Algorithms Include
Python Code Sample
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
algoritmo id rodomas, kai užvedate pelę virš algoritmo apdorojimo įrankinėje. parametrų žodynas teikia parametrų pavadinimus ir reikšmes. Daugiau informacijos apie tai, kaip vykdyti apdorojimo algoritmus Pythono konsolėje rasite skyriuje Using processing algorithms from the console.
Output Types
Directory
Įrašyti į laikiną aplanką
Įrašyti į aplanką
Praleisti išvestį
Įrašyti į laikiną aplanką
Įrašyti į aplanką
Failas
Įrašyti į laikiną failą
Įrašyti į failą…
Praleisti išvestį
Įrašyti į laikiną failą
Įrašyti į failą…
Sluoksnis
Kurti laikiną sluoksnį (
TEMPORARY_OUTPUT)Įrašyti į failą…
Įrašyti į geopackage…
Įrašyti į duombazės lentelę…
Čia taipogi galima pakeisti failo koduotę.
Kurti laikiną sluoksnį (
TEMPORARY_OUTPUT)Įrašyti į failą…
Įrašyti į geopackage…
Įrašyti į duombazės lentelę…
Pridėti į sluoksnį…
Čia taipogi galima pakeisti failo koduotę.
Praleisti išvestį
Kurti laikiną sluoksnį (
TEMPORARY_OUTPUT)Įrašyti į failą…
Įrašyti į geopackage…
Įrašyti į duombazės lentelę…
Čia taipogi galima pakeisti failo koduotę.
Extent Dropdown
Galimi metodai yra:
Skaičiuoti pagal sluoksnį…: naudoja dabartiniame projekte įkelto sluoksnio apimtį
Skaičiuoti pagal išdėstymo žemėlapį…: naudoja aktyvaus projekto išdėstymo žemėlapio elemento apimtį
Skaičiuoti pagal žymelę…: naudoja įrašytos žymelės apimtį
Naudoti žemėlapio drobės apimtį
Braižyti drobėje: spauskite ir tempkite stačiakampį, apibrėžianti norimą plotą
Įveskite koordinates kaip
xmin, xmax, ymin, ymax
Geometric predicates
Geometriniai predikatai yra funkcijos, kurios naudojamos nustatant, kokį erdvinį ryšį geoobjektas turi su kitu, lyginant ar ir kaip jų geometrijos dalinasi erdvės dalimi.
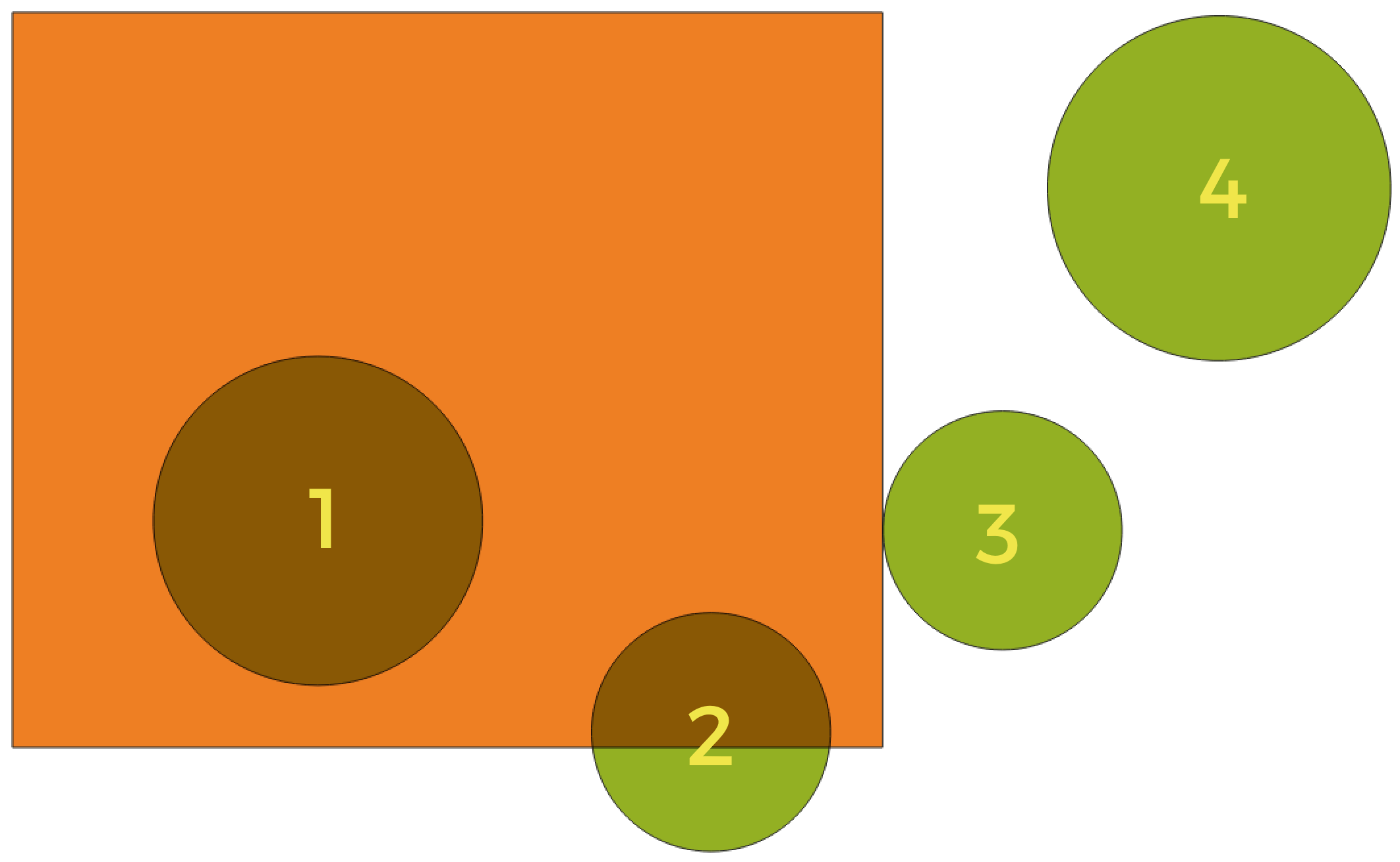
Erdvinių ryšių tarp sluoksnių paieška
Naudojant aukščiau pateiktą iliustraciją, mes ieškome žalių apskritimų, erdviškai lygindami juos su oranžiniu stačiakampiu geoobjektus. Galimi geometriniai predikatai yra:
- Susikerta
Tikrina, ar viena geometrija kerta kitą. Grąžina 1 (true), jei geometrijos erdviškai kertasi (dalinasi kažkokia erdvės dalimi - persidengia arba liečia) ir 0, jei to nėra. Iliustracijoje aukščiau True bus grąžinama apskritimams 1, 2 ir 3.
- Įtraukia
Grąžina 1 (true) tada ir tik tada, jei nei vienas b taškas nėra už a ribų, ir bent vienas b vidaus taškas yra a viduje. Iliustracijoje nei vienas apskritimas nebūtų grąžintas, bet stačiakampis būtų, jei jūs ieškotumėte atvirkščiai, nes pilnai stačiakampyje yra 1 apskritimas. Tai yra priešingybė yra viduje.
- Atskiras
Grąžina 1 (true), jei geometrijos nesidalina jokia erdvės dalimi (nėra persidengimo, nėra susilietimo). Grąžinamas tik 4 apskritimas.
- Lygūs
Grąžina 1 (true), tada ir tik tada, jei geometrijos yra lygiai tokios pačios. Negrąžinami jokie apskritimai.
- Liečia
Tikrina, ar geometrija liečia kitą geometriją. Grąžina 1 (true), jei geometrijos turi bent vieną bendrą tašką, bet jų vidus nepersidengia. Grąžinamas tik 3 apskritimas.
- Persidengia
Tikrina, ar viena geometrija persidengia su kita. Grąžina 1 (true), jei geometrijos dalinasi erdve, turi tokius pačius matmenis, bet nei viena iš jų nėra pilnai kitoje. Grąžinamas tik 2 apskritimas.
- Yra viduje
Tikrina, ar geometrija yra kitos viduje. Grąžina 1 (true), jei geometrija a yra pilnai geometrijos b viduje. Grąžinamas tik apskritimas 1.
- Kerta
Grąžina 1 (true), jei pateiktos geometrijos turi kelis, bet ne visus, bendrus vidaus taškus ir jų susikirtimas turi mažiau matmenų nei daugiausiai matmenų turinti geometrija. Pavyzdžiui, linijos ir poligono susikirtimas bus linija (true). Poligono ir poligono susikirtimas yra poligonas (false). Iliustracijoje nebūtų grąžinamas nei vienas apskritimas.
Notes on algorithms
Įspėjimas
Keičiama tik geometrija
Šis veiksmas keičia tik geoobjekto geometriją. Geoobjektų atributų reikšmės nekeičiamos, nors geoobjektų savybės, tokios kaip plotas ar ilgis, gali pasikeisti. Jei šios savybės laikomos atributuose, juos reikės pakeisti rankiniu būdu.
Raster data types
Without user input (native)
0 — Byte (aštuonių bitų sveikas skaičius be ženklo (quint8))
1 — Int16 (Šešiolikos bitų sveikas skaičius su ženklu (qint16))
2 — UInt16 (Šešiolikos bitų sveikas skaičius be ženklo (quint16))
3 — Int32 (Thirty two bit signed integer (qint32))
4 — UInt32 (Trisdešimt dviejų bitų sveikas skaičius be ženklo (quint32))
5 — Float32 (Trisdešimt dviejų bitų slankaus kablelio skaičius (float))
6 — Float64 (Šešiasdešimt keturių bitų slankaus kablelio skaičius (double))
7 — CInt16 (Kompleksinis Int16)
8 — CInt32 (Kompleksinis Int32)
9 — CFloat32 (Kompleksinis Float32)
10 — CFloat64 (Kompleksinis Float64)
11 — Int8 (Aštuonių bitų sveikas skaičius su ženklu (qint8))
Galimi variantai priklauso nuo GDAL versijos, su kuria sukurtas QGIS (žiūrėkite meniu )
Without user input
0 — Byte (aštuonių bitų sveikas skaičius be ženklo (quint8))
1 — Int16 (Šešiolikos bitų sveikas skaičius su ženklu (qint16))
2 — UInt16 (Šešiolikos bitų sveikas skaičius be ženklo (quint16))
3 — UInt32 (Trisdešimt dviejų bitų sveikas skaičius be ženklo (quint32))
4 — Int32 (Trisdešimt dviejų bitų sveikas skaičius su ženklu (qint32))
5 — Float32 (Trisdešimt dviejų bitų slankaus kablelio skaičius (float))
6 — Float64 (Šešiasdešimt keturių bitų slankaus kablelio skaičius (double))
7 — CInt16 (Kompleksinis Int16)
8 — CInt32 (Kompleksinis Int32)
9 — CFloat32 (Kompleksinis Float32)
10 — CFloat64 (Kompleksinis Float64)
11 — Int8 (Aštuonių bitų sveikas skaičius su ženklu (qint8))
Galimi variantai priklauso nuo GDAL versijos, su kuria sukurtas QGIS (žiūrėkite meniu )
With user input
0 — Naudoti įvesties sluoksnio duomenų tipa
1 — Byte (aštuonių bitų sveikas skaičius be ženklo (quint8))
2 — Int16 (Šešiolikos bitų sveikas skaičius su ženklu (qint16))
3 — UInt16 (Šešiolikos bitų sveikas skaičius be ženklo (quint16))
4 — UInt32 (Trisdešimt dviejų bitų sveikas skaičius be ženklo (quint32))
5 — Int32 (Trisdešimt dviejų bitų sveikas skaičius su ženklu (qint32))
6 — Float32 (Trisdešimt dviejų bitų slankaus kablelio skaičius (float))
7 — Float64 (Šešiasdešimt keturių bitų slankaus kablelio skaičius (double))
8 — CInt16 (Kompleksinis Int16)
9 — CInt32 (Kompleksinis Int32)
10 — CFloat32 (Kompleksinis Float32)
11 — CFloat64 (Kompleksinis Float64)
12 — Int8 (Aštuonių bitų sveikas skaičius su ženklu (qint8))
Galimi variantai priklauso nuo GDAL versijos, su kuria sukurtas QGIS (žiūrėkite meniu )
Resampling methods
0 — Artimiausias kaimynas
1 — Bitiesinis (2x2 branduolio)
2 — Kubinis (4x4 branduolio)
3 — Kubinis B-kreivės (4x4 branduolio)
4 — Lanczos (6x6 branduolio)
5 — Vidurkis
6 — Režimas
7 — Maksimalus
8 — Minimumas
9 — Mediana
10 — Pirmas kvartilis (Q1)
11 — Trečias kvartilis (Q3)
Vector field types
1 — Boolean
2 — Integer (32bit)
4 — Integer (64bit)
6 — Decimal (double)
9 — Integer list
9 — Integer (64bit) list
9 — Decimal (double) list
10 — Text (string)
11 — Eilučių sąrašas
12 — Dvejetainis objektas (BLOB)
14 — Data
15 — Laikas
16 — Data ir laikas
2 — Sveikų skaičių sąrašas
4 — Sveikų skaičių (64bit) sąrašas
6 — Dešimtainių (double) sąrašas
10 — Eilučių sąrašas
0 — Bet kokie kiti tipai