Data Capture¶
 |
Tavoitteet: |
Opi luomaan ja muokkaamaan vektoriaineistoja ja ominaisuustietoja. |
Avainsanat: |
Editing, data capture, heads-up, table, database. |
Yleiskatsaus¶
Kahdessa aikaisemmassa osiossa tarkastelimme vektoriaineistoja. Opimme että vektoriaineistoihin liittyy kaksi keskeistä käsitettä: geometria ja ominaisuudet. Vektoriaineiston geometria kuvaa kohteen muotoa ja sijaintia, kun taas ominaisuustiedot kuvaavat kohteen ominaisuuksia (väri, koko, ikä, jne.).
Tässä osioissa tutustumme tarkemmin vektoriaineistojen luomiseen ja muokkaamiseen —- sekä vektorikohteiden geometrian että niiden ominaisuustietojen osalta.
Miten digitaalinen paikkatietoaineisto tallentuu tietokoneen musitiin?¶
Tekstieditorit, taulukkolaskentaohjelmat ja grafiikkatyökalut ovat ohjelmia joilla voi luoda ja editoida digitaalisia aineistoja. Erilaiset sovellukset tallentavat aineistoja tietyn tiedostoformaatin mukaisesti. Esimerkiksi kuvankäsittelyohjelma sallii tiedostojen tallentamisen jpg JPEG-kuvana, tekstieditorit sallivat tiedoston tallentamisen .odt OpenDocument-formaatissa tai .doc Word Document -tiedostona ja niin edelleen.
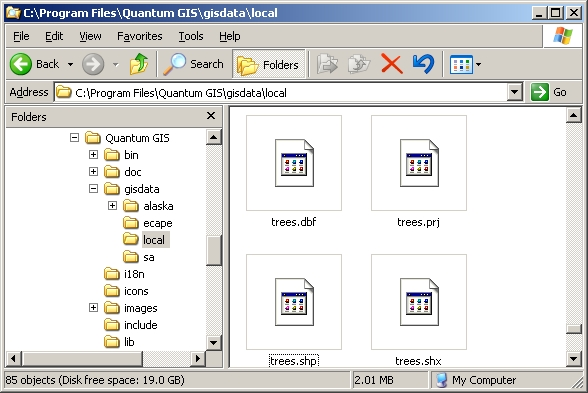
Kuten muutkin sovellukset, GIS-sovellukset tallentavat aineistoja tiedostoihin tietokoneen kovalevylle. Paikkatietoaineistoille on olemassa useita eri tiedostoformaatteja, mutta tunnetuin niistä on luultavasti ‘shape file’. Tiedostoformaatin nimi on hieman outo, sillä vaikka nimi on yksikkömuodossa (file = yksi tiedosto), se koostuu oikeasti vähintään kolmesta erillisestä tiedostosta jotka työskentelevät yhdessä tallentaakseen digitaalista vektoriaineistoa, kuten näkyy taulukosta_shapefile.
Tiedostopääte |
Kuvaus |
|---|---|
| .shp | Vektorikohteiden geometriatiedot on tallennettu tähän tiedostoon |
| .dbf | Vektorikohteiden ominaisuustiedot on tallennettu tähän tiedostoon |
| .shx | Tämä on indeksitiedosto, joka auttaa GIS-sovellusta löytämään oikeat kohteet nopeammin. |
Taulukko Shapefile 1: Tiedostot joista yksi ‘shapefile’ koostuu
Kun tarkastelet tiedostoja joista shapefile muodostuu tietokoneen kovalevyllä, näkymä on samankaltainen kuin figure_shapefile. Jos tahdot jakaa vektoriaineistoja shapefile-muodossa toisen käyttäjän kanssa sinun täytyy toimittaa hänelle kaikki tasoon kuuluvat tiedostot. Kuvan figure_shapefile tason ‘trees’ tapauksessa sinun täytyisi toimittaa toiselle käyttäjälle tiedostot trees.shp, trees.shx, trees.dbf, trees.prj sekä :file trees.qml.
Monet GIS-sovellukset kykenevät tallentamaan digitaalisia aineistoja tietokantaan. Paikkatietoaineistojen tallentaminen tietokantaan on yleisesti ottaen hyvä ratkaisu, sillä tietokanta tallentaa suuria määriä aineistoja tehokkaasti ja tuo aineistot nopeasti GIS-sovelluksen käyttöön. Tietokannan käyttäminen sallii myös sen että useampi ihminen työskentelee samanaikaisesti samoilla vektoriaineistoilla. Spatiaalista tietoa tallentavan tietokannan perustaminen on monimutkaisempaa kuin shapefile-tiedostojen käyttäminen, joten tässä kappaleessa keskitymme vain luomaan ja editoimaan shapefile-tiedostoja.
Suunnittele ennen kuin aloitat¶
Ennen kuin voit luoda uuden vektoritason (joka tallentuu shapefilena), sinun täytyy tietää minkälainen geometria tasolle tulee (piste, viiva, polygoni), ja sinun täytyy tietää mitä ominaisuustietoja tasoon liitetään. Katsotaan seuraavaksi muutamaa esimerkkiä aiheesta työskentelyn helpottamiseksi.
Esimerkki 1: Turistikartta¶
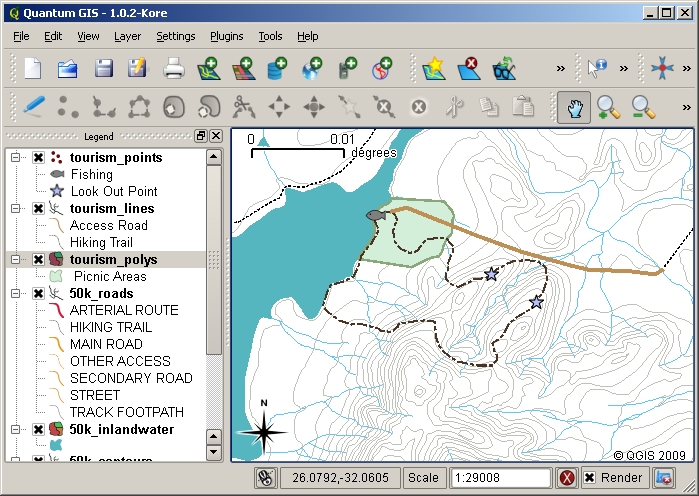
Kuvittele että haluaisit tehdä kivan turistikartan paikkakunnaltasi. Visionasi on 1:50 000 maastokartta johon on merkitty turisteille kiinnostavia kohteita. Mietitään ensin geometriaa. Tiedämme, että vektoritaso voidaa esittää pisteinä, viivoina tai polygoneina. Mikä olisi järkevin kohdetyyppi turistikarttaamme varten? Voisimme käyttää pisteitä osoittamaan tiettyjen paikkojen, kuten näköalapaikkojen, muistomerkkien tai historallisten taistelupaikkojen sijainnin. Voisi olla järkevää käyttää viivoja jos haluamme merkitä turisteja varten reitin, kuten esimerkiksi vuoristossa kulkevan vaellusreitin. Polygonit voisivat olla hyvä vaihtoehto, jos haluamme merkitä kartalle kokonaisen alueen, kuten luonnonsuojelualueen tai kulttuurisesti kiinnostavan kylän.
As you can see it’s often not easy to know what type of geometry you will need. One common approach to this problem is to make one layer for each geometry type you need. So, for example, if you look at digital data provided by the Chief Directorate: Surveys and Mapping, South Africa, they provide a river areas (polygons) layer and a rivers polyline layer. They use the river areas (polygons) to represent river stretches that are wide, and they use river polylines to represent narrow stretches of river. In figure_tourism we can see how our tourism layers might look on a map if we used all three geometry types.
Esimerkki 2: Karttaesitys veden epäpuhtauksista joen varrella¶
If you wanted to measure pollution levels along the course of a river you would typically travel along the river in a boat or walk along its banks. At regular intervals you would stop and take various measurements such as Dissolved Oxygen (DO) levels, Coliform Bacteria (CB) counts, Turbidity levels and pH. You would also need to make a map reading of your position or obtain your position using a GPS receiver.
To store the data collected from an exercise like this in a GIS Application, you would probably create a GIS layer with a point geometry. Using point geometry makes sense here because each sample taken represents the conditions at a very specific place.
For the attributes we would want a field for each thing that describes the sample site. So we may end up with an attribute table that looks something like table_river_attributes.
| SampleNo | pH | DO | CB | Turbidity | Collector | Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 7 | 6 | N | Low | Patience | 12/01/2009 |
| 2 | 6.8 | 5 | Y | Medium | Thabo | 12/01/2009 |
| 3 | 6.9 | 6 | Y | High | Victor | 12/01/2009 |
Table River Attributes 1: Drawing a table like this before you create your vector layer will let you decide what attribute fields (columns) you will need. Note that the geometry (positions where samples were taken) is not shown in the attribute table –– the GIS Application stores it separately!
Tyhjän shape-tiedoston luominen¶
Kun tiedät mitä kohteita haluat tallentaa, mikä kunkin kohteen geometriatyyppi on ja mitä attribuutteja kohteelle annetaan, voit edetä seuraavaan vaiheeseen, tyhjän shape-tiedoston luomiseen.
Prosessi alkaa tyypillisesti valitsemalla vaihtoehto ‘vektoritaso’ ja valitsemalla geometriatyyppi, siis piste, viiva tai alue kuten edellä todettiin
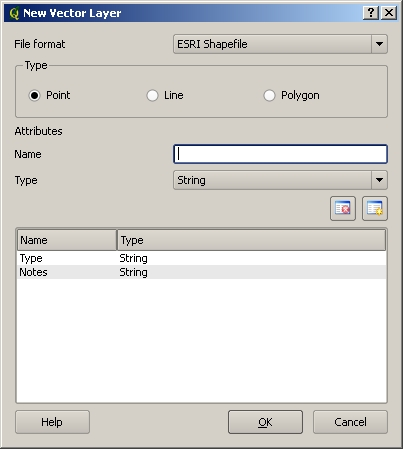
Vektoritason luominen käy helposti täyttämällä muutama dialogin kysymä tieto. Valitse ensin geometriatyyppi ja sen jälkeen lisää attribuuttikentät.
Seuraavaksi lisäät kentät attribuuttitauluun. Yleensä suositellaan lyhyitä kentän nimiä, joissa ei ole välilyöntejä eikä skandimerkkejä ja jotka kuvaavat minkälaista tietoa tietokenttään tallennetaan. Esimerkkejä suositelluista kentän nimistä ovat ‘pH’, ‘TieTyyppi’, ‘KatonVari’ jne. Lisäksi on määritettävä mikä on kenttään tallennettavan tiedon muoto, esim. numero, teksti, päivämäärä.
Computer programs usually call information that is made up of words or sentences ‘strings‘, so if you need to store something like a street name or the name of a river, you should use ‘String’ for the field type.
The shapefile format allows you to store the numeric field information as either a whole number (integer) or a decimal number (floating point) –– so you need to think before hand whether the numeric data you are going to capture will have decimal places or not.
The final step (as shown in figure_save_shapefile) for creating a shapefile is to give it a name and a place on the computer hard disk where it should be created. Once again it is a good idea to give the shapefile a short and meaningful name. Good examples are ‘rivers’, ‘watersamples’ and so on.
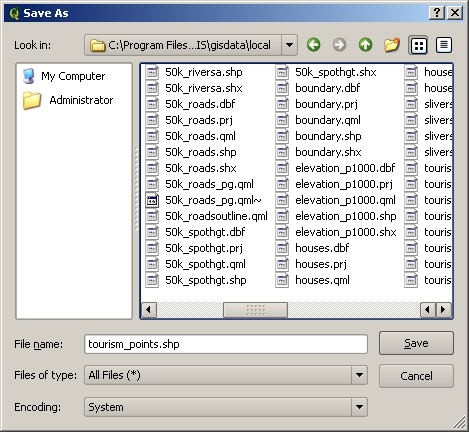
After defining our new layer’s geometry and attributes, we need to save it to disk. It is important to give a short but meaningful name to your shapefile.
Let’s recap the process again quickly. To create a shapefile you first say what kind of geometry it will hold, then you create one or more fields for the attribute table, and then you save the shapefile to the hard disk using an easy to recognise name. Easy as 1-2-3!
Adding data to your shapefile¶
So far we have only created an empty shapefile. Now we need to enable editing in the shapefile using the ‘enable editing’ menu option or tool bar icon in the GIS Application. Shapefiles are not enabled for editing by default to prevent accidentally changing or deleting the data they contain. Next we need to start adding data. There are two steps we need to complete for each record we add to the shapefile:
- Capturing geometry
- Entering attributes
The process of capturing geometry is different for points, polylines and polygons.
To capture a point, you first use the map pan and zoom tools to get to the correct geographical area that you are going to be recording data for. Next you will need to enable the point capture tool. Having done that, the next place you click with the left mouse button in the map view, is where you want your new point geometry to appear. After you click on the map, a window will appear and you can enter all of the attribute data for that point (see figure_attribute_dialog). If you are unsure of the data for a given field you can usually leave it blank, but be aware that if you leave a lot of fields blank it will be hard to make a useful map from your data!
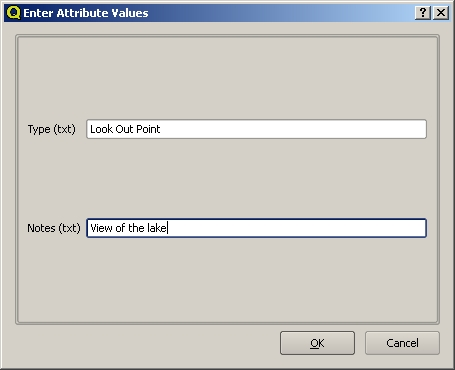
After you have captured the point geometry, you will be asked to describe its attributes. The attribute form is based on the fields you specified when you created the vector layer.
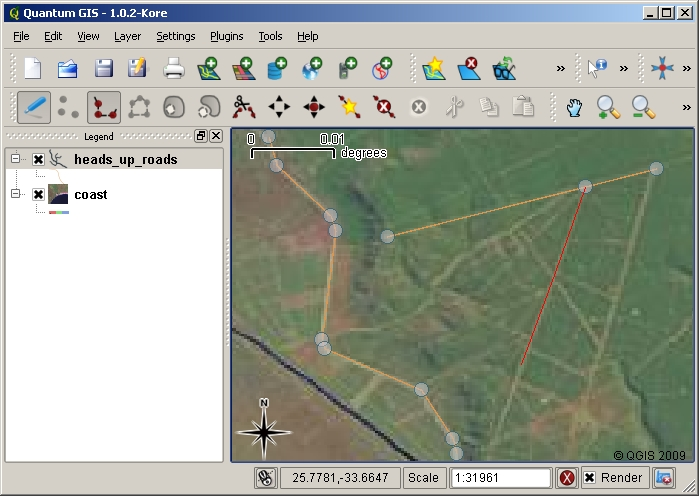
To capture a polyline the process is similar to that of a point, in that you need to first use the pan and zoom tools to move the map in the map view to the correct geographical area. You should be zoomed in enough so that your new vector polyline feature will have an appropriate scale (see Vector Data for more details on scale issues). When you are ready, you can click the polyline capture icon in the tool bar and then start drawing your line by clicking on the map. After you make your first click, you will notice that the line stretches like an elastic band to follow the mouse cursor around as you move it. Each time you click with the left mouse button, a new vertex will be added to the map. This process is shown in figure_capture_polyline.
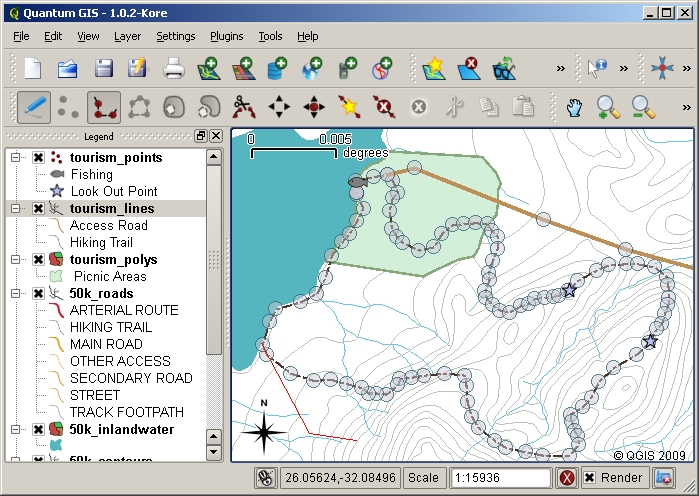
Capturing lines for a tourism map. When editing a line layer, the vertices are shown with circular markers which you can move about with the mouse to adjust the line’s geometry. When adding a new line (shown in red), each click of the mouse will add a new vertex.
When you have finished defining your line, use the right mouse button to tell the GIS Application that you have completed your edits. As with the procedure for capturing a point feature, you will then be asked to enter in the attribute data for your new polyline feature.
The process for capturing a polygon is almost the same as capturing a polyline except that you need to use the polygon capture tool in the toolbar. Also, you will notice that when you draw your geometry on the screen, the GIS Application always creates an enclosed area.
To add a new feature after you have created your first one, you can simply click again on the map with the point, polyline or polygon capture tool active and start to draw your next feature.
When you have no more features to add, always be sure to click the ‘allow editing’ icon to toggle it off. The GIS Application will then save your newly created layer to the hard disk.
Heads-up digitising¶
As you have probably discovered by now if you followed the steps above, it is pretty hard to draw the features so that they are spatially correct if you do not have other features that you can use as a point of reference. One common solution to this problem is to use a raster layer (such as an aerial photograph or a satellite image) as a backdrop layer. You can then use this layer as a reference map, or even trace the features off the raster layer into your vector layer if they are visible. This process is known as ‘heads-up digitising’ and is shown in figure_headsup_digitizing.
Digitising using a digitising table¶
Another method of capturing vector data is to use a digitising table. This approach is less commonly used except by GIS professionals, and it requires expensive equipment. The process of using a digitising table, is to place a paper map on the table. The paper map is held securely in place using clips. Then a special device called a ‘puck’ is used to trace features from the map. Tiny cross-hairs in the puck are used to ensure that lines and points are drawn accurately. The puck is connected to a computer and each feature that is captured using the puck gets stored in the computer’s memory. You can see what a digitising puck looks like in figure_digitizing_table.
After your features are digitised...¶
Once your features are digitised, you can use the techniques you learned in the previous topic to set the symbology for your layer. Choosing an appropriate symbology will allow you to better understand the data you have captured when you look at the map.
Common problems / things to be aware of¶
If you are digitising using a backdrop raster layer such as an aerial photograph or satellite image, it is very important that the raster layer is properly georeferenced. A layer that is georeferenced properly displays in the correct position in the map view based on the GIS Application’s internal model of the Earth. We can see the effect of a poorly georeferenced image in figure_georeference_issue.
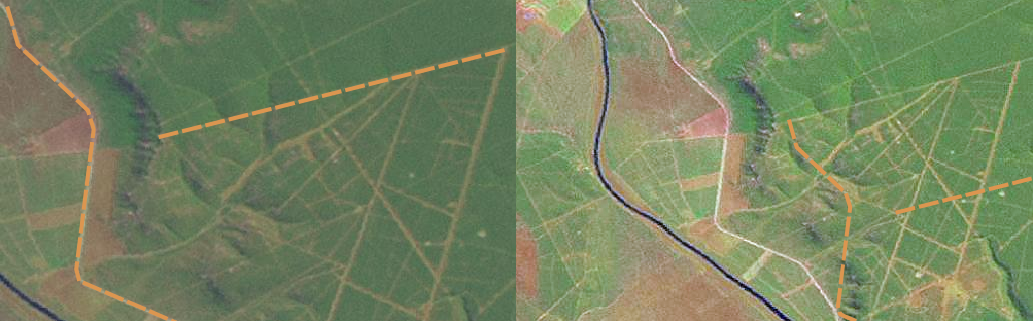
The importance of using properly georeferenced raster images for heads-up digitising. On the left we can see the image is properly georegistered and the road features (in orange) overlap perfectly. If the image is poorly georeferenced (as shown on the right) the features will not be well aligned. Worse still, if the image on the right is used as a reference when capturing new features, the newly captured data will be inaccurate!
Also remember that it is important that you are zoomed in to an appropriate scale so that the vector features you create are useful. As we saw in the previous topic on vector geometry, it is a bad idea to digitise your data when you are zoomed out to a scale of 1:1000 000 if you intend to use the data you capture at a scale of 1:50 000 later.
Mitä olemme oppineet?¶
Let’s wrap up what we covered in this worksheet:
- Digitising is the process of capturing knowledge of a feature’s geometry and attributes into a digital format stored on the computer’s disk.
- GIS Data can be stored in a database or as files.
- One commonly used file format is the shapefile which is actually a group of three or more files (.shp, .dbf and .shx).
- Before you create a new vector layer you need to plan both what geometry type and attribute fields it will contain.
- Geometry can be point, polyline or polygon.
- Attributes can be integers (whole numbers), floating points (decimal numbers), strings (words) or dates.
- The digitising process consists of drawing the geometry in the map view and then entering its attributes. This is repeated for each feature.
- Heads-up digitising is often used to provide orientation during digitising by using a raster image in the background.
- Professional GIS users sometimes use a digitising table to capture information from paper maps.
Nyt on sinun vuorosi yrittää!¶
Here are some ideas for you to try with your learners:
- Draw up a list of features in and around your school that you think would be interesting to capture. For example: the school boundary, the position of fire assembly points, the layout of each class room, and so on. Try to use a mix of different geometry types. Now split your learners into groups and assign each group a few features to capture. Have them symbolise their layers so that they are more meaningful to look at. Combine the layers from all the groups to create a nice map of your school and its surroundings!
- Find a local river and take water samples along its length. Make a careful note of the position of each sample using a GPS or by marking it on a toposheet. For each sample take measurements such as pH, dissolved oxygen etc. Capture the data using the GIS application and make maps that show the samples with a suitable symbology. Could you identify any areas of concern? Was the GIS Application able to help you to identify these areas?
Something to think about¶
If you don’t have a computer available, you can follow the same process by using transparency sheets and a notebook. Use an aerial photo, orthosheet or satellite image printout as your background layer. Draw columns down the page in your notebook and write in the column headings for each attribute field you want to store information about. Now trace the geometry of features onto the transparency sheet, writing a number next to each feature so that it can be identified. Now write the same number in the first column in your table in your notebook, and then fill in all the additional information you want to record.
Further reading¶
Website http://www.k12science.org/curriculum/waterproj/S00project/miami2000/miamiriverfinal/ — A school project to assess water quality in their local river.
The QGIS User Guide also has more detailed information on digitising vector data in QGIS.
What’s next?¶
In the section that follows we will take a closer look at raster data to learn all about how image data can be used in a GIS.