` `
DB Manager Plugin¶
The DB Manager Plugin is officially part of the QGIS core and is intended to be
the main tool to integrate and manage spatial database formats supported by QGIS
(PostGIS, SpatiaLite, GeoPackage, Oracle Spatial, Virtual layers) in one user interface.
The  DB Manager Plugin provides several features.
You can drag layers from the QGIS Browser into the DB Manager, and it will import your layer
into your spatial database. You can drag and drop tables between spatial databases
and they will get imported.
DB Manager Plugin provides several features.
You can drag layers from the QGIS Browser into the DB Manager, and it will import your layer
into your spatial database. You can drag and drop tables between spatial databases
and they will get imported.
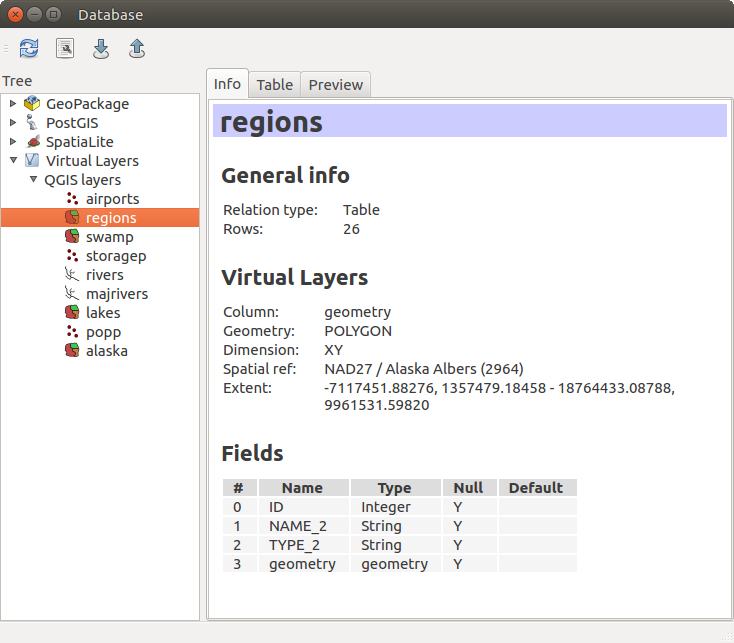
DB Manager dialog
The Database menu allows you to connect to an existing database, to start the SQL window and to exit the DB Manager Plugin. Once you are connected to an existing database, the menus Schema and Table additionally appear.
The Schema menu includes tools to create and delete (empty) schemas and, if topology is available (e.g., PostGIS 2), to start a TopoViewer.
The Table menu allows you to create and edit tables and to delete tables and views. It is also possible to empty tables and to move tables from one schema to another. As further functionality, you can perform a VACUUM and then an ANALYZE for each selected table. Plain VACUUM simply reclaims space and makes it available for reuse. ANALYZE updates statistics to determine the most efficient way to execute a query. Finally, you can import layers/files, if they are loaded in QGIS or exist in the file system. And you can export database tables to shape with the Export File feature.
The Tree window lists all existing databases supported by QGIS. With a double-click, you can connect to the database. With the right mouse button, you can rename and delete existing schemas and tables. Tables can also be added to the QGIS canvas with the context menu.
If connected to a database, the main window of the DB Manager offers three tabs. The Info tab provides information about the table and its geometry, as well as about existing fields, constraints and indexes. It also allows you to run Vacuum Analyze and to create a spatial index on a selected table, if not already done. The Table tab shows all attributes, and the Preview tab renders the geometries as preview.
Working with the SQL Window¶
You can also use the DB Manager to execute SQL queries against your spatial database and then view the spatial output for queries by adding the results to QGIS as a query layer. It is possible to highlight a portion of the SQL and only that portion will be executed when you press F5 or click the Execute (F5) button.
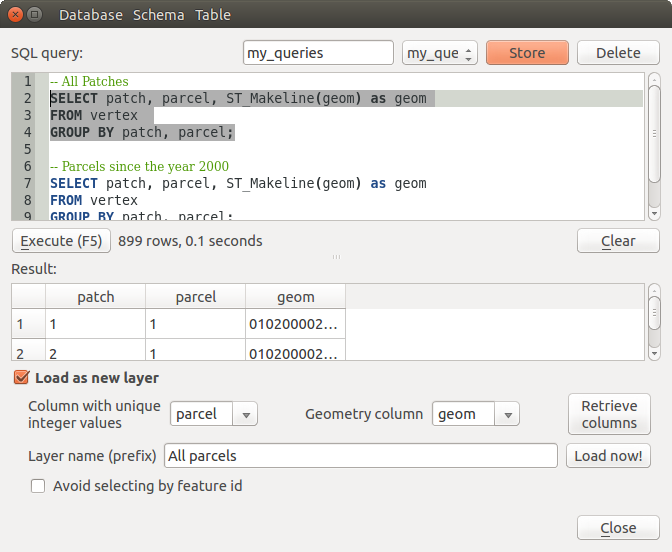
Executing SQL queries in the DB Manager SQL window
Muista
The SQL Window can also be used to create Virtual Layers. In that case, instead of selecting a database, select QGIS Layers under Virtual Layers before opening the SQL Window. See Creating virtual layers for instructions on the SQL syntax to use.