Getting Started¶
Installation¶
At this point, we will give a short and simple sample installation how-to for a minimal working configuration using Apache2 on Debian/Ubuntu. The first step is QGIS Server installation whose instructions are provided in QGIS installers page.
HTTP Server configuration¶
Apache¶
Install the Apache server in a separate virtual host listening on port 80. Enable the rewrite module to pass HTTP BASIC auth headers:
$ sudo a2enmod rewrite
$ cat /etc/apache2/conf-available/qgis-server-port.conf
Listen 80
$ sudo a2enconf qgis-server-port
This is the virtual host configuration, stored in /etc/apache2/sites-available/001-qgis-server.conf:
<VirtualHost *:80>
ServerAdmin webmaster@localhost
DocumentRoot /var/www/html
ErrorLog ${APACHE_LOG_DIR}/qgis-server-error.log
CustomLog ${APACHE_LOG_DIR}/qgis-server-access.log combined
# Longer timeout for WPS... default = 40
FcgidIOTimeout 120
FcgidInitialEnv LC_ALL "en_US.UTF-8"
FcgidInitialEnv PYTHONIOENCODING UTF-8
FcgidInitialEnv LANG "en_US.UTF-8"
FcgidInitialEnv QGIS_DEBUG 1
FcgidInitialEnv QGIS_SERVER_LOG_FILE /tmp/qgis-000.log
FcgidInitialEnv QGIS_SERVER_LOG_LEVEL 0
ScriptAlias /cgi-bin/ /usr/lib/cgi-bin/
<Directory "/usr/lib/cgi-bin">
AllowOverride All
Options +ExecCGI -MultiViews +FollowSymLinks
# for apache2 > 2.4
Require all granted
#Allow from all
</Directory>
</VirtualHost>
Now enable the virtual host and restart Apache:
$ sudo a2ensite 001-qgis-server
$ sudo service apache2 restart
NGINX¶
You can use QGIS Server with nginx.
On Debian based systems:
apt-get install nginx fcgiwrap
Introduce the following in your nginx server block configuration:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 | location ~ ^/cgi-bin/.*\.fcgi$ {
gzip off;
include fastcgi_params;
fastcgi_pass unix:/var/run/fcgiwrap.socket;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME /usr/lib/cgi-bin/qgis_mapserv.fcgi;
fastcgi_param QGIS_SERVER_LOG_FILE /logs/qgisserver.log;
fastcgi_param QGIS_SERVER_LOG_LEVEL 0;
fastcgi_param QGIS_DEBUG 1;
}
|
As you can see from lines 6-9 you can add parameters in your location block in the form of fastcgi_param param_name param_value, e.g. fastcgi_param DISPLAY ":99";.
The include fastcgi_params; is important as it adds the parameters from /etc/nginx/fastcgi_params:
fastcgi_param QUERY_STRING $query_string;
fastcgi_param REQUEST_METHOD $request_method;
fastcgi_param CONTENT_TYPE $content_type;
fastcgi_param CONTENT_LENGTH $content_length;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_NAME $fastcgi_script_name;
fastcgi_param REQUEST_URI $request_uri;
fastcgi_param DOCUMENT_URI $document_uri;
fastcgi_param DOCUMENT_ROOT $document_root;
fastcgi_param SERVER_PROTOCOL $server_protocol;
fastcgi_param REQUEST_SCHEME $scheme;
fastcgi_param HTTPS $https if_not_empty;
fastcgi_param GATEWAY_INTERFACE CGI/1.1;
fastcgi_param SERVER_SOFTWARE nginx/$nginx_version;
fastcgi_param REMOTE_ADDR $remote_addr;
fastcgi_param REMOTE_PORT $remote_port;
fastcgi_param SERVER_ADDR $server_addr;
fastcgi_param SERVER_PORT $server_port;
fastcgi_param SERVER_NAME $server_name;
# PHP only, required if PHP was built with --enable-force-cgi-redirect
fastcgi_param REDIRECT_STATUS 200;
Prepare a project to serve¶
To provide a new QGIS Server WMS, WFS or WCS, we have to create a QGIS project file with some data. Here, we use the ‘Alaska’ shapefile from the QGIS sample dataset. Define the colors and styles of the layers in QGIS and the project CRS, if not already defined.
Definitions for a QGIS Server WMS/WFS/WCS project
Then, go to the OWS Server menu of the
Project ‣ Project Properties dialog and provide
some information about the OWS in the fields under
Service Capabilities.
This will appear in the GetCapabilities response of the WMS, WFS or WCS.
If you don’t check  Service capabilities,
QGIS Server will use the information given in the wms_metadata.xml file
located in the cgi-bin folder.
Service capabilities,
QGIS Server will use the information given in the wms_metadata.xml file
located in the cgi-bin folder.
Warning
If you’re using the QGIS project with styling based on SVG files using relative paths then you should know that the server considers the path relative to its qgis_mapserv.fcgi file (not to the qgs file). So, if you deploy a project on the server and the SVG files are not placed accordingly, the output images may not respect the Desktop styling. To ensure this doesn’t happen, you can simply copy the SVG files relative to the qgis_mapserv.fcgi. You can also create a symbolic link in the directory where the fcgi file resides that points to the directory containing the SVG files (on Linux/Unix).
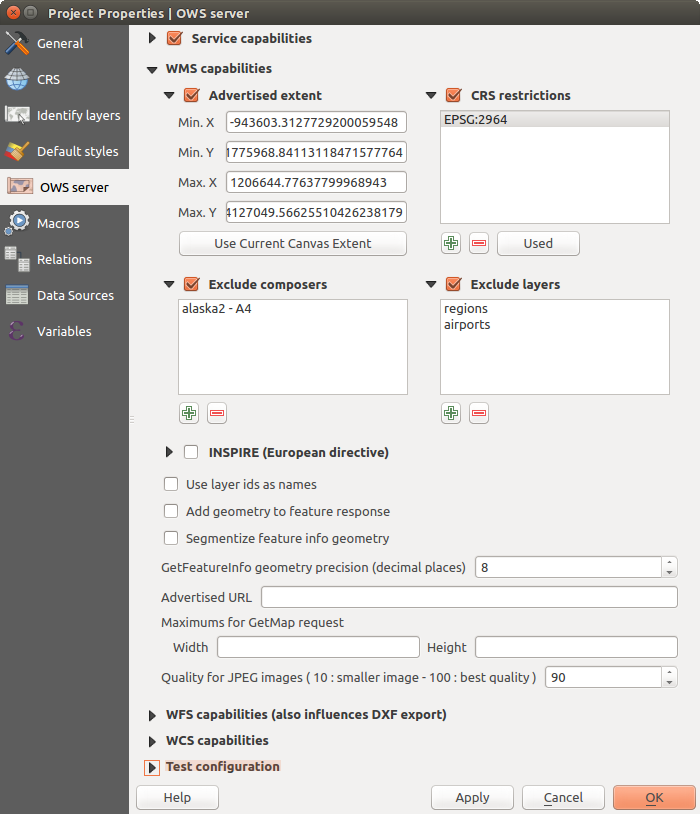
WMS capabilities¶
In the WMS capabilities section, you can define
the extent advertised in the WMS GetCapabilities response by entering
the minimum and maximum X and Y values in the fields under
Advertised extent.
Clicking Use Current Canvas Extent sets these values to the
extent currently displayed in the QGIS map canvas.
By checking  CRS restrictions, you can restrict
in which coordinate reference systems (CRS) QGIS Server will offer
to render maps.
Use the
CRS restrictions, you can restrict
in which coordinate reference systems (CRS) QGIS Server will offer
to render maps.
Use the  button below to select those CRSs
from the Coordinate Reference System Selector, or click Used
to add the CRSs used in the QGIS project to the list.
button below to select those CRSs
from the Coordinate Reference System Selector, or click Used
to add the CRSs used in the QGIS project to the list.
If you have print composers defined in your project, they will be listed in the
GetProjectSettings response, and they can be used by the GetPrint request to
create prints, using one of the print composer layouts as a template.
This is a QGIS-specific extension to the WMS 1.3.0 specification.
If you want to exclude any print composer from being published by the WMS,
check  Exclude composers and click the
Exclude composers and click the
 button below.
Then, select a print composer from the Select print composer dialog
in order to add it to the excluded composers list.
button below.
Then, select a print composer from the Select print composer dialog
in order to add it to the excluded composers list.
If you want to exclude any layer or layer group from being published by the
WMS, check  Exclude Layers and click the
Exclude Layers and click the
 button below.
This opens the Select restricted layers and groups dialog, which
allows you to choose the layers and groups that you don’t want to be published.
Use the Shift or Ctrl key if you want to select multiple entries.
button below.
This opens the Select restricted layers and groups dialog, which
allows you to choose the layers and groups that you don’t want to be published.
Use the Shift or Ctrl key if you want to select multiple entries.
You can receive requested GetFeatureInfo as plain text, XML and GML. Default is XML, text or GML format depends the output format chosen for the GetFeatureInfo request.
If you wish, you can check  Add geometry to feature response.
This will include in the GetFeatureInfo response the geometries of the
features in a text format. If you want QGIS Server to advertise specific request URLs
in the WMS GetCapabilities response, enter the corresponding URL in the
Advertised URL field.
Furthermore, you can restrict the maximum size of the maps returned by the
GetMap request by entering the maximum width and height into the respective
fields under Maximums for GetMap request.
Add geometry to feature response.
This will include in the GetFeatureInfo response the geometries of the
features in a text format. If you want QGIS Server to advertise specific request URLs
in the WMS GetCapabilities response, enter the corresponding URL in the
Advertised URL field.
Furthermore, you can restrict the maximum size of the maps returned by the
GetMap request by entering the maximum width and height into the respective
fields under Maximums for GetMap request.
If one of your layers uses the Map Tip display (i.e. to show text using expressions) this will be listed inside the GetFeatureInfo output. If the layer uses a Value Map for one of its attributes, this information will also be shown in the GetFeatureInfo output.
WFS capabilities¶
In the WFS capabilities area you can select the layers you want to publish as WFS, and specify if they will allow update, insert and delete operations. If you enter a URL in the Advertised URL field of the WFS capabilities section, QGIS Server will advertise this specific URL in the WFS GetCapabilities response.
WCS capabilities¶
In the WCS capabilities area, you can select the layers that you want to publish as WCS. If you enter a URL in the Advertised URL field of the WCS capabilities section, QGIS Server will advertise this specific URL in the WCS GetCapabilities response.
Fine tuning your OWS¶
For vector layers, the Fields menu of the Layer ‣ Properties dialog allows you to define for each attribute if it will be published or not. By default, all the attributes are published by your WMS and WFS. If you don’t want a specific attribute to be published, uncheck the corresponding checkbox in the WMS or WFS column.
You can overlay watermarks over the maps produced by your WMS by adding text annotations or SVG annotations to the project file. See the Annotation Tools section for instructions on creating annotations. For annotations to be displayed as watermarks on the WMS output, the Fixed map position checkbox in the Annotation text dialog must be unchecked. This can be accessed by double clicking the annotation while one of the annotation tools is active. For SVG annotations, you will need either to set the project to save absolute paths (in the General menu of the Project ‣ Project Properties dialog) or to manually modify the path to the SVG image so that it represents a valid relative path.
Serve the project¶
Now, save the session in a project file alaska.qgs. To provide the project as a WMS/WFS, create a new folder /usr/lib/cgi-bin/project with admin privileges and add the project file alaska.qgs and a copy of the qgis_mapserv.fcgi file - that’s all.
Now test your project WMS, WFS and WCS. Add the WMS, WFS and WCS as described in Loading WMS/WMTS Layers, WFS and WFS-T Client and WCS Client to QGIS and load the data. The URL is:
http://localhost/cgi-bin/project/qgis_mapserv.fcgi
Cascading OGC layers¶
A QGIS project can of course contain layers coming from remote OGC servers (regardless of the underlying OGC server software used). This way QGIS will effectively cascade those layers through its OGC (QGIS Server based) services.
If the external OGC layers are coming from services that make use of the HTTPS protocol you must take care of some extra QGIS Server configuration. Example for the Apache web server:
$ mkdir /srv/qgis/.qgis2
$ chown www-data:www-data /srv/qgis/.qgis2
$ chmod 774 /srv/qgis/.qgis2
This ensures that the web server is able to write in some user defined folder. Then add the following line to the Apache virtual host file to ensure that Apache will use such folder:
FcgidInitialEnv HOME "/srv/qgis"
Restart Apache.