Svarbu
Vertimas yra bendruomenės pastangos, prie kurių jūs galite prisijungti. Šis puslapis šiuo metu išverstas 72.65%.
24.1.19. Vektorių analizė
24.1.19.1. Bazinė laukų statistika
Kuria bazinę vektorinio sluoksnio atributų lentelės lauko statistiką. Palaikomi skaitiniai, datos, laiko ir tekstiniai laukai. Grąžinama statistika priklauso nuo lauko tipo.
Statistiką galima kurti kaip lentelę arba kaip HTML failą, o pasiekti ją galima per meniu .
Numatytas meniu:
Parametrai
Užrašas |
Pavadinimas |
Tipas |
Aprašymas |
|---|---|---|---|
Įvesties vektorius |
|
[vektorius: bet koks] |
Vektorinis sluoksnis, kurio statistiką reikia skaičiuoti |
Laukas, kurio statistiką reikia skaičiuoti |
|
[lentelės laukas: bet koks] |
Bet koks palaikomas lentelės laukas, kurio statistiką reikia skaičiuoti |
Statistika Pasirinktinis |
|
[vektorius: lentelė] Numatytas: |
Nurodykite išvesties lentelę sukurtai statistikai. Vienas iš:
Čia taipogi galima pakeisti failo koduotę. |
Statistikos ataskaita Pasirinktinis |
|
[html] Numatytas: |
Paskaičiuotos statistikos failo specifikacija. Vienas iš:
|
Išvestys
Užrašas |
Pavadinimas |
Tipas |
Aprašymas |
|---|---|---|---|
Statistika |
|
[vektorius: lentelė] |
Lentelė su paskaičiuota statistika |
Statistikos ataskaita |
|
[html] |
HTML failas su paskaičiuota statistika |
Skaičius |
|
[skaičius: sveikas skaičius] |
|
Unikalių reikšmių skaičius |
|
[skaičius: sveikas skaičius] |
|
Tuščių (null) reikšmių skaičius |
|
[skaičius: sveikas skaičius] |
|
Netuščių reikšmių skaičius |
|
[skaičius: sveikas skaičius] |
|
Minimali reikšmė |
|
[toks pat, kaip įvestis] |
|
Maksimali reikšmė |
|
[toks pat, kaip įvestis] |
|
Minimalus ilgis |
|
[skaičius: sveikas skaičius] |
|
Maksimalus ilgis |
|
[skaičius: sveikas skaičius] |
|
Vidutinis ilgis |
|
[skaičius: slankaus kablelio] |
|
Variacijos koeficientas |
|
[skaičius: slankaus kablelio] |
|
Suma |
|
[skaičius: slankaus kablelio] |
|
Vidutinė reikšmė |
|
[skaičius: slankaus kablelio] |
|
Standartinis nuokrypis |
|
[skaičius: slankaus kablelio] |
|
Diapazonas |
|
[skaičius: slankaus kablelio] |
|
Mediana |
|
[skaičius: slankaus kablelio] |
|
Mažuma (rečiausiai pasitaikanti reikšmė) |
|
[toks pat, kaip įvestis] |
|
Dauguma (dažniausiai pasitaikanti reikšmė) |
|
[toks pat, kaip įvestis] |
|
Pirmas kvartilis |
|
[skaičius: slankaus kablelio] |
|
Trečias kvartilis |
|
[skaičius: slankaus kablelio] |
|
Tarpkvartilinis diapazonas (IQR) |
|
[skaičius: slankaus kablelio] |
Pythono kodas
Algoritmo ID: qgis:basicstatisticsforfields
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
algoritmo id rodomas, kai užvedate pelę virš algoritmo apdorojimo įrankinėje. parametrų žodynas teikia parametrų pavadinimus ir reikšmes. Daugiau informacijos apie tai, kaip vykdyti apdorojimo algoritmus Pythono konsolėje rasite skyriuje Using processing algorithms from the console.
24.1.19.2. Pakilimas linija
Skaičiuoja bendrą pakilimą ar nusileidimą palei linijos geometriją. Įvesties sluoksnis turi turėti Z reikšmes. Jei Z reikšmių nėra, galima naudoti algoritmą Drape (set Z value from raster) Z reikšmių užpildymui pagal DEM sluoksnį.
Išvesties sluoksnis yra įvesties sluoksnio kopija su papildomai laukais, kuriuose yra bendras pakilimas (climb), bendras nusileidimas (descent), minimalus aukštis (minelev) ir maksimalus aukštis (maxelev) kiekvienai linijos geometrijai. Jei įvesties sluoksnyje yra laukai su tokiais pačiais pavadinimais, kaip nurodyti, jie bus pervadinti (laukų pavadinimai bus pakeisti į „pavadinimas_2“, „pavadinimas_3“, ir t.t., randant pirmą nepasikartojantį pavadinimą).
Parametrai
Užrašas |
Pavadinimas |
Tipas |
Aprašymas |
|---|---|---|---|
Linijų sluoksnis |
|
[vektorius: linija] |
Linijų sluoksnis, kuriam reikia skaičiuoti pakilimą. Privalo turėti Z reikšmes |
Pakilimo sluoksnis |
|
[vektorius: linija] Numatytas: |
Išvesties (linijų) sluoksnio specifikacija. Vienas iš:
Čia taipogi galima pakeisti failo koduotę. |
Išvestys
Užrašas |
Pavadinimas |
Tipas |
Aprašymas |
|---|---|---|---|
Pakilimo sluoksnis |
|
[vektorius: linija] |
Linijų sluoksnis su naujais pakilimo skaičiavimo atributais. |
Bendras pakilimas |
|
[skaičius: slankaus kablelio] |
Pakilimo suma visoms įvesties sluoksnio geometrijoms |
Bendras nusileidimas |
|
[skaičius: slankaus kablelio] |
Nusileidimo suma visoms įvesties sluoksnio geometrijoms |
Minimalus aukštis |
|
[skaičius: slankaus kablelio] |
Minimalus sluoksnio geometrijų aukštis |
Maksimalus aukštis |
|
[skaičius: slankaus kablelio] |
Maksimalus sluoksnio geometrijų aukštis |
Pythono kodas
Algoritmo ID: qgis:climbalongline
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
algoritmo id rodomas, kai užvedate pelę virš algoritmo apdorojimo įrankinėje. parametrų žodynas teikia parametrų pavadinimus ir reikšmes. Daugiau informacijos apie tai, kaip vykdyti apdorojimo algoritmus Pythono konsolėje rasite skyriuje Using processing algorithms from the console.
24.1.19.3. Skaičiuoti taškus poligone
Ima taškų ir poligonų sluoksnį ir suskaičiuoja, kiek taškų sluoksnyje yra taškų, kurie yra kiekviename poligono sluoksnio poligone.
Sukuriamas naujas poligonų sluoksnis su lygiai tokiu pačiu turiniu, kaip ir įvesties poligonų sluoksnis, tik jame yra papildomas laukas su kiekvieno poligono taškų skaičiumi.
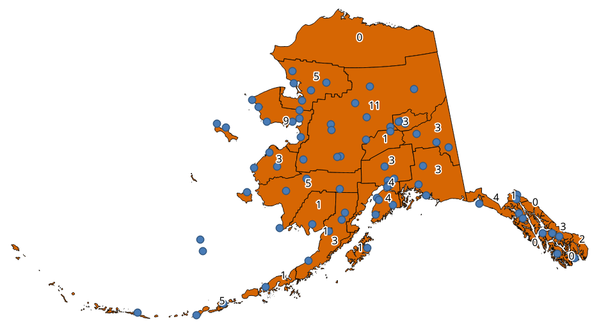
Fig. 24.40 Užrašai poligonuose rodo taškų skaičių
Galima naudoti neprivalomą svorio lauką, kuriam bus priskirtas kiekvieno taško svoris. Alternatyviai, galima nurodyti unikalios klasės lauką. Jei naudojami abu variantai, svorio laukas bus naudojamas, o unikalios klasės laukas bus ignoruojamas.
 Leidžia vietoje keisti poligonų geoobjektus
Leidžia vietoje keisti poligonų geoobjektus
Numatytas meniu:
Parametrai
Užrašas |
Pavadinimas |
Tipas |
Aprašymas |
|---|---|---|---|
Poligonai |
|
[vektorius: poligonas] |
Poligonų sluoksnis, kurio geoobjektai susiejami su į juos patenkančių taškų skaičiumi |
Taškai |
|
[vektorius: taškas] |
Taškų sluoksnis su skaičiuojamais geoobjektais |
Svorio laukas Pasirinktinis |
|
[lentelės laukas: bet koks] |
Taškų sluoksnio laukas. Bus paskaičiuota suma svorio lauko reikšmių iš taškų, patenkančių į poligoną. Jei svoris nėra skaitinis, skaičius bus |
Klasės laukas Pasirinktinis |
|
[lentelės laukas: bet koks] |
Taškai klasifikuojami pagal parinktą atributą, o jei keli taškai su ta pačia atributo reikšme yra poligone, tik vienas iš jų bus paskaičiuotas. Taip paskaičiuojamas galutinis taškų su skirtingomis klasėmis poligone skaičius. |
Skaičiaus lauko pavadinimas |
|
[tekstas] Numatytas: ‚NUMPOINTS‘ |
Pavadinimas lauko, į kurį reikia įrašyti taškų skaičių |
Skaičius |
|
[vektorius: poligonas] Numatytas: |
Išvesties sluoksnio specifikacija. Vienas iš:
Čia taipogi galima pakeisti failo koduotę. |
Išvestys
Užrašas |
Pavadinimas |
Tipas |
Aprašymas |
|---|---|---|---|
Skaičius |
|
[vektorius: poligonas] |
Gaunamas sluoksnis su atributų lentele, kurioje yra naujas laukas su taškų skaičiumi |
Pythono kodas
Algoritmo ID: native:countpointsinpolygon
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
algoritmo id rodomas, kai užvedate pelę virš algoritmo apdorojimo įrankinėje. parametrų žodynas teikia parametrų pavadinimus ir reikšmes. Daugiau informacijos apie tai, kaip vykdyti apdorojimo algoritmus Pythono konsolėje rasite skyriuje Using processing algorithms from the console.
24.1.19.4. DBSCAN clustering
Clusters point features based on a 2D implementation of Density-based spatial clustering of applications with noise (DBSCAN) algorithm.
The algorithm requires two parameters, a minimum cluster size, and the maximum distance allowed between clustered points.
Taip pat žiūrėkite
Parametrai
Baziniai parametrai
Užrašas |
Pavadinimas |
Tipas |
Aprašymas |
|---|---|---|---|
Įvesties sluoksnis |
|
[vektorius: taškas] |
Layer to analyze |
Minimum cluster size |
|
[skaičius: sveikas skaičius] Numatytas: 5 |
Minimum number of features to generate a cluster |
Maximum distance between clustered points |
|
[skaičius: slankaus kablelio] Numatytas: 1.0 |
Distance beyond which two features can not belong to the same cluster (eps) |
Clusters |
|
[vektorius: taškas] Numatytas: |
Specify the vector layer for the result of the clustering. One of:
Čia taipogi galima pakeisti failo koduotę. |
Išmanesni parametrai
Užrašas |
Pavadinimas |
Tipas |
Aprašymas |
|---|---|---|---|
Treat border points as noise (DBSCAN*) |
|
[boolean] Numatytas: ne |
If checked, points on the border of a cluster are themselves treated as unclustered points, and only points in the interior of a cluster are tagged as clustered. |
Cluster field name |
|
[tekstas] Default: ‚CLUSTER_ID‘ |
Name of the field where the associated cluster number shall be stored |
Cluster size field name |
|
[tekstas] Default: ‚CLUSTER_SIZE‘ |
Name of the field with the count of features in the same cluster |
Išvestys
Užrašas |
Pavadinimas |
Tipas |
Aprašymas |
|---|---|---|---|
Clusters |
|
[vektorius: taškas] |
Vector layer containing the original features with a field setting the cluster they belong to |
Number of clusters |
|
[skaičius: sveikas skaičius] |
The number of clusters discovered |
Pythono kodas
Algorithm ID: native:dbscanclustering
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
algoritmo id rodomas, kai užvedate pelę virš algoritmo apdorojimo įrankinėje. parametrų žodynas teikia parametrų pavadinimus ir reikšmes. Daugiau informacijos apie tai, kaip vykdyti apdorojimo algoritmus Pythono konsolėje rasite skyriuje Using processing algorithms from the console.
24.1.19.5. Distance matrix
Calculates for point features distances to their nearest features in the same layer or in another layer.
Numatytas meniu:
Taip pat žiūrėkite
Parametrai
Užrašas |
Pavadinimas |
Tipas |
Aprašymas |
|---|---|---|---|
Input point layer |
|
[vektorius: taškas] |
Point layer for which the distance matrix is calculated (from points) |
Input unique ID field |
|
[lentelės laukas: bet koks] |
Field to use to uniquely identify features of the input layer. Used in the output attribute table. |
Target point layer |
|
[vektorius: taškas] |
Point layer containing the nearest point(s) to search (to points) |
Target unique ID field |
|
[lentelės laukas: bet koks] |
Field to use to uniquely identify features of the target layer. Used in the output attribute table. |
Output matrix type |
|
[sąrašas] Numatytas: 0 |
Different types of calculation are available:
|
Use only the nearest (k) target points |
|
[skaičius: sveikas skaičius] Numatytas: 0 |
You can choose to calculate the distance to all the points in the target layer (0) or limit to a number (k) of closest features. |
Distance matrix |
|
[vektorius: taškas] Numatytas: |
Išvesties vektorinio sluoksnio specifikacija. Vienas iš:
Čia taipogi galima pakeisti failo koduotę. |
Išvestys
Užrašas |
Pavadinimas |
Tipas |
Aprašymas |
|---|---|---|---|
Distance matrix |
|
[vektorius: taškas] |
Point (or MultiPoint for the „Linear (N * k x 3)“ case) vector layer containing the distance calculation for each input feature. Its features and attribute table depend on the selected output matrix type. |
Pythono kodas
Algorithm ID: qgis:distancematrix
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
algoritmo id rodomas, kai užvedate pelę virš algoritmo apdorojimo įrankinėje. parametrų žodynas teikia parametrų pavadinimus ir reikšmes. Daugiau informacijos apie tai, kaip vykdyti apdorojimo algoritmus Pythono konsolėje rasite skyriuje Using processing algorithms from the console.
24.1.19.6. Distance to nearest hub (line to hub)
Creates lines that join each feature of an input vector to the nearest feature in a destination layer. Distances are calculated based on the center of each feature.
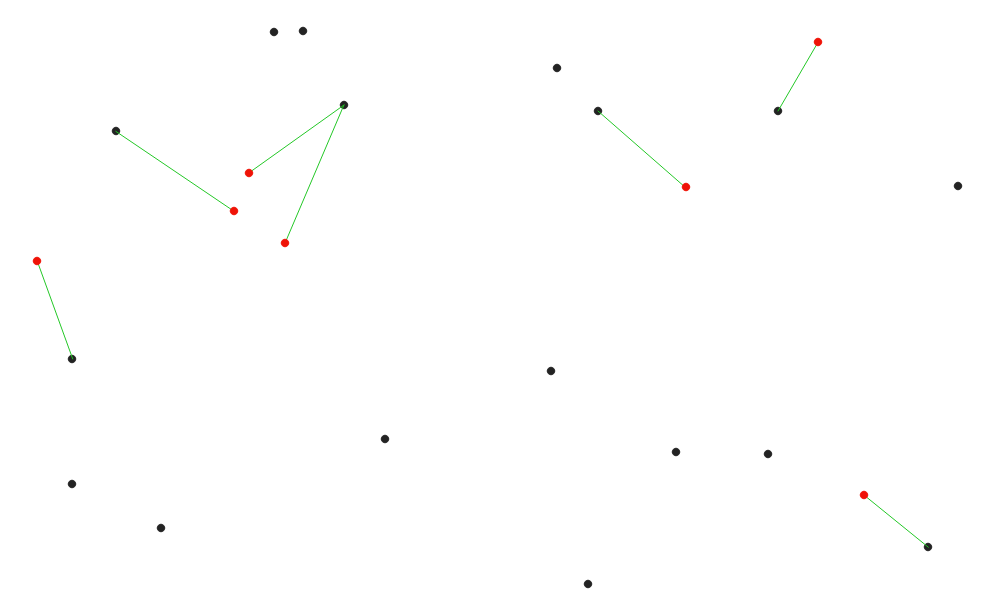
Fig. 24.41 Display the nearest hub for the red input features
Taip pat žiūrėkite
Distance to nearest hub (points), Join attributes by nearest
Parametrai
Užrašas |
Pavadinimas |
Tipas |
Aprašymas |
|---|---|---|---|
Source points layer |
|
[vektorius: geometrija] |
Vector layer for which the nearest feature is searched |
Destination hubs layer |
|
[vektorius: geometrija] |
Vector layer containing the features to search for |
Hub layer name attribute |
|
[lentelės laukas: bet koks] |
Field to use to uniquely identify features of the destination layer. Used in the output attribute table |
Measurement unit |
|
[sąrašas] Numatytas: 0 |
Units in which to report the distance to the closest feature:
|
Hub distance |
|
[vektorius: linija] Numatytas: |
Specify the output line vector layer connecting the matching points. One of:
Čia taipogi galima pakeisti failo koduotę. |
Išvestys
Užrašas |
Pavadinimas |
Tipas |
Aprašymas |
|---|---|---|---|
Hub distance |
|
[vektorius: linija] |
Line vector layer with the attributes of the input features, the identifier of their closest feature and the calculated distance. |
Pythono kodas
Algorithm ID: qgis:distancetonearesthublinetohub
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
algoritmo id rodomas, kai užvedate pelę virš algoritmo apdorojimo įrankinėje. parametrų žodynas teikia parametrų pavadinimus ir reikšmes. Daugiau informacijos apie tai, kaip vykdyti apdorojimo algoritmus Pythono konsolėje rasite skyriuje Using processing algorithms from the console.
24.1.19.7. Distance to nearest hub (points)
Creates a point layer representing the center of the input features with the addition of two fields containing the identifier of the nearest feature (based on its center point) and the distance between the points.
Taip pat žiūrėkite
Distance to nearest hub (line to hub), Join attributes by nearest
Parametrai
Užrašas |
Pavadinimas |
Tipas |
Aprašymas |
|---|---|---|---|
Source points layer |
|
[vektorius: bet koks] |
Vector layer for which the nearest feature is searched |
Destination hubs layer |
|
[vektorius: bet koks] |
Vector layer containing the features to search for |
Hub layer name attribute |
|
[lentelės laukas: bet koks] |
Field to use to uniquely identify features of the destination layer. Used in the output attribute table |
Measurement unit |
|
[sąrašas] Numatytas: 0 |
Units in which to report the distance to the closest feature:
|
Hub distance |
|
[vektorius: taškas] Numatytas: |
Specify the output point vector layer with the nearest hub. One of:
Čia taipogi galima pakeisti failo koduotę. |
Išvestys
Užrašas |
Pavadinimas |
Tipas |
Aprašymas |
|---|---|---|---|
Hub distance |
|
[vektorius: taškas] |
Point vector layer representing the center of the source features with their attributes, the identifier of their closest feature and the calculated distance. |
Pythono kodas
Algorithm ID: qgis:distancetonearesthubpoints
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
algoritmo id rodomas, kai užvedate pelę virš algoritmo apdorojimo įrankinėje. parametrų žodynas teikia parametrų pavadinimus ir reikšmes. Daugiau informacijos apie tai, kaip vykdyti apdorojimo algoritmus Pythono konsolėje rasite skyriuje Using processing algorithms from the console.
24.1.19.8. Join by lines (hub lines)
Creates hub and spoke diagrams by connecting lines from points on the Spoke layer to matching points in the Hub layer.
Determination of which hub goes with each point is based on a match between the Hub ID field on the hub points and the Spoke ID field on the spoke points.
If input layers are not point layers, a point on the surface of the geometries will be taken as the connecting location.
Optionally, geodesic lines can be created, which represent the shortest path on the surface of an ellipsoid. When geodesic mode is used, it is possible to split the created lines at the antimeridian (±180 degrees longitude), which can improve rendering of the lines. Additionally, the distance between vertices can be specified. A smaller distance results in a denser, more accurate line.
Įspėjimas
Šis algoritmas išmeta esamus pirminius raktus ar FID reikšmes ir perkuria jas išvesties sluoksniuose.
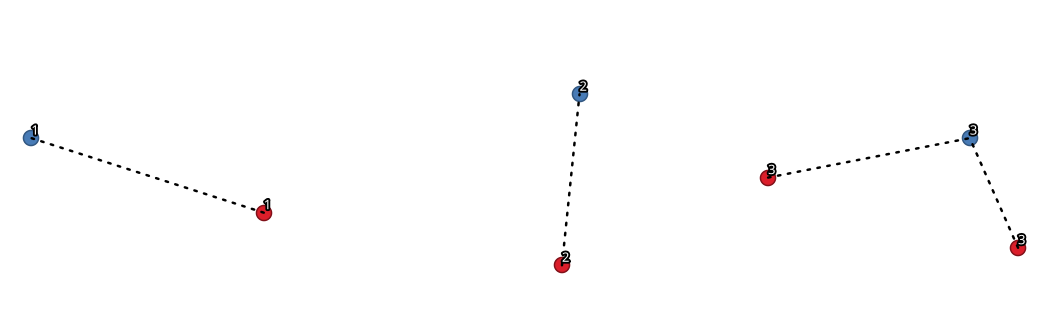
Fig. 24.42 Join points based on a common field / attribute
Parametrai
Baziniai parametrai
Užrašas |
Pavadinimas |
Tipas |
Aprašymas |
|---|---|---|---|
Hub layer |
|
[vektorius: geometrija] |
Input layer |
Hub ID field |
|
[lentelės laukas: bet koks] |
Field of the hub layer with ID to join |
Hub layer fields to copy (leave empty to copy all fields) Pasirinktinis |
|
[lentelės laukas: bet koks] [sąrašas] |
The field(s) of the hub layer to be copied. If no field(s) are chosen all fields are taken. |
Spoke layer |
|
[vektorius: geometrija] |
Additional spoke point layer |
Spoke ID field |
|
[lentelės laukas: bet koks] |
Field of the spoke layer with ID to join |
Spoke layer fields to copy (leave empty to copy all fields) Pasirinktinis |
|
[lentelės laukas: bet koks] [sąrašas] |
Field(s) of the spoke layer to be copied. If no fields are chosen all fields are taken. |
Create geodesic lines |
|
[boolean] Numatytas: ne |
Create geodesic lines (the shortest path on the surface of an ellipsoid) |
Hub lines |
|
[vektorius: linija] Numatytas: |
Specify the output hub line vector layer. One of:
Čia taipogi galima pakeisti failo koduotę. |
Išmanesni parametrai
Užrašas |
Pavadinimas |
Tipas |
Aprašymas |
|---|---|---|---|
Distance between vertices (geodesic lines only) |
|
[skaičius: slankaus kablelio] Default: 1000.0 (kilometers) |
Distance between consecutive vertices (in kilometers). A smaller distance results in a denser, more accurate line |
Split lines at antimeridian (±180 degrees longitude) |
|
[boolean] Numatytas: ne |
Split lines at ±180 degrees longitude (to improve rendering of the lines) |
Išvestys
Užrašas |
Pavadinimas |
Tipas |
Aprašymas |
|---|---|---|---|
Hub lines |
|
[vektorius: linija] |
The resulting line layer connecting matching points in input layers |
Pythono kodas
Algorithm ID: native:hublines
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
algoritmo id rodomas, kai užvedate pelę virš algoritmo apdorojimo įrankinėje. parametrų žodynas teikia parametrų pavadinimus ir reikšmes. Daugiau informacijos apie tai, kaip vykdyti apdorojimo algoritmus Pythono konsolėje rasite skyriuje Using processing algorithms from the console.
24.1.19.9. K-means clustering
Calculates the 2D distance based k-means cluster number for each input feature.
K-means clustering aims to partition the features into k clusters in which each feature belongs to the cluster with the nearest mean. The mean point is represented by the barycenter of the clustered features.
If input geometries are lines or polygons, the clustering is based on the centroid of the feature.
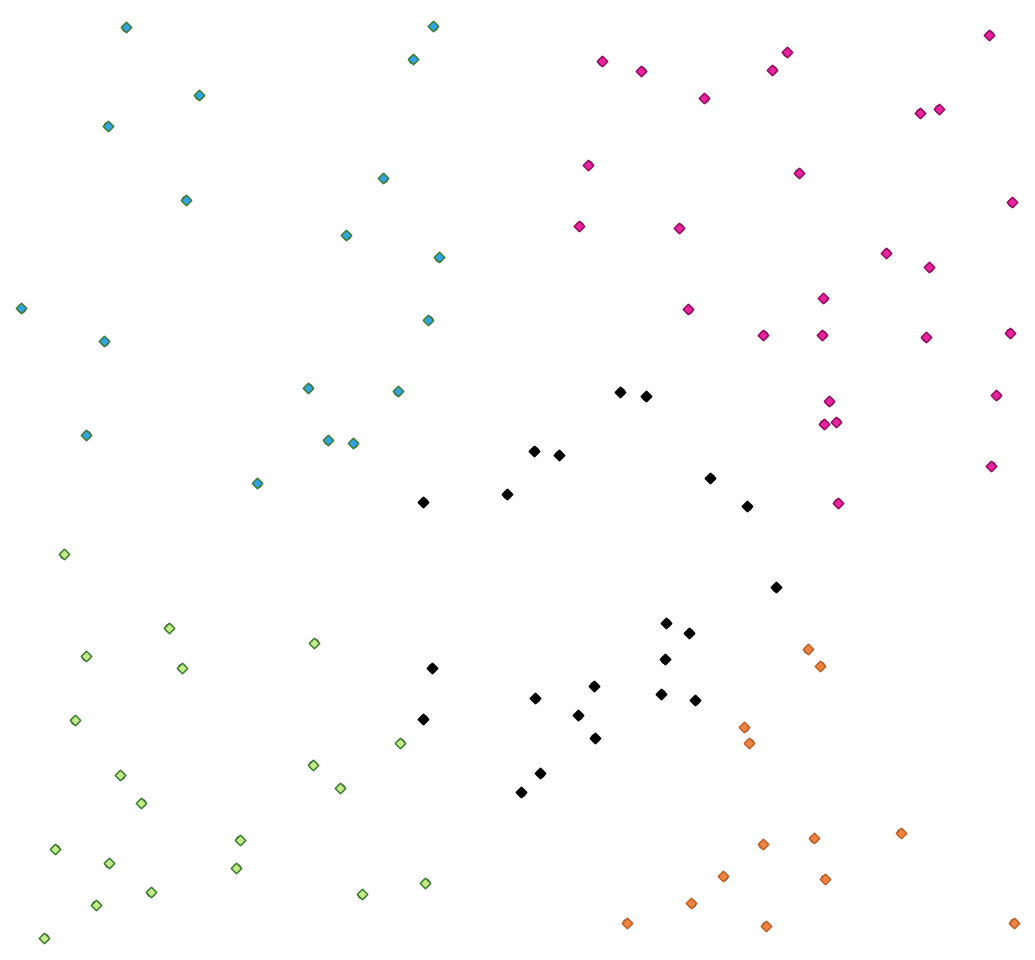
Fig. 24.43 A five class point clusters
Taip pat žiūrėkite
Parametrai
Užrašas |
Pavadinimas |
Tipas |
Aprašymas |
|---|---|---|---|
Įvesties sluoksnis |
|
[vektorius: geometrija] |
Layer to analyze |
Number of clusters |
|
[skaičius: sveikas skaičius] Numatytas: 5 |
Number of clusters to create with the features |
Clusters |
|
[vector: same as input] Default: |
Specify the output vector layer for the generated clusters. One of:
Čia taipogi galima pakeisti failo koduotę. |
Išmanesni parametrai
Užrašas |
Pavadinimas |
Tipas |
Aprašymas |
|---|---|---|---|
Cluster field name |
|
[tekstas] Default: ‚CLUSTER_ID‘ |
Name of the field where the associated cluster number shall be stored |
Cluster size field name |
|
[tekstas] Default: ‚CLUSTER_SIZE‘ |
Name of the field with the count of features in the same cluster |
Išvestys
Užrašas |
Pavadinimas |
Tipas |
Aprašymas |
|---|---|---|---|
Clusters |
|
[vector: same as input] |
Vector layer containing the original features with fields specifying the cluster they belong to and their number in it |
Pythono kodas
Algorithm ID: native:kmeansclustering
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
algoritmo id rodomas, kai užvedate pelę virš algoritmo apdorojimo įrankinėje. parametrų žodynas teikia parametrų pavadinimus ir reikšmes. Daugiau informacijos apie tai, kaip vykdyti apdorojimo algoritmus Pythono konsolėje rasite skyriuje Using processing algorithms from the console.
24.1.19.10. List unique values
Lists unique values of an attribute table field and counts their number.
Numatytas meniu:
Parametrai
Užrašas |
Pavadinimas |
Tipas |
Aprašymas |
|---|---|---|---|
Įvesties sluoksnis |
|
[vektorius: bet koks] |
Layer to analyze |
Target field(s) |
|
[lentelės laukas: bet koks] [sąrašas] |
Field(s) to analyze |
Unique values Pasirinktinis |
|
[vektorius: lentelė] Default: |
Specify the summary table layer with unique values. One of:
Čia taipogi galima pakeisti failo koduotę. |
HTML report Pasirinktinis |
|
[html] Default: |
HTML report of unique values in the . One of:
|
Išvestys
Užrašas |
Pavadinimas |
Tipas |
Aprašymas |
|---|---|---|---|
Unique values |
|
[vektorius: lentelė] |
Summary table layer with unique values |
HTML report |
|
[html] |
HTML report of unique values. Can be opened from the |
Total unique values |
|
[skaičius: sveikas skaičius] |
The number of unique values in the input field |
Unique values concatenated |
|
[tekstas] |
A string with the comma separated list of unique values found in the input field |
Pythono kodas
Algorithm ID: qgis:listuniquevalues
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
algoritmo id rodomas, kai užvedate pelę virš algoritmo apdorojimo įrankinėje. parametrų žodynas teikia parametrų pavadinimus ir reikšmes. Daugiau informacijos apie tai, kaip vykdyti apdorojimo algoritmus Pythono konsolėje rasite skyriuje Using processing algorithms from the console.
24.1.19.11. Mean coordinate(s)
Computes a point layer with the center of mass of geometries in an input layer.
An attribute can be specified as containing weights to be applied to each feature when computing the center of mass.
If an attribute is selected in the parameter, features will be grouped according to values in this field. Instead of a single point with the center of mass of the whole layer, the output layer will contain a center of mass for the features in each category.
Numatytas meniu:
Parametrai
Užrašas |
Pavadinimas |
Tipas |
Aprašymas |
|---|---|---|---|
Įvesties sluoksnis |
|
[vektorius: geometrija] |
Įvesties vektorinis sluoksnis |
Svorio laukas Pasirinktinis |
|
[lentelės laukas: skaičius] |
Field to use if you want to perform a weighted mean |
Unique ID field |
|
[lentelės laukas: bet koks] |
Unique field on which the calculation of the mean will be made |
Mean coordinates |
|
[vektorius: taškas] Default: |
Specify the (point vector) layer for the result. One of:
Čia taipogi galima pakeisti failo koduotę. |
Išvestys
Užrašas |
Pavadinimas |
Tipas |
Aprašymas |
|---|---|---|---|
Mean coordinates |
|
[vektorius: taškas] |
Resulting point(s) layer |
Pythono kodas
Algorithm ID: native:meancoordinates
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
algoritmo id rodomas, kai užvedate pelę virš algoritmo apdorojimo įrankinėje. parametrų žodynas teikia parametrų pavadinimus ir reikšmes. Daugiau informacijos apie tai, kaip vykdyti apdorojimo algoritmus Pythono konsolėje rasite skyriuje Using processing algorithms from the console.
24.1.19.12. Nearest neighbour analysis
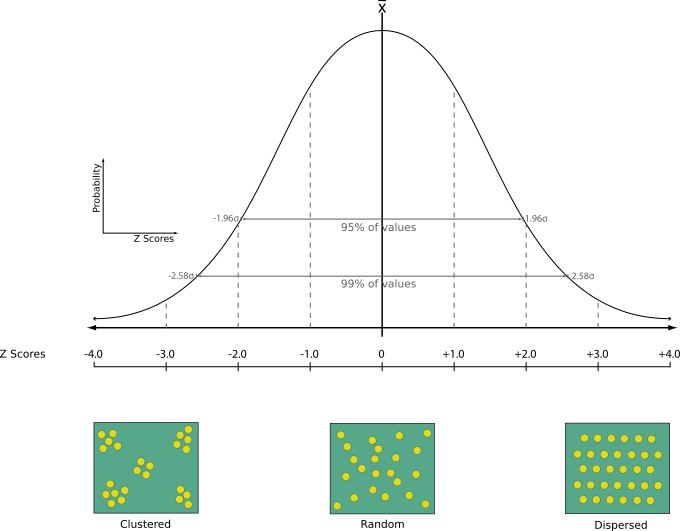
Performs nearest neighbor analysis for a point layer. The output tells you how your data are distributed (clustered, randomly or distributed).
Output is generated as an HTML file with the computed statistical values:
Observed mean distance
Expected mean distance
Nearest neighbour index
Number of points
Z-Score: Comparing the Z-Score with the normal distribution tells you how your data are distributed. A low Z-Score means that the data are unlikely to be the result of a spatially random process, while a high Z-Score means that your data are likely to be a result of a spatially random process.
Pastaba
Šis algoritmas naudoja elipse paremtus skaičiavimus ir atsižvelgia į dabartinius elipsoido nustatymus.
Numatytas meniu:
Taip pat žiūrėkite
Parametrai
Užrašas |
Pavadinimas |
Tipas |
Aprašymas |
|---|---|---|---|
Įvesties sluoksnis |
|
[vektorius: taškas] |
Point vector layer to calculate the statistics on |
Nearest neighbour Pasirinktinis |
|
[html] Default: |
Specification of the HTML file for the computed statistics. One of:
|
Išvestys
Užrašas |
Pavadinimas |
Tipas |
Aprašymas |
|---|---|---|---|
Nearest neighbour |
|
[html] |
HTML file with the computed statistics |
Observed mean distance |
|
[skaičius: slankaus kablelio] |
Observed mean distance |
Expected mean distance |
|
[skaičius: slankaus kablelio] |
Expected mean distance |
Nearest neighbour index |
|
[skaičius: sveikas skaičius] |
Nearest neighbour index |
Number of points |
|
[skaičius: sveikas skaičius] |
Number of points |
Z-Score |
|
[skaičius: slankaus kablelio] |
Z-Score |
Pythono kodas
Algorithm ID: native:nearestneighbouranalysis
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
algoritmo id rodomas, kai užvedate pelę virš algoritmo apdorojimo įrankinėje. parametrų žodynas teikia parametrų pavadinimus ir reikšmes. Daugiau informacijos apie tai, kaip vykdyti apdorojimo algoritmus Pythono konsolėje rasite skyriuje Using processing algorithms from the console.
24.1.19.13. Overlap analysis
Calculates the area and percentage cover by which features from an input layer are overlapped by features from a selection of overlay layers.
New attributes are added to the output layer reporting the total area of overlap and percentage of the input feature overlapped by each of the selected overlay layers.
Pastaba
Šis algoritmas naudoja elipse paremtus skaičiavimus ir atsižvelgia į dabartinius elipsoido nustatymus.
Parametrai
Baziniai parametrai
Užrašas |
Pavadinimas |
Tipas |
Aprašymas |
|---|---|---|---|
Įvesties sluoksnis |
|
[vektorius: poligonas] |
Įvesties sluoksnis. |
Perdengimo sluoksniai |
|
[vector: polygon] [list] |
The overlay layers. |
Overlap |
|
[toks pat, kaip įvestis] Numatytas: |
Nurodykite išvesties vektorinį sluoksnį Vienas iš:
Čia taipogi galima pakeisti failo koduotę. |
Išmanesni parametrai
Užrašas |
Pavadinimas |
Tipas |
Aprašymas |
|---|---|---|---|
Tinklelio dydis Pasirinktinis |
|
[skaičius: slankaus kablelio] Numatytas: jokio |
Jei nurodyta, įvesties geometrijos pritraukiamos prie nurodyto dydžio tinklelio, o rezultato viršūnės skaičiuojamos tame pačiame tinklelyje. Reikalauja GEOS 3.9.0 ar naujesnio. |
Išvestys
Užrašas |
Pavadinimas |
Tipas |
Aprašymas |
|---|---|---|---|
Overlap |
|
[toks pat, kaip įvestis] |
The output layer with additional fields reporting the overlap (in map units and percentage) of the input feature overlapped by each of the selected layers. |
Pythono kodas
Algorithm ID: native:calculatevectoroverlaps
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
algoritmo id rodomas, kai užvedate pelę virš algoritmo apdorojimo įrankinėje. parametrų žodynas teikia parametrų pavadinimus ir reikšmes. Daugiau informacijos apie tai, kaip vykdyti apdorojimo algoritmus Pythono konsolėje rasite skyriuje Using processing algorithms from the console.
24.1.19.14. Shortest line between features
Creates a line layer as the shortest line between the source and the destination layer. By default only the first nearest feature of the destination layer is taken into account. The n-nearest neighboring features number can be specified. If a maximum distance is specified, then only features which are closer than this distance will be considered.
The output features will contain all the source layer attributes, all the attributes from the n-nearest feature and the additional field of the distance.
Svarbu
This algorithm uses purely Cartesian calculations for distance, and does not consider geodetic or ellipsoid properties when determining feature proximity. The measurement and output coordinate system is based on the coordinate system of the source layer.
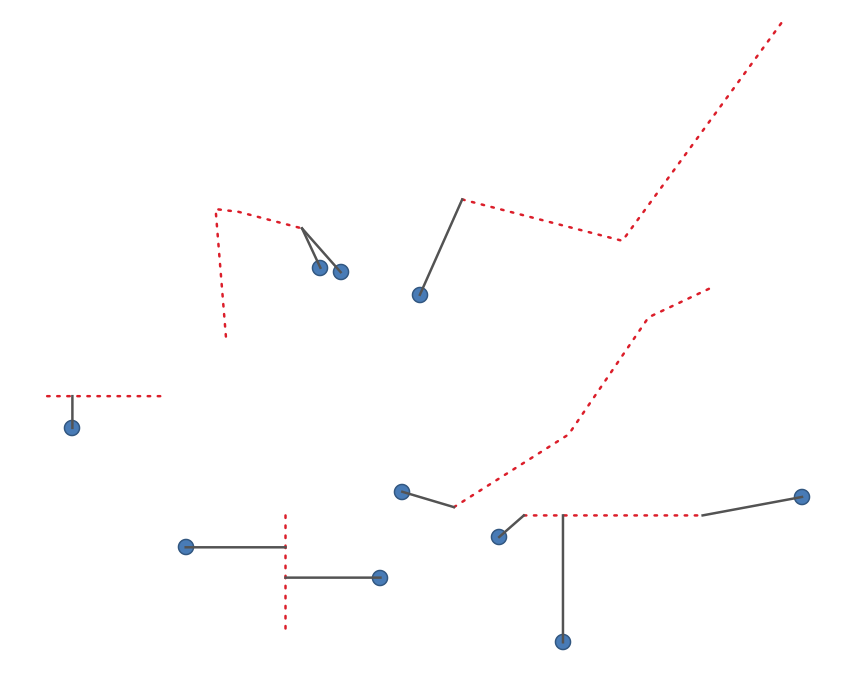
Fig. 24.44 Shortest line from point features to lines
Parametrai
Užrašas |
Pavadinimas |
Tipas |
Aprašymas |
|---|---|---|---|
Source layer |
|
[vektorius: geometrija] |
Origin layer for which to search for nearest neighbors |
Destination layer |
|
[vektorius: geometrija] |
Target Layer in which to search for nearest neighbors |
Metodas |
|
[sąrašas] Numatytas: 0 |
Shortest distance calculation method Possible values are:
|
Maximum number of neighbors |
|
[skaičius: sveikas skaičius] Numatytas: 1 |
Maximum number of neighbors to look for |
Maximum distance Pasirinktinis |
|
[skaičius: slankaus kablelio] |
Only destination features which are closer than this distance will be considered. |
Shortest lines |
|
[vektorius: linija] Numatytas: |
Nurodykite išvesties vektorinį sluoksnį Vienas iš:
Čia taipogi galima pakeisti failo koduotę. |
Išvestys
Užrašas |
Pavadinimas |
Tipas |
Aprašymas |
|---|---|---|---|
Išvesties sluoksnis |
|
[vektorius: linija] |
Line vector layer joining source features to their nearest neighbor(s) in the destination layer. Contains all attributes for both source and destination features, and the computed distance. |
Pythono kodas
Algorithm ID: native:shortestline
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
algoritmo id rodomas, kai užvedate pelę virš algoritmo apdorojimo įrankinėje. parametrų žodynas teikia parametrų pavadinimus ir reikšmes. Daugiau informacijos apie tai, kaip vykdyti apdorojimo algoritmus Pythono konsolėje rasite skyriuje Using processing algorithms from the console.
24.1.19.15. ST-DBSCAN clustering
Clusters point features based on a 2D implementation of spatiotemporal Density-based clustering of applications with noise (ST-DBSCAN) algorithm.
Taip pat žiūrėkite
Parametrai
Baziniai parametrai
Užrašas |
Pavadinimas |
Tipas |
Aprašymas |
|---|---|---|---|
Įvesties sluoksnis |
|
[vektorius: taškas] |
Layer to analyze |
Date/time field |
|
[tablefield: date] |
Field containing the temporal information |
Minimum cluster size |
|
[skaičius: sveikas skaičius] Numatytas: 5 |
Minimum number of features to generate a cluster |
Maximum distance between clustered points |
|
[skaičius: slankaus kablelio] Numatytas: 1.0 |
Distance beyond which two features can not belong to the same cluster (eps) |
Maximum time duration between clustered points |
|
[skaičius: slankaus kablelio] Default: 0.0 (days) |
Time duration beyond which two features can not belong to the same cluster (eps2). Available time units are milliseconds, seconds, minutes, hours, days and weeks. |
Clusters |
|
[vektorius: taškas] Numatytas: |
Specify the vector layer for the result of the clustering. One of:
Čia taipogi galima pakeisti failo koduotę. |
Išmanesni parametrai
Užrašas |
Pavadinimas |
Tipas |
Aprašymas |
|---|---|---|---|
Treat border points as noise (DBSCAN*) |
|
[boolean] Numatytas: ne |
If checked, points on the border of a cluster are themselves treated as unclustered points, and only points in the interior of a cluster are tagged as clustered. |
Cluster field name |
|
[tekstas] Default: ‚CLUSTER_ID‘ |
Name of the field where the associated cluster number shall be stored |
Cluster size field name |
|
[tekstas] Default: ‚CLUSTER_SIZE‘ |
Name of the field with the count of features in the same cluster |
Išvestys
Užrašas |
Pavadinimas |
Tipas |
Aprašymas |
|---|---|---|---|
Clusters |
|
[vektorius: taškas] |
Vector layer containing the original features with a field setting the cluster they belong to |
Number of clusters |
|
[skaičius: sveikas skaičius] |
The number of clusters discovered |
Pythono kodas
Algorithm ID: native:stdbscanclustering
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
algoritmo id rodomas, kai užvedate pelę virš algoritmo apdorojimo įrankinėje. parametrų žodynas teikia parametrų pavadinimus ir reikšmes. Daugiau informacijos apie tai, kaip vykdyti apdorojimo algoritmus Pythono konsolėje rasite skyriuje Using processing algorithms from the console.
24.1.19.16. Statistics by categories
Calculates statistics of a field depending on a parent class. The parent class is a combination of values from other fields.
Parametrai
Užrašas |
Pavadinimas |
Tipas |
Aprašymas |
|---|---|---|---|
Input vector layer |
|
[vektorius: bet koks] |
Input vector layer with unique classes and values |
Field to calculate statistics on (if empty, only count is calculated) Pasirinktinis |
|
[lentelės laukas: bet koks] |
If empty only the count will be calculated |
Field(s) with categories |
|
[lentelės laukas: bet koks] [sąrašas] |
The fields that (combined) define the categories |
Statistics by category |
|
[vektorius: lentelė] Numatytas: |
Nurodykite išvesties lentelę sukurtai statistikai. Vienas iš:
Čia taipogi galima pakeisti failo koduotę. |
Išvestys
Užrašas |
Pavadinimas |
Tipas |
Aprašymas |
|---|---|---|---|
Statistics by category |
|
[vektorius: lentelė] |
Table containing the statistics |
Depending on the type of the field being analyzed, the following statistics are returned for each grouped value:
Statistika |
Tekstas |
Numeric |
Data |
|---|---|---|---|
Count ( |
|||
Unique values ( |
|||
Empty (null) values ( |
|||
Non-empty values ( |
|||
Minimal value ( |
|||
Maximal value ( |
|||
Range ( |
|||
Sum ( |
|||
Mean value ( |
|||
Median value ( |
|||
Standard Deviation ( |
|||
Coefficient of variation ( |
|||
Minority (rarest occurring value - |
|||
Majority (most frequently occurring value - |
|||
First Quartile ( |
|||
Third Quartile ( |
|||
Inter Quartile Range ( |
|||
Minimum Length ( |
|||
Mean Length ( |
|||
Maximum Length ( |
Pythono kodas
Algorithm ID: qgis:statisticsbycategories
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
algoritmo id rodomas, kai užvedate pelę virš algoritmo apdorojimo įrankinėje. parametrų žodynas teikia parametrų pavadinimus ir reikšmes. Daugiau informacijos apie tai, kaip vykdyti apdorojimo algoritmus Pythono konsolėje rasite skyriuje Using processing algorithms from the console.
24.1.19.17. Sum line lengths
Takes a polygon layer and a line layer and measures the total length of lines and the total number of them that cross each polygon.
The resulting layer has the same features as the input polygon layer, but with two additional attributes containing the length and count of the lines across each polygon.
Pastaba
Šis algoritmas naudoja elipse paremtus skaičiavimus ir atsižvelgia į dabartinius elipsoido nustatymus.
 Leidžia vietoje keisti poligonų geoobjektus
Leidžia vietoje keisti poligonų geoobjektus
Numatytas meniu:
Parametrai
Užrašas |
Pavadinimas |
Tipas |
Aprašymas |
|---|---|---|---|
Lines |
|
[vektorius: linija] |
Input vector line layer |
Poligonai |
|
[vektorius: poligonas] |
Polygon vector layer |
Lines length field name |
|
[tekstas] Default: ‚LENGTH‘ |
Name of the field for the lines length |
Lines count field name |
|
[tekstas] Default: ‚COUNT‘ |
Name of the field for the lines count |
Line length |
|
[vektorius: poligonas] Numatytas: |
Specify the output polygon layer with generated statistics. One of:
Čia taipogi galima pakeisti failo koduotę. |
Išvestys
Užrašas |
Pavadinimas |
Tipas |
Aprašymas |
|---|---|---|---|
Line length |
|
[vektorius: poligonas] |
Polygon output layer with fields of lines length and line count |
Pythono kodas
Algorithm ID: native:sumlinelengths
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
algoritmo id rodomas, kai užvedate pelę virš algoritmo apdorojimo įrankinėje. parametrų žodynas teikia parametrų pavadinimus ir reikšmes. Daugiau informacijos apie tai, kaip vykdyti apdorojimo algoritmus Pythono konsolėje rasite skyriuje Using processing algorithms from the console.