Algorithms Include
Python Code Sample
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
ID алгоритма отображается при наведении мыши на алгоритм в Инструментах анализа. Словарь parameter dictionary содержит ключи параметров и их значения. См. Изпользование алгоритмов геообработки в консоли для детального описания того, как запускать алгоритмы анализа из консоли Python.
Output Types
Directory
Save to a Temporary Directory
Save to Directory
Skip Output
Save to a Temporary Directory
Save to Directory
Файл
Сохранить во временный файл
Save to File…
Skip Output
Сохранить во временный файл
Save to File…
Слой
Create Temporary Layer (
TEMPORARY_OUTPUT)Save to File…
Save to Geopackage…
Save to Database Table…
The file encoding can also be changed here.
Create Temporary Layer (
TEMPORARY_OUTPUT)Save to File…
Save to Geopackage…
Save to Database Table…
Append to Layer…
The file encoding can also be changed here.
Skip Output
Create Temporary Layer (
TEMPORARY_OUTPUT)Save to File…
Save to Geopackage…
Save to Database Table…
The file encoding can also be changed here.
Extent Dropdown
Available methods are:
Calculate from layer…: uses extent of a layer loaded in the current project
Calculate from layout map…: uses extent of a layout map item in the active project
Calculate from bookmark…: uses extent of a saved bookmark
Use map canvas extent
Draw on canvas: click and drag a rectangle delimiting the area to take into account
Enter the coordinates as
xmin, xmax, ymin, ymax
Geometric predicates
Geometric predicates are boolean functions used to determine the spatial relation a feature has with another by comparing whether and how their geometries share a portion of space.
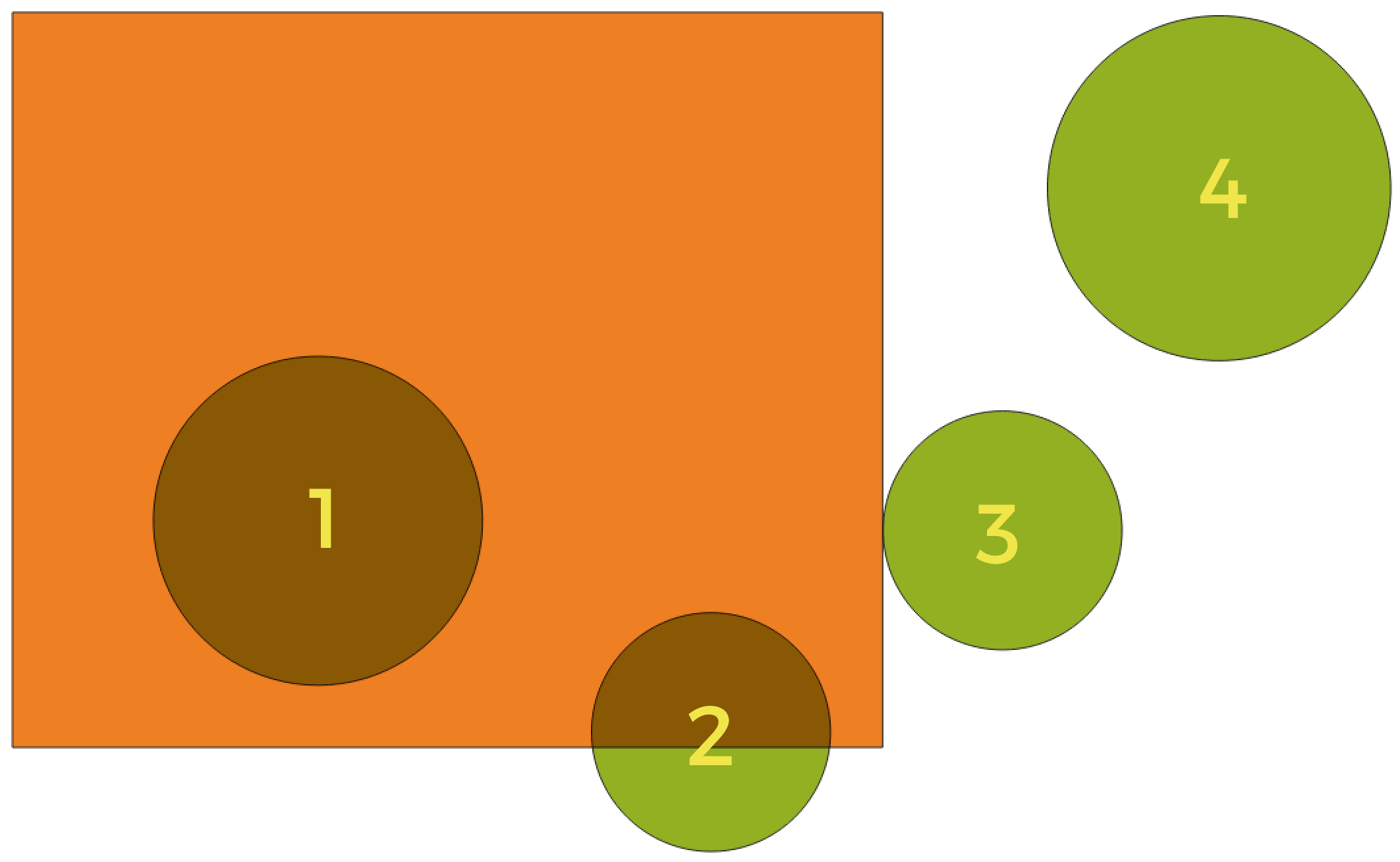
Looking for spatial relations between layers
Using the figure above, we are looking for the green circles by spatially comparing them to the orange rectangle feature. Available geometric predicates are:
- Intersect
Tests whether a geometry intersects another. Returns 1 (true) if the geometries spatially intersect (share any portion of space - overlap or touch) and 0 if they don’t. In the picture above, this will return circles 1, 2 and 3.
- Contain
Returns 1 (true) if and only if no points of b lie in the exterior of a, and at least one point of the interior of b lies in the interior of a. In the picture, no circle is returned, but the rectangle would be if you would look for it the other way around, as it contains circle 1 completely. This is the opposite of are within.
- Disjoint
Returns 1 (true) if the geometries do not share any portion of space (no overlap, not touching). Only circle 4 is returned.
- Equal
Returns 1 (true) if and only if geometries are exactly the same. No circles will be returned.
- Touch
Tests whether a geometry touches another. Returns 1 (true) if the geometries have at least one point in common, but their interiors do not intersect. Only circle 3 is returned.
- Overlap
Tests whether a geometry overlaps another. Returns 1 (true) if the geometries share space, are of the same dimension, but are not completely contained by each other. Only circle 2 is returned.
- Are within
Tests whether a geometry is within another. Returns 1 (true) if geometry a is completely inside geometry b. Only circle 1 is returned.
- Cross
Returns 1 (true) if the supplied geometries have some, but not all, interior points in common and the actual crossing is of a lower dimension than the highest supplied geometry. For example, a line crossing a polygon will cross as a line (true). Two lines crossing will cross as a point (true). Two polygons cross as a polygon (false). In the picture, no circles will be returned.
Notes on algorithms
Предупреждение
Geometry modification only
This operation modifies only the features geometry. The attribute values of the features are not modified, although properties such as area or length of the features will be modified by the overlay operation. If such properties are stored as attributes, those attributes will have to be manually updated.
Raster data types
Without user input (native)
0 — Byte (Eight bit unsigned integer (quint8))
1 — Int16 (Sixteen bit signed integer (qint16))
2 — UInt16 (Sixteen bit unsigned integer (quint16))
3 — Int32 (Thirty two bit signed integer (qint32))
4 — UInt32 (Thirty two bit unsigned integer (quint32))
5 — Float32 (Thirty two bit floating point (float))
6 — Float64 (Sixty four bit floating point (double))
7 — CInt16 (Complex Int16)
8 — CInt32 (Complex Int32)
9 — CFloat32 (Complex Float32)
10 — CFloat64 (Complex Float64)
11 — Int8 (Eight bit signed integer (qint8))
Available options depend on the GDAL version built with QGIS (see menu)
Without user input
0 — Byte (Eight bit unsigned integer (quint8))
1 — Int16 (Sixteen bit signed integer (qint16))
2 — UInt16 (Sixteen bit unsigned integer (quint16))
3 — UInt32 (Thirty two bit unsigned integer (quint32))
4 — Int32 (Thirty two bit signed integer (qint32))
5 — Float32 (Thirty two bit floating point (float))
6 — Float64 (Sixty four bit floating point (double))
7 — CInt16 (Complex Int16)
8 — CInt32 (Complex Int32)
9 — CFloat32 (Complex Float32)
10 — CFloat64 (Complex Float64)
11 — Int8 (Eight bit signed integer (qint8))
Available options depend on the GDAL version built with QGIS (see menu)
With user input
0 — Use Input Layer Data Type
1 — Byte (Eight bit unsigned integer (quint8))
2 — Int16 (Sixteen bit signed integer (qint16))
3 — UInt16 (Sixteen bit unsigned integer (quint16))
4 — UInt32 (Thirty two bit unsigned integer (quint32))
5 — Int32 (Thirty two bit signed integer (qint32))
6 — Float32 (Thirty two bit floating point (float))
7 — Float64 (Sixty four bit floating point (double))
8 — CInt16 (Complex Int16)
9 — CInt32 (Complex Int32)
10 — CFloat32 (Complex Float32)
11 — CFloat64 (Complex Float64)
12 — Int8 (Eight bit signed integer (qint8))
Available options depend on the GDAL version built with QGIS (see menu)
Resampling methods
0 — Nearest Neighbour
1 — Bilinear (2x2 kernel)
2 — Cubic (4x4 kernel)
3 — Cubic B-Spline (4x4 kernel)
4 — Lanczos (6x6 kernel)
5 — Average
6 — Mode
7 — Maximum
8 — Minimum
9 — Median
10 — First quartile (Q1)
11 — Third quartile (Q3)
Vector field types
1 — Boolean
2 — Integer (32bit)
4 — Integer (64bit)
6 — Decimal (double)
9 — Integer list
9 — Integer (64bit) list
9 — Decimal (double) list
10 — Text (string)
11 — String list
12 — Binary Object (BLOB)
14 — Date
15 — Time
16 — Date & Time
2 — Integer list
4 — Integer (64bit) list
6 — Decimal (double) list
10 — String list
0 — Any other types