Importante
A tradução é um esforço comunitário você pode contribuir. Esta página está atualmente traduzida em 40.00%.
12.1. Lesson: GRASS Setup
Using GRASS in QGIS requires you to think of the interface in a slightly different way. Remember that you’re not working in QGIS directly, but working in GRASS via QGIS. Hence, make sure you have installed QGIS Desktop with Grass support.
 Para abrir uma sessão de QGIS com GRASS disponível no Windows você tem que clicar no ícone
Para abrir uma sessão de QGIS com GRASS disponível no Windows você tem que clicar no ícone QGIS Desktop com GRASS.
El objetivo de esta lección: Comenzar un proyecto GRASS en QGIS.
12.1.1. ★☆☆ Follow Along: Start a New GRASS Session
Para lançar GRASS de dentro do QGIS, você precisa ativá-lo como em qualquer outro plugin:
Primeiro, abra um novo projeto QGIS.
In the Plugin Manager, enable
 GRASS 8 in the list:
GRASS 8 in the list:
The GRASS toolbar and the GRASS panel will appear:
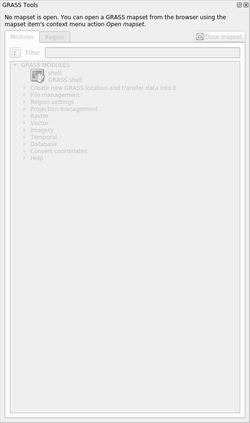
Fig. 12.118 GRASS Toolbar and Panel
O painel GRASS não está ativo porque, antes que você possa usar o GRASS, é necessário criar um Mapset. O GRASS sempre funciona em um ambiente de banco de dados, o que significa que você precisa importar todos os dados que deseja usar em um banco de dados GRASS.
The GRASS database has a straightforward structure, even if at a first look it
seems very complicated. The most important thing you should know is that the
upper level of the database is the Location. Each Location can contain
different Mapset: in every Mapset you will find the PERMANENT
Mapset because it is created by default by GRASS. Each Mapset contains the
data (raster, vector, etc) in a particular structure, but don’t worry, GRASS will
take care of this for you.
Just remember: Location contains Mapset that contains the data. For more
information visit the GRASS website.
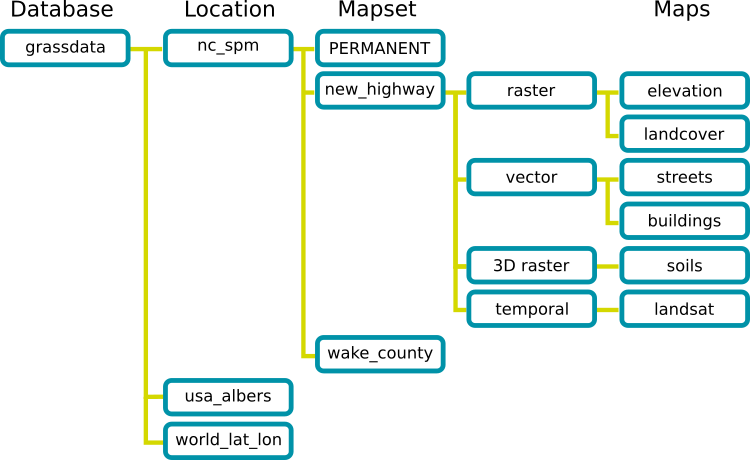
Fig. 12.119 GRASS database structure (from GRASS docs)
12.1.2. ★☆☆ Follow Along: Start a New GRASS Project
Click on the menu:
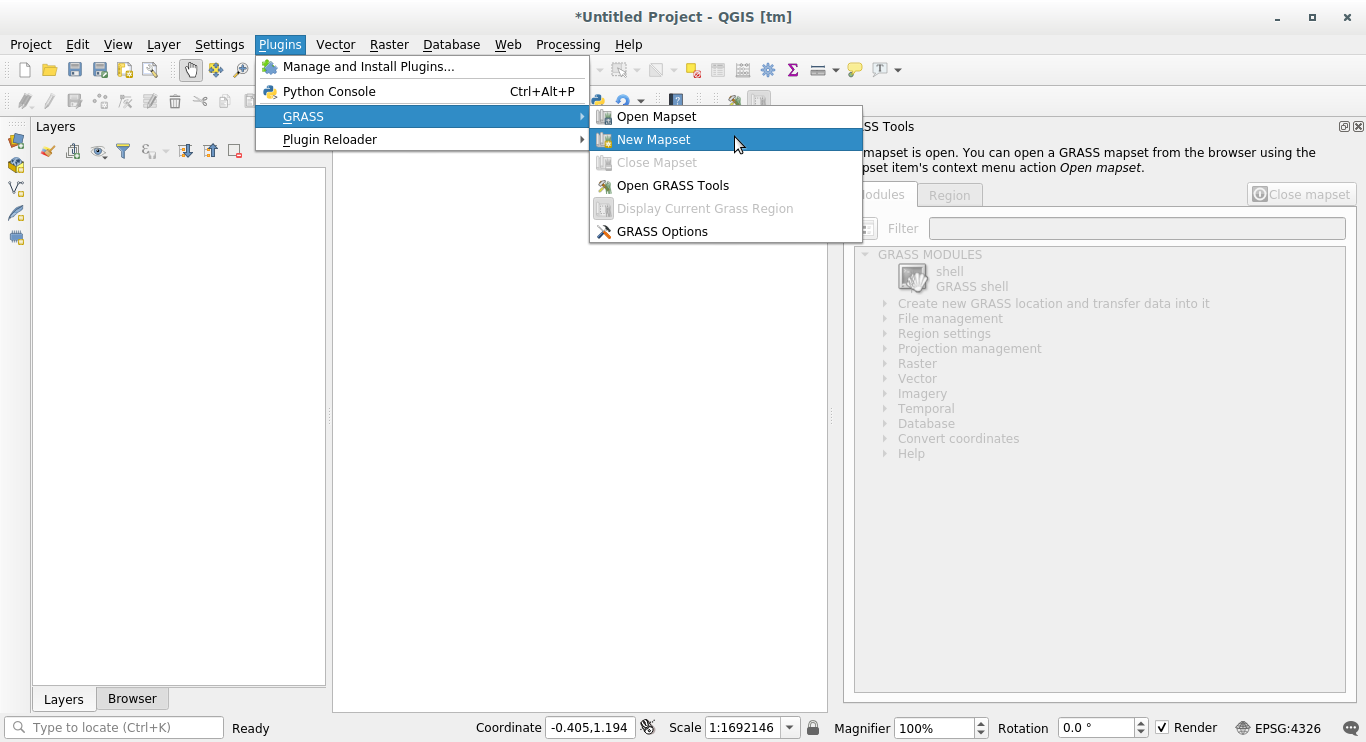
Você será solicitado a escolher a localização do banco de dados GRASS.
Definelo como el directorio que será usado por GRASS para crear su base de datos:
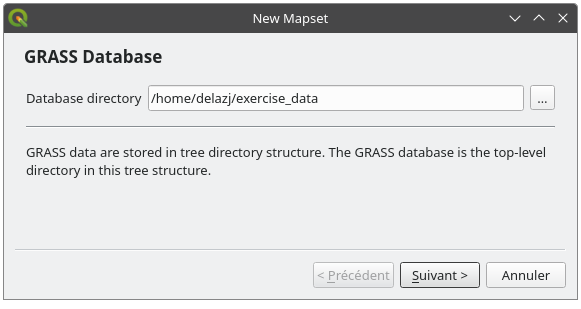
Haz clic en Siguiente.
GRASS needs to create a Location, which describes the maximum extent of the
geographic area you’ll be working in, also known as Grass Region.
Nota
the Region is extremely important for GRASS because it describes the area in which all layers will be taken into account for GRASS. Everything that is outside will not be considered. Don’t worry, you can always change the extent of the GRASS Region after the Location has been created
Chame o novo local
ÁfricadoSul: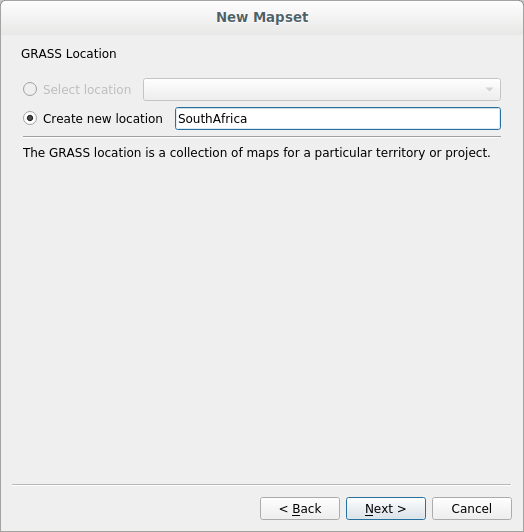
Haz clic en Siguiente.
Estaremos trabalhando com
WGS 84, então procure e selecione este SRC: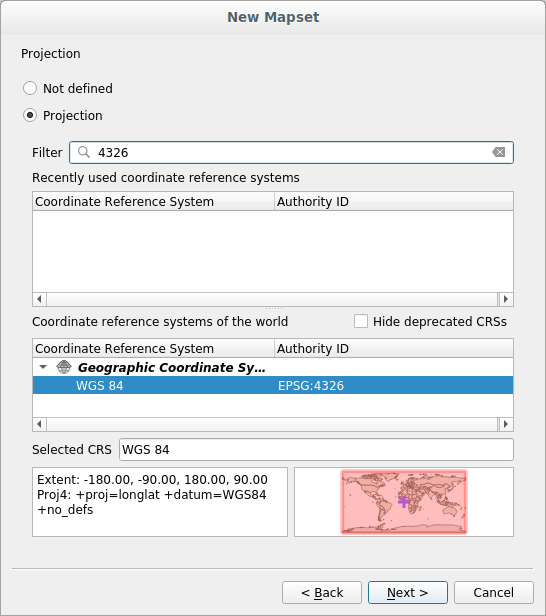
Haz clic en Siguiente.
Ahora, selecciona la región South Africa del menú desplegable y haz clic en Establecer:
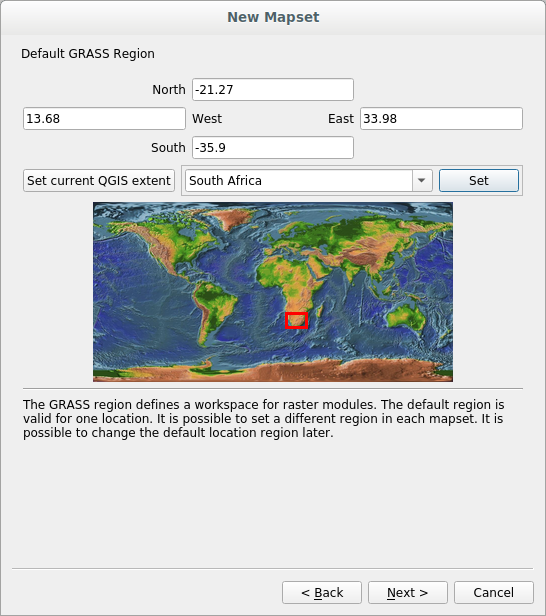
Haz clic en Siguiente.
Crea un directorio de mapa, que el archivo de mapa con el que estarás trabajando.
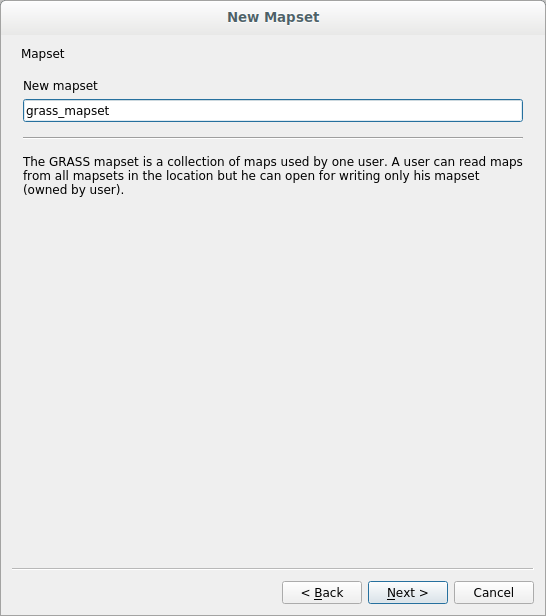
Uma vez terminado, você verá uma caixa de diálogo com um resumo de todas as informações inseridas.
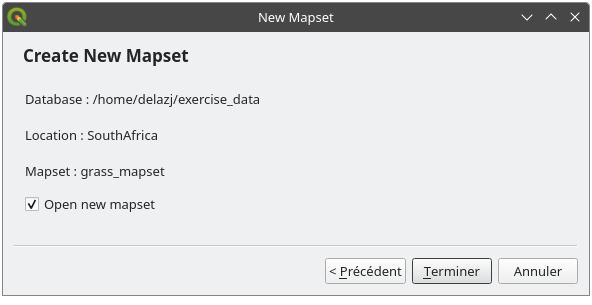
Clic Terminar.
Haz clic en Aceptar en el diálogo de éxito.
You will see that the GRASS Panel will become active and you can start to use all GRASS tools.
12.1.3. ★☆☆ Follow Along: Loading Vector Data into GRASS
Agora você tem um mapa em branco e, antes de começar a usar todas as ferramentas GRASS, precisa carregar dados no banco de dados GRASS, especificamente no Mapset. Você não pode usar ferramentas GRASS com camadas que não são carregadas em um Mapset GRASS.
There are many different ways to load data in the GRASS database. Let’s start with the first one.
★☆☆ Follow Along: Load data using the QGIS Browser
In section ★☆☆ The Browser Panel we saw that the easiest and quickest way to load the data in QGIS is the Browser Panel.
GRASS data are recognized from the QGIS Browser as real GRASS data and you can
notice it because you will see the GRASS icon next to the GRASS Mapset. Moreover
you will see the  icon next to the Mapset that is opened.
icon next to the Mapset that is opened.
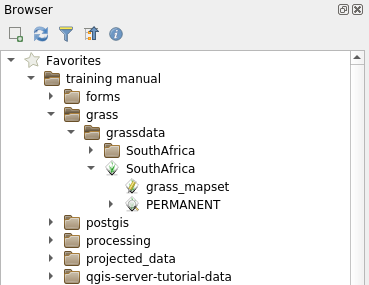
Nota
You will see a replication of the GRASS Location as normal folder:
GRASS Mapset data are those within the  folder
folder
You can easily drag and drop layers from a folder to the GRASS Mapset.
Let’s try to import the roads layer into the grass_mapset Mapset
of the SouthAfrica Location.
Vá para o Navegador e simplesmente arraste a camada roads do arquivo GeoPackage training_data.gpkg para o Mapset grass_mapset.
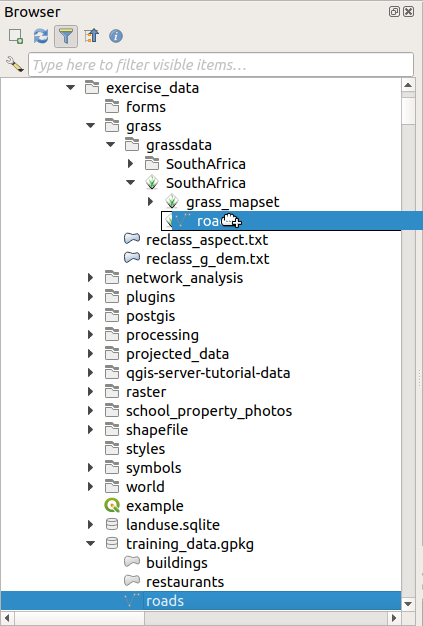
That’s it! If you expand the Mapset you will see the imported roads layer.
You can now load in QGIS the imported layer like all the other layers.
Dica
You can also load layers from the Layer Legend Panel to Mapset in the Browser Panel. This will speed up incredibly your workflow!
★☆☆ Follow Along: Load data using the GRASS Panel
We will use now the long method to load the rivers.shp layer into the
same Mapset.
Load data into QGIS as usual. Use the
rivers.shpdataset (found in theexercise_data/shapefile/folder)As soon as it is loaded, click on the Filter box of the
GRASS Paneland find the vector import tool by entering the termv.in.ogr.qgis(available under ):Aviso
There are 2 similar tools:
v.in.ogr.qgisandv.in.ogr.qgis.loc. We are looking for the first one.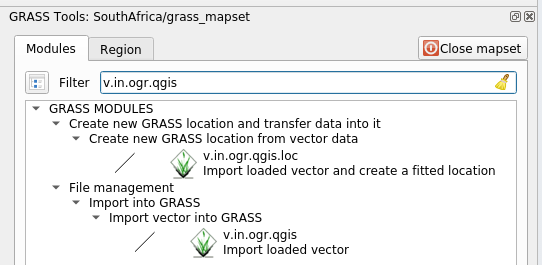
O
vsignifica vetor,insignifica uma função para importar dados para o banco de dados GRASS,ogré a biblioteca de software usada para ler dados vetoriais eqgissignifica que a ferramenta procurará um vetor dentre os vetores já carregados no QGIS.Depois de encontrar essa ferramenta, clique nela para abrir a própria ferramenta. Escolha a camada rivers na caixa Camada Carregada e digite e nomeie-o
g_riverspara evitar confusão: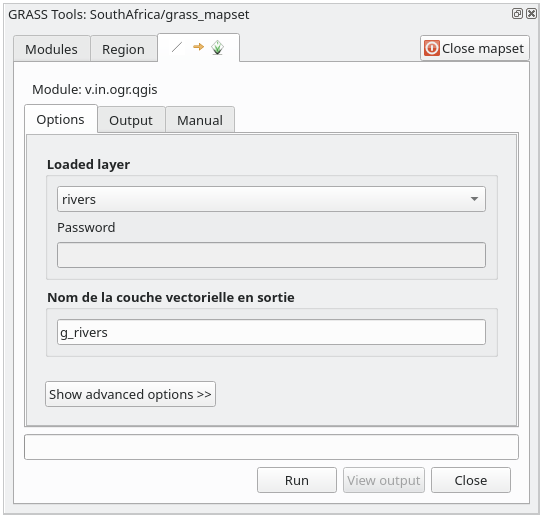
Nota
★★★ Note the extra import options provided under Advanced Options. These include the ability to add a WHERE clause for the SQL query used for importing the data.
Haz clic en Ejecutar para comenzar la importación.
Cuando termine, haz clic en el botón Ver salida para ver la capa recien importada a GRASS en el mapa.
Fechar primeiro a ferramenta de importação (clique no botão Fechar imediatamente à direita de Ver saída), em seguida, feche a janela : guilabel: Ferramentas GRASS.
Remove the original rivers layer.
Ahora tienes solamente la capa importada de GRASS visible en tu mapa de QGIS.
12.1.4. ★☆☆ Follow Along: Loading Raster Data into GRASS
Você pode importar uma camada raster da mesma maneira que importamos as camadas vetoriais.
We are going to import in the GRASS Mapset the layer srtm_41_19_4326.tif.
Nota
the raster layer is already in the correct CRS, WGS 84. If you
have layers in different CRS you must reproject them in the same CRS of the
GRASS Mapset
Load the
srtm_41_19_4326.tiflayer in QGISAbre el diálogo Herramientas GRASS de nuevo.
Click on the Modules tab.
Search for
r.in.gdal.qgis(available under ) and double click the tool to open the tool’s dialog.Set it up so that the input layer is
srtm_41_19_4326.tifand the output isg_dem.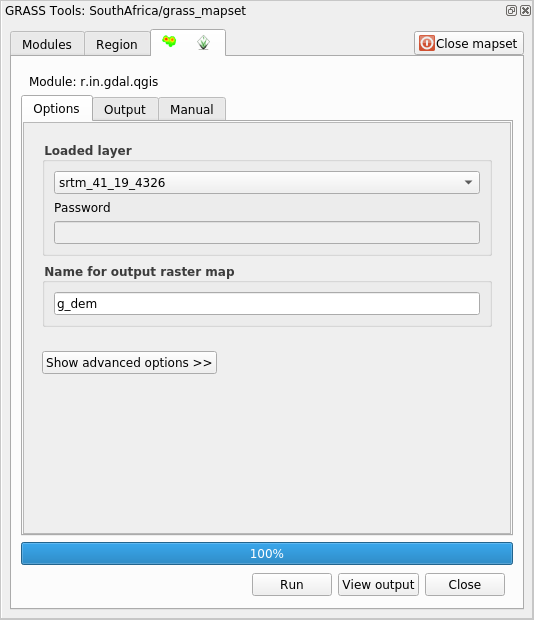
Haz clic en Run.
Cuando el proceso termine, haz clic en Ver salida.
Haz clic en Cerrar para cerrar la pestaña, y entonces haz clic en Cerrar para cerrar el cuadro de diálogo completo.
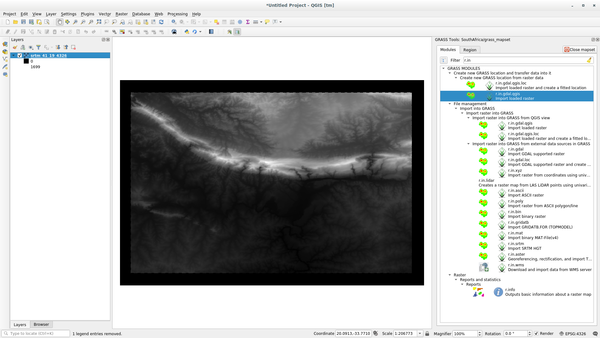
You may now remove the original
srtm_41_19_4326.tiflayer.
12.1.5. ★☆☆ Try Yourself: Add Layers to Mapset
Try to import in the GRASS Mapset the vector layers water.shp and
places.shp from the exercise_data/shapefile/ folder. As we did
for rivers rename the imported layer as g_water and g_places
to avoid confusion
Responda
You can add layers (both vector and raster) into a GRASS Mapset by drag and
drop them in the Browser (see ★☆☆ Follow Along: Load data using the QGIS Browser) or by using the
v.in.gdal.qgis for vector and r.in.gdal.qgis for raster layers.
12.1.6. ★☆☆ Open an existing GRASS Mapset
If you have an existing GRASS Mapset you can easily reopen it in another session of QGIS.
You have several method to open a GRASS Mapset, let’s explore some of them.
Let’s close the Mapset by clicking on the Close Mapset button of the GRASS Tools window.
★☆☆ Follow Along: Using the GRASS plugin
Click on the menu.
Browse to the GRASS database folder: be careful! You must choose the parent folder, not the GRASS Mapset one. Indeed GRASS will read all the
Locationsof the database and all theMapsetsof eachLocation: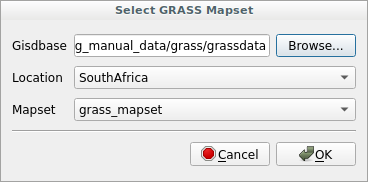
Choose the
LocationSouthAfrica and theMapsetgrass_mapset that we have created before.
That’s it! The GRASS Panel will become active meaning that the Mapset has been correctly opened.
★☆☆ Follow Along: Using the QGIS Browser
Even faster and easier is opening a Mapset using the QGIS Browser:
Close the Mapset (if it is open) by clicking on the Close Mapset button of the GRASS Tools window.
In the QGIS Browser, browse to the folder of the GRASS database.
Right click on the Mapset (remember, the Mapset has the
 GRASS icon
next to it). You will see some options.
GRASS icon
next to it). You will see some options.Clique em Abrir mapset:
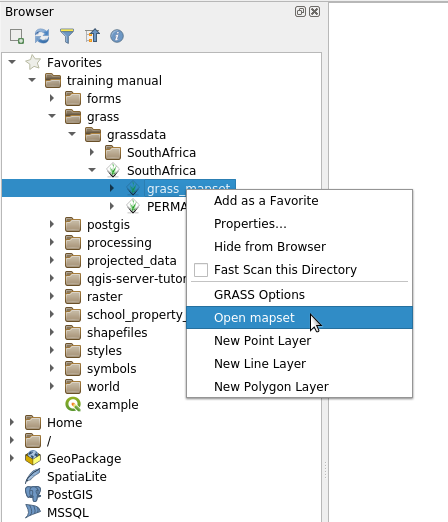
The Mapset is now open and ready to use!
Dica
Right click on a GRASS Mapset offers you a lot of different settings. Try to explore them and see all the useful options.
12.1.7. In Conclusion
La cadena de trabajo en GRASS para procesar datos es diferente del método que QGIS utiliza porque GRASS carga sus datos en una estructura de base de datos espacial. Sin embargo, utilizando QGIS como interfaz, puedes hacer los ajustes de un directorio de mapas de GRASS más fácilmente utilizando capas existentes en QGIS como fuente de datos para GRASS.
12.1.8. What’s Next?
Ahora que los datos están importado a GRASS, podemos ver las operaciones de análisis avanzado que GRASS ofrece.