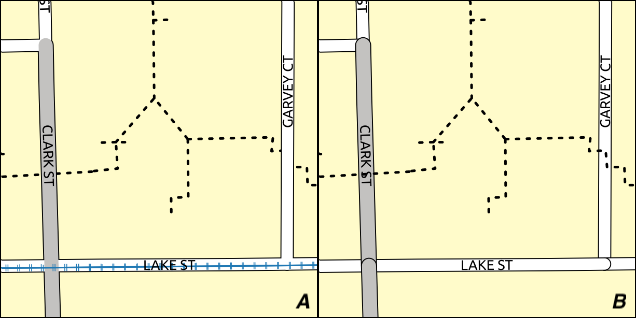
Fig. 14.16 Symbol levels activated (A) and deactivated (B) difference
14.1.3.3.2. Data-defined size legend
When a layer is rendered with the proportional symbol or the multivariate rendering or when a scaled size diagram is applied to the layer, you can allow the display of the scaled symbols in both the Layers panel and the print layout legend.
To enable the Data-defined Size Legend dialog to render symbology, select the eponym option in the Advanced button below the saved symbols list. For diagrams, the option is available under the Legend tab. The dialog provides the following options to:
select the type of legend:
 Legend not enabled,
Legend not enabled,
 Separated legend items and
Separated legend items and  Collapsed legend. For the latter option, you can select whether
the legend items are aligned at the Bottom or at the Center;
Collapsed legend. For the latter option, you can select whether
the legend items are aligned at the Bottom or at the Center;set the symbol to use for legend representation;
insert the title in the legend;
resize the classes to use: by default, QGIS provides you with a legend of five classes (based on natural pretty breaks) but you can apply your own classification using the
 Manual size classes option.
Use the
Manual size classes option.
Use the  and
and  buttons to set your custom classes
values and labels.
buttons to set your custom classes
values and labels.
A preview of the legend is displayed in the right panel of the dialog and updated as you set the parameters. For collapsed legend, a leader line from the horizontal center of the symbol to the corresponding legend text is drawn.
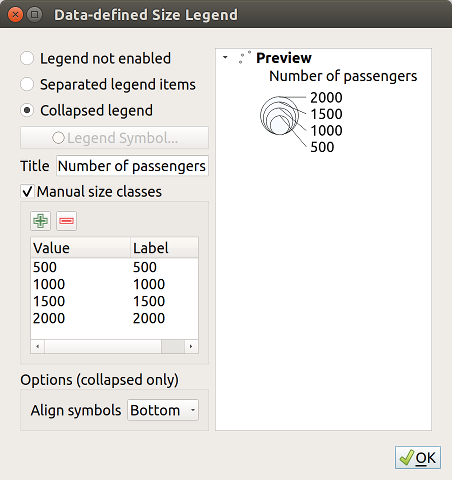
Fig. 14.17 Setting size scaled legend
Note
Currently, data-defined size legend for layer symbology can only be applied to point layer using single, categorized or graduated symbology.
14.1.3.3.3. Draw effects
In order to improve layer rendering and avoid (or at least reduce)
the resort to other software for final rendering of maps, QGIS provides another
powerful functionality: the ![]() Draw Effects options,
which adds paint effects for customizing the visualization of vector layers.
Draw Effects options,
which adds paint effects for customizing the visualization of vector layers.
The option is available in the dialog, under the Layer rendering group (applying to the whole layer) or in symbol layer properties (applying to corresponding features). You can combine both usage.
Paint effects can be activated by checking the  Draw effects option
and clicking the
Draw effects option
and clicking the ![]() Customize effects button. That will open
the Effect Properties Dialog (see figure_effects_source). The following
effect types, with custom options are available:
Customize effects button. That will open
the Effect Properties Dialog (see figure_effects_source). The following
effect types, with custom options are available:
Source: Draws the feature’s original style according to the configuration of the layer’s properties. The Opacity of its style can be adjusted as well as the Blend mode and Draw mode. These are common properties for all types of effects.
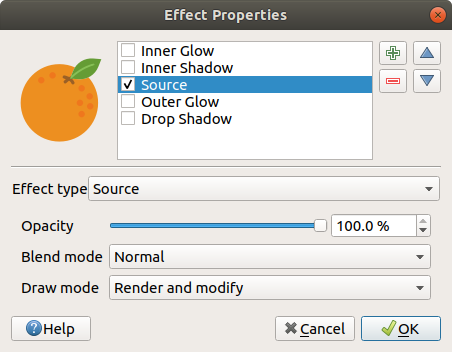
Fig. 14.18 Draw Effects: Source dialog
Blur: Adds a blur effect on the vector layer. The custom options that you can change are the Blur type (Stack blur (fast) or Gaussian blur (quality)) and the Blur strength.
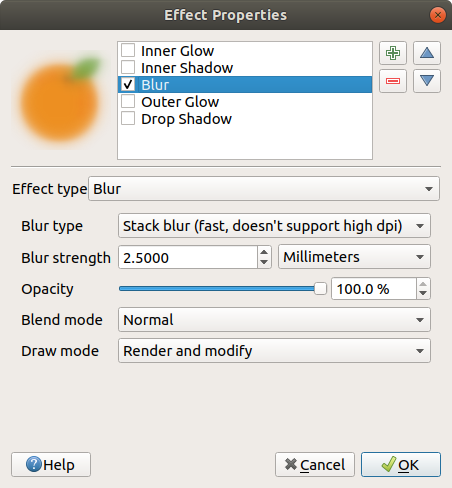
Fig. 14.19 Draw Effects: Blur dialog
Colorise: This effect can be used to make a version of the style using one single hue. The base will always be a grayscale version of the symbol and you can:
Use the
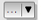 Grayscale to select how to create it:
options are ‘By lightness’, ‘By luminosity’, ‘By average’ and ‘Off’.
Grayscale to select how to create it:
options are ‘By lightness’, ‘By luminosity’, ‘By average’ and ‘Off’.If
 Colorise is selected, it will be possible to mix
another color and choose how strong it should be.
Colorise is selected, it will be possible to mix
another color and choose how strong it should be.Control the Brightness, Contrast and Saturation levels of the resulting symbol.
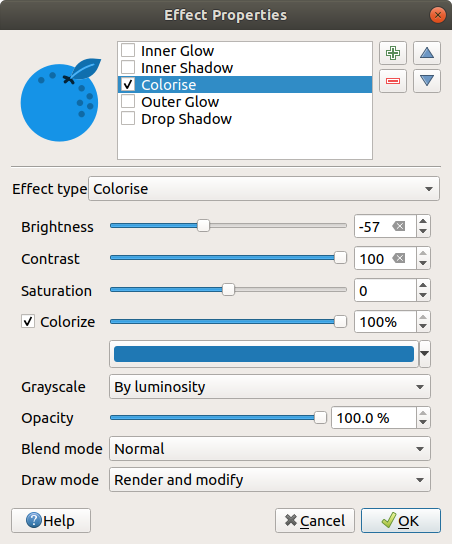
Fig. 14.20 Draw Effects: Colorize dialog
Drop Shadow: Using this effect adds a shadow on the feature, which looks like adding an extra dimension. This effect can be customized by changing the Offset angle and distance, determining where the shadow shifts towards to and the proximity to the source object. also has the option to change the Blur radius and the Color of the effect.
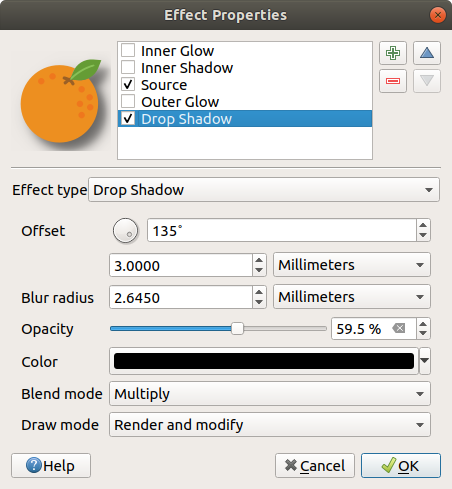
Fig. 14.21 Draw Effects: Drop Shadow dialog
Inner Shadow: This effect is similar to the Drop Shadow effect, but it adds the shadow effect on the inside of the edges of the feature. The available options for customization are the same as the Drop Shadow effect.
Fig. 14.22 Draw Effects: Inner Shadow dialog
Inner Glow: Adds a glow effect inside the feature. This effect can be customized by adjusting the Spread (width) of the glow, or the Blur radius. The latter specifies the proximity from the edge of the feature where you want any blurring to happen. Additionally, there are options to customize the color of the glow using a Single color or a Color ramp.
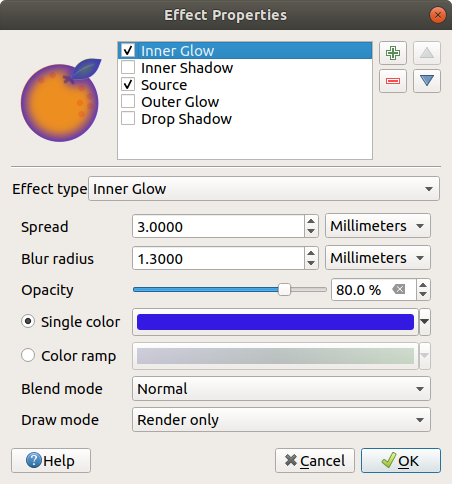
Fig. 14.23 Draw Effects: Inner Glow dialog
Outer Glow: This effect is similar to the Inner Glow effect, but it adds the glow effect on the outside of the edges of the feature. The available options for customization are the same as the Inner Glow effect.
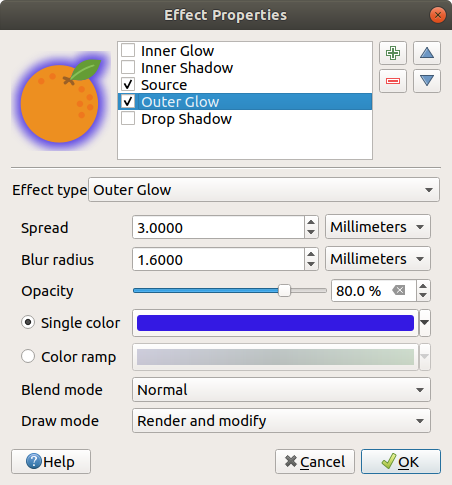
Fig. 14.24 Draw Effects: Outer Glow dialog
Transform: Adds the possibility of transforming the shape of the symbol. The first options available for customization are the Reflect horizontal and Reflect vertical, which actually create a reflection on the horizontal and/or vertical axes. The other options are:
Shear X,Y: Slants the feature along the X and/or Y axis.
Scale X,Y: Enlarges or minimizes the feature along the X and/or Y axis by the given percentage.
Rotation: Turns the feature around its center point.
and Translate X,Y changes the position of the item based on a distance given on the X and/or Y axis.
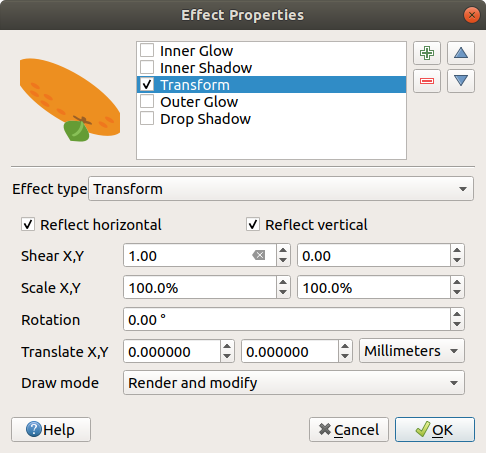
Fig. 14.25 Draw Effects: Transform dialog
One or more effect types can be used at the same time. You (de)activate an effect
using its checkbox in the effects list. You can change the selected effect type by
using the  Effect type option. You can reorder the effects
using
Effect type option. You can reorder the effects
using  Move up and
Move up and 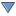 Move down
buttons, and also add/remove effects using the
Move down
buttons, and also add/remove effects using the  Add new effect
and
Add new effect
and  Remove effect buttons.
Remove effect buttons.
There are some common options available for all draw effect types. Opacity and Blend mode options work similar to the ones described in Layer rendering and can be used in all draw effects except for the transform one.
There is also a  Draw mode option available for
every effect, and you can choose whether to render and/or modify the
symbol, following some rules:
Draw mode option available for
every effect, and you can choose whether to render and/or modify the
symbol, following some rules:
Effects render from top to bottom.
Render only mode means that the effect will be visible.
Modifier only mode means that the effect will not be visible but the changes that it applies will be passed to the next effect (the one immediately below).
The Render and Modify mode will make the effect visible and pass any changes to the next effect. If the effect is at the top of the effects list or if the immediately above effect is not in modify mode, then it will use the original source symbol from the layers properties (similar to source).
14.1.4. Labels Properties
The  Labels properties provides you with all the needed
and appropriate capabilities to configure smart labeling on vector layers. This
dialog can also be accessed from the Layer Styling panel, or using
the
Labels properties provides you with all the needed
and appropriate capabilities to configure smart labeling on vector layers. This
dialog can also be accessed from the Layer Styling panel, or using
the  Layer Labeling Options button of the Labels toolbar.
Layer Labeling Options button of the Labels toolbar.
The first step is to choose the labeling method from the drop-down list. Available methods are:
 No labels: the default value, showing no labels
from the layer
No labels: the default value, showing no labels
from the layer Single labels: Show labels on the map using a single
attribute or an expression
Single labels: Show labels on the map using a single
attribute or an expressionand
 Blocking: allows to set a layer as just an
obstacle for other layer’s labels without rendering any labels of its own.
Blocking: allows to set a layer as just an
obstacle for other layer’s labels without rendering any labels of its own.
The next steps assume you select the  Single labels
option, opening the following dialog.
Single labels
option, opening the following dialog.
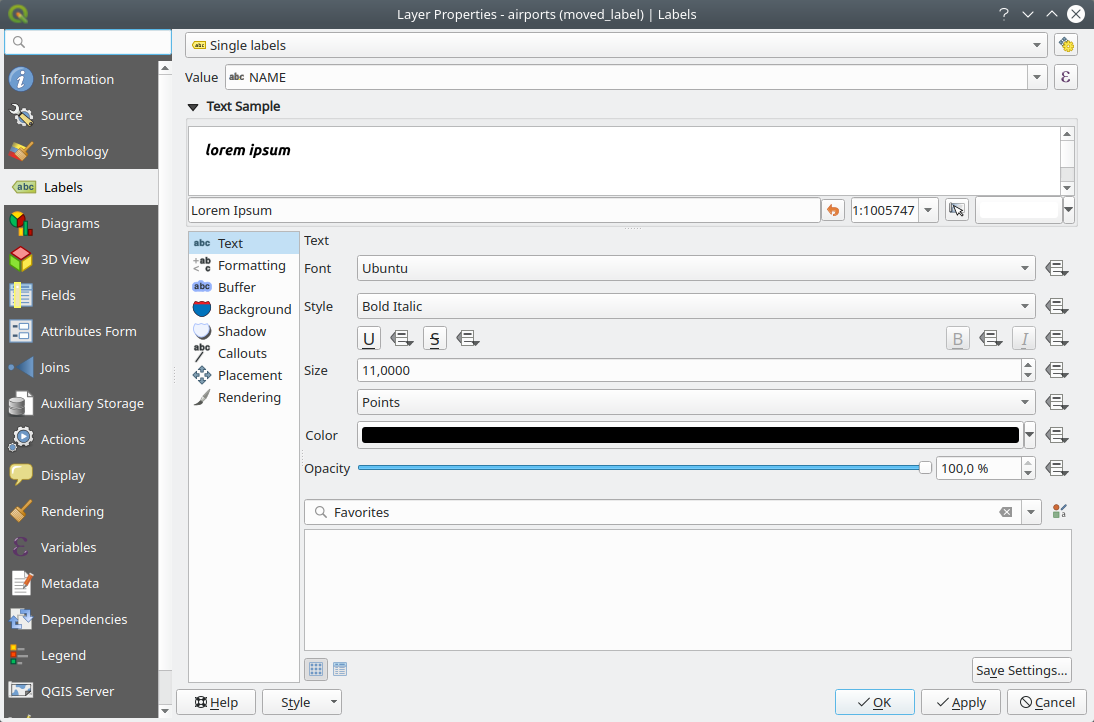
Fig. 14.26 Layer labeling settings - Single labels
At the top of the dialog, a Value drop-down list is enabled.
You can select an attribute column to use for labeling. By default, the
display field is used. Click ![]() if you want to define
labels based on expressions - See Define labels based on expressions.
if you want to define
labels based on expressions - See Define labels based on expressions.
Below are displayed options to customize the labels, under various tabs:
Description of how to set each property is exposed at Setting a label.
14.1.4.1. Setting the automated placement engine
You can use the automated placement settings to configure a global and
automated behavior of the labels. In the top right corner of the
Labels tab, click the ![]() Automated placement
settings (applies to all layers) button, opening a dialog with the following
options:
Automated placement
settings (applies to all layers) button, opening a dialog with the following
options:
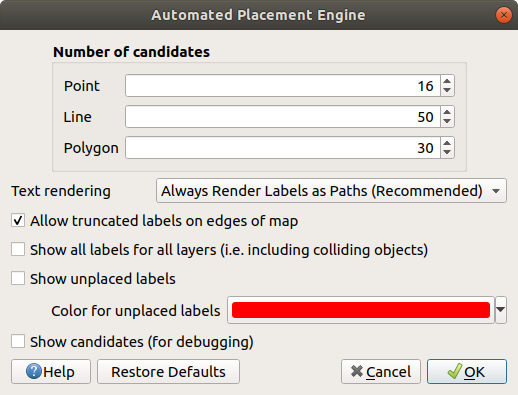
Fig. 14.27 The labels automated placement engine
The Number of candidates controls how many label placement candidates should be generated for each feature type. The more candidates generated, the better the labeling will be - but at a cost of rendering speed. Smaller number of candidates results in less labels placed but faster redraws.
Text rendering: sets the default value for label rendering widgets when exporting a map canvas or a layout to PDF or SVG. If Always render labels as text is selected then labels can be edited in external applications (e.g. Inkscape) as normal text. BUT the side effect is that the rendering quality is decreased, and there are issues with rendering when certain text settings like buffers are in place. That’s why Always render labels as paths (recommended) which exports labels as outlines, is recommended.
 Allow truncated labels on edges of map: controls
whether labels which fall partially outside of the map extent should be
rendered. If checked, these labels will be shown (when there’s no way to
place them fully within the visible area). If unchecked then partially
visible labels will be skipped. Note that this setting has no effects on
labels’ display in the layout map item.
Allow truncated labels on edges of map: controls
whether labels which fall partially outside of the map extent should be
rendered. If checked, these labels will be shown (when there’s no way to
place them fully within the visible area). If unchecked then partially
visible labels will be skipped. Note that this setting has no effects on
labels’ display in the layout map item. Show all labels for all layers (i.e. including
colliding objects). Note that this option can be also set per layer (see
Rendering tab)
Show all labels for all layers (i.e. including
colliding objects). Note that this option can be also set per layer (see
Rendering tab) Show unplaced labels: allows to determine whether any
important labels are missing from the maps (e.g. due to overlaps or other
constraints). They are displayed using a customizable color.
Show unplaced labels: allows to determine whether any
important labels are missing from the maps (e.g. due to overlaps or other
constraints). They are displayed using a customizable color. Show candidates (for debugging): controls whether boxes
should be drawn on the map showing all the candidates generated for label placement.
Like the label says, it’s useful only for debugging and testing the effect different
labeling settings have. This could be handy for a better manual placement with
tools from the label toolbar.
Show candidates (for debugging): controls whether boxes
should be drawn on the map showing all the candidates generated for label placement.
Like the label says, it’s useful only for debugging and testing the effect different
labeling settings have. This could be handy for a better manual placement with
tools from the label toolbar.
14.1.4.2. Rule-based labeling
With rule-based labeling multiple label configurations can be defined and applied selectively on the base of expression filters and scale range, as in Rule-based rendering.
To create a rule, select the  Rule-based labeling option in the main
drop-down list from the Labels tab and click the
Rule-based labeling option in the main
drop-down list from the Labels tab and click the  button
at the bottom of the dialog. Then fill the new dialog with a description and an
expression to filter features. You can also set a scale range in which the label rule should be applied. The other
options available in this dialog are the common settings
seen beforehand.
button
at the bottom of the dialog. Then fill the new dialog with a description and an
expression to filter features. You can also set a scale range in which the label rule should be applied. The other
options available in this dialog are the common settings
seen beforehand.
Fig. 14.28 Rule settings
A summary of existing rules is shown in the main dialog (see figure_labels_rule_based).
You can add multiple rules, reorder or imbricate them with a drag-and-drop.
You can as well remove them with the  button or edit them with
button or edit them with
 button or a double-click.
button or a double-click.
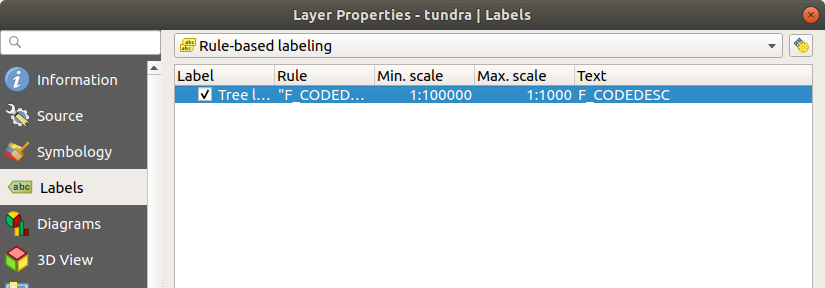
Fig. 14.29 Rule based labeling panel
14.1.4.3. Define labels based on expressions
Whether you choose single or rule-based labeling type, QGIS allows using expressions to label features.
Assuming you are using the Single labels method, click the
![]() button near the Value drop-down list in the
button near the Value drop-down list in the
 Labels tab of the properties dialog.
Labels tab of the properties dialog.
In figure_labels_expression, you see a sample expression to label the alaska
trees layer with tree type and area, based on the field ‘VEGDESC’, some
descriptive text, and the function $area in combination with
format_number() to make it look nicer.
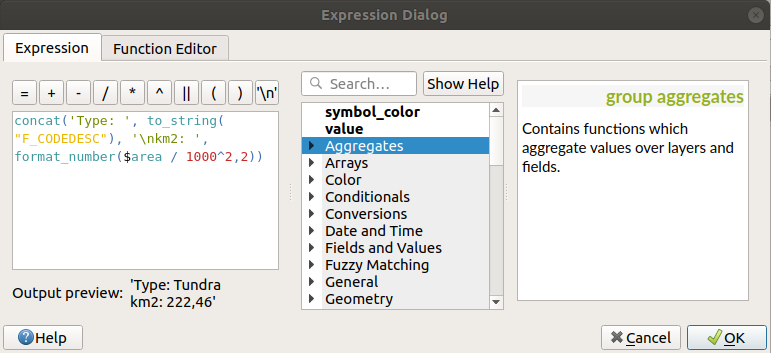
Fig. 14.30 Using expressions for labeling
Expression based labeling is easy to work with. All you have to take care of is that:
You may need to combine all elements (strings, fields, and functions) with a string concatenation function such as
concat,+or||. Be aware that in some situations (when null or numeric value are involved) not all of these tools will fit your need.Strings are written in ‘single quotes’.
Fields are written in “double quotes” or without any quote.
Let’s have a look at some examples:
Label based on two fields ‘name’ and ‘place’ with a comma as separator:
"name" || ', ' || "place"
Returns:
John Smith, Paris
Label based on two fields ‘name’ and ‘place’ with other texts:
'My name is ' + "name" + 'and I live in ' + "place" 'My name is ' || "name" || 'and I live in ' || "place" concat('My name is ', name, ' and I live in ', "place")Returns:
My name is John Smith and I live in Paris
Label based on two fields ‘name’ and ‘place’ with other texts combining different concatenation functions:
concat('My name is ', name, ' and I live in ' || place)Returns:
My name is John Smith and I live in Paris
Or, if the field ‘place’ is NULL, returns:
My name is John Smith
Multi-line label based on two fields ‘name’ and ‘place’ with a descriptive text:
concat('My name is ', "name", '\n' , 'I live in ' , "place")Returns:
My name is John Smith I live in Paris
Label based on a field and the $area function to show the place’s name and its rounded area size in a converted unit:
'The area of ' || "place" || ' has a size of ' || round($area/10000) || ' ha'
Returns:
The area of Paris has a size of 10500 ha
Create a CASE ELSE condition. If the population value in field population is <= 50000 it is a town, otherwise it is a city:
concat('This place is a ', CASE WHEN "population" <= 50000 THEN 'town' ELSE 'city' END)Returns:
This place is a town
Display name for the cities and no label for the other features (for the “city” context, see example above):
CASE WHEN "population" > 50000 THEN "NAME" END
Returns:
Paris
As you can see in the expression builder, you have hundreds of functions available to create simple and very complex expressions to label your data in QGIS. See Expressions chapter for more information and examples on expressions.
14.1.4.4. Using data-defined override for labeling
With the ![]() Data defined override function, the settings for
the labeling are overridden by entries in the attribute table or expressions
based on them. This feature can be used to
set values for most of the labeling options described above.
Data defined override function, the settings for
the labeling are overridden by entries in the attribute table or expressions
based on them. This feature can be used to
set values for most of the labeling options described above.
For example, using the Alaska QGIS sample dataset, let’s label the airports
layer with their name, based on their militarian USE, i.e. whether the airport
is accessible to :
military people, then display it in gray color, size 8;
others, then show in blue color, size 10.
To do this, after you enabled the labeling on the NAME field of the layer
(see Setting a label):
Activate the Text tab.
Select Edit… and type:
CASE WHEN "USE" like '%Military%' THEN 8 -- because compatible values are 'Military' -- and 'Joint Military/Civilian' ELSE 10 END
Press OK to validate. The dialog closes and the
 button
becomes
button
becomes  meaning that an rule is being run.
meaning that an rule is being run.Then click the button next to the color property, type the expression below and validate:
CASE WHEN "USE" like '%Military%' THEN '150, 150, 150' ELSE '0, 0, 255' END
Likewise, you can customize any other property of the label, the way you want.
See more details on the ![]() Data-define override widget’s
description and manipulation in Data defined override setup section.
Data-define override widget’s
description and manipulation in Data defined override setup section.
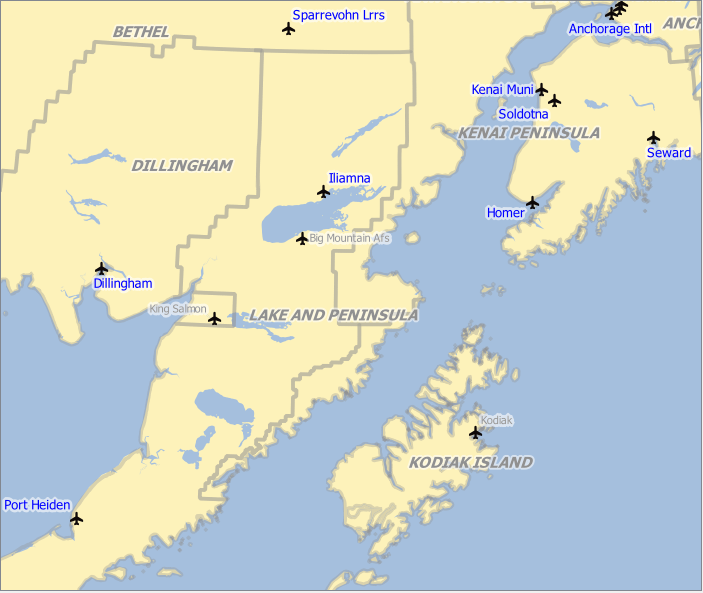
Fig. 14.31 Airports labels are formatted based on their attributes
Tip
Use the data-defined override to label every part of multi-part features
There is an option to set the labeling for multi-part features independently from
your label properties. Choose the  Rendering,
Rendering,
Feature options, go to the ![]() Data-define override button
next to the checkbox
Data-define override button
next to the checkbox  Label every part of multipart-features
and define the labels as described in Data defined override setup.
Label every part of multipart-features
and define the labels as described in Data defined override setup.
14.1.4.4.1. The Label Toolbar
The Label Toolbar provides some tools to manipulate  label or
label or  diagram
properties.
diagram
properties.

Fig. 14.32 The Label toolbar
While for readability, label has been used below to describe the Label
toolbar, note that when mentioned in their name, the tools work almost the
same way with diagrams:
 Highlight Pinned Labels and Diagrams. If the
vector layer of the label is editable, then the highlighting is green,
otherwise it’s blue.
Highlight Pinned Labels and Diagrams. If the
vector layer of the label is editable, then the highlighting is green,
otherwise it’s blue. Toggles Display of Unplaced Labels: Allows to
determine whether any important labels are missing from the maps (e.g. due
to overlaps or other constraints). They are displayed with a customizable
color (see Setting the automated placement engine).
Toggles Display of Unplaced Labels: Allows to
determine whether any important labels are missing from the maps (e.g. due
to overlaps or other constraints). They are displayed with a customizable
color (see Setting the automated placement engine). Pin/Unpin Labels and Diagrams. By clicking or draging an
area, you pin label(s). If you click or drag an area holding Shift,
label(s) are unpinned. Finally, you can also click or drag an area holding
Ctrl to toggle the pin status of label(s).
Pin/Unpin Labels and Diagrams. By clicking or draging an
area, you pin label(s). If you click or drag an area holding Shift,
label(s) are unpinned. Finally, you can also click or drag an area holding
Ctrl to toggle the pin status of label(s). Show/Hide Labels and Diagrams. If you click on the labels,
or click and drag an area holding Shift, they are hidden.
When a label is hidden, you just have to click on the feature to restore its
visibility. If you drag an area, all the labels in the area will be restored.
Show/Hide Labels and Diagrams. If you click on the labels,
or click and drag an area holding Shift, they are hidden.
When a label is hidden, you just have to click on the feature to restore its
visibility. If you drag an area, all the labels in the area will be restored. Moves a Label or Diagram. You just have to drag the label to
the desired place.
Moves a Label or Diagram. You just have to drag the label to
the desired place. Rotates a Label. Click the label and move around and
you get the text rotated.
Rotates a Label. Click the label and move around and
you get the text rotated. Change Label Properties. It opens a dialog to change the
clicked label properties; it can be the label itself, its coordinates, angle,
font, size, multiline alignment … as long as this property has been mapped
to a field. Here you can set the option to
Change Label Properties. It opens a dialog to change the
clicked label properties; it can be the label itself, its coordinates, angle,
font, size, multiline alignment … as long as this property has been mapped
to a field. Here you can set the option to  Label every
part of a feature.
Label every
part of a feature.
Warning
Label tools overwrite current field values
Using the Label toolbar to customize the labeling actually writes the new value of the property in the mapped field. Hence, be careful to not inadvertently replace data you may need later!
Note
The Auxiliary Storage Properties mechanism may be used to customize labeling (position, and so on) without modifying the underlying data source.
14.1.4.4.2. Customize the labels from the map canvas
Combined with the Label Toolbar, the data defined override setting
helps you manipulate labels in the map canvas (move, edit, rotate).
We now describe an example using the data-defined override function for the
 Move label function (see figure_labels_coordinate_data_defined).
Move label function (see figure_labels_coordinate_data_defined).
Import
lakes.shpfrom the QGIS sample dataset.Double-click the layer to open the Layer Properties. Click on Labels and Placement. Select
 Offset from centroid.
Offset from centroid.Look for the Data defined entries. Click the
 icon
to define the field type for the Coordinate. Choose
icon
to define the field type for the Coordinate. Choose xlabelfor X andylabelfor Y. The icons are now highlighted in yellow.
Fig. 14.33 Labeling of vector polygon layers with data-defined override
Zoom into a lake.
Go to the Label toolbar and click the
 icon.
Now you can shift the label manually to another position (see figure_labels_move).
The new position of the label is saved in the
icon.
Now you can shift the label manually to another position (see figure_labels_move).
The new position of the label is saved in the xlabelandylabelcolumns of the attribute table.Using The Geometry Generator with the expression below, you can also add a linestring symbol layer to connect each lake to its moved label:
make_line( centroid( $geometry ), make_point( "xlabel", "ylabel" ) )
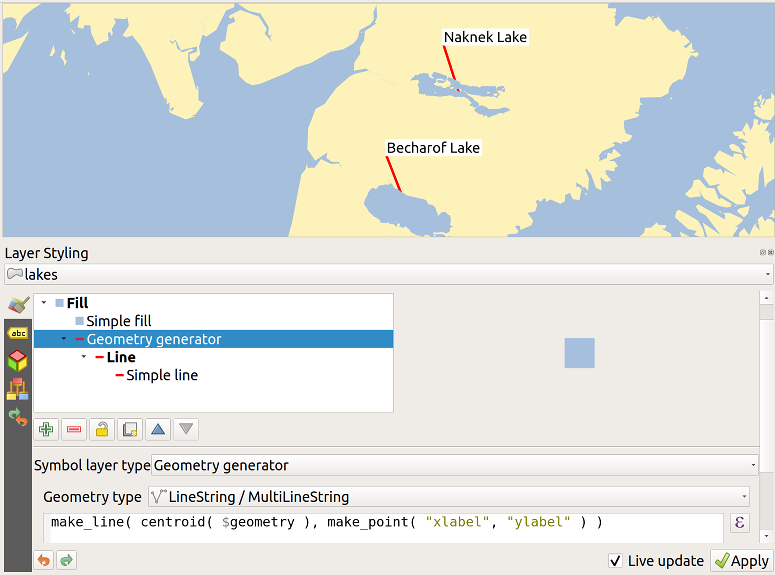
Fig. 14.34 Moved labels
Note
The Auxiliary Storage Properties mechanism may be used with data-defined properties without having an editable data source.
14.1.5. Diagrams Properties
 The Diagrams tab allows you to add a graphic overlay to
a vector layer (see figure_diagrams_attributes).
The Diagrams tab allows you to add a graphic overlay to
a vector layer (see figure_diagrams_attributes).
The current core implementation of diagrams provides support for:
 No diagrams: the default value with no diagram
displayed over the features;
No diagrams: the default value with no diagram
displayed over the features; Pie charts, a circular statistical graphic divided into
slices to illustrate numerical proportion. The arc length of each slice is
proportional to the quantity it represents;
Pie charts, a circular statistical graphic divided into
slices to illustrate numerical proportion. The arc length of each slice is
proportional to the quantity it represents; Text diagrams, a horizontaly divided circle showing statistics
values inside;
Text diagrams, a horizontaly divided circle showing statistics
values inside;
In the top right corner of the Diagrams tab, the ![]() Automated placement settings (applies to all layers) button provides
means to control diagram labels placement on the
map canvas.
Automated placement settings (applies to all layers) button provides
means to control diagram labels placement on the
map canvas.
Tip
Switch quickly between types of diagrams
Given that the settings are almost common to the different types of diagram, when designing your diagram, you can easily change the diagram type and check which one is more appropriate to your data without any loss.
For each type of diagram, the properties are divided into several tabs:
14.1.5.1. Attributes
Attributes defines which variables to display in the diagram.
Use  add item button to select the desired fields into
the ‘Assigned Attributes’ panel. Generated attributes with Expressions
can also be used.
add item button to select the desired fields into
the ‘Assigned Attributes’ panel. Generated attributes with Expressions
can also be used.
You can move up and down any row with click and drag, sorting how attributes are displayed. You can also change the label in the ‘Legend’ column or the attribute color by double-clicking the item.
This label is the default text displayed in the legend of the print layout or of the layer tree.
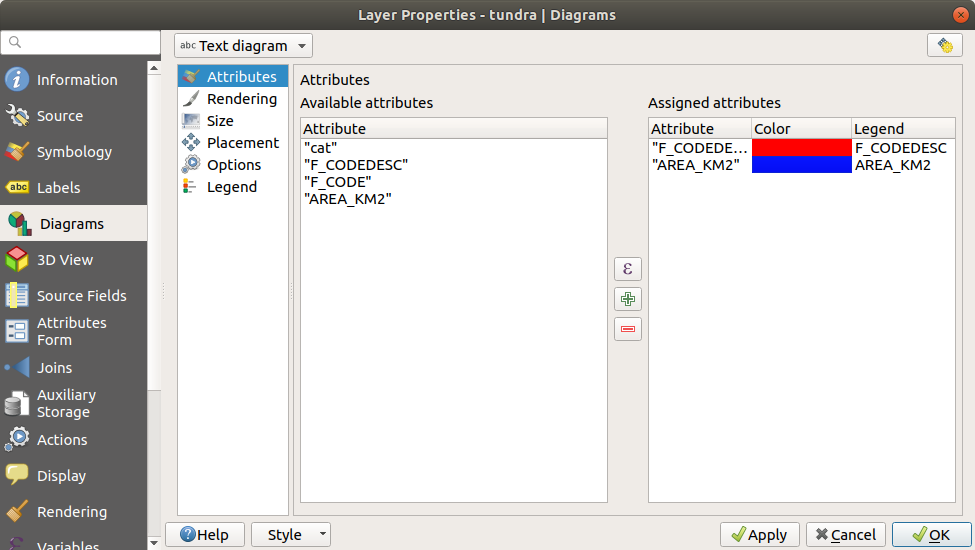
Fig. 14.35 Diagram properties - Attributes tab
14.1.5.2. Rendering
Rendering defines how the diagram looks like. It provides general settings that do not interfere with the statistic values such as:
the graphic’s opacity, its outline width and color;
and, depending on the type of diagram:
the width of the bar in case of histogram;
the circle background color in case of text diagram, and the font used for texts;
the orientation of the left line of the first slice represented in pie chart. Note that slices are displayed clockwise.
In this tab, you can also manage and fine tune the diagram visibility with different options:
Diagram z-index: controls how diagrams are drawn on top of each other and on top of labels. A diagram with a high index is drawn over diagrams and labels;
 Show all diagrams: shows all the diagrams even if they
overlap each other;
Show all diagrams: shows all the diagrams even if they
overlap each other;Show diagram: allows only specific diagrams to be rendered;
Always Show: selects specific diagrams to always render, even when they overlap other diagrams or map labels;
setting the Scale dependent visibility;
Discourage diagrams and labels from covering features: defines features to use as obstacles, ie QGIS will try to not place diagrams nor labels over these features.
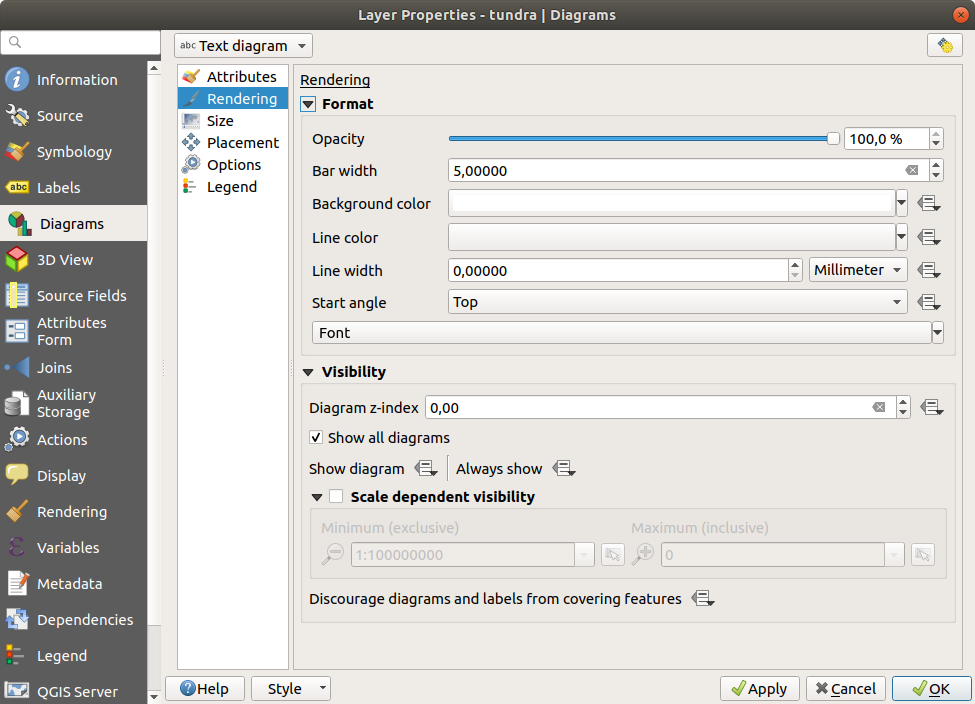
Fig. 14.36 Diagram properties - Rendering tab
14.1.5.3. Size
Size is the main tab to set how the selected statistics are represented. The diagram size units can be ‘Millimeter’, ‘Points’, Pixels, ‘Map Units’ or ‘Inches’. You can use :
Fixed size, an unique size to represent the graphic of all the features, except when displaying histogram
or Scaled size, based on an expression using layer attributes.
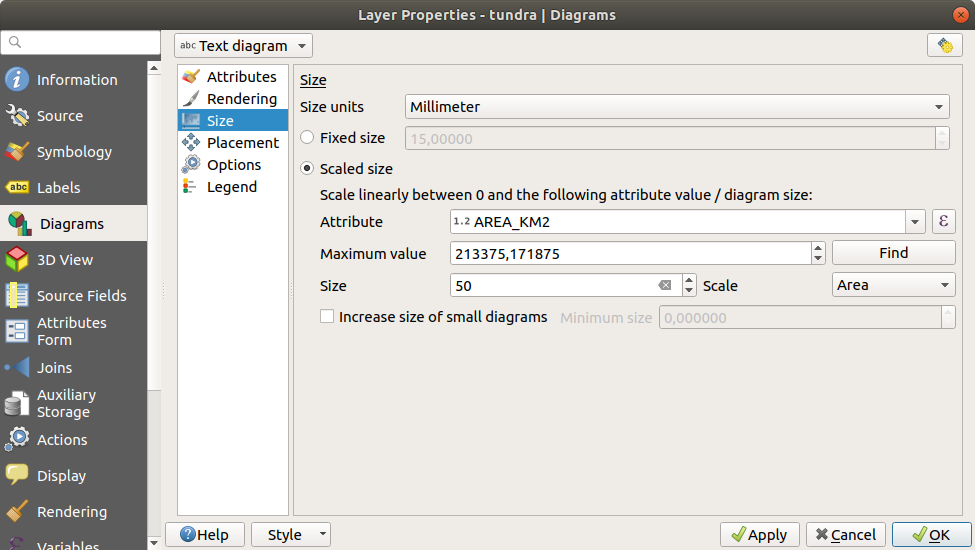
Fig. 14.37 Diagram properties - Size tab
14.1.5.4. Placement
Placement helps to define diagram position. According to the layer geometry type, it offers different options for the placement:
‘Over the point’ or ‘Around the point’ for point geometry. The latter variable requires a radius to follow.
‘Over the line’ or ‘Around the line’ for line geometry. Like point feature, the last variable requires a distance to respect and user can specify the diagram placement relative to the feature (‘above’, ‘on’ and/or ‘below’ the line) It’s possible to select several options at once. In that case, QGIS will look for the optimal position of the diagram. Remember that here you can also use the line orientation for the position of the diagram.
‘Over the centroid’, ‘Around the centroid’ (with a distance set), ‘Perimeter’ and anywhere ‘Inside polygon’ are the options for polygon features.
The diagram can also be placed using feature data to fill the coordinates X
and Y fields.
The placement of the diagrams can interact with the labeling, so you can detect and solve position conflicts between diagrams and labels by setting the Priority slider value.
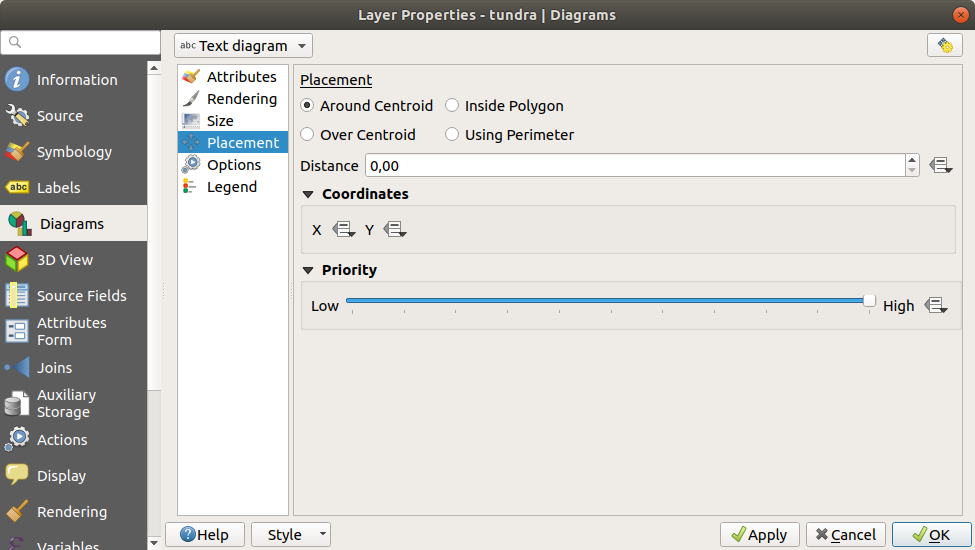
Fig. 14.38 Vector properties dialog with diagram properties, Placement tab
14.1.5.5. Options
The Options tab has settings only in case of histogram. You can choose whether the bar orientation should be ‘Up’, ‘Down’, ‘Right’ and ‘Left’.
14.1.5.6. Legend
From the Legend tab, you can choose to display items of the diagram in the Layers Panel, and in the print layout legend, next to the layer symbology:
check Show legend entries for diagram attributes to display in the legends the
ColorandLegendproperties, as previously assigned in the Attributes tab;and, when a scaled size is being used for the diagrams, push the Legend Entries for Diagram Size… button to configure the diagram symbol aspect in the legends. This opens the Data-defined Size Legend dialog whose options are described in Data-defined size legend.
When set, the diagram legend items (attributes with color and diagram size) are also displayed in the print layout legend, next to the layer symbology.
14.1.5.7. Case Study
We will demonstrate an example and overlay on the Alaska boundary layer a text diagram showing temperature data from a climate vector layer. Both vector layers are part of the QGIS sample dataset (see section Downloading sample data).
First, click on the
 Load Vector icon, browse
to the QGIS sample dataset folder, and load the two vector shape layers
Load Vector icon, browse
to the QGIS sample dataset folder, and load the two vector shape layers
alaska.shpandclimate.shp.Double click the
climatelayer in the map legend to open the Layer Properties dialog.Click on the Diagrams tab and from the Diagram type
 combo box, select ‘Text diagram’.
combo box, select ‘Text diagram’.In the Appearance tab, we choose a light blue as background color, and in the Size tab, we set a fixed size to 18 mm.
In the Position tab, placement could be set to ‘Around Point’.
In the diagram, we want to display the values of the three columns
T_F_JAN,T_F_JULandT_F_MEAN. So, in the Attributes tab first selectT_F_JANand click the button, then repeat with
button, then repeat with
T_F_JULand finallyT_F_MEAN.Now click Apply to display the diagram in the QGIS main window.
You can adapt the chart size in the Size tab. Activate the
 Scaled size and set the size of the diagrams on
the basis of the maximum value of an attribute and the
Size option.
If the diagrams appear too small on the screen, you can activate the
Scaled size and set the size of the diagrams on
the basis of the maximum value of an attribute and the
Size option.
If the diagrams appear too small on the screen, you can activate the
 Increase size of small diagrams checkbox and define
the minimum size of the diagrams.
Increase size of small diagrams checkbox and define
the minimum size of the diagrams.Change the attribute colors by double clicking on the color values in the Assigned attributes field. Figure_diagrams_mapped gives an idea of the result.
Finally, click OK.
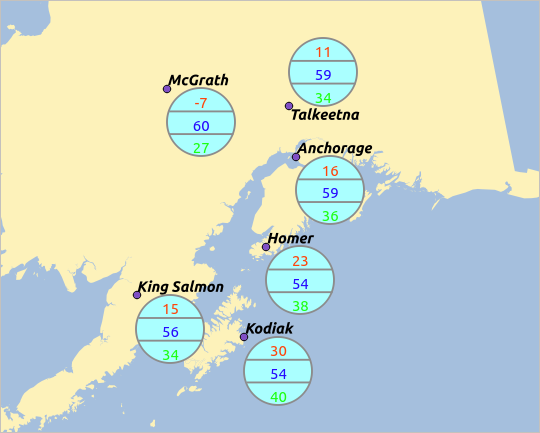
Fig. 14.39 Diagram from temperature data overlayed on a map
Remember that in the Position tab, a  Data
defined position of the diagrams is possible. Here, you can use attributes
to define the position of the diagram.
You can also set a scale-dependent visibility in the Appearance tab.
Data
defined position of the diagrams is possible. Here, you can use attributes
to define the position of the diagram.
You can also set a scale-dependent visibility in the Appearance tab.
The size and the attributes can also be an expression.
Use the ![]() button to add an expression.
See Expressions chapter for more information and example.
button to add an expression.
See Expressions chapter for more information and example.
14.1.5.8. Using data-defined override
As mentioned above, you can use some custom data-defined to tune the diagrams rendering:
position in Placement tab by filling
XandYfieldsvisibility in Appearance tab by filling the
Visibilityfield
See Using data-defined override for labeling for more information.
14.1.6. 3D View Properties
 The 3D View tab provides settings for vector layers that should
be depicted in the 3D Map view tool.
The 3D View tab provides settings for vector layers that should
be depicted in the 3D Map view tool.
To display a layer in 3D, select from the combobox at the top of the tab, either:
Single symbol: features are rendered using a common symbol whose properties can be data-defined or not
Rule-based: multiple symbol configurations can be defined and applied selectively based on expression filters and scale range. More details on how-to at Rule-based rendering.
Depending on the layer geometry type, various properties are available for 3D rendering.
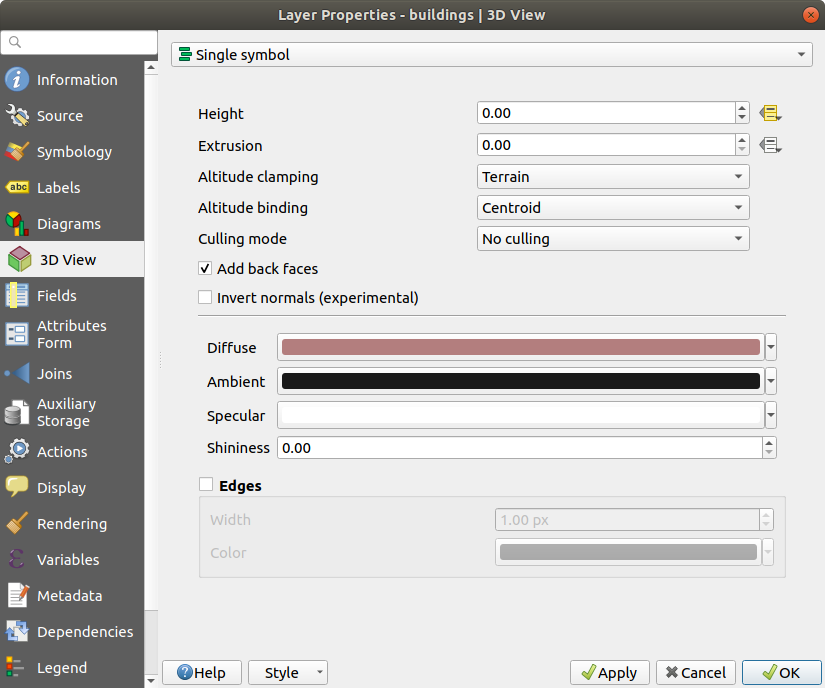
Fig. 14.40 3D properties of a polygon layer
14.1.6.1. Point Layers
You can define different simple 3D shapes like Sphere, Cylinder, Cube, Cone, Plane and Torus defined by their Radius, Size or Length. The unit of size of the 3D shapes refers to the CRS of the project.
The shading of the 3D shapes can be defined by the menus Diffuse, Ambient, Specular and Shininess (see https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Phong_reflection_model#Description)
If you choose 3D Model, the location will be determined by a simple point coordinate.
For visualizing 3D point clouds you can use Billboard Shapes defined by the Billboard Height, Billboard symbol and Altitude clamping. The symbol will have a stable size.
Altitude clamping can be set to Absolute, Relative or Terrain. The Absolute setting can be used when height values of the 3d vectors are provided as absolute measures from 0. Relative and Terrain add given elevation values to the underlying terrain elevation.
Translation can be used to move objects in x, y and z axis.
You can define a Scale factor for the 3D shape as well as a Rotation around the x-, y- and z-axis.
14.1.6.2. Line layers
Beneath the Width and Height settings you can define the Extrusion of the vector lines. If the lines do not have z-values, you can define the 3d volumes with this setting.
With the Altitude clamping you define the position of the 3D lines relative to the underlying terrain surface, if you have included raster elevation data or other 3D vectors.
The Altitude binding defines how the feature is clamped to the terrain. Either every Vertex of the feature will be clamped to the terrain or this will be done by the Centroid.
The shading can be defined in the menus Diffuse, Ambient, Specular and Shininess.
14.1.6.3. Polygon Layers
14.1.6.4. Application example
To go through the settings explained above you can have a look at https://public.cloudmergin.com/projects/saber/luxembourg/tree.
14.1.7. Fields Properties
 The Fields tab provides information on
fields related to the layer and helps you organize them.
The Fields tab provides information on
fields related to the layer and helps you organize them.
The layer can be made editable using the  Toggle editing mode. At this moment, you can modify its structure using
the
Toggle editing mode. At this moment, you can modify its structure using
the  New field and
New field and  Delete field
buttons.
Delete field
buttons.
You can also rename fields by double-clicking its name. This is only supported for data providers like PostgreSQL, Oracle, Memory layer and some OGR layer depending on the OGR data format and version.
If set in the underlying data source or in the forms properties, the field’s alias is also displayed. An alias is a human readable field name you can use in the feature form or the attribute table. Aliases are saved in the project file.
Depending on the data provider, you can associate a comment with a field, for example at its creation. This information is retrieved and shown in the Comment column and is later displayed when hovering over the field label in a feature form.
Other than the fields contained in the dataset, virtual fields and Auxiliary Storage included, the Fields tab also lists fields from any joined layers. Depending on the origin of the field, a different background color is applied to it.
For each listed field, the dialog also lists read-only characteristics such as
its type, type name, length and precision. When serving the
layer as WMS or WFS, you can also check here which fields could be retrieved.
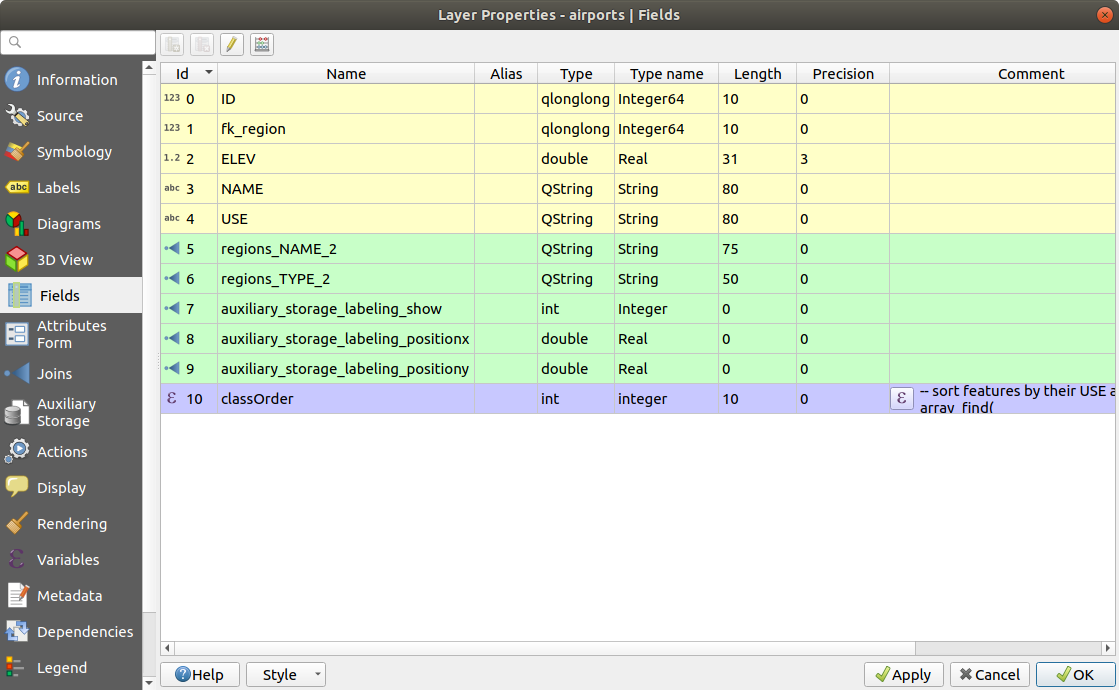
Fig. 14.41 Fields properties tab
14.1.8. Attributes Form Properties
 The Attributes Form tab helps you set up the form to
display when creating new features or querying existing one. You can define:
The Attributes Form tab helps you set up the form to
display when creating new features or querying existing one. You can define:
the look and the behavior of each field in the feature form or the attribute table (label, widget, constraints…);
the form’s structure (custom or autogenerated):
extra logic in Python to handle interaction with the form or field widgets.
At the top right of the dialog, you can set whether the form is opened by default when creating new features. This can be configured per layer or globally with the Suppress attribute form pop-up after feature creation option in the menu.
14.1.8.1. Customizing a form for your data
By default, when you click on a feature with the  Identify
Features tool or switch the attribute table to the form view mode, QGIS
displays a basic form with predefined widgets (generally spinboxes and
textboxes — each field is represented on a dedicated row by its label next
to the widget). If relations are set on the layer,
fields from the referencing layers are shown in an embedded frame
at the bottom of the form, following the same basic structure.
Identify
Features tool or switch the attribute table to the form view mode, QGIS
displays a basic form with predefined widgets (generally spinboxes and
textboxes — each field is represented on a dedicated row by its label next
to the widget). If relations are set on the layer,
fields from the referencing layers are shown in an embedded frame
at the bottom of the form, following the same basic structure.
This rendering is the result of the default Autogenerate value of the
Attribute editor layout setting in the tab. This property holds three different
values:
Autogenerate: keeps the basic structure of “one row - one field” for the form but allows to customize each corresponding widget.Drag-and-drop designer: other than widget customization, the form structure can be made more complex eg, with widgets embedded in groups and tabs.Provide ui file: allows to use a Qt designer file, hence a potentially more complex and fully featured template, as feature form.
14.1.8.1.1. The autogenerated form
When the Autogenerate option is on, the Available widgets panel
shows lists of fields (from the layer and its relations) that would be shown in
the form. Select a field and you can configure its appearance and behavior in
the right panel:
adding custom label and automated checks to the field;
setting a particular widget to use.
14.1.8.1.2. The drag and drop designer
The drag and drop designer allows you to create a form with several containers (tabs or groups) to present the attribute fields, as shown for example in figure_fields_form.
Fig. 14.42 Resulting built-in form with tabs and named groups
Choose
Drag and drop designerfrom the Select attribute layout editor combobox. This enables the Form Layout panel next to the Available widgets panel, filled with existing fields. The selected field displays its properties (that you can customize) in a third panel.Select fields you do not want to use in your Form Layout panel and hit the
 button to remove them. Drag and drop fields
from the other panel to re-add them. The same field can be added multiple times.
button to remove them. Drag and drop fields
from the other panel to re-add them. The same field can be added multiple times.Drag and drop fields within the Form Layout panel to reorder their position.
Add containers (tab or group frames) to associate fields that belong to the same category and better structure the form.
The first step is to use the
 icon to create a tab in which
fields and groups will be displayed
icon to create a tab in which
fields and groups will be displayedThen set the properties of the container, ie:
the name
the type, ie a tab or a group in container (a group inside a tab or another group)
and the number of columns the embedded fields should be distributed over
Fig. 14.43 Dialog to create containers with the Attribute editor layout
These, and other properties can later be updated by selecting the item and, from the third panel:
hide or show the container’s label
display the container as a group box (only available for tabs).
rename the container
set the number of columns
enter an expression to control the container’s visibility. The expression will be re-evaluated every time values in the form change, and the tab or group box shown/hidden accordingly
add a background color
You can create as many containers as you want; press the
 icon again to create another tab or a group frame under
an existing tab.
icon again to create another tab or a group frame under
an existing tab.
The next step is to assign the relevant fields to each container, by simple drag and drop. Groups and tabs can also be moved in the same way.
In case the layer is involved in a one or many to many relation, drag-and-drop the relation name from the Available widgets panel to the Form Layout panel. The associated layer attribute form will be embedded at the chosen place in the current layer’s form. As for the other items, select the relation label to configure some properties:
hide or show the relation label
show the link button
show the unlink button
Apply the layer’s properties dialog
Open a feature attribute form (eg, using the
 Identify features
tool) and it should display the new form.
Identify features
tool) and it should display the new form.
14.1.8.1.3. Using custom ui-file
The Provide ui-file option allows you to use complex dialogs made with
Qt-Designer. Using a UI-file allows a great deal of freedom in creating a
dialog. Note that, in order to link the graphical objects (textbox,
combobox…) to the layer’s fields, you need to give them the same name.
Use the Edit UI to define the path to the file to use.
UI-files can also be hosted on a remote server. In this case, you provide the URL of the form instead of the file path in Edit UI.
You’ll find some example in the Creating a new form lesson of the QGIS Training Manual. For more advanced information, see https://woostuff.wordpress.com/2011/09/05/qgis-tips-custom-feature-forms-with-python-logic/.
14.1.8.1.4. Enhance your form with custom functions
QGIS forms can have a Python function that is called when the dialog is opened. Use this function to add extra logic to your dialogs. The form code can be specified in three different ways:
load from the environment: use a function, for example instartup.pyor from an installed pluginload from an external file: a file chooser will let you select a Python file from your filesystem or enter a URL for a remote file.provide code in this dialog: a Python editor will appear where you can directly type the function to use.
In all cases you must enter the name of the function that will be called
(open in the example below).
An example is (in module MyForms.py):
def open(dialog,layer,feature):
geom = feature.geometry()
control = dialog.findChild(QWidged,"My line edit")
Reference in Python Init Function like so: open
14.1.8.2. Configure the field behavior
The main part of the Attributes Form tab helps you set the type of widget used to fill or display values of the field, in the attribute table or the feature form: you can define how user interacts with each field and the values or range of values that are allowed to be added to each.
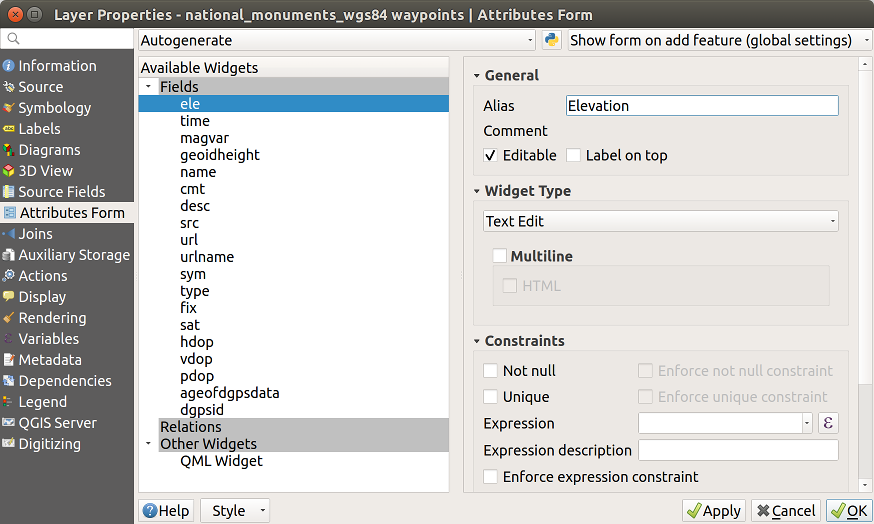
Fig. 14.44 Dialog to select an edit widget for an attribute column
14.1.8.2.1. Common settings
Regardless the type of widget applied to the field, there are some common properties you can set to control whether and how a field can be edited.
14.1.8.2.1.1. Widget display
Show label: indicates whether the field name should be displayed in the form.
14.1.8.2.1.2. General options
Alias: a human readable name to use for fields. The alias will be displayed in the feature form, the attribute table, or in the Identify results panel. It can also be used as field name replacement in the expression builder, easing expressions understanding and reviews. Aliases are saved in project file.
Comment: displays the field’s comment as shown in the Fields tab, in a read-only state. This information is shown as tooltip when hovering over the field label in a feature form.
 Editable: uncheck this option to set the field read-only
(not manually modifiable) even when the layer is in edit mode. Note that
checking this setting doesn’t override any edit limitation from the provider.
Editable: uncheck this option to set the field read-only
(not manually modifiable) even when the layer is in edit mode. Note that
checking this setting doesn’t override any edit limitation from the provider. Label on top: places the field name above or beside
the widget in the feature form.
Label on top: places the field name above or beside
the widget in the feature form.
14.1.8.2.1.3. Default values
Default value: for new features, automatically populates by default the field with a predefined value or an expression-based one. For example, you can:
use
$x,$length,$areato automatically populate a field with the feature’s X coordinate, length, area or any geometric information at its creation;increment a field by 1 for each new feature using
maximum("field")+1;save the feature creation datetime using
now();use variables in expressions, making it easier to e.g. insert the operator name (
@user_full_name), the project file path (@project_path), …
A preview of the resulting default value is displayed at the bottom of the widget.
Note
The
Default valueoption is not aware of the values in any other field of the feature being created so it won’t be possible to use an expression combining any of those values i.e using an expression likeconcat(field1, field2)may not work. Apply default value on update: whenever the feature
attribute or geometry is changed, the default value is recalculated. This
could be handy to save values like last user that modifies data, last time it
was changed…
Apply default value on update: whenever the feature
attribute or geometry is changed, the default value is recalculated. This
could be handy to save values like last user that modifies data, last time it
was changed…
14.1.8.2.1.4. Constraints
You can constrain the value to insert in the field. This constraint can be:
 Unique: guarantee the inserted value to be unique
throughout the field;
Unique: guarantee the inserted value to be unique
throughout the field;based on a custom expression: e.g.
regexp_match(col0,'A-Za-z')to ensure that the value of the field col0 has only alphabetical letter. A short description can be added to help you remember the constraint.
Whenever a value is added or edited in a field, it’s submitted to the existing constraints and:
if it meets all the requirements, a green check is shown beside the field in the form;
if it does not meet all the requirements, then a yellow or red cross is displayed near the field. You can hover over the cross to remind which constraints are applied to the field and fix the value:
A yellow cross appears when the unmet constraint is an unenforced one and it does not prevent you to save the changes with the “wrong” values;
A red cross can not be ignored and does not allow you to save your modifications until they meet the constraints. It appears when the
 Enforce constraint option is checked.
Enforce constraint option is checked.
14.1.8.2.2. Edit widgets
Based on the field type, QGIS automatically determines and assigns a default widget type to it. You can then replace the widget with any other compatible with the field type. The available widgets are:
Checkbox: Displays a checkbox whose state defines the value to insert.
Classification: Only available when a categorized symbology is applied to the layer, displays a combo box with the values of the classes.
Color: Displays a color widget allowing to select a color; the color value is stored as a html notation in the attribute table.
Date/Time: Displays a line field which can open a calendar widget to enter a date, a time or both. Column type must be text. You can select a custom format, pop-up a calendar, etc.
Enumeration: Opens a combo box with predefined values fetched from the database. This is currently only supported by the PostgreSQL provider, for fields of
enumtype.Attachment: Uses a “Open file” dialog to store file path in a relative or absolute mode. It can also be used to display a hyperlink (to document path), a picture or a web page.
Hidden: A hidden attribute column is invisible. The user is not able to see its contents.
Key/Value: Displays a two-columns table to store sets of key/value pairs within a single field. This is currently supported by the PostgreSQL provider, for fields of
hstoretype.List: Displays a single column table to add different values within a single field. This is currently supported by the PostgreSQL provider, for fields of
arraytype.Range: Allows you to set numeric values from a specific range. The edit widget can be either a slider or a spin box.
Relation Reference: This widget lets you embed the feature form of the referenced layer on the feature form of the actual layer. See Creating one or many to many relations.
Text Edit (default): This opens a text edit field that allows simple text or multiple lines to be used. If you choose multiple lines you can also choose html content.
Unique Values: You can select one of the values already used in the attribute table. If ‘Editable’ is activated, a line edit is shown with autocompletion support, otherwise a combo box is used.
Uuid Generator: Generates a read-only UUID (Universally Unique Identifiers) field, if empty.
Value Map: A combo box with predefined items. The value is stored in the attribute, the description is shown in the combo box. You can define values manually or load them from a layer or a CSV file.
Value Relation: Offers values from a related table in a combobox. You can select layer, key column and value column. Several options are available to change the standard behaviors: allow null value, order by value, allow multiple selections and use of auto-completer. The forms will display either a drop-down list or a line edit field when completer checkbox is enabled.
Tip
Relative Path in Attachment widget
If the path which is selected with the file browser is located in the same
directory as the .qgs project file or below, paths are converted to
relative paths. This increases portability of a .qgs project with
multimedia information attached.
14.1.9. Joins Properties
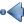 The Joins tab allows you to associate features
of the current layer (called
The Joins tab allows you to associate features
of the current layer (called Target layer) to features from another
loaded vector layer (or table). The join is based on an attribute that is shared by the
layers. The layers can be geometryless (tables) or not but their join attribute
should be of the same type.
To create a join:
Click the
 Add new join button. The Add vector
join dialog appears.
Add new join button. The Add vector
join dialog appears.Select the Join layer you want to connect with the target vector layer
Specify the Join field and the Target field that are common to both the join layer and the target layer
Press OK and a summary of selected parameters is added to the Join panel.
Fig. 14.45 Join an attribute table to an existing vector layer
The steps above will create a join, where ALL the attributes of the first matching feature in the join layer is added to the target layer’s feature. QGIS provides more options to tweak the join:
 Cache join layer in virtual memory: allows you to cache
values in memory (without geometries) from the joined layer in order to speed
up lookups.
Cache join layer in virtual memory: allows you to cache
values in memory (without geometries) from the joined layer in order to speed
up lookups. Dynamic form: helps to synchronize join fields on the
fly, according to the Target field. This way, constraints for
join fields are also correctly updated. Note that it’s deactivated by default
because it may be very time consuming if you have a lot of features or a
myriad of joins.
Dynamic form: helps to synchronize join fields on the
fly, according to the Target field. This way, constraints for
join fields are also correctly updated. Note that it’s deactivated by default
because it may be very time consuming if you have a lot of features or a
myriad of joins.If the target layer is editable, then some icons will be displayed in the attribute table next to fields, in order to inform about their status:
 : the join layer is not configured to be
editable. If you want to be able to edit join features from the target
attribute table, then you have to check the option
: the join layer is not configured to be
editable. If you want to be able to edit join features from the target
attribute table, then you have to check the option
 Editable join layer.
Editable join layer. : the join layer is well configured to be
editable, but its current status is read only.
: the join layer is well configured to be
editable, but its current status is read only. : the join layer is editable, but synchronization
mechanisms are not activated. If you want to automatically add a feature in
the join layer when a feature is created in the target layer, then you have
to check the option
: the join layer is editable, but synchronization
mechanisms are not activated. If you want to automatically add a feature in
the join layer when a feature is created in the target layer, then you have
to check the option  Upsert on edit. Symmetrically,
the option
Upsert on edit. Symmetrically,
the option  Delete cascade may be activated if you
want to automatically delete join features.
Delete cascade may be activated if you
want to automatically delete join features.
 Joined fields: instead of adding all the fields from
the joined layer, you can specify a subset.
Joined fields: instead of adding all the fields from
the joined layer, you can specify a subset. Custom field name prefix for joined fields, in order
to avoid name collision
Custom field name prefix for joined fields, in order
to avoid name collision
QGIS currently has support for joining non-spatial table formats supported by OGR (e.g., CSV, DBF and Excel), delimited text and the PostgreSQL provider.
14.1.10. Auxiliary Storage Properties
The regular way to customize styling and labeling is to use data-defined properties as described in Data defined override setup. However, it may not be possible if the underlying data is read only. Moreover, configuring these data-defined properties may be very time consuming or not desirable! For example, if you want to fully use map tools coming with The Label Toolbar, then you need to add and configure more than 20 fields in your original data source (X and Y positions, rotation angle, font style, color and so on).
The Auxiliary Storage mechanism provides the solution to these limitations and awkward configurations. Auxiliary fields are a roundabout way to automatically manage and store these data-defined properties (labels, diagram, symbology…) in a SQLite database thanks to editable joins. This allows you to store properties for layers that aren’t editable.
A tab is available in vector layer properties dialog to manage auxiliary storage:
Fig. 14.46 Auxiliary Storage tab
14.1.10.1. Labeling
Considering that the data source may be customized thanks to data-defined properties without being editable, labeling map tools described in The Label Toolbar are always available as soon as labeling is activated.
Actually, the auxiliary storage system needs an auxiliary layer to store these properties in a SQLite database (see Auxiliary storage database). Its creation process is run the first time you click on the map while a labeling map tool is currently activated. Then, a window is displayed, allowing you to select the primary key to use for joining (to ensure that features are uniquely identified):
Fig. 14.47 Auxiliary Layer creation dialog
As soon as an auxiliary layer is configured for the current data source, you can retrieve its information in the tab:
Fig. 14.48 Auxiliary Layer key
The auxiliary layer now has these characteristics:
the primary key is
ID,there are
0features using an auxiliary field,there are
0auxiliary fields.
Now that the auxiliary layer is created, you can edit the layer labels.
Click on a label while the  Change Label
map tool is activated, then you can update styling properties like sizes,
colors, and so on. The corresponding data-defined properties are created
and can be retrieved:
Change Label
map tool is activated, then you can update styling properties like sizes,
colors, and so on. The corresponding data-defined properties are created
and can be retrieved:
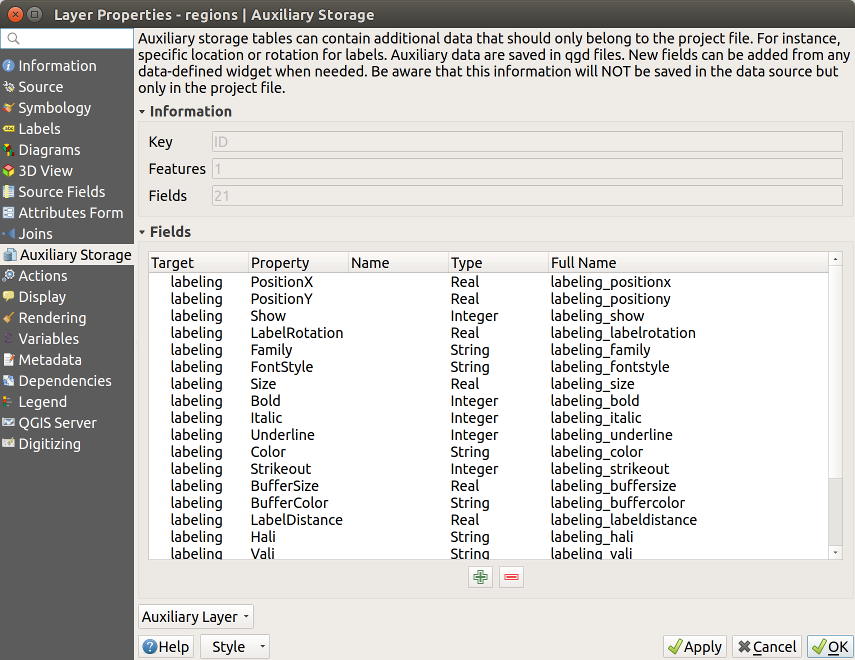
Fig. 14.49 Auxiliary Fields
As you can see in the figure above, 21 fields are automatically created and
configured for labeling. For example, the FontStyle auxiliary field type is
a String and is named labeling_fontstyle in the underlying SQLite
database. There is also 1 feature which is currently using these auxiliary
fields.
Notice that the icon ![]() is displayed in the Labels
properties tab indicating that the data-defined override options are set
correctly:
is displayed in the Labels
properties tab indicating that the data-defined override options are set
correctly:
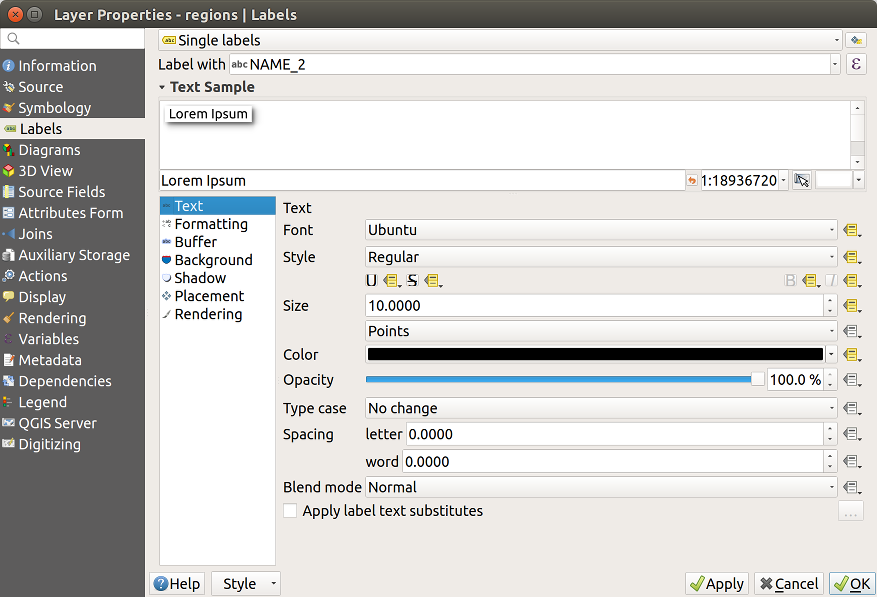
Fig. 14.50 Data-defined properties automatically created
Otherwise, there’s another way to create an auxiliary field for a
specific property thanks to the
![]() data-defined override button.
By clicking on Store data in the project, an auxiliary
field is automatically created for the Opacity field.
If you click on this button and the auxiliary layer is not created
yet, a window (Fig. 14.47) is first
displayed to select the primary key to use for joining.
data-defined override button.
By clicking on Store data in the project, an auxiliary
field is automatically created for the Opacity field.
If you click on this button and the auxiliary layer is not created
yet, a window (Fig. 14.47) is first
displayed to select the primary key to use for joining.
14.1.10.2. Symbology
Like the method described above for customizing labels, auxiliary fields can
also be used to stylize symbols and diagrams. To do this, click on
![]() Data-defined override and select Store data in
the project for a specific property. For example, the Fill
color field:
Data-defined override and select Store data in
the project for a specific property. For example, the Fill
color field:
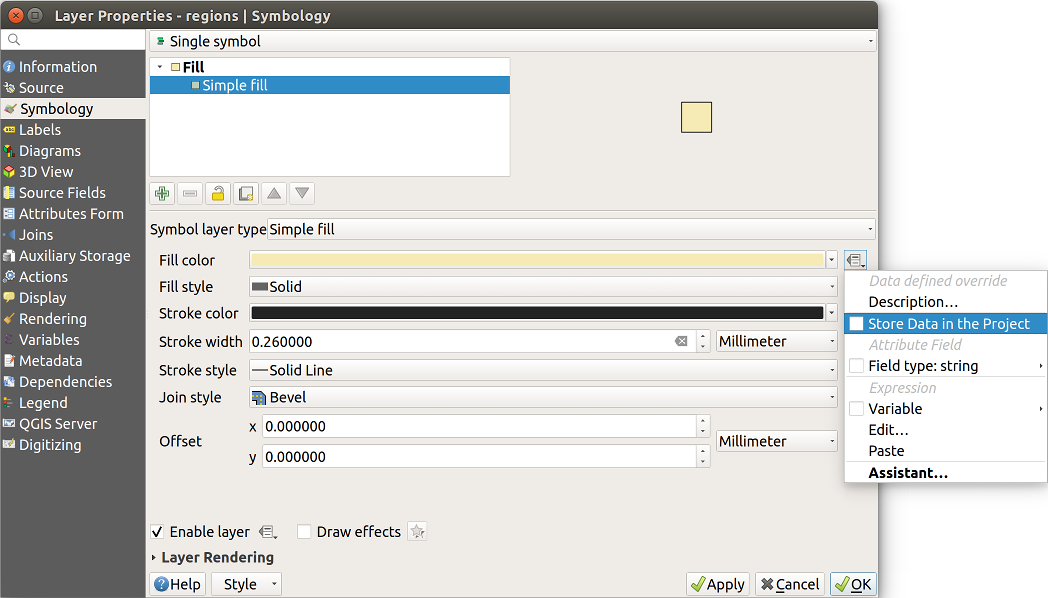
Fig. 14.51 Data-defined property menu for symbol
There are different attributes for each symbol (e.g. fill style, fill color, stroke color, etc…), so each auxiliary field representing an attribute requires a unique name to avoid conflicts. After selecting Store data in the project, a window opens and displays the Type of the field and prompts you to enter a unique name for the auxiliary field. For example, when creating a Fill color auxiliary field the following window opens:
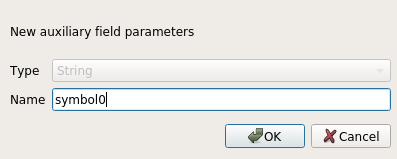
Fig. 14.52 Name of the auxiliary field for a symbol
Once created, the auxiliary field can be retrieved in the auxiliary storage tab:
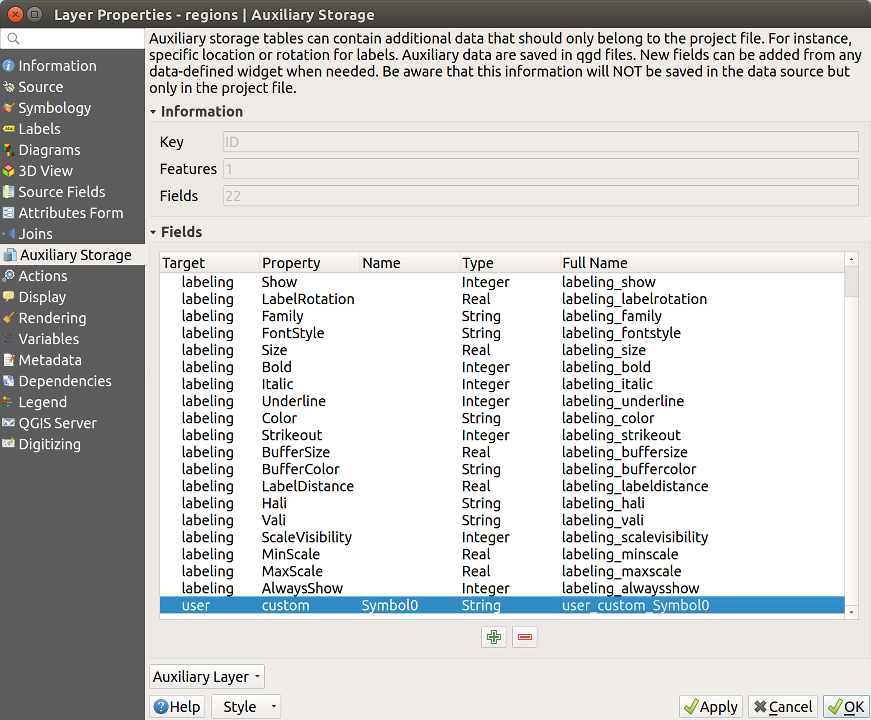
Fig. 14.53 Auxiliary field symbol
14.1.10.3. Attribute table and widgets
Auxiliary fields can be edited using the attribute table. However, not all auxiliary fields are initially visible in the attribute table.
Auxiliary fields representing attributes of a layer’s symbology, labeling,
appearance, or diagrams will appear automatically in the attribute table. The
exception are attributes that can be modified using the Label Toolbar
which are hidden by default. Auxiliary fields representing a Color have a
widget Color set by default, otherwise auxiliary fields default to the
Text Edit widget.
Auxiliary fields that represent attributes that can be modified using the Label toolbar are Hidden in the attribute table by default. To make a field visible, open the Attribute Form properties tab and change the value of an auxiliary field Widget Type from Hidden to another relevant value. For example, change the auxiliary_storage_labeling_size to Text Edit or change auxiliary_storage_labeling_color to the Color widget. Those fields will now be visible in the attribute table.
Auxiliary fields in the attribute table will appear like the following image:
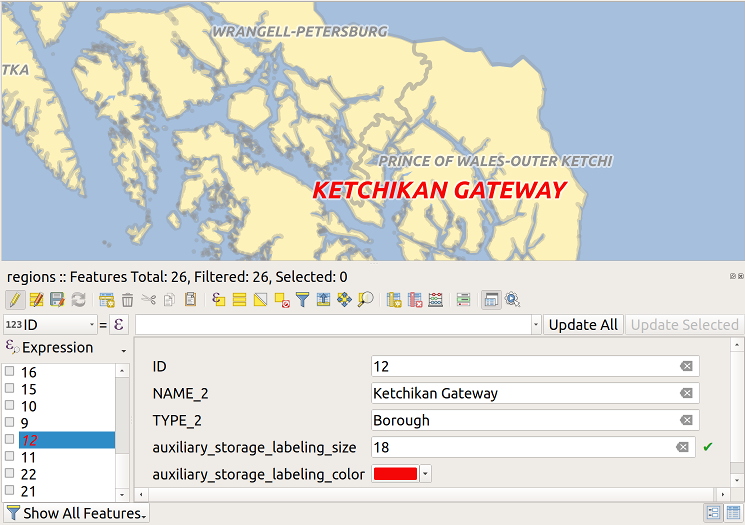
Fig. 14.54 Form with auxiliary fields
14.1.10.4. Management
The Auxiliary Layer menu allows you to manage the auxiliary fields:
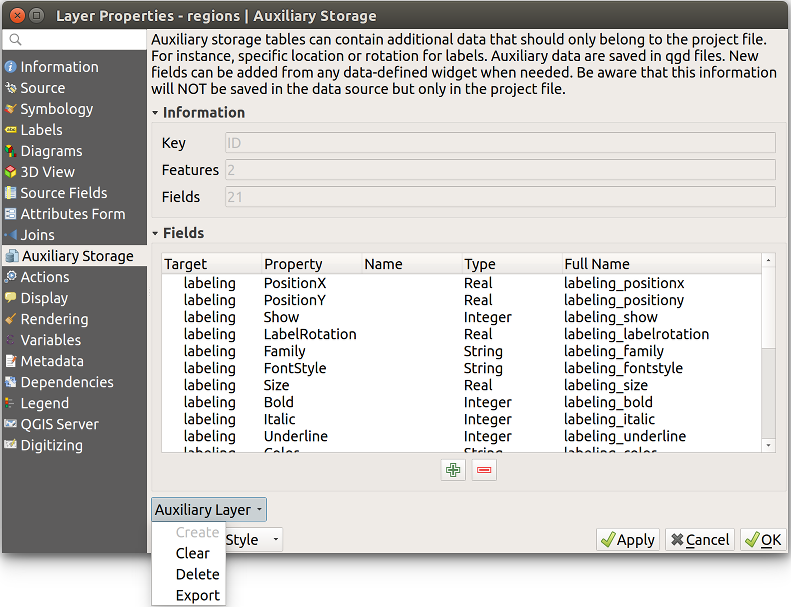
Fig. 14.55 Auxiliary layer management
The first item Create is disabled in this case because the auxiliary layer is already created. But in case of a fresh work, you can use this action to create an auxiliary layer. As explained in Labeling, a primary key will be needed then.
The Clear action allows to keep all auxiliary fields, but remove
their contents. This way, the number of features using these fields will fall to
0.
The Delete action completely removes the auxiliary layer. In other words, the corresponding table is deleted from the underlying SQLite database and properties customization are lost.
Finally, the Export action allows to save the auxiliary layer as a new vector layer. Note that geometries are not stored in auxiliary storage. However, in this case, geometries are exported from the original data source too.
14.1.10.5. Auxiliary storage database
When you save your project with the .qgs format, the SQLite database
used for auxiliary storage is saved at the same place but with the extension
.qgd.
For convenience, an archive may be used instead thanks to the .qgz format.
In this case, .qgd and .qgs files are both embedded in the archive.
14.1.11. Actions Properties
 QGIS provides the ability to perform an action based on the attributes
of a feature. This can be used to perform any number of actions, for example,
running a program with arguments built from the attributes of a feature or
passing parameters to a web reporting tool.
QGIS provides the ability to perform an action based on the attributes
of a feature. This can be used to perform any number of actions, for example,
running a program with arguments built from the attributes of a feature or
passing parameters to a web reporting tool.
Fig. 14.56 Overview action dialog with some sample actions
Actions are useful when you frequently want to run an external application or view a web page based on one or more values in your vector layer. They are divided into six types and can be used like this:
Generic, Mac, Windows and Unix actions start an external process.
Python actions execute a Python expression.
Generic and Python actions are visible everywhere.
Mac, Windows and Unix actions are visible only on the respective platform (i.e., you can define three ‘Edit’ actions to open an editor and the users can only see and execute the one ‘Edit’ action for their platform to run the editor).
There are several examples included in the dialog. You can load them by clicking on Create Default Actions. To edit any of the examples, double-click its row. One example is performing a search based on an attribute value. This concept is used in the following discussion.
The  Show in Attribute Table allows you to display in the
attribute table dialog the checked feature-scoped actions, either as Combo
Box or as Separate Buttons (see Configuring the columns).
Show in Attribute Table allows you to display in the
attribute table dialog the checked feature-scoped actions, either as Combo
Box or as Separate Buttons (see Configuring the columns).
14.1.11.1. Defining Actions
To define an attribute action, open the vector Layer
Properties dialog and click on the Actions tab. In the
Actions tab, click the  Add a new action
to open the Edit Action dialog.
Add a new action
to open the Edit Action dialog.
Select the action Type and provide a descriptive name
for the action. The action itself must contain the name of the application
that will be executed when the action is invoked.
You can add one or more attribute field values as arguments to the application.
When the action is invoked, any set of characters that start with a %
followed by the name of a field will be replaced by the value of that field.
The special characters %% will be replaced by the value of the field
that was selected from the identify results or attribute table (see using_actions
below). Double quote marks can be used to group text into a single argument to
the program, script or command. Double quotes will be ignored if preceded by a
backslash.
The Action Scopes allows you to define where the action should be available. You have 4 different choices:
Feature Scope: action is available when right click in the cell within the attribute table.
Field Scope: action is available when right click in the cell within the attribute table, in the feature form and in the default action button of the main toolbar.
Layer Scope: action is available in the action button in the attribute table toolbar. Be aware that this type of action involves the entire layer and not the single features.
Canvas: action is available in the main action button in the toolbar.
If you have field names that are substrings of other field names (e.g.,
col1 and col10), you should indicate that by surrounding the field name
(and the % character) with square brackets (e.g., [%col10]). This will
prevent the %col10 field name from being mistaken for the %col1 field
name with a 0 on the end. The brackets will be removed by QGIS when it
substitutes in the value of the field. If you want the substituted field to be
surrounded by square brackets, use a second set like this: [[%col10]].
Using the Identify Features tool, you can open the
Identify Results dialog. It includes a (Derived) item that contains
information relevant to the layer type. The values in this item can be accessed
in a similar way to the other fields by proceeding the derived field name with
(Derived).. For example, a point layer has an X and Y field, and the
values of these fields can be used in the action with %(Derived).X and
%(Derived).Y. The derived attributes are only available from the
Identify Results dialog box, not the Attribute Table dialog box.
Two example actions are shown below:
konqueror https://www.google.com/search?q=%namkonqueror https://www.google.com/search?q=%%
In the first example, the web browser konqueror is invoked and passed a URL
to open. The URL performs a Google search on the value of the nam field
from our vector layer. Note that the application or script called by the
action must be in the path, or you must provide the full path. To be certain, we
could rewrite the first example as:
/opt/kde3/bin/konqueror https://www.google.com/search?q=%nam. This will
ensure that the konqueror application will be executed when the action is
invoked.
The second example uses the %% notation, which does not rely on a particular field for its value. When the action is invoked, the %% will be replaced by the value of the selected field in the identify results or attribute table.
14.1.11.2. Using Actions
QGIS offers many ways to execute actions you enabled on a layer. Depending on their settings, they can be available:
in the drop-down menu of
 Run Feature Action button from
the Attributes toolbar or Attribute table dialog;
Run Feature Action button from
the Attributes toolbar or Attribute table dialog;when right-clicking a feature with the
 Identify Features tool
(see Identifying Features for more information);
Identify Features tool
(see Identifying Features for more information);from the Identify Results panel, under the Actions section;
as items of an Actions column in the Attribute Table dialog.
If you are invoking an action that uses the %% notation, right-click on the
field value in the Identify Results dialog or the
Attribute Table dialog that you wish to pass to the application
or script.
Here is another example that pulls data out of a vector layer and inserts
it into a file using bash and the echo command (so it will only work on
 or perhaps
or perhaps  ). The layer in question has fields for a species name
). The layer in question has fields for a species name
taxon_name, latitude lat and longitude long. We would like to be
able to make a spatial selection of localities and export these field values
to a text file for the selected record (shown in yellow in the QGIS map area).
Here is the action to achieve this:
bash -c "echo \"%taxon_name %lat %long\" >> /tmp/species_localities.txt"
After selecting a few localities and running the action on each one, opening the output file will show something like this:
Acacia mearnsii -34.0800000000 150.0800000000
Acacia mearnsii -34.9000000000 150.1200000000
Acacia mearnsii -35.2200000000 149.9300000000
Acacia mearnsii -32.2700000000 150.4100000000
As an exercise, we can create an action that does a Google search on the lakes
layer. First, we need to determine the URL required to perform a search on a
keyword. This is easily done by just going to Google and doing a simple
search, then grabbing the URL from the address bar in your browser. From this
little effort, we see that the format is https://www.google.com//search?q=QGIS,
where QGIS is the search term. Armed with this information, we can proceed:
Make sure the
lakeslayer is loaded.Open the Layer Properties dialog by double-clicking on the layer in the legend, or right-click and choose from the pop-up menu.
Click on the Actions tab.
Choose the Open action type,
Enter a name for the action, for example
Google Search.Additionally you can add a Short Name or even an Icon.
Choose the action Scope. See Defining Actions for further information. Leave the default settings for this example.
For the action, we need to provide the name of the external program to run. In this case, we can use Firefox. If the program is not in your path, you need to provide the full path.
Following the name of the external application, add the URL used for doing a Google search, up to but not including the search term:
https://www.google.com//search?q=The text in the Action field should now look like this:
https://www.google.com//search?q=Click on the drop-down box containing the field names for the
lakeslayer. It’s located just to the left of the Insert button.From the drop-down box, select ‘NAMES’ and click Insert.
Your action text now looks like this:
https://www.google.com//search?q=[%NAMES%]To finalize and add the action, click the OK button.
Fig. 14.57 Edit action dialog configured with the example
This completes the action, and it is ready to use. The final text of the action should look like this:
https://www.google.com//search?q=[%NAMES%]
We can now use the action. Close the Layer Properties dialog and
zoom in to an area of interest. Make sure the lakes layer is active and
identify a lake. In the result box you’ll now see that our action is visible:
Fig. 14.58 Select feature and choose action
When we click on the action, it brings up Firefox and navigates to the URL
https://www.google.com/search?q=Tustumena. It is also possible to add further
attribute fields to the action. Therefore, you can add a + to the end of
the action text, select another field and click on Insert Field. In
this example, there is just no other field available that would make sense
to search for.
You can define multiple actions for a layer, and each will show up in the Identify Results dialog.
You can also invoke actions from the attribute table by selecting a row and right-clicking, then choosing the action from the pop-up menu.
There are all kinds of uses for actions. For example, if you have a point layer containing locations of images or photos along with a file name, you could create an action to launch a viewer to display the image. You could also use actions to launch web-based reports for an attribute field or combination of fields, specifying them in the same way we did in our Google search example.
We can also make more complex examples, for instance, using Python actions.
Usually, when we create an action to open a file with an external application, we can use absolute paths, or eventually relative paths. In the second case, the path is relative to the location of the external program executable file. But what about if we need to use relative paths, relative to the selected layer (a file-based one, like Shapefile or SpatiaLite)? The following code will do the trick:
command = "firefox"
imagerelpath = "images_test/test_image.jpg"
layer = qgis.utils.iface.activeLayer()
import os.path
layerpath = layer.source() if layer.providerType() == 'ogr'
else (qgis.core.QgsDataSourceURI(layer.source()).database()
if layer.providerType() == 'spatialite' else None)
path = os.path.dirname(str(layerpath))
image = os.path.join(path,imagerelpath)
import subprocess
subprocess.Popen( [command, image ] )
We just have to remember that the action is one of type Python and the command and imagerelpath variables must be changed to fit our needs.
But what about if the relative path needs to be relative to the (saved) project file? The code of the Python action would be:
command = "firefox"
imagerelpath = "images/test_image.jpg"
projectpath = qgis.core.QgsProject.instance().fileName()
import os.path
path = os.path.dirname(str(projectpath)) if projectpath != '' else None
image = os.path.join(path, imagerelpath)
import subprocess
subprocess.Popen( [command, image ] )
Another Python action example is the one that allows us to add new layers to the project. For instance, the following examples will add to the project respectively a vector and a raster. The names of the files to be added to the project and the names to be given to the layers are data driven (filename and layername are column names of the table of attributes of the vector where the action was created):
qgis.utils.iface.addVectorLayer('/yourpath/[% "filename" %].shp',
'[% "layername" %]', 'ogr')
To add a raster (a TIF image in this example), it becomes:
qgis.utils.iface.addRasterLayer('/yourpath/[% "filename" %].tif',
'[% "layername" %]')
14.1.12. Display Properties
 The Display tab helps you configure fields to use for
feature identification:
The Display tab helps you configure fields to use for
feature identification:
The Display name: based on a field or an expression. This is:
the label shown on top of the feature information in the Identify tool results;
the field used in the locator bar when looking for features in all layers;
the feature identifier in the attribute table form view;
the map tip information, i.e. the message displayed in the map canvas when hovering over a feature of the active layer with the
 Show
Map Tips icon pressed. Applicable when no HTML Map Tip is set.
Show
Map Tips icon pressed. Applicable when no HTML Map Tip is set.
The HTML Map Tip is specifically created for the map tips: it’s a more complex and full HTML text mixing fields, expressions and html tags (multiline, fonts, images, hyperlink…).
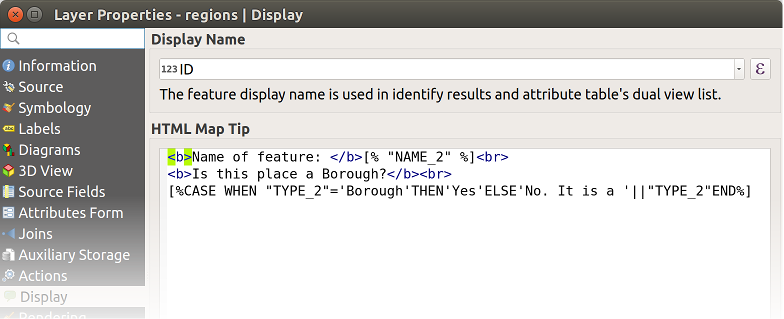
Fig. 14.59 HTML code for map tip
To activate map tips, select the menu option or click on the  Show Map Tips icon of the
Attributes Toolbar. Map tip is a cross-session feature meaning that
once activated, it stays on and apply to any layer in any project, even in
future QGIS sessions until it’s toggled off.
Show Map Tips icon of the
Attributes Toolbar. Map tip is a cross-session feature meaning that
once activated, it stays on and apply to any layer in any project, even in
future QGIS sessions until it’s toggled off.
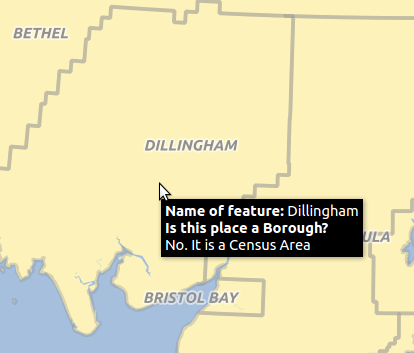
Fig. 14.60 Map tip made with HTML code
14.1.13. Rendering Properties
14.1.13.1. Scale dependent visibility
You can set the Maximum (inclusive) and Minimum
(exclusive) scale, defining a range of scale in which features will be
visible. Out of this range, they are hidden. The  Set to current canvas scale button helps you use the current map
canvas scale as boundary of the range visibility.
See Scale Dependent Rendering for more information.
Set to current canvas scale button helps you use the current map
canvas scale as boundary of the range visibility.
See Scale Dependent Rendering for more information.
14.1.13.2. Simplify geometry
QGIS offers support for on-the-fly feature generalisation. This can
improve rendering times when drawing many complex features at small scales.
This feature can be enabled or disabled in the layer settings using the
 Simplify geometry option. There is also a global
setting that enables generalisation by default for newly added layers (see
global simplification for more information).
Simplify geometry option. There is also a global
setting that enables generalisation by default for newly added layers (see
global simplification for more information).
Fig. 14.61 Layer Geometry Simplification dialog
Note
Feature generalisation may introduce artefacts into your rendered output in some cases. These may include slivers between polygons and inaccurate rendering when using offset-based symbol layers.
While rendering extremely detailed layers (e.g. polygon layers with a huge number of nodes), this can cause layout exports in PDF/SVG format to be huge as all nodes are included in the exported file. This can also make the resultant file very slow to work with/open in other programs.
Checking  Force layer to render as raster forces these
layers to be rasterised so that the exported files won’t have to include all
the nodes contained in these layers and the rendering is therefore sped up.
Force layer to render as raster forces these
layers to be rasterised so that the exported files won’t have to include all
the nodes contained in these layers and the rendering is therefore sped up.
You can also do this by forcing the layout to export as a raster, but that is an all-or-nothing solution, given that the rasterisation is applied to all layers.
Refresh layer at interval (seconds): set a timer to automatically refresh individual layers at a matching interval. Canvas updates are deferred in order to avoid refreshing multiple times if more than one layer has an auto update interval set.
Depending on the data provider (e.g. PostgreSQL), notifications can be sent to
QGIS when changes are applied to the data source, out of QGIS. Use the  Refresh layer on notification option to trigger an update.
You can also limit the layer refresh to a specific message set in the
Refresh layer on notification option to trigger an update.
You can also limit the layer refresh to a specific message set in the  Only if message is text box.
Only if message is text box.
14.1.14. Variables Properties
![]() The Variables tab lists all the variables available at
the layer’s level (which includes all global and project’s variables).
The Variables tab lists all the variables available at
the layer’s level (which includes all global and project’s variables).
It also allows the user to manage layer-level variables. Click the  button to add a new custom layer-level variable. Likewise, select a custom
layer-level variable from the list and click the
button to add a new custom layer-level variable. Likewise, select a custom
layer-level variable from the list and click the  button to remove
it.
button to remove
it.
More information on variables usage in the General Tools Storing values in Variables section.
14.1.15. Metadata Properties
 The Metadata tab provides you with options to create
and edit a metadata report on your layer. Information to fill concern:
The Metadata tab provides you with options to create
and edit a metadata report on your layer. Information to fill concern:
the data Identification: basic attribution of the dataset (parent, identifier, title, abstract, language…);
the Categories the data belongs to. Alongside the ISO categories, you can add custom ones;
the Keywords to retrieve the data and associated concepts following a standard based vocabulary;
the Access to the dataset (licenses, rights, fees, and constraints);
the Extent of the dataset, either spatial one (CRS, map extent, altitudes) or temporal;
the Contact of the owner(s) of the dataset;
the Links to ancillary resources and related information;
the History of the dataset.
A summary of the filled information is provided in the Validation tab and helps you identify potential issues related to the form. You can then either fix them or ignore them.
Metadata are currently saved in the project file. They can also be saved in a
.qmd file alongside file based layers or in a local .sqlite
database for remote layers (e.g. PostGIS).
14.1.16. Dependencies Properties
 The Dependencies tab allows to declare data
dependencies between layers. A data dependency occurs when a data modification
in a layer, not by direct user manipulation, may modify data of other layers.
This is the case for instance when geometry of a layer is updated by a
database trigger or custom PyQGIS scripting after modification of another
layer’s geometry.
The Dependencies tab allows to declare data
dependencies between layers. A data dependency occurs when a data modification
in a layer, not by direct user manipulation, may modify data of other layers.
This is the case for instance when geometry of a layer is updated by a
database trigger or custom PyQGIS scripting after modification of another
layer’s geometry.
In the Dependencies tab, you can select any layers which may externally alter the data in the current layer. Correctly specifying dependent layers allows QGIS to invalidate caches for this layer when the dependent layers are altered.
14.1.17. Legend Properties
 The Legend properties tab provides you with advanced
settings for the Layers panel and/or the print
layout legend. These options include:
The Legend properties tab provides you with advanced
settings for the Layers panel and/or the print
layout legend. These options include:
 Text on symbols: In some cases it can be useful to add
extra information to the symbols in the legend. With this frame, you can
affect to any of the symbols used in the layer symbology a text that is
displayed over the symbol, in both Layers panel and print layout
legend. This mapping is done by typing each text next to the symbol in the
table widget or filling the table using the Set Labels from Expression
button. Text appearance is handled through the font and color selector
widgets of the Text Format button.
Text on symbols: In some cases it can be useful to add
extra information to the symbols in the legend. With this frame, you can
affect to any of the symbols used in the layer symbology a text that is
displayed over the symbol, in both Layers panel and print layout
legend. This mapping is done by typing each text next to the symbol in the
table widget or filling the table using the Set Labels from Expression
button. Text appearance is handled through the font and color selector
widgets of the Text Format button.
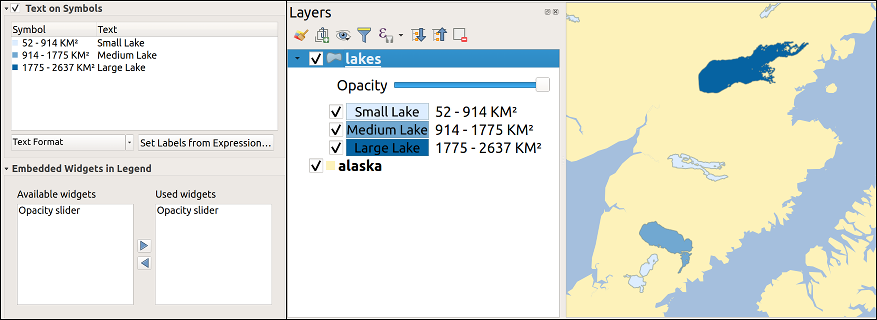
Fig. 14.62 Setting text on symbols (left) and its rendering in the Layers panel (right)
a list of widgets you can embed within the layer tree in the Layers panel. The idea is to have a way to quickly access some actions that are often used with the layer (setup transparency, filtering, selection, style or other stuff…).
By default, QGIS provides transparency widget but this can be extended by plugins registering their own widgets and assign custom actions to layers they manage.
14.1.18. QGIS Server Properties
 The QGIS Server tab consists of Description,
Attribution, MetadataURL, and LegendUrl sections.
The QGIS Server tab consists of Description,
Attribution, MetadataURL, and LegendUrl sections.
You can add or edit a title and abstract for the layer in the Description section. It’s also possible to define a Keyword list here. These keyword lists can be used in a metadata catalog. If you want to use a title from an XML metadata file, you have to fill in a link in the DataUrl field.
Use Attribution to get attribute data from an XML metadata catalog.
In MetadataUrl, you can define the general path to the XML metadata catalog. This information will be saved in the QGIS project file for subsequent sessions and will be used for QGIS server.
In the LegendUrl section, you can provide the url of a legend image in the url field. You can use the Format drop-down option to apply the appropriate format of the image. Currently png, jpg and jpeg image formats are supported.
Fig. 14.63 QGIS Server tab in vector layers properties dialog
14.1.19. Digitizing Properties
 The Digitizing tab gives access to options that help to ensure the
quality of digitized geometries.
The Digitizing tab gives access to options that help to ensure the
quality of digitized geometries.
Fig. 14.64 The QGIS Digitizing tab in the vector layers properties dialog
14.1.19.1. Automatic Fixes
Options in the Automatic Fixes section will directly affect the vertices
of any geometry which is added or modified.
If the  Remove duplicate nodes option is checked, any two subsequent
vertices with exactly the same coordinates will be removed.
If the Geometry precision is set, all vertices will be rounded to
the closest multiple of the configured geometry precision. The rounding will
happen in the layer coordinate reference system. Z and M values are not
rounded. With many map tools, a grid is shown on the canvas while digitizing.
Remove duplicate nodes option is checked, any two subsequent
vertices with exactly the same coordinates will be removed.
If the Geometry precision is set, all vertices will be rounded to
the closest multiple of the configured geometry precision. The rounding will
happen in the layer coordinate reference system. Z and M values are not
rounded. With many map tools, a grid is shown on the canvas while digitizing.
14.1.19.2. Geometry Checks
In the Geometry checks section, additional validations on a per
geometry basis can be activated. Immediately after any geometry modification,
failures in these checks are reported to the user in the geometry validation panel.
As long as a check is failing, it is not possible to save the layer.
The  Is valid check will run basic validity checks like self intersection on
geometries.
Is valid check will run basic validity checks like self intersection on
geometries.
14.1.19.3. Topology Checks
In the Topology checks section, additional topology validation checks can be activated. Topology checks will be executed when the user saves the layer. Check errors will be reported in the geometry validation panel. As long as validation errors are present, the layer can not be saved. Topology checks are executed in the area of the bounding box of the modified features. Since other features may be present in the same area, topological errors concerning these features are reported as well as errors introduced in the current edit session.
14.1.19.3.1. Gap check exceptions
Sometimes it is desirable to keep gaps inside an area in a polygon layer that otherwise is fully covered by polygons. For example, a land use layer may have acceptable holes for lakes. It is possible to define areas that are ignored in the gap check. Since gaps inside these areas are allowed, we will refer to them as Allowed Gaps areas.
In the options for the gap checks under Allowed Gaps, an Allowed Gaps layer can be configured.
Whenever the gap check is executed, gaps which are covered by one or more polygons in the Allowed Gaps Layer are not reported as topology errors.
It is also possible to configure an additional Buffer. This buffer is applied to each polygon on the Allowed Gaps Layer. This makes it possible to make the tests less susceptible to small changes in the outlines at the borders of gaps.
When Allowed Gaps are enabled, an additional button (Add Allowed Gap) for detected gap errors is available in the geometry validation dock, where gaps are reported during digitizing. If the Add Allowed Gap button is pushed, a new polygon with the geometry of the detected gap is inserted into the Allowed Gaps Layer. This makes it possible to quickly flag gaps as allowed.