21.1. Authentication System Overview
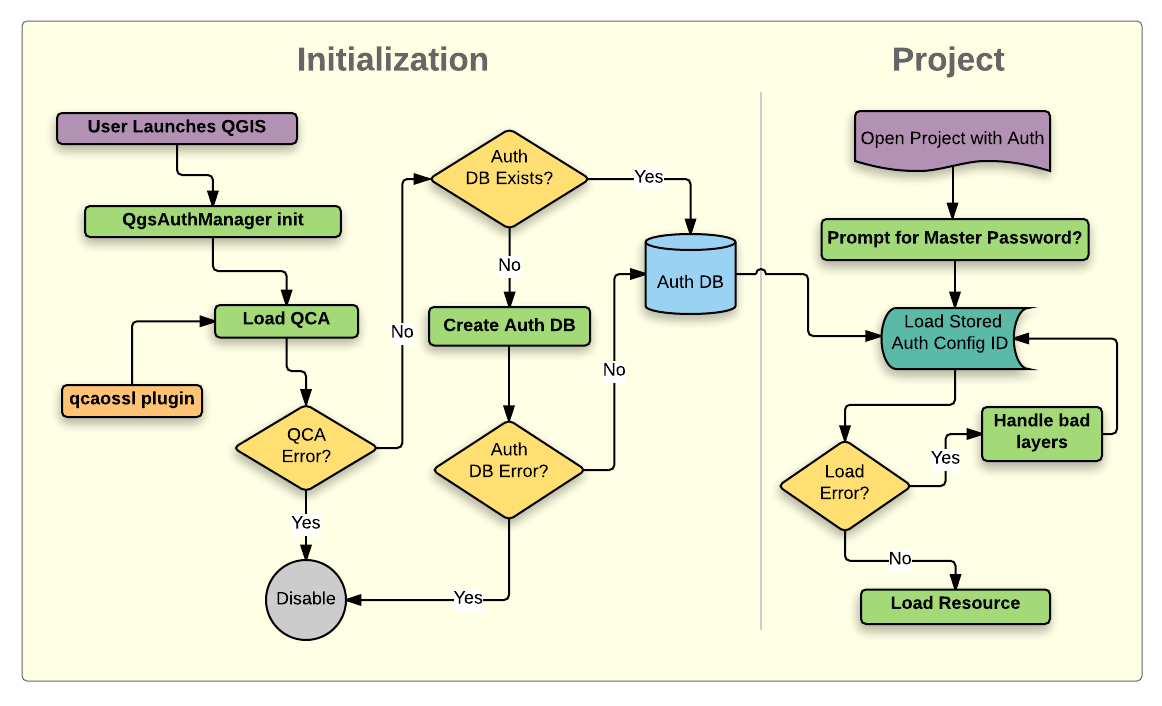
Fig. 21.1 Anatomy of authentication system
21.1.1. Authentication database
The authentication system stores authentication configurations in an
SQLite database file located, by default, at <profile directory>/qgis-auth.db.
This authentication database can be moved between QGIS installations without affecting other current QGIS user preferences, as it is completely separate from normal QGIS settings. A configuration ID (a random 7-character alphanumeric string) is generated when initially storing a configuration to the database. This represents the configuration, thereby allowing the ID to be stored in plain text application components, (such as project, plugin, or settings files) without disclosure of its associated credentials.
Note
The parent directory of the qgis-auth.db can be set using the following
environment variable, QGIS_AUTH_DB_DIR_PATH, or set on the command line
during launch with the --authdbdirectory option.
21.1.2. Custom authentication databases
QGIS can be configured to use a custom authentication database instead of the above mentioned default SQLite one: any database suppported by the Qt SQL module can be used (e.g. PostgreSQL, MySQL, etc), provided that the corresponding Qt SQL driver is available in the system.
This can be useful in scenarios where a user wants to share the same authentication database between multiple QGIS installations, or when a user wants to use a different authentication database than the default SQLite one or when a centralized authentication database is used by QGIS server.
The only way to configure a custom authentication database is by setting the
QGIS_AUTH_DB_URI environment variable to the URI of the connection, the URI
is in the form of driver://username:password@hostname:port/database?options.
- Where:
driveris the name of the Qt SQL driver to use, e.g.QPSQLfor PostgreSQL,QMYSQLfor MySQL, etc.usernameis the username to use to connect to the databasepasswordis the password to use to connect to the databasehostnameis the hostname of the database serverportis the port of the database serverdatabaseis the name of the database to useoptionsare the options to pass to the driver, e.g.sslmode=requirefor PostgreSQL
Note
The schema can be specified in the URI options, e.g. QPSQL://username:password@hostname:port/database?schema=schema_name
The database must exist before starting QGIS, and the user must have the necessary permissions to connect to the database and to create the required tables if they do not exist.
Warning
The password in the URI is stored in plain text in the environment variable, so it is recommended to use a passwordless user or a user with limited permissions to connect to the database.
Warning
Any database not based on SQLite is considered to be read-only (this can be changed by Python plugins if necessary).
This is an advanced feature, designed to allow one or more custom authentication databases or even custom Python implementations of credentials storages to be used by QGIS.
The system is also designed to allow for multiple authentication databases to be used but there is currently no user facing interface to manage multiple credential storages so its usage requires manual configuration and management, typically from a Python plugin.
21.1.3. Master password
To store or access sensitive information within the database, a user must define a master password. A new master password is requested and verified when initially storing any encrypted data to the database. When sensitive information is accessed, the user is prompted for the master password. The password is then cached for the remainder of the session (until application is quit), unless the user manually chooses an action to clear its cached value. Some instances of using the authentication system do not require input of the master password, such as when selecting an existing authentication configuration, or applying a configuration to a server configuration (such as when adding a WMS layer).
You can choose to save the password in the Wallet/Keyring of your
computer.
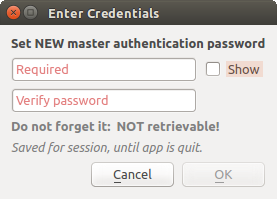
Fig. 21.2 Input new master password
Note
A path to a file containing the master password can be set using the
following environment variable, QGIS_AUTH_PASSWORD_FILE.
21.1.3.1. Managing the master password
Once set, the master password can be reset; the current master password will be needed prior to resetting. During this process, there is an option to generate a complete backup of the current database.
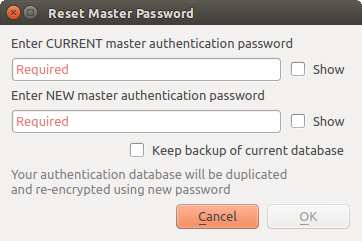
Fig. 21.3 Resetting master password
If the user forgets the master password, there is no way to retrieve or override it. There is also no means of retrieving encrypted information without knowing the master password.
If a user inputs their existing password incorrectly three times, the dialog will offer to erase the database.
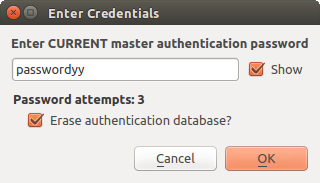
Fig. 21.4 Password prompt after three invalid attempts
21.1.4. Authentication Configurations
You can manage authentication configurations from Configurations in the Authentication tab of the QGIS Options dialog ().

Fig. 21.5 Configurations editor
To create a new authentication configuration:
Provide a Name and optional Resource URL
A seven-characters ID will be assigned to the configuration for identification purpose. It can be customized after you pressed the
 Unlock to edit ID button.
Be aware that updating that ID may break things.
Unlock to edit ID button.
Be aware that updating that ID may break things.Select the target method and fill the corresponding connection details
Once done, click Save to save the configuration. The saved configuration appears in the list of authentication configurations and can be used with supported connections.
The saved configuration can later be edited using  Edit selected configuration
or removed using
Edit selected configuration
or removed using 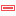 Delete selected configuration.
Delete selected configuration.
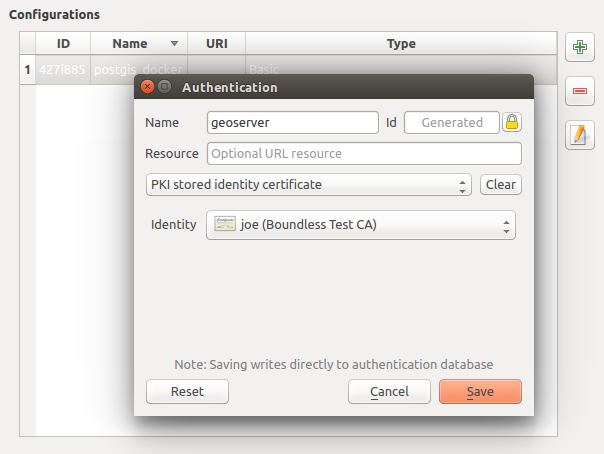
Fig. 21.6 Adding config from within Configuration editor
The same type of operations for authentication configuration management (Add, Edit and Remove) can be done when configuring a given service connection, such as configuring an OWS service connection. For that, there are action buttons within the configuration selector for fully managing configurations found within the authentication database. In this case, there is no need to go to the configurations in Authentication tab of QGIS options unless you need to do more comprehensive configuration management.

Fig. 21.7 WMS connection dialog showing authentication configuration widget
When creating or editing an authentication configuration, the info required is a name, an authentication method and any other info that the authentication method requires (see more about the available authentication types in Authentication Methods).
21.1.5. Authentication Methods
Available authentications are provided by C++ plugins much in the same way data
provider plugins are supported by QGIS. The method of authentication that can
be selected is relative to the access needed for the resource/provider, e.g.
HTTP(S) or database, and whether there is support in both QGIS code and a
plugin. As such, some authentication method plugins may not be applicable
everywhere an authentication configuration selector is shown. A list of
available authentication method plugins and their compatible resource/providers
can be accessed going to and, in the
Authentication tab, click the  Installed Plugins
button.
Installed Plugins
button.
Fig. 21.8 Available method plugins list
Plugins can be created for new authentication methods that do not require QGIS to be recompiled. Since the support for plugins is currently C++-only, QGIS will need to be restarted for the new dropped-in plugin to become available to the user. Ensure your plugin is compiled against the same target version of QGIS if you intend to add it to an existing target install.
21.1.5.1. API Header Authentication
The API Header authentication method allows you to connect to services
that require custom HTTP headers, such as API keys.
For example, if a WMS service requires an API key sent as a header
(e.g. X-API-KEY), you can use this method to provide it.
You can add one or more headers with the  button; provide a
Header Name and Header Value for each entry. Use
button; provide a
Header Name and Header Value for each entry. Use
 to delete the selected header or the Clear
button to remove all entries.
to delete the selected header or the Clear
button to remove all entries.

Fig. 21.9 API Header authentication configs
21.1.5.2. AWS S3 Authentication
The AWS S3 authentication method allows you to connect to Amazon S3 resources by providing a Name, Resource, Username, Password, and Region.

Fig. 21.10 AWS S3 authentication configs
21.1.5.3. Basic Authentication
The Basic authentication method is used for services that require standard HTTP authentication with a Username, Password and Realm.

Fig. 21.11 Basic HTTP authentication configs
21.1.5.4. ESRI Token Authentication
The ESRI token authentication method is used for ArcGIS REST Servers that require token-based authentication.

Fig. 21.12 ESRI Token authentication configs
21.1.5.5. Identity certificate authentication
The Identity certificate authentication method allows you to connect using a client identity certificate.

Fig. 21.13 Identity-cert authentication configs
21.1.5.6. MapTiler HMAC-SHA256 Authentication
The MapTiler HMAC-SHA256 authentication method is used to connect to MapTiler services that require HMAC-SHA256 authorization.

Fig. 21.14 MapTiler HmacSha256 authentication configs
21.1.5.7. OAuth2 Authentication
The OAuth2 authentication method is used to connect to services that require OAuth2 2.0 authorization, allowing secure access using client credential and token-based authentication.
Note
The OAuth2 authentication method now allows using localhost as the redirect host,
providing compatibility with services that do not accept http://127.0.0.1 redirects
(for example, Microsoft SharePoint).

Fig. 21.15 OAuth2 authentication configs
21.1.5.8. PKI-Paths Authentication
The PKI-Paths authentication method allows you to connect using separate certificate and key files stored on your system.

Fig. 21.16 PKI paths authentication configs
21.1.5.9. PKI-PKCS#12 Authentication
The PKI-PKCS#12 authentication method allows you to connect using a single bundle file containing both the certificate and private key, with an optional passphrase for the key.

Fig. 21.17 PKI PKCS#12 file paths authentication configs
21.1.5.10. Planetary Computer Authentication
The Planetary Computer authentication method allows QGIS to access Microsoft Planetary Computer data. It supports two modes:
Open Planetary Computer - uses SAS tokens to sign assets for access.
Planetary Pro Computer - requires SAS signing plus OAuth2 authentication.

Fig. 21.18 Microsoft Planetary Computer authentication configs
This method can be applied to STAC connections or directly to individual GDAL or point cloud layers. When a layer is added, the authentication configuration is appended to its URI so QGIS uses it for network requests. Support for encoding/decoding this configuration is also available for point cloud layers.
21.1.6. Master Password and Auth Config Utilities
Under the Options menu () in the Authentication tab, there are several utility actions to manage the authentication database and configurations:
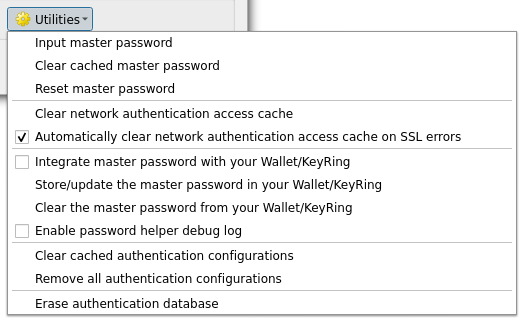
Fig. 21.19 Utilities menu
Input master password…: opens the master password input dialog, independent of performing any authentication database command
Clear cached master password: unsets the master password if it has been set
Reset master password…: opens a dialog to change the master password (the current password must be known) and optionally back up the current database
Clear network authentication access cache: clears the authentication cache of all connections
Automatically clear network authentication access cache on SSL errors: the connection cache stores all authentication data for connections, also when the connection fails. If you change authentication configurations or certification authorities, you should clear the authentication cache or restart QGIS. When this option is checked, the authentication cache will be automatically cleared every time an SSL error occurs and you choose to abort the connection
Integrate master password with the Wallet: adds the master password to your personal Wallet/Keyring
Clear the master password from the Wallet…: deletes the master password from your Wallet/Keyring
Enable password helper debug log: enables a debug tool that will contain all the log information of the authentication methods
Clear cached authentication configurations: clears the internal lookup cache for configurations, used to speed up network connections. This does not clear QGIS’s core network access manager’s cache, which requires a relaunch of QGIS.
Remove all authentication configurations…: clears the database of all configuration records, without removing other stored records.
Import authentication configurations from file…: imports from an
.XMLfile details for creating custom authentication configurations.Export selected authentication configurations to file…: exports the selected items to a possibly encrypted
.XMLfile.Erase authentication database…: schedules a backup of the current database and complete rebuild of the database table structure. The actions are scheduled for a later time, to ensure that other operations, like project loading, do not interrupt the operation or cause errors due to a temporarily missing database.
21.1.7. Using authentication configurations
Typically, an authentication configuration is selected in a configuration dialog for a network services (such as WMS). However, the selector widget can be embedded anywhere authentication is needed or in non-core functionality, like in third-party PyQGIS or C++ plugins.
When using the selector, No authentication is displayed in the
pop-up menu control when nothing is selected, when there are no configurations
to choose from, or when a previously assigned configuration can no longer be
found in the database. Use the drop-down menu to select an existing authentication
configuration or press  Create a new autentication configuration
to create a configuration you could use.
More details at Authentication.
Create a new autentication configuration
to create a configuration you could use.
More details at Authentication.

Fig. 21.20 Authentication configuration selector with selected config
21.1.8. Python bindings
All classes and public functions have sip bindings, except QgsAuthCrypto, since management of the master password hashing and auth database encryption should be handled by the main app, and not via Python.
Once the master password is entered, the API is open to access authentication configs in the authentication database, similar to how Firefox works. However, no wall against PyQGIS access has been defined. This may lead to issues where a user downloads/installs a malicious PyQGIS plugin or standalone app that gains access to authentication credentials.