` `
The QGIS Commander¶
Processing includes a practical tool that allows you to run algorithms without having to use the toolbox, but just by typing the name of the algorithm you want to run.
This tool is known as the QGIS commander, and it is just a simple text box with autocompletion where you type the command you want to run.
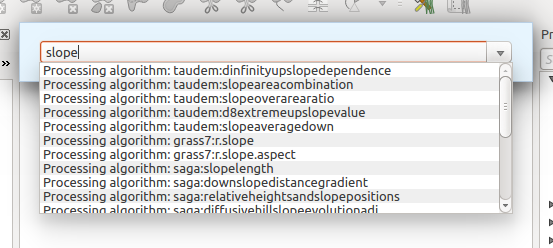
The QGIS Commander
The Commander is started from the Processing menu or, more practically, by pressing Shift + Ctrl + M (you can change that default keyboard shortcut in the QGIS configuration if you prefer a different one). To close it, just press ESC. Apart from executing Processing algorithms, the Commander gives you access to most of the functionality in QGIS, which means that it gives you a practical and efficient way of running QGIS tasks and allows you to control QGIS with reduced usage of buttons and menus.
Moreover, the Commander is configurable, so you can add your custom commands and have them just a few keystrokes away, making it a powerful tool to help you become more productive in your daily work with QGIS.
Komando yang tersedia¶
The commands available in the Commander fall in the following categories:
- Processing algorithms. These are shown as Processing algorithm: <name of the algorithm>.
- Menu items. These are shown as Menu item: <menu entry text>. All menus items available from the QGIS interface are available, even if they are included in a submenu.
- Python functions. You can create short Python functions that will be then included in the list of available commands. They are shown as Function: <function name>.
To run any of the above, just start typing and then select the corresponding element from the list of available commands that appears after filtering the whole list of commands with the text you have entered.
In the case of calling a Python function, you can select the entry in the list, which is prefixed by Function: (for instance, Function: removeall), or just directly type the function name (removeall in the previous example). There is no need to add brackets after the function name.
Creating custom functions¶
Custom functions are added by entering the corresponding Python code in the commands.py file that is found in the .qgis2/processing/commander directory in your user folder. It is just a simple Python file where you can add the functions that you need.
The file is created with a few example functions the first time you open the Commander. If you haven’t launched the Commander yet, you can create the file yourself. To edit the commands file, use your favourite text editor. You can also use a built-in editor by calling the edit command from the Commander. It will open the editor with the commands file, and you can edit it directly and then save your changes.
For instance, you can add the following function, which removes all layers:
from qgis.gui import *
def removeall():
mapreg = QgsMapLayerRegistry.instance()
mapreg.removeAllMapLayers()
Once you have added the function, it will be available in the Commander, and you can invoke it by typing removeall. There is no need to do anything apart from writing the function itself.
Functions can receive parameters. Add *args to your function definition to receive arguments. When calling the function from the Commander, parameters have to be passed separated by spaces.
Here is an example of a function that loads a layer and takes a parameter with the filename of the layer to load.
import processing
def load(*args):
processing.load(args[0])
If you want to load the layer in ;file:/home/myuser/points.shp, type in the Commander text box:
load /home/myuser/points.shp