23.1.9. Raster analysis
23.1.9.1. Raster boolean AND
Calculates the boolean AND for a set of input rasters.
If all of the input rasters have a non-zero value for a pixel, that
pixel will be set to 1 in the output raster.
If any of the input rasters have 0 values for the pixel it will
be set to 0 in the output raster.
The reference layer parameter specifies an existing raster layer to use as a reference when creating the output raster. The output raster will have the same extent, CRS, and pixel dimensions as this layer.
By default, a nodata pixel in ANY of the input layers will result in a
nodata pixel in the output raster.
If the Treat nodata values as false option is checked,
then nodata inputs will be treated the same as a 0 input value.
See also
23.1.9.1.1. Parameters
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Input layers |
|
[raster] [list] |
List of input raster layers |
Reference layer |
|
[raster] |
The reference layer to create the output layer from (extent, CRS, pixel dimensions) |
Treat nodata values as false |
|
[boolean] Default: False |
Treat nodata values in the input files as 0 when performing the operation |
Output no data value |
|
[number] Default: -9999.0 |
Value to use for nodata in the output layer |
Output data type |
|
[enumeration] Default: 5 |
Output raster data type. Options:
|
Output layer |
|
[raster] |
Output raster layer |
23.1.9.1.2. Outputs
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Extent |
|
[extent] |
The extent of the output raster layer |
CRS authority identifier |
|
[crs] |
The coordinate reference system of the output raster layer |
Width in pixels |
|
[integer] |
The width in pixels of the output raster layer |
Height in pixels |
|
[integer] |
The height in pixels of the output raster layer |
Total pixel count |
|
[integer] |
The count of pixels in the output raster layer |
NODATA pixel count |
|
[integer] |
The count of nodata pixels in the output raster layer |
True pixel count |
|
[integer] |
The count of True pixels (value = 1) in the output raster layer |
False pixel count |
|
[integer] |
The count of False pixels (value = 0) in the output raster layer |
Output layer |
|
[raster] |
Output raster layer containing the result |
23.1.9.1.3. Python code
Algorithm ID: qgis:rasterbooleanand
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
The algorithm id is displayed when you hover over the algorithm in the Processing Toolbox. The parameter dictionary provides the parameter NAMEs and values. See Using processing algorithms from the console for details on how to run processing algorithms from the Python console.
23.1.9.2. Raster boolean OR
Calculates the boolean OR for a set of input rasters.
If all of the input rasters have a zero value for a pixel, that
pixel will be set to 0 in the output raster.
If any of the input rasters have 1 values for the pixel it will
be set to 1 in the output raster.
The reference layer parameter specifies an existing raster layer to use as a reference when creating the output raster. The output raster will have the same extent, CRS, and pixel dimensions as this layer.
By default, a nodata pixel in ANY of the input layers will result in a
nodata pixel in the output raster.
If the Treat nodata values as false option is checked,
then nodata inputs will be treated the same as a 0 input value.
See also
23.1.9.2.1. Parameters
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Input layers |
|
[raster] [list] |
List of input raster layers |
Reference layer |
|
[raster] |
The reference layer to create the output layer from (extent, CRS, pixel dimensions) |
Treat nodata values as false |
|
[boolean] Default: False |
Treat nodata values in the input files as 0 when performing the operation |
Output no data value |
|
[number] Default: -9999.0 |
Value to use for nodata in the output layer |
Output data type |
|
[enumeration] Default: 5 |
Output raster data type. Options:
|
Output layer |
|
[raster] |
Output raster layer |
23.1.9.2.2. Outputs
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Extent |
|
[extent] |
The extent of the output raster layer |
CRS authority identifier |
|
[crs] |
The coordinate reference system of the output raster layer |
Width in pixels |
|
[integer] |
The width in pixels of the output raster layer |
Height in pixels |
|
[integer] |
The height in pixels of the output raster layer |
Total pixel count |
|
[integer] |
The count of pixels in the output raster layer |
NODATA pixel count |
|
[integer] |
The count of nodata pixels in the output raster layer |
True pixel count |
|
[integer] |
The count of True pixels (value = 1) in the output raster layer |
False pixel count |
|
[integer] |
The count of False pixels (value = 0) in the output raster layer |
Output layer |
|
[raster] |
Output raster layer containing the result |
23.1.9.2.3. Python code
Algorithm ID: qgis:rasterbooleanor
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
The algorithm id is displayed when you hover over the algorithm in the Processing Toolbox. The parameter dictionary provides the parameter NAMEs and values. See Using processing algorithms from the console for details on how to run processing algorithms from the Python console.
23.1.9.3. Raster calculator
Performs algebraic operations using raster layers.
The resulting layer will have its values computed according to an expression. The expression can contain numerical values, operators and references to any of the layers in the current project.
Note
When using the calculator in The batch processing interface or from
the QGIS Python console the files to use have to be specified.
The corresponding layers are referred using the base name of the
file (without the full path).
For instance, if using a layer at path/to/my/rasterfile.tif,
the first band of that layer will be referred as
rasterfile.tif@1.
23.1.9.3.1. Parameters
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Layers |
GUI only |
Shows the list of all raster layers loaded in the legend.
These can be used to fill the expression box (double click to
add).
Raster layers are referred by their name and the number of the
band: |
|
Operators |
GUI only |
Contains some calculator like buttons that can be used to fill the expression box. |
|
Expression |
|
[string] |
Expression that will be used to calculate the output raster layer. You can use the operator buttons provided to type directly the expression in this box. |
Predefined expressions |
GUI only |
You can use the predefined |
|
Reference layer(s) (used for automated extent, cellsize, and CRS) Optional |
|
[raster] [list] |
Layer(s) that will be used to fetch extent, cell size and CRS.
By choosing the layer in this box you avoid filling in all the
other parameters by hand.
Raster layers are referred by their name and the number of
the band: |
Cell size (use 0 or empty to set it automatically) Optional |
|
[number] |
Cell size of the output raster layer. If the cell size is not specified, the minimum cell size of the selected reference layer(s) will be used. The cell size will be the same for the X and Y axes. |
Output extent (xmin, xmax, ymin, ymax) |
|
[extent] |
Extent of the output raster layer. If the extent is not specified, the minimum extent that covers all the selected reference layers will be used. |
Output CRS Optional |
|
[crs] |
CRS of the output raster layer. If the output CRS is not specified, the CRS of the first reference layer will be used. |
Output |
|
[raster] Default: |
Specification of the output raster. One of:
The file encoding can also be changed here. |
23.1.9.3.2. Outputs
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Output |
|
[raster] |
Output raster file with the calculated values. |
23.1.9.3.3. Python code
Algorithm ID: qgis:rastercalculator
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
The algorithm id is displayed when you hover over the algorithm in the Processing Toolbox. The parameter dictionary provides the parameter NAMEs and values. See Using processing algorithms from the console for details on how to run processing algorithms from the Python console.
23.1.9.4. Raster layer statistics
Calculates basic statistics from the values in a given band of the raster layer. The output is loaded in the menu.
23.1.9.4.1. Parameters
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Input layer |
|
[raster] |
Input raster layer |
Band number |
|
[raster band] Default: The first band of the input layer |
If the raster is multiband, choose the band you want to get statistics for. |
Output |
|
[html] Default: |
Specification of the output file:
The file encoding can also be changed here. |
23.1.9.4.2. Outputs
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Maximum value |
|
[number] |
|
Mean value |
|
[number] |
|
Minimum value |
|
[number] |
|
Output |
|
[html] |
The output file contains the following information:
|
Range |
|
[number] |
|
Standard deviation |
|
[number] |
|
Sum |
|
[number] |
|
Sum of the squares |
|
[number] |
23.1.9.4.3. Python code
Algorithm ID: qgis:rasterlayerstatistics
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
The algorithm id is displayed when you hover over the algorithm in the Processing Toolbox. The parameter dictionary provides the parameter NAMEs and values. See Using processing algorithms from the console for details on how to run processing algorithms from the Python console.
23.1.9.5. Raster layer unique values report
Returns the count and area of each unique value in a given raster layer.
23.1.9.5.1. Parameters
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Input layer |
|
[raster] |
Input raster layer |
Band number |
|
[raster band] Default: The first band of the input layer |
If the raster is multiband, choose the band you want to get statistics for. |
Unique values report |
|
[file] Default: |
Specification of the output file:
The file encoding can also be changed here. |
Unique values table |
|
[table] Default: |
Specification of the table for unique values:
The file encoding can also be changed here. |
23.1.9.5.2. Outputs
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
CRS authority identifier |
|
[crs] |
|
Extent |
|
[extent] |
|
Height in pixels |
|
[number] |
|
NODATA pixel count |
|
[number] |
|
Total pixel count |
|
[number] |
|
Unique values report |
|
[html] |
The output HTML file contains the following information:
|
Unique values table |
|
[table] |
A table with three columns:
|
Width in pixels |
|
[number] |
23.1.9.5.3. Python code
Algorithm ID: qgis:rasterlayeruniquevaluesreport
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
The algorithm id is displayed when you hover over the algorithm in the Processing Toolbox. The parameter dictionary provides the parameter NAMEs and values. See Using processing algorithms from the console for details on how to run processing algorithms from the Python console.
23.1.9.6. Raster layer zonal statistics
Calculates statistics for a raster layer’s values, categorized by zones defined in another raster layer.
See also
23.1.9.6.1. Parameters
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Input Layer |
|
[raster] |
Input raster layer |
Band number |
|
[raster band] Default: The first band of the raster layer |
If the raster is multiband choose the band for which you want to calculate the statistics. |
Zones layer |
|
[raster] |
Raster layer defining zones. Zones are given by contiguous pixels having the same pixel value. |
Zones band number |
|
[raster band] Default: The first band of the raster layer |
If the raster is multiband, choose the band that defines the zones |
Reference layer Optional |
|
[enumeration] Default: 0 |
Raster layer used to calculate the centroids that will be used as reference when determining the zones in the output layer. One of:
|
Statistics |
|
[table] |
Table with the calculated statistics |
23.1.9.6.2. Outputs
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
CRS authority identifier |
|
[crs] |
|
Extent |
|
[extent] |
|
Height in pixels |
|
[number] |
|
NODATA pixel count |
|
[number] |
|
Statistics |
|
[table] |
The output layer contains the following information for each zone:
|
Total pixel count |
|
[number] |
|
Width in pixels |
|
[number] |
23.1.9.6.3. Python code
Algorithm ID: qgis:rasterlayerzonalstats
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
The algorithm id is displayed when you hover over the algorithm in the Processing Toolbox. The parameter dictionary provides the parameter NAMEs and values. See Using processing algorithms from the console for details on how to run processing algorithms from the Python console.
23.1.9.7. Raster surface volume
Calculates the volume under a raster surface relative to a given base level. This is mainly useful for Digital Elevation Models (DEM).
23.1.9.7.1. Parameters
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
INPUT layer |
|
[raster] |
Input raster, representing a surface |
Band number |
|
[raster band] Default: The first band of the raster layer |
If the raster is multiband, choose the band that shall define the surface. |
Base level |
|
[number] Default: 0.0 |
Define a base or reference value.
This base is used in the volume calculation according to the
|
Method |
|
[enumeration] Default: 0 |
Define the method for the volume calculation given by the
difference between the raster pixel value and the
|
Surface volume report |
|
[html] Default: |
Specification of the output HTML report. One of:
The file encoding can also be changed here. |
Surface volume table |
|
[table] Default: |
Specification of the output table. One of:
The file encoding can also be changed here. |
23.1.9.7.2. Outputs
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Volume |
|
[number] |
The calculated volume |
Area |
|
[number] |
The area in square map units |
Pixel_count |
|
[number] |
The total number of pixels that have been analyzed |
Surface volume report |
|
[html] |
The output report (containing volume, area and pixel count) in HTML format |
Surface volume table |
|
[table] |
The output table (containing volume, area and pixel count) |
23.1.9.7.3. Python code
Algorithm ID: qgis:rastersurfacevolume
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
The algorithm id is displayed when you hover over the algorithm in the Processing Toolbox. The parameter dictionary provides the parameter NAMEs and values. See Using processing algorithms from the console for details on how to run processing algorithms from the Python console.
23.1.9.8. Reclassify by layer
Reclassifies a raster band by assigning new class values based on the ranges specified in a vector table.
23.1.9.8.1. Parameters
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Raster layer |
|
[raster] |
Raster layer to reclassify |
Band number |
|
[raster band] Default: The first band of the raster layer |
If the raster is multiband, choose the band you want to reclassify. |
Layer containing class breaks |
|
[vector: any] |
Vector layer containing the values to use for classification. |
Minimum class value field |
|
[tablefield: numeric] |
Field with the minimum value of the range for the class. |
Maximum class value field |
|
[tablefield: numeric] |
Field with the maximum value of the range for the class. |
Output value field |
|
[tablefield: numeric] |
Field with the value that will be assigned to the pixels that fall in the class (between the corresponding min and max values). |
Output no data value |
|
[number] Default: -9999.0 |
Value to apply to no data values. |
Range boundaries |
|
[enumeration] Default: 0 |
Defines comparison rules for the classification. Options:
|
Use no data when no range matches value |
|
[boolean] Default: False |
Values that do not belong to a class will result in the no data value. If False, the original value is kept. |
Output data type |
|
[enumeration] Default: 5 |
Defines the data type of the output raster file. Options:
|
Reclassified raster |
|
[raster] |
Specification of the output raster. One of:
The file encoding can also be changed here. |
23.1.9.8.2. Outputs
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Reclassified raster |
|
[raster] |
Output raster layer with reclassified band values |
23.1.9.8.3. Python code
Algorithm ID: qgis:reclassifybylayer
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
The algorithm id is displayed when you hover over the algorithm in the Processing Toolbox. The parameter dictionary provides the parameter NAMEs and values. See Using processing algorithms from the console for details on how to run processing algorithms from the Python console.
23.1.9.9. Reclassify by table
Reclassifies a raster band by assigning new class values based on the ranges specified in a fixed table.
23.1.9.9.1. Parameters
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Raster layer |
|
[raster] |
Raster layer to reclassify |
Band number |
|
[raster band] Default: 1 |
Raster band for which you want to recalculate values. |
Reclassification table |
|
[table] |
A 3-columns table to fill with the values to set the boundaries
of each class ( |
Output no data value |
|
[number] Default: -9999.0 |
Value to apply to no data values. |
Range boundaries |
|
[enumeration] Default: 0 |
Defines comparison rules for the classification. Options:
|
Use no data when no range matches value |
|
[boolean] Default: False |
Applies the no data value to band values that do not fall in any class. If False, the original value is kept. |
Output data type |
|
[enumeration] Default: 5 |
Defines the format of the output raster file. Options:
|
Reclassified raster |
|
[raster] Default: ‘[Save to temporary file]’ |
Specification of the output raster layer. One of:
The file encoding can also be changed here |
23.1.9.9.2. Outputs
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Reclassified raster |
|
[raster] Default: ‘[Save to temporary file]’ |
The output raster layer. |
23.1.9.9.3. Python code
Algorithm ID: qgis:reclassifybytable
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
The algorithm id is displayed when you hover over the algorithm in the Processing Toolbox. The parameter dictionary provides the parameter NAMEs and values. See Using processing algorithms from the console for details on how to run processing algorithms from the Python console.
23.1.9.10. Sample raster values
Extracts raster values at the point locations. If the raster layer is multiband, each band is sampled.
The attribute table of the resulting layer will have as many new columns as the raster layer band count.
23.1.9.10.1. Parameters
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Input Point Layer |
|
[vector: point] |
Point vector layer to use for sampling |
Raster Layer to sample |
|
[raster] |
Raster layer to sample at the given point locations. |
Output column prefix |
|
[string] Default: ‘rvalue’ |
Prefix for the names of the added columns. |
Sampled Points (Optional) |
|
[vector: point] Default: |
Specify the output layer containing the sampled values. One of:
The file encoding can also be changed here. |
23.1.9.10.2. Outputs
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Sampled Points (Optional) |
|
[vector: point] |
The output layer containing the sampled values. |
23.1.9.10.3. Python code
Algorithm ID: qgis:rastersampling
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
The algorithm id is displayed when you hover over the algorithm in the Processing Toolbox. The parameter dictionary provides the parameter NAMEs and values. See Using processing algorithms from the console for details on how to run processing algorithms from the Python console.
23.1.9.11. Zonal histogram
Appends fields representing counts of each unique value from a raster layer contained within polygon features.
The output layer attribute table will have as many fields as the unique values of the raster layer that intersects the polygon(s).
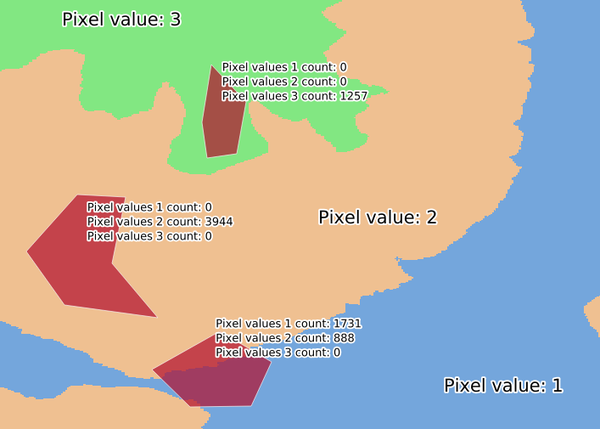
Fig. 23.7 Raster layer histogram example
23.1.9.11.1. Parameters
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Raster layer |
|
[raster] |
Input raster layer. |
Band number |
|
[raster band] Default: The first band of the input layer |
If the raster is multiband, choose a band. |
Vector layer containing zones |
|
[vector: polygon] |
Vector polygon layer that defines the zones. |
Output column prefix |
Optional |
[string] Default: ‘HISTO_’ |
Prefix for the output columns names. |
Output zones |
|
[vector: polygon] Default: |
Specify the output vector polygon layer. One of:
The file encoding can also be changed here. |
23.1.9.11.2. Outputs
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Output zones (Optional) |
|
[vector: polygon] Default: |
The output vector polygon layer. |
23.1.9.11.3. Python code
Algorithm ID: qgis:zonalhistogram
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
The algorithm id is displayed when you hover over the algorithm in the Processing Toolbox. The parameter dictionary provides the parameter NAMEs and values. See Using processing algorithms from the console for details on how to run processing algorithms from the Python console.
23.1.9.12. Zonal statistics
Calculates statistics of a raster layer for each feature of an overlapping polygon vector layer.
Warning
No new output file will be created. The algorithm adds new columns to the source vector layer.
23.1.9.12.1. Parameters
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Raster layer |
|
[raster] |
Input raster layer. |
Raster band |
|
[raster band] Default: The first band of the input layer |
If the raster is multiband, choose a band for the statistics. |
Vector layer containing zones |
|
[vector: polygon] |
Vector polygon layer that defines the zones. |
Output column prefix |
|
[string] Default: ‘_’ |
Prefix for the output columns names. |
Statistics to calculate |
|
[enumeration] [list] Default: [0,1,2] |
List of statistical operator for the output. Options:
|
23.1.9.12.2. Outputs
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Vector layer containing zones |
|
[vector: polygon] |
The input zone vector layer with added statistics. |
23.1.9.12.3. Python code
Algorithm ID: qgis:zonalstatistics
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
The algorithm id is displayed when you hover over the algorithm in the Processing Toolbox. The parameter dictionary provides the parameter NAMEs and values. See Using processing algorithms from the console for details on how to run processing algorithms from the Python console.