Docs for ‘QGIS testing’. Visit http://docs.qgis.org/2.8 for QGIS 2.8 docs and translations.
Query Builder¶
The Query Builder allows you to define a subset of a table using a SQL-like WHERE clause and to display the result in the main window. The query result can then be saved as a new vector layer.
Query¶
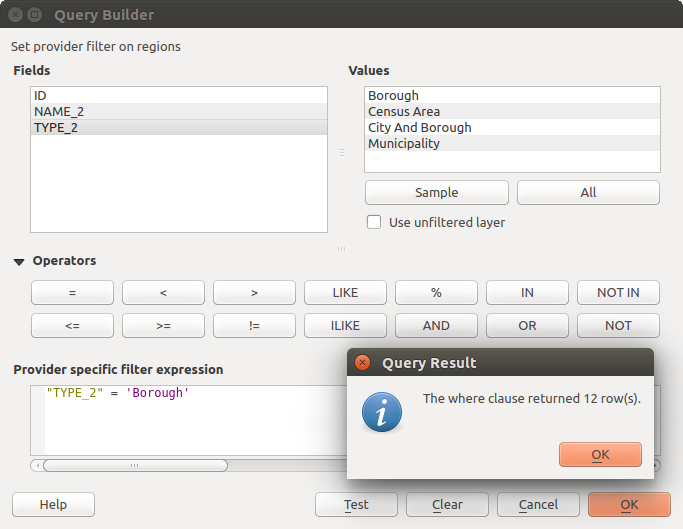
Open the Query Builder by opening the Layer Properties and going to the General menu. Under Feature subset, click on the [Query Builder] button to open the Query builder. For example, if you have a regions layer with a TYPE_2 field, you could select only regions that are borough in the Provider specific filter expression box of the Query Builder. Figure_attributes_2 shows an example of the Query Builder populated with the regions.shp layer from the QGIS sample data. The Fields, Values and Operators sections help you to construct the SQL-like query.
Figure Attributes 2:
The Fields list contains all attribute columns of the attribute table to be searched. To add an attribute column to the SQL WHERE clause field, double click its name in the Fields list. Generally, you can use the various fields, values and operators to construct the query, or you can just type it into the SQL box.
The Values list lists the values of an attribute table. To list all possible values of an attribute, select the attribute in the Fields list and click the [all] button. To list the first 25 unique values of an attribute column, select the attribute column in the Fields list and click the [Sample] button. To add a value to the SQL WHERE clause field, double click its name in the Values list.
The Operators section contains all usable operators. To add an operator to the SQL WHERE clause field, click the appropriate button. Relational operators ( = , > , ...), string comparison operator (LIKE), and logical operators (AND, OR, ...) are available.
The [Test] button shows a message box with the number of features satisfying the current query, which is useful in the process of query construction. The [Clear] button clears the text in the SQL WHERE clause text field. The [OK] button closes the window and selects the features satisfying the query. The [Cancel] button closes the window without changing the current selection.
QGIS treats the resulting subset acts as if it where the entire layer. For example if you applied the filter above for ‘Borough’, you can not display, query, save or edit Anchorage, because that is a ‘Municipality’ and therefore not part of the subset.
The only exception is that unless your layer is part of a database, using a subset will prevent you from editing the layer.